An acid dissociation constant, Ka, (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction
The dissociation constant is defined by
where quantities in square brackets represent the concentrations of the species at equilibrium.
Theoretical background
The acid dissociation constant for an acid is a direct consequence of the underlying thermodynamics of the dissociation reaction; the pKa value is directly proportional to the standard Gibbs free energy change for the reaction. The value of the pKa changes with temperature and can be understood qualitatively based on Le Châtelier's principle: when the reaction is endothermic, Ka increases and pKa decreases with increasing temperature; the opposite is true for exothermic reactions.
The value of pKa also depends on molecular structure of the acid in many ways. For example, Pauling proposed two rules: one for successive pKa of polyprotic acids (see Polyprotic acids below), and one to estimate the pKa of oxyacids based on the number of =O and −OH groups (see Factors that affect pKa values below). Other structural factors that influence the magnitude of the acid dissociation constant include inductive effects, mesomeric effects, and hydrogen bonding. Hammett type equations have frequently been applied to the estimation of pKa.
The quantitative behaviour of acids and bases in solution can be understood only if their pKa values are known. In particular, the pH of a solution can be predicted when the analytical concentration and pKa values of all acids and bases are known; conversely, it is possible to calculate the equilibrium concentration of the acids and bases in solution when the pH is known. These calculations find application in many different areas of chemistry, biology, medicine, and geology. For example, many compounds used for medication are weak acids or bases, and a knowledge of the pKa values, together with the octanol-water partition coefficient, can be used for estimating the extent to which the compound enters the blood stream. Acid dissociation constants are also essential in aquatic chemistry and chemical oceanography, where the acidity of water plays a fundamental role. In living organisms, acid–base homeostasis and enzyme kinetics are dependent on the pKa values of the many acids and bases present in the cell and in the body. In chemistry, a knowledge of pKa values is necessary for the preparation of buffer solutions and is also a prerequisite for a quantitative understanding of the interaction between acids or bases and metal ions to form complexes. Experimentally, pKa values can be determined by potentiometric (pH) titration, but for values of pKa less than about 2 or more than about 11, spectrophotometric or NMR measurements may be required due to practical difficulties with pH measurements.
Definitions
According to Arrhenius's original molecular definition, an acid is a substance that dissociates in aqueous solution, releasing the hydrogen ion H+ (a proton):
- HA ⇌ A− + H+.
The equilibrium constant for this dissociation reaction is known as a dissociation constant. The liberated proton combines with a water molecule to give a hydronium (or oxonium) ion H3O+ (naked protons do not exist in solution), and so Arrhenius later proposed that the dissociation should be written as an acid–base reaction:
- HA + H2O ⇌ A− + H3O+.
Brønsted and Lowry generalised this further to a proton exchange reaction:
- acid + base ⇌ conjugate base + conjugate acid.
The acid loses a proton, leaving a conjugate base; the proton is transferred to the base, creating a conjugate acid. For aqueous solutions of an acid HA, the base is water; the conjugate base is A− and the conjugate acid is the hydronium ion. The Brønsted–Lowry definition applies to other solvents, such as dimethyl sulfoxide: the solvent S acts as a base, accepting a proton and forming the conjugate acid SH+.
- HA + S ⇌ A− + SH+.
In solution chemistry, it is common to use H+ as an abbreviation for the solvated hydrogen ion, regardless of the solvent. In aqueous solution H+ denotes a solvated hydronium ion rather than a proton.
The designation of an acid or base as "conjugate" depends on the context. The conjugate acid BH+ of a base B dissociates according to
- BH+ + OH− ⇌ B + H2O
which is the reverse of the equilibrium
- H2O (acid) + B (base) ⇌ OH− (conjugate base) + BH+ (conjugate acid).
The hydroxide ion OH−, a well known base, is here acting as the conjugate base of the acid water. Acids and bases are thus regarded simply as donors and acceptors of protons respectively.
A broader definition of acid dissociation includes hydrolysis, in which protons are produced by the splitting of water molecules. For example, boric acid (B(OH)3) produces H3O+ as if it were a proton donor, but it has been confirmed by Raman spectroscopy that this is due to the hydrolysis equilibrium:
- B(OH)3 + 2 H2O ⇌ B(OH)4− + H3O+.
Similarly, metal ion hydrolysis causes ions such as [Al(H2O)6]3+ to behave as weak acids:
- [Al(H2O)6]3+ + H2O ⇌ [Al(H2O)5(OH)]2+ + H3O+.
According to Lewis's original definition, an acid is a substance that accepts an electron pair to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Equilibrium constant
An acid dissociation constant is a particular example of an equilibrium constant. The dissociation of a monoprotic acid, HA, in dilute solution can be written as
- HA ⇌ A− + H+
The thermodynamic equilibrium constant, can be defined by
where {X} represents the activity, at equilibrium, of the chemical species X. is dimensionless since activity is dimensionless. Activities of the products of dissociation are placed in the numerator, activities of the reactants are placed in the denominator. See activity coefficient for a derivation of this expression.
Since activity is the product of concentration and activity coefficient (γ) the definition could also be written as
To avoid the complications involved in using activities, dissociation constants are determined, where possible, in a medium of high ionic strength, that is, under conditions in which can be assumed to be always constant. For example, the medium might be a solution of 0.1 molar (M) sodium nitrate or 3 M potassium perchlorate. With this assumption,
Cumulative and stepwise constants
A cumulative equilibrium constant, denoted by , is related to the product of stepwise constants, denoted by . For a dibasic acid the relationship between stepwise and overall constants is as follows
Note that in the context of metal-ligand complex formation, the equilibrium constants for the formation of metal complexes are usually defined as association constants. In that case, the equilibrium constants for ligand protonation are also defined as association constants. The numbering of association constants is the reverse of the numbering of dissociation constants; in this example
Association and dissociation constants
When discussing the properties of acids it is usual to specify equilibrium constants as acid dissociation constants, denoted by Ka, with numerical values given the symbol pKa.
