Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are a class of materials that form two- or three- dimensional structures through reactions between organic precursors resulting in strong, covalent bonds to afford porous, stable, and crystalline materials. COFs emerged as a field from the overarching domain of organic materials as researchers optimized both synthetic control and precursor selection. These improvements to coordination chemistry enabled non-porous and amorphous organic materials such as organic polymers to advance into the construction of porous, crystalline materials with rigid structures that granted exceptional material stability in a wide range of solvents and conditions. Through the development of reticular chemistry, precise synthetic control was achieved and resulted in ordered, nano-porous structures with highly preferential structural orientation and properties which could be synergistically enhanced and amplified. With judicious selection of COF secondary building units (SBUs), or precursors, the final structure could be predetermined, and modified with exceptional control enabling fine-tuning of emergent properties. This level of control facilitates the COF material to be designed, synthesized, and utilized in various applications, many times with metrics on scale or surpassing that of the current state-of-the-art approaches.
History
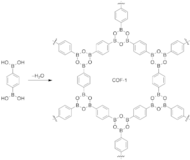
While at University of Michigan, Omar M. Yaghi (currently at UCBerkeley) and Adrien P Cote published the first paper of COFs in 2005, reporting a series of 2D COFs. They reported the design and successful synthesis of COFs by condensation reactions of phenyl diboronic acid (C6H4[B(OH)2]2) and hexahydroxytriphenylene (C18H6(OH)6). Powder X-ray diffraction studies of the highly crystalline products having empirical formulas (C3H2BO)6·(C9H12)1 (COF-1) and C9H4BO2 (COF-5) revealed 2-dimensional expanded porous graphitic layers that have either staggered conformation (COF-1) or eclipsed conformation (COF-5). Their crystal structures are entirely held by strong bonds between B, C, and O atoms to form rigid porous architectures with pore sizes ranging from 7 to 27 Angstroms. COF-1 and COF-5 exhibit high thermal stability (to temperatures up to 500 to 600 C), permanent porosity, and high surface areas (711 and 1590 square meters per gram, respectively).
The synthesis of 3D COFs has been hindered by longstanding practical and conceptual challenges until it was first achieved in 2007 by Omar M. Yaghi and colleagues. Unlike 0D and 1D systems, which are soluble, the insolubility of 2D and 3D structures precludes the use of stepwise synthesis, making their isolation in crystalline form very difficult. This first challenge, however, was overcome by judiciously choosing building blocks and using reversible condensation reactions to crystallize COFs.
Structure
Porous crystalline solids consists of secondary building units (SBUs) which assemble to form a periodic and porous framework. An almost infinite numbers of frameworks can be formed through various SBU combinations leading to unique material properties for applications in separations, storage, and heterogeneous catalysis.
Types of porous crystalline solids include zeolites, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), and covalent organic frameworks (COFs). Zeolites are microporous, aluminosilicate minerals commonly used as commercial adsorbents. MOFs are a class of porous polymeric material, consisting of metal ions linked together by organic bridging ligands and are a new development on the interface between molecular coordination chemistry and materials science.
COFs are another class of porous polymeric materials, consisting of porous, crystalline, covalent bonds that usually have rigid structures, exceptional thermal stabilities (to temperatures up to 600 °C), are stable in water and low densities. They exhibit permanent porosity with specific surface areas surpassing those of well-known zeolites and porous silicates.
Secondary Building Units
The term ‘secondary building unit’ has been used for some time to describe conceptual fragments which can be compared as bricks used to build a house of zeolites; in the context of this page it refers to the geometry of the units defined by the points of extension.
Reticular Synthesis
Reticular synthesis enables facile bottom-up synthesis of the framework materials to introduce precise perturbations in chemical composition, resulting in the highly controlled tunability of framework properties. Through a bottom-up approach, a material is built from atomic or molecular components synthetically as opposed to a top-down approach, which forms a material from the bulk through approaches such as exfoliation, lithography, or other varieties of post-synthetic modification. The bottom-up approach is especially advantageous with respect to materials such as COFs because the synthetic methods are designed to directly result in an extended, highly crosslinked framework that can be tuned with exceptional control at the nanoscale level. Geometrical and dimensional principles govern the framework's resulting topology as the SBUs combine to form predetermined structures. This level of synthetic control has also been termed "molecular engineering", abiding by the concept termed by Arthur R. von Hippel in 1956.
