In
mathematics, a
Lie group // is a
group that is also a
differentiable manifold, with the property that the group operations are compatible with the
smooth structure. Lie groups are named after
Sophus Lie, who laid the foundations of the theory of continuous
transformation groups. The term
groupes de Lie first appeared in French in 1893 in the thesis of Lie’s student
Arthur Tresse, page 3.
[1]
Lie groups represent the best-developed theory of
continuous symmetry of
mathematical objects and
structures, which makes them indispensable tools for many parts of contemporary mathematics, as well as for modern
theoretical physics. They provide a natural framework for analysing the continuous symmetries of
differential equations (
differential Galois theory), in much the same way as
permutation groups are used in
Galois theory for analysing the discrete symmetries of
algebraic equations. An extension of Galois theory to the case of continuous symmetry groups was one of Lie's principal motivations.
Overview

The
circle of center 0 and radius 1 in the
complex plane is a Lie group with complex multiplication.
Lie groups are smooth
[Note 1] differentiable manifolds and as such can be studied using
differential calculus, in contrast with the case of more general
topological groups. One of the key ideas in the theory of Lie groups is to replace the
global object, the group, with its
local or linearized version, which Lie himself called its "infinitesimal group" and which has since become known as its
Lie algebra.
Lie groups play an enormous role in modern
geometry, on several different levels.
Felix Klein argued in his
Erlangen program that one can consider various "geometries" by specifying an appropriate transformation group that leaves certain geometric properties invariant. Thus
Euclidean geometry corresponds to the choice of the group
E(3) of distance-preserving transformations of the Euclidean space
R3,
conformal geometry corresponds to enlarging the group to the
conformal group, whereas in
projective geometry one is interested in the properties invariant under the
projective group. This idea later led to the notion of a
G-structure, where
G is a Lie group of "local" symmetries of a manifold. On a "global" level, whenever a Lie group
acts on a geometric object, such as a
Riemannian or a
symplectic manifold, this action provides a measure of rigidity and yields a rich algebraic structure. The presence of continuous symmetries expressed via a Lie group action on a manifold places strong constraints on its geometry and facilitates
analysis on the manifold. Linear actions of Lie groups are especially important, and are studied in
representation theory.
In the 1940s–1950s,
Ellis Kolchin,
Armand Borel, and
Claude Chevalley realised that many foundational results concerning Lie groups can be developed completely algebraically, giving rise to the theory of
algebraic groups defined over an arbitrary
field. This insight opened new possibilities in pure algebra, by providing a uniform construction for most
finite simple groups, as well as in
algebraic geometry. The theory of
automorphic forms, an important branch of modern
number theory, deals extensively with analogues of Lie groups over
adele rings; p-adic
Lie groups play an important role, via their connections with Galois representations in number theory.
Definitions and examples
A
real Lie group is a
group that is also a finite-dimensional real
smooth manifold, in which the group operations of
multiplication and inversion are
smooth maps. Smoothness of the group multiplication

means that μ is a smooth mapping of the product manifold
G×
G into
G. These two requirements can be combined to the single requirement that the mapping
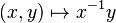
be a smooth mapping of the product manifold into
G.
First examples
-