On the other hand, association constants are used for bases.
However, general purpose computer programs that are used to derive equilibrium constant values from experimental data use association constants for both acids and bases. Because stability constants for a metal-ligand complex are always specified as association constants, ligand protonation must also be specified as an association reaction. The definitions show that the value of an acid dissociation constant is the reciprocal of the value of the corresponding association constant.
- Kdissoc = 1 / Kassoc
- log Kdissoc = −log Kassoc
- pKdissoc = log Kassoc
Notes
- For a given acid or base pKa + pKb = pKw, the self-ionization constant of water.
- The association constant for the formation of a supramolecular complex may be denoted as Ka; in such cases "a" stands for "association", not "acid".
- For polyprotic acids, the numbering of stepwise association
constants is the reverse of the numbering of the dissociation constants.
For example, for phosphoric acid (details in #polyprotic acids, below)
Temperature dependence
All equilibrium constants vary with temperature according to the van 't Hoff equation
R is the gas constant and T is the absolute temperature. Thus, for exothermic reactions, the standard enthalpy change, , is negative and K decreases with temperature. For endothermic reactions, is positive and K increases with temperature.
The standard enthalpy change for a reaction is itself a function of temperature, according to Kirchhoff's law of thermochemistry:
Dimensionality
In the equation
Ka appears to have dimensions of concentration. However, since , the equilibrium constant, , cannot have a physical dimension. This apparent paradox can be resolved in various ways.
- Assume that the quotient of activity coefficients has a numerical value of 1, so that has the same numerical value as the thermodynamic equilibrium constant .
- Express each concentration value as the ratio c/c0, where c0 is the concentration in a [hypothetical] standard state, with a numerical value of 1, by definition.
- Express the concentrations on the mole fraction scale. Since mole fraction has no dimension, the quotient of concentrations will, by definition, be a pure number.
The procedures, (1) and (2), give identical numerical values for an equilibrium constant. Furthermore, since a concentration, , is simply proportional to mole fraction, and density,
It is common practice in biochemistry to quote a value with a dimension as, for example, "Ka = 30 mM" in order to indicate the scale, millimolar (mM) or micromolar (μM) of the concentration values used for its calculation.
Strong acids and bases
An acid is classified as "strong" when the concentration of its undissociated species is too low to be measured. Any aqueous acid with a pKa value of less than 0 is almost completely deprotonated and is considered a strong acid. All such acids transfer their protons to water and form the solvent cation species (H3O+ in aqueous solution) so that they all have essentially the same acidity, a phenomenon known as solvent leveling. They are said to be fully dissociated in aqueous solution because the amount of undissociated acid, in equilibrium with the dissociation products, is below the detection limit. Likewise, any aqueous base with an association constant pKb less than about 0, corresponding to pKa greater than about 14, is leveled to OH− and is considered a strong base.
Nitric acid, with a pK value of ca. -1.7, behaves as a strong acid in aqueous solutions with a pH greater than 1. At lower pH values it behaves as a weak acid.
pKa values for strong acids have been estimated by theoretical means. For example, the pKa value of aqueous HCl has been estimated as −9.3.
Monoprotic acids
After rearranging the expression defining Ka, and putting pH = −log10[H+], one obtains
This is the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation, from which the following conclusions can be drawn.
- At half-neutralization the ratio [A−]/[HA] = 1; since log(1) = 0, the pH at half-neutralization is numerically equal to pKa. Conversely, when pH = pKa, the concentration of HA is equal to the concentration of A−.
- The buffer region extends over the approximate range pKa ± 2. Buffering is weak outside the range pKa ± 1. At pH ≤ pKa − 2 the substance is said to be fully protonated and at pH ≥ pKa + 2 it is fully dissociated (deprotonated).
- If the pH is known, the ratio may be calculated. This ratio is independent of the analytical concentration of the acid.
In water, measurable pKa values range from about −2 for a strong acid to about 12 for a very weak acid (or strong base).
A buffer solution of a desired pH can be prepared as a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base. In practice, the mixture can be created by dissolving the acid in water, and adding the requisite amount of strong acid or base. When the pKa and analytical concentration of the acid are known, the extent of dissociation and pH of a solution of a monoprotic acid can be easily calculated using an ICE table.
Polyprotic acids
A polyprotic acid is a compound which may lose more than 1 proton. Stepwise dissociation constants are each defined for the loss of a single proton. The constant for dissociation of the first proton may be denoted as Ka1 and the constants for dissociation of successive protons as Ka2, etc. Phosphoric acid, H3PO4, is an example of a polyprotic acid as it can lose three protons.
Equilibrium pK definition and value H
3PO
4 ⇌ H
2PO−
4 + H+H
2PO−
4 ⇌ HPO2−
4 + H+HPO2−
4 ⇌ PO3−
4 + H+
When the difference between successive pK values is about four or more, as in this example, each species may be considered as an acid in its own right; In fact salts of H
2PO−
4 may be crystallised from solution by adjustment of pH to about 5.5 and salts of HPO2−
4
may be crystallised from solution by adjustment of pH to about 10. The
species distribution diagram shows that the concentrations of the two
ions are maximum at pH 5.5 and 10.
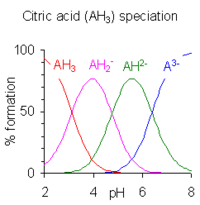
When the difference between successive pK values is less than about four there is overlap between the pH range of existence of the species in equilibrium. The smaller the difference, the more the overlap. The case of citric acid is shown at the right; solutions of citric acid are buffered over the whole range of pH 2.5 to 7.5.