It has been established in the literature that, when integrated into an isoreticular framework, such as a COF, properties from monomeric compounds can be synergistically enhanced and amplified. COF materials possess the unique ability for bottom-up reticular synthesis to afford robust, tunable frameworks that synergistically enhance the properties of the precursors, which, in turn, offers many advantages in terms of improved performance in different applications. As a result, the COF material is highly modular and tuned efficiently by varying the SBUs’ identity, length, and functionality depending on the desired property change on the framework scale. Ergo, there exists the ability to introduce diverse functionality directly into the framework scaffold to allow for a variety of functions which would be cumbersome, if not impossible, to achieve through a top-down method. such as lithographic approaches or chemical-based nanofabrication. Through reticular synthesis, it is possible to molecularly engineer modular, framework materials with highly porous scaffolds that exhibit unique electronic, optical, and magnetic properties while simultaneously integrating desired functionality into the COF skeleton.
Reticular synthesis is different from retrosynthesis of organic compounds, because the structural integrity and rigidity of the building blocks in reticular synthesis remain unaltered throughout the construction process—an important aspect that could help to fully realize the benefits of design in crystalline solid-state frameworks. Similarly, reticular synthesis should be distinguished from supramolecular assembly, because in the former, building blocks are linked by strong bonds throughout the crystal.
Synthetic Chemistry
Reticular synthesis was used by Yaghi and coworkers in 2005 to construct the first two COFs reported in the literature: COF-1, using a dehydration reaction of benzenediboronic acid (BDBA), and COF-5, via a condensation reaction between hexahydroxytriphenylene (HHTP) and BDBA. These framework scaffolds were interconnected through the formation of boroxine and boronate linkages, respectively, using solvothermal synthetic methods.
COF Linkages
Since Yaghi and coworkers’ seminal work in 2005, COF synthesis has expanded to include a wide range of organic connectivity such as boron-, nitrogen-, other atom-containing linkages. The linkages in the figures shown are not comprehensive as other COF linkages exist in the literature, especially for the formation of 3D COFs.
Boron condensation
The most popular COF synthesis route is a boron condensation reaction which is a molecular dehydration reaction between boronic acids. In case of COF-1, three boronic acid molecules converge to form a planar six-membered B3O3 (boroxine) ring with the elimination of three water molecules.
Triazine based trimerization
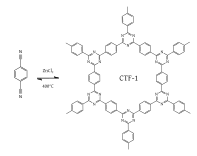
Another class of high performance polymer frameworks with regular porosity and high surface area is based on triazine materials which can be achieved by dynamic trimerization reaction of simple, cheap, and abundant aromatic nitriles in ionothermal conditions (molten zinc chloride at high temperature (400 °C)). CTF-1 is a good example of this chemistry.
Imine condensation
The imine condensation reaction which eliminates water (exemplified by reacting aniline with benzaldehyde using an acid catalyst) can be used as a synthetic route to reach a new class of COFs. The 3D COF called COF-300 and the 2D COF named TpOMe-DAQ are good examples of this chemistry. When 1,3,5-triformylphloroglucinol (TFP) is used as one of the SBUs, two complementary tautomerizations occur (an enol to keto and an imine to enamine) which result in a β-ketoenamine moiety as depicted in the DAAQ-TFP framework. Both DAAQ-TFP and TpOMe-DAQ COFs are stable in acidic aqueous conditions and contain the redox active linker 2,6-diaminoanthroquinone which enables these materials to reversibly store and release electrons within a characteristic potential window. Consequently, both of these COFs have been investigated as electrode materials for potential use in supercapacitors.
Solvothermal Synthesis
The solvothermal approach is the most common used in the literature but typically requires long reaction times due to the insolubility of the organic SBUs in nonorganic media and the time necessary to reach thermodynamic COF products.
Templated Synthesis
Morphological control on the nanoscale is still limited as COFs lack synthetic control in higher dimensions due to the lack of dynamic chemistry during synthesis. To date, researchers have attempted to establish better control through different synthetic methods such as solvothermal synthesis, interface-assisted synthesis, solid templation as well as seeded growth. First one of the precursors is deposited onto the solid support followed by the introduction of the second precursor in vapor form. This results in the deposition of the COF as a thin film on the solid support.