According to Pauling's first rule, successive pK values of a given acid increase (pKa2 > pKa1). For oxyacids with more than one ionizable hydrogen on the same atom, the pKa values often increase by about 5 units for each proton removed, as in the example of phosphoric acid above.
It can be seen in the table above that the second proton is removed from a negatively charged species. Since the proton carries a positive charge extra work is needed to remove it. That why pKa2 is greater than pKa1. pKa3 is greater than pKa2 because there is further charge separation. When an exception to Pauling's rule is found, it indicates that a major change in structure is also occurring. In the case of VO2+ (aq.), the vanadium is octahedral, 6-coordinate, whereas vanadic acid is tetrahedral, 4-coordinate. This means that four "particles" are released with the first dissociation, but only two "particles" are released with the other dissociations, resulting in a much greater entropy contribution to the standard Gibbs free energy change for the first reaction than for the others.
Equilibrium pKa [VO2(H2O)4]+ ⇌ H3VO4 + H+ + 2H2O H3VO4 ⇌ H
2VO−
4 + H+H
2VO−
4 ⇌ HVO2−
4 + H+HVO2−
4 ⇌ VO3−
4 + H+
Isoelectric point
For substances in solution, the isoelectric point (pI) is defined as the pH at which the sum, weighted by charge value, of concentrations of positively charged species is equal to the weighted sum of concentrations of negatively charged species. In the case that there is one species of each type, the isoelectric point can be obtained directly from the pK values. Take the example of glycine, defined as AH. There are two dissociation equilibria to consider.
- AH+
2 ⇌ AH + H+; [AH][H+] = K1[AH+
2] - AH ⇌ A− + H+; [A−][H+] = K2[AH]
Substitute the expression for [AH] from the second equation into the first equation
- [A−][H+]2 = K1K2[AH+
2]
At the isoelectric point the concentration of the positively charged species, AH2+, is equal to the concentration of the negatively charged species, A−, so
- [H+]2 = K1K2
Therefore, taking cologarithms, the pH is given by
pI values for amino acids are listed at proteinogenic amino acid. When more than two charged species are in equilibrium with each other a full speciation calculation may be needed.
Bases and basicity
The equilibrium constant Kb for a base is usually defined as the association constant for protonation of the base, B, to form the conjugate acid, HB+.
- B + H2O ⇌ HB+ + OH−
Using similar reasoning to that used before
Kb is related to Ka for the conjugate acid. In water, the concentration of the hydroxide ion, [OH−], is related to the concentration of the hydrogen ion by Kw = [H+][OH−], therefore
Substitution of the expression for [OH−] into the expression for Kb gives
When Ka, Kb and Kw are determined under the same conditions of temperature and ionic strength, it follows, taking cologarithms, that pKb = pKw − pKa. In aqueous solutions at 25 °C, pKw is 13.9965, so
with sufficient accuracy for most practical purposes. In effect there is no need to define pKb separately from pKa, but it is done here as often only pKb values can be found in the older literature.
For an hydrolyzed metal ion, Kb can also be defined as a stepwise dissociation constant
This is the reciprocal of an association constant for formation of the complex.
Basicity expressed as dissociation constant of conjugate acid
Because the relationship pKb = pKw − pKa holds only in aqueous solutions (though analogous relationships apply for other amphoteric solvents), subdisciplines of chemistry like organic chemistry that usually deal with nonaqueous solutions generally do not use pKb as a measure of basicity. Instead, the pKa of the conjugate acid, denoted by pKaH, is quoted when basicity needs to be quantified. For base B and its conjugate acid BH+ in equilibrium, this is defined as
A higher value for pKaH corresponds to a stronger base. For example, the values pKaH(C5H5N) = 5.25 and pKaH((CH3CH2)3N) = 10.75 indicate that (CH3CH2)3N (triethylamine) is a stronger base than C5H5N (pyridine).
Amphoteric substances
An amphoteric
substance is one that can act as an acid or as a base, depending on pH.
Water (below) is amphoteric. Another example of an amphoteric molecule
is the bicarbonate ion HCO−
3 that is the conjugate base of the carbonic acid molecule H2CO3 in the equilibrium
- H2CO3 + H2O ⇌ HCO−
3 + H3O+
but also the conjugate acid of the carbonate ion CO2−
3 in (the reverse of) the equilibrium
- HCO−
3 + OH− ⇌ CO2−
3 + H2O.or
Carbonic acid equilibria are important for acid–base homeostasis in the human body.
An amino acid is also amphoteric with the added complication that the neutral molecule is subject to an internal acid–base equilibrium in which the basic amino group attracts and binds the proton from the acidic carboxyl group, forming a zwitterion.
- NH2CHRCO2H ⇌ NH+
3CHRCO−
2
At pH less than about 5 both the carboxylate group and the amino group are protonated. As pH increases the acid dissociates according to
- NH+
3CHRCO
2H ⇌ NH+
3CHRCO−
2 + H+
At high pH a second dissociation may take place.
- NH+
3CHRCO−
2 ⇌ NH
2CHRCO−
2 + H+
Thus the amino acid molecule is amphoteric because it may either be protonated or deprotonated.
Water self-ionization
The water molecule may either gain or lose a proton. It is said to be amphiprotic. The ionization equilibrium can be written
- H2O ⇌ OH− + H+
where in aqueous solution H+ denotes a solvated proton. Often this is written as the hydronium ion H3O+, but this formula is not exact because in fact there is solvation by more than one water molecule and species such as H5O2+, H7O3+ and H9O4+ are also present.
The equilibrium constant is given by
With solutions in which the solute concentrations are not very high, the concentration [H2O] can be assumed to be constant, regardless of solute(s); this expression may then be replaced by
The self-ionization constant of water, Kw, is thus just a special case of an acid dissociation constant. A logarithmic form analogous to pKa may also be defined
| T (°C) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pKw | 14.943 | 14.734 | 14.535 | 14.346 | 14.167 | 13.997 | 13.830 | 13.680 | 13.535 | 13.396 | 13.262 |
These data can be fitted to a parabola with
- pKw = 14.94 − 0.04209T + 0.0001718T2
From this equation, pKw = 14 at 24.87 °C. At that temperature both hydrogen and hydroxide ions have a concentration of 10−7 M.
Acidity in nonaqueous solutions
A solvent will be more likely to promote ionization of a dissolved acidic molecule in the following circumstances:
- It is a protic solvent, capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
- It has a high donor number, making it a strong Lewis base.
- It has a high dielectric constant (relative permittivity), making it a good solvent for ionic species.
pKa values of organic compounds are often obtained using the aprotic solvents dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and acetonitrile (ACN).
| Solvent | Donor number | Dielectric constant |
|---|---|---|
| Acetonitrile | 14 | 37 |
| Dimethylsulfoxide | 30 | 47 |
| Water | 18 | 78 |
DMSO is widely used as an alternative to water because it has a lower dielectric constant than water, and is less polar and so dissolves non-polar, hydrophobic substances more easily. It has a measurable pKa range of about 1 to 30. Acetonitrile is less basic than DMSO, and, so, in general, acids are weaker and bases are stronger in this solvent. Some pKa values at 25 °C for acetonitrile (ACN) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) are shown in the following tables. Values for water are included for comparison.
| HA ⇌ A− + H+ | ACN | DMSO | Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid | 8.5 | 0.9 | Strong |
| 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 16.66 | 5.1 | 3.9 |
| Benzoic acid | 21.51 | 11.1 | 4.2 |
| Acetic acid | 23.51 | 12.6 | 4.756 |
| Phenol | 29.14 | 18.0 | 9.99 |
| BH+ ⇌ B + H+ | ACN | DMSO | Water |
| Pyrrolidine | 19.56 | 10.8 | 11.4 |
| Triethylamine | 18.82 | 9.0 | 10.72 |
| Proton sponge | 18.62 | 7.5 | 12.1 |
| Pyridine | 12.53 | 3.4 | 5.2 |
| Aniline | 10.62 | 3.6 | 4.6 |
Ionization of acids is less in an acidic solvent than in water. For example, hydrogen chloride is a weak acid when dissolved in acetic acid. This is because acetic acid is a much weaker base than water.
- HCl + CH3CO2H ⇌ Cl− + CH
3C(OH)+
2 - acid + base ⇌ conjugate base + conjugate acid
Compare this reaction with what happens when acetic acid is dissolved in the more acidic solvent pure sulfuric acid
H2SO4 + CH3CO2H ⇌ HSO−
4 + CH
3C(OH)+
2
The unlikely geminal diol species CH
3C(OH)+
2 is stable in these environments. For aqueous solutions the pH scale is the most convenient acidity function. Other acidity functions have been proposed for non-aqueous media, the most notable being the Hammett acidity function, H0, for superacid media and its modified version H− for superbasic media.
In aprotic solvents, oligomers, such as the well-known acetic acid dimer, may be formed by hydrogen bonding. An acid may also form hydrogen bonds to its conjugate base. This process, known as homoconjugation, has the effect of enhancing the acidity of acids, lowering their effective pKa values, by stabilizing the conjugate base. Homoconjugation enhances the proton-donating power of toluenesulfonic acid in acetonitrile solution by a factor of nearly 800.
In aqueous solutions, homoconjugation does not occur, because water forms stronger hydrogen bonds to the conjugate base than does the acid.
Mixed solvents
When a compound has limited solubility in water it is common practice (in the pharmaceutical industry, for example) to determine pKa values in a solvent mixture such as water/dioxane or water/methanol, in which the compound is more soluble. In the example shown at the right, the pKa value rises steeply with increasing percentage of dioxane as the dielectric constant of the mixture is decreasing.
A pKa value obtained in a mixed solvent cannot be used directly for aqueous solutions. The reason for this is that when the solvent is in its standard state its activity is defined as one. For example, the standard state of water:dioxane mixture with 9:1 mixing ratio is precisely that solvent mixture, with no added solutes. To obtain the pKa value for use with aqueous solutions it has to be extrapolated to zero co-solvent concentration from values obtained from various co-solvent mixtures.
These facts are obscured by the omission of the solvent from the expression that is normally used to define pKa, but pKa values obtained in a given mixed solvent can be compared to each other, giving relative acid strengths. The same is true of pKa values obtained in a particular non-aqueous solvent such a DMSO.
A universal, solvent-independent, scale for acid dissociation constants has not been developed, since there is no known way to compare the standard states of two different solvents.
Factors that affect pKa values
Pauling's second rule is that the value of the first pKa for acids of the formula XOm(OH)n depends primarily on the number of oxo groups m, and is approximately independent of the number of hydroxy groups n, and also of the central atom X. Approximate values of pKa are 8 for m = 0, 2 for m = 1, −3 for m = 2 and < −10 for m = 3. Alternatively, various numerical formulas have been proposed including pKa = 8 − 5m (known as Bell's rule), pKa = 7 − 5m, or pKa = 9 − 7m. The dependence on m correlates with the oxidation state of the central atom, X: the higher the oxidation state the stronger the oxyacid. For example, pKa for HClO is 7.2, for HClO2 is 2.0, for HClO3 is −1 and HClO4 is a strong acid (pKa ≪ 0). The increased acidity on adding an oxo group is due to stabilization of the conjugate base by delocalization of its negative charge over an additional oxygen atom. This rule can help assign molecular structure: for example, phosphorous acid (H3PO3) has a pKa near 2, which suggested that the structure is HPO(OH)2, as later confirmed by NMR spectroscopy, and not P(OH)3, which would be expected to have a pKa near 8.