Properties
Porosity
A defining advantage of COFs is the exceptional porosity that results from the substitution of analogous SBUs of varying sizes. Pore sizes range from 7-23 Å and feature a diverse range of shapes and dimensionalities that remain stable during the evacuation of solvent. The rigid scaffold of the COF structure enables the material to be evacuated of solvent and retain its structure, resulting in high surface areas as seen by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis. This high surface area to volume ratio and incredible stability enables the COF structure to serve as exceptional materials for gas storage and separation.
Crystallinity
There are several COF single crystals synthesized to date. There are a variety of techniques employed to improve crystallinity of COFs. The use of modulators, monofunctional version of precursors, serve to slow the COF formation to allow for more favorable balance between kinetic and thermodynamic control, hereby enabling crystalline growth. This was employed by Yaghi and coworkers for 3D imine-based COFs (COF-300, COF 303, LZU-79, and LZU-111). However, the vast majority of COFs are not able to crystallize into single crystals but instead are insoluble powders. The improvement of crystallinity of these polycrystalline materials can be improved through tuning the reversibility of the linkage formation to allow for corrective particle growth and self-healing of defects that arise during COF formation.
Conductivity
Integration of SBUs into a covalent framework results in the synergistic emergence of conductivities much greater than the monomeric values. The nature of the SBUs can improve conductivity. Through the use of highly conjugated linkers throughout the COF scaffold, the material can be engineered to be fully conjugated, enabling high charge carrier density as well as through- and in-plane charge transport. For instance, Mirica and coworkers synthesized a COF material (NiPc-Pyr COF) from nickel phthalocyanine (NiPc) and pyrene organic linkers that had a conductivity of 2.51 x 10−3 S/m, which was several orders of magnitude larger than the undoped molecular NiPc, 10−11 S/m. A similar COF structure made by Jiang and coworkers, CoPc-Pyr COF, exhibited a conductivity of 3.69 x 10−3 S/m. In both previously mentioned COFs, the 2D lattice allows for full π-conjugation in the x and y directions as well as π-conduction along the z axis due to the fully conjugated, aromatic scaffold and π-π stacking, respectively. Emergent electrical conductivity in COF structures is especially important for applications such as catalysis and energy storage where quick and efficient charge transport is required for optimal performance.
Characterization
There exists a wide range of characterization methods for COF materials. There are several COF single crystals synthesized to date. For these highly crystalline materials, X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful tool capable of determining COF crystal structure. The majority of COF materials suffer from decreased crystallinity so powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) is used. In conjunction with simulated powder packing models, PXRD can determine COF crystal structure.
In order to verify and analyze COF linkage formation, various techniques can be employed such as infrared (IR) spectroscopy, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Precursor and COF IR spectra enables comparison between vibrational peaks to ascertain that certain key bonds present in the COF linkages appear and that peaks of precursor functional groups disappear. In addition, solid-state NMR enables probing of linkage formation as well and is well suited for large, insoluble materials like COFs. Gas adsorption-desorption studies quantify the porosity of the material via calculation of the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and pore diameter from gas adsorption isotherms. Electron imagine techniques such as scanning electron microscope (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) can resolve surface structure and morphology, and microstructural information, respectively. Scanning tunneling microscope (STM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) have also been used to characterize COF microstructural information as well. Additionally, methods like X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), and combustion analysis can be used to identify elemental composition and ratios.
Applications
Gas Storage and Separation
Due to the exceptional porosity of COFs, they have been used extensively in the storage and separation of gases such as hydrogen, methane, etc.
Hydrogen Storage
Omar M. Yaghi and William A. Goddard III reported COFs as exceptional hydrogen storage materials. They predicted the highest excess H2 uptakes at 77 K are 10.0 wt % at 80 bar for COF-105, and 10.0 wt % at 100 bar for COF-108, which have higher surface area and free volume, by grand canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) simulations as a function of temperature and pressure. This is the highest value reported for associative H2 storage of any material. Thus 3-D COFs are most promising new candidates in the quest for practical H2 storage materials. In 2012, the lab of William A. Goddard III reported the uptake for COF102, COF103, and COF202 at 298 K and they also proposed new strategies to obtain higher interaction with H2. Such strategy consist on metalating the COF with alkaline metals such as Li. These complexes composed of Li, Na and K with benzene ligands (such as 1,3,5-benzenetribenzoate, the ligand used in MOF-177) have been synthesized by Krieck et al. and Goddard showed that the THF is important of their stability. If the metalation with alkaline is performed in the COFs, Goddard et al. calculated that some COFs can reach 2010 DOE gravimetric target in delivery units at 298 K of 4.5 wt %: COF102-Li (5.16 wt %), COF103-Li (4.75 wt %), COF102-Na (4.75 wt %) and COF103-Na (4.72 wt %). COFs also perform better in delivery units than MOFs because the best volumetric performance is for COF102-Na (24.9), COF102-Li (23.8), COF103-Na (22.8), and COF103-Li (21.7), all using delivery g H2/L units for 1–100 bar. These are the highest gravimetric molecular hydrogen uptakes for a porous material under these thermodynamic conditions.