With organic acids inductive effects and mesomeric effects affect the pKa values. A simple example is provided by the effect of replacing the hydrogen atoms in acetic acid by the more electronegative chlorine atom. The electron-withdrawing effect of the substituent makes ionisation easier, so successive pKa values decrease in the series 4.7, 2.8, 1.4, and 0.7 when 0, 1, 2, or 3 chlorine atoms are present. The Hammett equation, provides a general expression for the effect of substituents.
- log(Ka) = log(K0
a) + ρσ.
Ka is the dissociation constant of a substituted compound, K0
a
is the dissociation constant when the substituent is hydrogen, ρ is a
property of the unsubstituted compound and σ has a particular value for
each substituent. A plot of log(Ka) against σ is a straight line with intercept log(K0
a) and slope ρ. This is an example of a linear free energy relationship as log(Ka) is proportional to the standard free energy change. Hammett originally formulated the relationship with data from benzoic acid with different substituents in the ortho- and para- positions: some numerical values are in Hammett equation. This and other studies allowed substituents to be ordered according to their electron-withdrawing or electron-releasing power, and to distinguish between inductive and mesomeric effects.
Alcohols do not normally behave as acids in water, but the presence of a double bond adjacent to the OH group can substantially decrease the pKa by the mechanism of keto–enol tautomerism. Ascorbic acid is an example of this effect. The diketone 2,4-pentanedione (acetylacetone) is also a weak acid because of the keto–enol equilibrium. In aromatic compounds, such as phenol, which have an OH substituent, conjugation with the aromatic ring as a whole greatly increases the stability of the deprotonated form.
Structural effects can also be important. The difference between fumaric acid and maleic acid is a classic example. Fumaric acid is (E)-1,4-but-2-enedioic acid, a trans isomer, whereas maleic acid is the corresponding cis isomer, i.e. (Z)-1,4-but-2-enedioic acid (see cis-trans isomerism). Fumaric acid has pKa values of approximately 3.0 and 4.5. By contrast, maleic acid has pKa values of approximately 1.5 and 6.5. The reason for this large difference is that when one proton is removed from the cis isomer (maleic acid) a strong intramolecular hydrogen bond is formed with the nearby remaining carboxyl group. This favors the formation of the maleate H+, and it opposes the removal of the second proton from that species. In the trans isomer, the two carboxyl groups are always far apart, so hydrogen bonding is not observed.
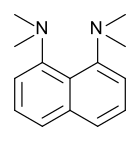
Proton sponge, 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene, has a pKa value of 12.1. It is one of the strongest amine bases known. The high basicity is attributed to the relief of strain upon protonation and strong internal hydrogen bonding.
Effects of the solvent and solvation should be mentioned also in this section. It turns out, these influences are more subtle than that of a dielectric medium mentioned above. For example, the expected (by electronic effects of methyl substituents) and observed in gas phase order of basicity of methylamines, Me3N > Me2NH > MeNH2 > NH3, is changed by water to Me2NH > MeNH2 > Me3N > NH3. Neutral methylamine molecules are hydrogen-bonded to water molecules mainly through one acceptor, N–HOH, interaction and only occasionally just one more donor bond, NH–OH2. Hence, methylamines are stabilized to about the same extent by hydration, regardless of the number of methyl groups. In stark contrast, corresponding methylammonium cations always utilize all the available protons for donor NH–OH2 bonding. Relative stabilization of methylammonium ions thus decreases with the number of methyl groups explaining the order of water basicity of methylamines.
Thermodynamics
An equilibrium constant is related to the standard Gibbs energy change for the reaction, so for an acid dissociation constant
- .
R is the gas constant and T is the absolute temperature. Note that pKa = −log(Ka) and 2.303 ≈ ln(10). At 25 °C, ΔG⊖ in kJ·mol−1 ≈ 5.708 pKa (1 kJ·mol−1 = 1000 joules per mole). Free energy is made up of an enthalpy term and an entropy term.
The standard enthalpy change can be determined by calorimetry or by using the van 't Hoff equation, though the calorimetric method is preferable. When both the standard enthalpy change and acid dissociation constant have been determined, the standard entropy change is easily calculated from the equation above. In the following table, the entropy terms are calculated from the experimental values of pKa and ΔH⊖. The data were critically selected and refer to 25 °C and zero ionic strength, in water.
| Compound | Equilibrium | pKa | ΔG⊖ (kJ·mol−1) | ΔH⊖ (kJ·mol−1) | −TΔS⊖ (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA = Acetic acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 4.756 | 27.147 | −0.41 | 27.56 |
| H2A+ = GlycineH+ | H2A+ ⇌ HA + H+ | 2.351 | 13.420 | 4.00 | 9.419 |
|
|
HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 9.78 | 55.825 | 44.20 | 11.6 |
| H2A = Maleic acid | H2A ⇌ HA− + H+ | 1.92 | 10.76 | 1.10 | 9.85 |
|
|
HA− ⇌ H+ + A2− | 6.27 | 35.79 | −3.60 | 39.4 |
| H3A = Citric acid | H3A ⇌ H2A− + H+ | 3.128 | 17.855 | 4.07 | 13.78 |
|
|
H2A− ⇌ HA2− + H+ | 4.76 | 27.176 | 2.23 | 24.9 |
|
|
HA2− ⇌ A3− + H+ | 6.40 | 36.509 | −3.38 | 39.9 |
| H3A = Boric acid | H3A ⇌ H2A− + H+ | 9.237 | 52.725 | 13.80 | 38.92 |
| H3A = Phosphoric acid | H3A ⇌ H2A− + H+ | 2.148 | 12.261 | −8.00 | 20.26 |
|
|
H2A− ⇌ HA2− + H+ | 7.20 | 41.087 | 3.60 | 37.5 |
|
|
HA2− ⇌ A3− + H+ | 12.35 | 80.49 | 16.00 | 54.49 |
| HA− = Hydrogen sulfate | HA− ⇌ A2− + H+ | 1.99 | 11.36 | −22.40 | 33.74 |
| H2A = Oxalic acid | H2A ⇌ HA− + H+ | 1.27 | 7.27 | −3.90 | 11.15 |
|
|
HA− ⇌ A2− + H+ | 4.266 | 24.351 | −7.00 | 31.35 |
- Computed here, from ΔH and ΔG values supplied in the citation, using −TΔS⊖ = ΔG⊖ − ΔH⊖
| Compound | Equilibrium | pKa | ΔH⊖ (kJ·mol−1) | −TΔS⊖ (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B = Ammonia | HB+ ⇌ B + H+ | 9.245 | 51.95 | 0.8205 |
| B = Methylamine | HB+ ⇌ B + H+ | 10.645 | 55.34 | 5.422 |
| B = Triethylamine | HB+ ⇌ B + H+ | 10.72 | 43.13 | 18.06 |
The first point to note is that, when pKa is positive, the standard free energy change for the dissociation reaction is also positive. Second, some reactions are exothermic and some are endothermic, but, when ΔH⊖ is negative TΔS⊖ is the dominant factor, which determines that ΔG⊖ is positive. Last, the entropy contribution is always unfavourable (ΔS⊖ < 0) in these reactions. Ions in aqueous solution tend to orient the surrounding water molecules, which orders the solution and decreases the entropy. The contribution of an ion to the entropy is the partial molar entropy which is often negative, especially for small or highly charged ions. The ionization of a neutral acid involves formation of two ions so that the entropy decreases (ΔS⊖ < 0). On the second ionization of the same acid, there are now three ions and the anion has a charge, so the entropy again decreases.
Note that the standard free energy change for the reaction is for the changes from the reactants in their standard states to the products in their standard states. The free energy change at equilibrium is zero since the chemical potentials of reactants and products are equal at equilibrium.
Experimental determination
The experimental determination of pKa values is commonly performed by means of titrations, in a medium of high ionic strength and at constant temperature. A typical procedure would be as follows. A solution of the compound in the medium is acidified with a strong acid to the point where the compound is fully protonated. The solution is then titrated with a strong base until all the protons have been removed. At each point in the titration pH is measured using a glass electrode and a pH meter. The equilibrium constants are found by fitting calculated pH values to the observed values, using the method of least squares.
The total volume of added strong base should be small compared to the initial volume of titrand solution in order to keep the ionic strength nearly constant. This will ensure that pKa remains invariant during the titration.
A calculated titration curve for oxalic acid is shown at the right. Oxalic acid has pKa values of 1.27 and 4.27. Therefore, the buffer regions will be centered at about pH 1.3 and pH 4.3. The buffer regions carry the information necessary to get the pKa values as the concentrations of acid and conjugate base change along a buffer region.
Between the two buffer regions there is an end-point, or equivalence point, at about pH 3. This end-point is not sharp and is typical of a diprotic acid whose buffer regions overlap by a small amount: pKa2 − pKa1 is about three in this example. (If the difference in pK values were about two or less, the end-point would not be noticeable.) The second end-point begins at about pH 6.3 and is sharp. This indicates that all the protons have been removed. When this is so, the solution is not buffered and the pH rises steeply on addition of a small amount of strong base. However, the pH does not continue to rise indefinitely. A new buffer region begins at about pH 11 (pKw − 3), which is where self-ionization of water becomes important.
It is very difficult to measure pH values of less than two in aqueous solution with a glass electrode, because the Nernst equation breaks down at such low pH values. To determine pK values of less than about 2 or more than about 11 spectrophotometric or NMR measurements may be used instead of, or combined with, pH measurements.
When the glass electrode cannot be employed, as with non-aqueous solutions, spectrophotometric methods are frequently used. These may involve absorbance or fluorescence measurements. In both cases the measured quantity is assumed to be proportional to the sum of contributions from each photo-active species; with absorbance measurements the Beer–Lambert law is assumed to apply.
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) may be used to determine both a pK value and the corresponding standard enthalpy for acid dissociation. Software to perform the calculations is supplied by the instrument manufacturers for simple systems.
Aqueous solutions with normal water cannot be used for 1H NMR measurements but heavy water, D2O, must be used instead. 13C NMR data, however, can be used with normal water and 1H NMR spectra can be used with non-aqueous media. The quantities measured with NMR are time-averaged chemical shifts, as proton exchange is fast on the NMR time-scale. Other chemical shifts, such as those of 31P can be measured.
Micro-constants
For some molecules, dissociation (or association) can occur at more than one nonequivalent site, and the observed macroscopic equilibrium constant or macroconstant is a combination of microconstants involving distinct species. When one reactant forms two products in parallel, the macroconstant is a sum of two microconstants, . This is true for example for the deprotonation of the amino acid cysteine, which exists in solution as a neutral zwitterion HS-CH2-CH(NH3+)-COO−. The two microconstants represent deprotonation either at sulphur or at nitrogen, and the macroconstant sum here is the acid dissociation constant Ka = Ka(-SH) + Ka(-NH3+).
Similarly, a base such as spermine has more than one site where protonation can occur. For example, monoprotonation can occur at a terminal –NH2 group or at internal –NH– groups. The Kb values for dissociation of spermine protonated at one or other of the sites are examples of micro-constants. They cannot be determined directly by means of pH, absorbance, fluorescence or NMR measurements; a measured Kb value is the sum of the K values for the micro-reactions.
Nevertheless, the site of protonation is very important for biological function, so mathematical methods have been developed for the determination of micro-constants.
When two reactants form a single product in parallel, the macroconstant . For example, the abovementioned equilibrium for spermine may be considered in terms of Ka values of two tautomeric conjugate acids, with macroconstant In this case . This is equivalent to the preceding expression since is proportional to .