Methane Storage
Omar M. Yaghi and William A. Goddard III also reported COFs as exceptional methane storage materials. The best COF in terms of total volume of CH4 per unit volume COF absorbent is COF-1, which can store 195 v/v at 298 K and 30 bar, exceeding the U.S. Department of Energy target for CH4 storage of 180 v/v at 298 K and 35 bar. The best COFs on a delivery amount basis (volume adsorbed from 5 to 100 bar) are COF-102 and COF-103 with values of 230 and 234 v(STP: 298 K, 1.01 bar)/v, respectively, making these promising materials for practical methane storage. More recently, new COFs with better delivery amount have been designed in the lab of William A. Goddard III, and they have been shown to be stable and overcome the DOE target in delivery basis. COF-103-Eth-trans and COF-102-Ant, are found to exceed the DOE target of 180 v(STP)/v at 35 bar for methane storage. They reported that using thin vinyl bridging groups aid performance by minimizing the interaction methane-COF at low pressure.
Gas Separation
In addition to storage, COF materials are exceptional at gas separation. For instance, COFs like imine-linked COF LZU1 and azine-linked COF ACOF-1 were used as a bilayer membrane for the selective separation of the following mixtures: H2/CO2, H2/N2, and H2/CH4. The COFs outperformed molecular sieves due to the inherent thermal and operational stability of the structures. It has also been shown that COFs inherently act as adsorbents, adhering to the gaseous molecules to enable storage and separation.
Optical properties
A highly ordered π-conjugation TP-COF, consisting of pyrene and triphenylene functionalities alternately linked in a mesoporous hexagonal skeleton, is highly luminescent, harvests a wide wavelength range of photons, and allows energy transfer and migration. Furthermore, TP-COF is electrically conductive and capable of repetitive on–off current switching at room temperature.
Porosity/surface-area effects
Most studies to date have focused on the development of synthetic methodologies with the aim of maximizing pore size and surface area for gas storage. That means the functions of COFs have not yet been well explored, but COFs can be used as catalysts, or for gas separation, etc.
Carbon capture
In 2015 the use of highly porous, catalyst-decorated COFs for converting carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide was reported. MOF under solvent-free conditions can also be used for catalytic activity in the cycloaddition of CO2 and epoxides into cyclic organic carbonates with enhanced catalyst recyclability.
Sensing
Due to defining molecule-framework interactions, COFs can be used as chemical sensors in a wide range of environments and applications. Properties of the COF change when their functionalities interact with various analytes enabling the materials to serve as devices in various conditions: as chemiresistive sensors, as well as electrochemical sensors for small molecules.
Catalysis
Due to the ability to introduce diverse functionality into COFs’ structure, catalytic sites can be fine-tuned in conjunction with other advantageous properties like conductivity and stability to afford efficient and selective catalysts. COFs have been used as heterogeneous catalysts in organic, electrochemical, as well as photochemical reactions.
Electrocatalysis
COFs have been studied as non-metallic electrocatalyst for energy-related catalysis, including carbon dioxide electro-reduction and water splitting reaction. However, such researches are still in the very earlier stage. Most of the efforts have been focusing on solving the key issues, such as conductivity, stability in electrochemical processes.
Energy Storage
A few COFs possess the stability and conductivity necessary to perform well in energy storage applications like lithium-ion batteries, and various different metal-ion batteries and cathodes.
Water filtration
A prototype 2 nanometer thick COF layer on a graphene substrate was used to filter dye from industrial wastewater. Once full, the COF can be cleaned and reused.