When a reactant undergoes two reactions in series, the macroconstant for the combined reaction is the product of the microconstant for the two steps. For example, the abovementioned cysteine zwitterion can lose two protons, one from sulphur and one from nitrogen, and the overall macroconstant for losing two protons is the product of two dissociation constants K = Ka(-SH) Ka(-NH3+). This can also be written in terms of logarithmic constants as pK = pKa(-SH) + pKa(-NH3+).
Applications and significance
A knowledge of pKa values is important for the quantitative treatment of systems involving acid–base equilibria in solution. Many applications exist in biochemistry; for example, the pKa values of proteins and amino acid side chains are of major importance for the activity of enzymes and the stability of proteins. Protein pKa values cannot always be measured directly, but may be calculated using theoretical methods. Buffer solutions are used extensively to provide solutions at or near the physiological pH for the study of biochemical reactions; the design of these solutions depends on a knowledge of the pKa values of their components. Important buffer solutions include MOPS, which provides a solution with pH 7.2, and tricine, which is used in gel electrophoresis. Buffering is an essential part of acid base physiology including acid–base homeostasis, and is key to understanding disorders such as acid–base disorder. The isoelectric point of a given molecule is a function of its pK values, so different molecules have different isoelectric points. This permits a technique called isoelectric focusing, which is used for separation of proteins by 2-D gel polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Buffer solutions also play a key role in analytical chemistry. They are used whenever there is a need to fix the pH of a solution at a particular value. Compared with an aqueous solution, the pH of a buffer solution is relatively insensitive to the addition of a small amount of strong acid or strong base. The buffer capacity of a simple buffer solution is largest when pH = pKa. In acid–base extraction, the efficiency of extraction of a compound into an organic phase, such as an ether, can be optimised by adjusting the pH of the aqueous phase using an appropriate buffer. At the optimum pH, the concentration of the electrically neutral species is maximised; such a species is more soluble in organic solvents having a low dielectric constant than it is in water. This technique is used for the purification of weak acids and bases.
A pH indicator is a weak acid or weak base that changes colour in the transition pH range, which is approximately pKa ± 1. The design of a universal indicator requires a mixture of indicators whose adjacent pKa values differ by about two, so that their transition pH ranges just overlap.
In pharmacology, ionization of a compound alters its physical behaviour and macro properties such as solubility and lipophilicity, log p). For example, ionization of any compound will increase the solubility in water, but decrease the lipophilicity. This is exploited in drug development to increase the concentration of a compound in the blood by adjusting the pKa of an ionizable group.
Knowledge of pKa values is important for the understanding of coordination complexes, which are formed by the interaction of a metal ion, Mm+, acting as a Lewis acid, with a ligand, L, acting as a Lewis base. However, the ligand may also undergo protonation reactions, so the formation of a complex in aqueous solution could be represented symbolically by the reaction
- [M(H2O)n]m+ + LH ⇌ [M(H2O)n−1L](m−1)+ + H3O+
To determine the equilibrium constant for this reaction, in which the ligand loses a proton, the pKa of the protonated ligand must be known. In practice, the ligand may be polyprotic; for example EDTA4− can accept four protons; in that case, all pKa values must be known. In addition, the metal ion is subject to hydrolysis, that is, it behaves as a weak acid, so the pK values for the hydrolysis reactions must also be known.
Assessing the hazard associated with an acid or base may require a knowledge of pKa values. For example, hydrogen cyanide is a very toxic gas, because the cyanide ion inhibits the iron-containing enzyme cytochrome c oxidase. Hydrogen cyanide is a weak acid in aqueous solution with a pKa of about 9. In strongly alkaline solutions, above pH 11, say, it follows that sodium cyanide is "fully dissociated" so the hazard due to the hydrogen cyanide gas is much reduced. An acidic solution, on the other hand, is very hazardous because all the cyanide is in its acid form. Ingestion of cyanide by mouth is potentially fatal, independently of pH, because of the reaction with cytochrome c oxidase.
In environmental science acid–base equilibria are important for lakes and rivers; for example, humic acids are important components of natural waters. Another example occurs in chemical oceanography: in order to quantify the solubility of iron(III) in seawater at various salinities, the pKa values for the formation of the iron(III) hydrolysis products Fe(OH)2+, Fe(OH)+
2 and Fe(OH)3 were determined, along with the solubility product of iron hydroxide.
Values for common substances
There are multiple techniques to determine the pKa of a chemical, leading to some discrepancies between different sources. Well measured values are typically within 0.1 units of each other. Data presented here were taken at 25 °C in water. More values can be found in the Thermodynamics section, above. A table of pKa of carbon acids, measured in DMSO, can be found on the page on carbanions.
| Chemical | Equilibrium | pKa |
|---|---|---|
| BH = Adenine | BH ⇌ B− + H+ | 4.17 |
| BH+ 2 ⇌ BH + H+ |
9.65 | |
| H3A = Arsenic acid | H3A ⇌ H2A− + H+ | 2.22 |
| H2A− ⇌ HA2− + H+ | 6.98 | |
| HA2− ⇌ A3− + H+ | 11.53 | |
| HA = Benzoic acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 4.204 |
| HA = Butyric acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 4.82 |
| H2A = Chromic acid | H2A ⇌ HA− + H+ | 0.98 |
| HA− ⇌ A2− + H+ | 6.5 | |
| B = Codeine | BH+ ⇌ B + H+ | 8.17 |
| HA = Cresol | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 10.29 |
| HA = Formic acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 3.751 |
| HA = Hydrofluoric acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 3.17 |
| HA = Hydrocyanic acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 9.21 |
| HA = Hydrogen selenide | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 3.89 |
| HA = Hydrogen peroxide (90%) | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 11.7 |
| HA = Lactic acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 3.86 |
| HA = Propionic acid | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 4.87 |
| HA = Phenol | HA ⇌ H+ + A− | 9.99 |
| H2A = L-(+)-Ascorbic Acid | H2A ⇌ HA− + H+ | 4.17 |
| HA− ⇌ A2− + H+ | 11.57 |

![{\displaystyle K_{\text{a}}=\mathrm {\frac {[A^{-}][H^{+}]}{[HA]}} ,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7cdd9efda0e3a32060020b5c9e5b2c78981b2a93)
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {p} K_{{\ce {a}}}=-\log _{10}K_{\text{a}}=\log _{10}{\frac {{\ce {[HA]}}}{[{\ce {A^-}}][{\ce {H+}}]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d7af05bf129db2f9bc618fe809660b6e4ff8dce9)



![{\displaystyle K^{\ominus }={{\frac {[{\ce {A^-}}][{\ce {H+}}]}{{\ce {[HA]}}}}\Gamma },\quad \Gamma ={\frac {\gamma _{{\ce {A^-}}}\ \gamma _{{\ce {H+}}}}{\gamma _{{\ce {HA}}}\ }}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6e9373db7091aeb4f51a26757a677b420f0a8418)

![{\displaystyle K_{\text{a}}={\frac {K^{\ominus }}{\Gamma }}=\mathrm {\frac {[A^{-}][H^{+}]}{[HA]}} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2a5a59c740de89347ec4c96d982292fc05c64b2f)
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {p} K_{{\ce {a}}}=-\log _{10}{\frac {[{\ce {A^-}}][{\ce {H^+}}]}{[{\ce {HA}}]}}=\log _{10}{\frac {{\ce {[HA]}}}{[{\ce {A^-}}][{\ce {H+}}]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bed5fbab82167a42994a6d735931d08b06f1e7a5)



![{\displaystyle \beta _{2}={\frac {{\ce {[H_2A]}}}{[{\ce {A^{2-}}}][{\ce {H+}}]^{2}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3306fbf9ccf8d12352eab96dfb5461897f2c3a15)


![{\displaystyle K_{\text{dissoc}}=\mathrm {\frac {[A^{-}][H^{+}]}{[HA]}} :\mathrm {p} K_{\text{a}}=-\log K_{\text{dissoc}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c5f9c1efd45de9edf690ebf6a72cc806eb2b0331)
![{\displaystyle K_{\text{assoc}}=\mathrm {\frac {[HA]}{[A^{-}][H^{+}]}} :\mathrm {p} K_{\text{b}}=-\log K_{\text{assoc}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/77a0453338b1d420214ac7c127d3faa13374fce0)




![{\displaystyle K_{\mathrm {a} }=\mathrm {\frac {[A^{-}][H^{+}]}{[HA]}} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4df1424aa532585fc7ad6dd660a596705ee31a2b)








![{\displaystyle \mathrm {pH} =\mathrm {p} K_{\text{a}}+\log \mathrm {\frac {[A^{-}]}{[HA]}} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/25e874f2b8ea8e4127605788c356393cfd7fff37)

![{\displaystyle \mathrm {p} K_{{\ce {a1}}}=\log _{10}{\frac {[{\ce {H_3PO_4}}]}{[{\ce {H_2PO_4^{-}}}][{\ce {H^+}}]}}=2.14}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/dff6e67381cb8a691b8873fbf884dad30b001352)
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {p} K_{{\ce {a2}}}=\log _{10}{\frac {[{\ce {H_2PO_4^{-}}}]}{[{\ce {HPO_4^{2-}}}][{\ce {H^+}}]}}=7.2}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/efe9f5a620a62c8de4a6567f58faf01e66829903)
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {p} K_{{\ce {a3}}}=\log _{10}{\frac {[{\ce {HPO_4^{2-}}}]}{[{\ce {PO_4^{3-}}}][{\ce {H^+}}]}}=12.37}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bf6cf97c1d47ba55db3a383374b9d8cd4eda22ee)





![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}K_{\text{b}}&=\mathrm {\frac {[HB^{+}][OH^{-}]}{[B]}} \\\mathrm {p} K_{\text{b}}&=-\log _{10}\left(K_{\text{b}}\right)\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5dea1aac629a595476e18c042a8f4365a50f0efc)
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {[OH^{-}]} ={\frac {K_{\mathrm {w} }}{\mathrm {[H^{+}]} }}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ab7f583da9f8b50145990ffa4342919930edfa16)
![{\displaystyle K_{\text{b}}={\frac {[\mathrm {HB^{+}} ]K_{\text{w}}}{\mathrm {[B][H^{+}]} }}={\frac {K_{\text{w}}}{K_{\text{a}}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/921c3abd37a1c5c00c31831509d3b090394c0d47)


![{\displaystyle K_{\mathrm {b} }={\frac {[\mathrm {M} _{p}(\mathrm {OH} )_{q-1}^{+}][\mathrm {OH} ^{-}]}{[\mathrm {M} _{p}(\mathrm {OH} )_{q}]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/aeb70331666676f62afda8017ff13fd1e941241a)
![{\displaystyle \mathrm {p} K_{\mathrm {aH} }(\mathrm {B} )=\mathrm {p} K_{\mathrm {a} }(\mathrm {BH} ^{+})=-\log _{10}{\Big (}{\frac {[\mathrm {B} ][\mathrm {H^{+}} ]}{[\mathrm {BH} ^{+}]}}{\Big )}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fa04a34c3fecca06d502586ca2f7c523c391233a)
![{\displaystyle K_{\text{a}}=\mathrm {\frac {[H^{+}][OH^{-}]}{[H_{2}O]}} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cdc540ad193c8f1661c1897698be93153fc5fb84)
![{\displaystyle K_{\text{w}}=[\mathrm {H} ^{+}][\mathrm {OH} ^{-}]\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c0039f77db244ea2f6d03d3475dc7a232a8ccb16)