- This is a four-dimensional noncompact real Lie group. This group is disconnected; it has two connected components corresponding to the positive and negative values of the determinant.
- The rotation matrices form a subgroup of GL(2, R), denoted by SO(2, R). It is a Lie group in its own right: specifically, a one-dimensional compact connected Lie group which is diffeomorphic to the circle. Using the rotation angle
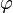 as a parameter, this group can be parametrized as follows:
as a parameter, this group can be parametrized as follows:
-
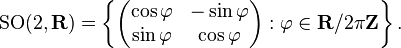
- Addition of the angles corresponds to multiplication of the elements of SO(2, R), and taking the opposite angle corresponds to inversion. Thus both multiplication and inversion are differentiable maps.
All of the previous examples of Lie groups fall within the class of
classical groups.
Related concepts
A
complex Lie group is defined in the same way using
complex manifolds rather than real ones (example: SL(2,
C)), and similarly, using an alternate
metric completion of
Q, one can define a
p-adic Lie group over the
p-adic numbers, a topological group in which each point has a
p-adic neighborhood.
Hilbert's fifth problem asked whether replacing differentiable manifolds with topological or analytic ones can yield new examples. The answer to this question turned out to be negative: in 1952,
Gleason,
Montgomery and
Zippin showed that if
G is a topological manifold with continuous group operations, then there exists exactly one analytic structure on
G which turns it into a Lie group (see also
Hilbert–Smith conjecture). If the underlying manifold is allowed to be infinite-dimensional (for example, a
Hilbert manifold), then one arrives at the notion of an infinite-dimensional Lie group. It is possible to define analogues of many
Lie groups over finite fields, and these give most of the examples of
finite simple groups.
The language of
category theory provides a concise definition for Lie groups: a Lie group is a
group object in the
category of smooth manifolds. This is important, because it allows generalization of the notion of a Lie group to
Lie supergroups.
More examples of Lie groups
Lie groups occur in abundance throughout mathematics and physics.
Matrix groups or
algebraic groups are (roughly) groups of matrices (for example,
orthogonal and
symplectic groups), and these give most of the more common examples of Lie groups.
Examples with a specific number of dimensions
- The circle group S1 consisting of angles mod 2π under addition or, alternatively, the complex numbers with absolute value 1 under multiplication. This is a one-dimensional compact connected abelian Lie group.
- The 3-sphere S3 forms a Lie group by identification with the set of quaternions of unit norm, called versors. The only other spheres that admit the structure of a Lie group are the 0-sphere S0 (real numbers with absolute value 1) and the circle S1 (complex numbers with absolute value 1). For example, for even n > 1, Sn is not a Lie group because it does not admit a nonvanishing vector field and so a fortiori cannot be parallelizable as a differentiable manifold. Of the spheres only S0, S1, S3, and S7 are parallelizable. The last carries the structure of a Lie quasigroup (a nonassociative group), which can be identified with the set of unit octonions.
- The (3-dimensional) metaplectic group is a double cover of SL(2, R) playing an important role in the theory of modular forms. It is a connected Lie group that cannot be faithfully represented by matrices of finite size, i.e., a nonlinear group.
- The Heisenberg group is a connected nilpotent Lie group of dimension 3, playing a key role in quantum mechanics.
- The Lorentz group is a 6-dimensional Lie group of linear isometries of the Minkowski space.
- The Poincaré group is a 10-dimensional Lie group of affine isometries of the Minkowski space.
- The group U(1)×SU(2)×SU(3) is a Lie group of dimension 1+3+8=12 that is the gauge group of the Standard Model in particle physics. The dimensions of the factors correspond to the 1 photon + 3 vector bosons + 8 gluons of the standard model
- The exceptional Lie groups of types G2, F4, E6, E7, E8 have dimensions 14, 52, 78, 133, and 248. Along with the A-B-C-D series of simple Lie groups, the exceptional groups complete the list of simple Lie groups. There is also a Lie group named E7½ of dimension 190, but it is not a simple Lie group.
Examples with n dimensions
- Euclidean space Rn with ordinary vector addition as the group operation becomes an n-dimensional noncompact abelian Lie group.
- The Euclidean group E(n, R) is the Lie group of all Euclidean motions, i.e., isometric affine maps, of n-dimensional Euclidean space Rn.
- The orthogonal group O(n, R), consisting of all n × n orthogonal matrices with real entries is an n(n − 1)/2-dimensional Lie group. This group is disconnected, but it has a connected subgroup SO(n, R) of the same dimension consisting of orthogonal matrices of determinant 1, called the special orthogonal group (for n = 3, the rotation group SO(3)).
- The unitary group U(n) consisting of n × n unitary matrices (with complex entries) is a compact connected Lie group of dimension n2. Unitary matrices of determinant 1 form a closed connected subgroup of dimension n2 − 1 denoted SU(n), the special unitary group.
- Spin groups are double covers of the special orthogonal groups, used for studying fermions in quantum field theory (among other things).
- The group GL(n, R) of invertible matrices (under matrix multiplication) is a Lie group of dimension n2, called the general linear group. It has a closed connected subgroup SL(n, R), the special linear group, consisting of matrices of determinant 1 which is also a Lie group.
- The symplectic group Sp(2n, R) consists of all 2n × 2n matrices preserving a symplectic form on R2n. It is a connected Lie group of dimension 2n2 + n.
- The group of invertible upper triangular n by n matrices is a solvable Lie group of dimension n(n + 1)/2. (cf. Borel subgroup)
- The A-series, B-series, C-series and D-series, whose elements are denoted by An, Bn, Cn, and Dn, are infinite families of simple Lie groups.
Constructions
There are several standard ways to form new Lie groups from old ones:
- The product of two Lie groups is a Lie group.
- Any topologically closed subgroup of a Lie group is a Lie group. This is known as the Closed subgroup theorem or Cartan's theorem.
- The quotient of a Lie group by a closed normal subgroup is a Lie group.
- The universal cover of a connected Lie group is a Lie group. For example, the group R is the universal cover of the circle group S1. In fact any covering of a differentiable manifold is also a differentiable manifold, but by specifying universal cover, one guarantees a group structure (compatible with its other structures).
Related notions
Some examples of groups that are
not Lie groups (except in the trivial sense that any group can be viewed as a 0-dimensional Lie group, with the
discrete topology), are:
- Infinite-dimensional groups, such as the additive group of an infinite-dimensional real vector space. These are not Lie groups as they are not finite-dimensional manifolds
- Some totally disconnected groups, such as the Galois group of an infinite extension of fields, or the additive group of the p-adic numbers. These are not Lie groups because their underlying spaces are not real manifolds. (Some of these groups are "p-adic Lie groups"). In general, only topological groups having similar local properties to Rn for some positive integer n can be Lie groups (of course they must also have a differentiable structure)
Basic concepts
The Lie algebra associated with a Lie group
To every Lie group we can associate a
Lie algebra whose underlying vector space is the tangent space of the Lie group at the identity element and which completely captures the local structure of the group. Informally we can think of elements of the Lie algebra as elements of the group that are "
infinitesimally close" to the identity, and the Lie bracket is related to the
commutator of two such infinitesimal elements. Before giving the abstract definition we give a few examples:
- The Lie algebra of the vector space Rn is just Rn with the Lie bracket given by
[A, B] = 0.
(In general the Lie bracket of a connected Lie group is always 0 if and only if the Lie group is abelian.)
- The Lie algebra of the general linear group GL(n, R) of invertible matrices is the vector space M(n, R) of square matrices with the Lie bracket given by
[A, B] = AB − BA.
If G is a closed subgroup of GL(n, R) then the Lie algebra of G can be thought of informally as the matrices m of M(n, R) such that 1 + εm is in G, where ε is an infinitesimal positive number with ε2 = 0 (of course, no such real number ε exists). For example, the orthogonal group O(n, R) consists of matrices A with AAT = 1, so the Lie algebra consists of the matrices m with (1 + εm)(1 + εm)T = 1, which is equivalent to m + mT = 0 because ε2 = 0.
- Formally, when working over the reals, as here, this is accomplished by considering the limit as ε → 0; but the "infinitesimal" language generalizes directly to Lie groups over general rings.[clarification needed]
The concrete definition given above is easy to work with, but has some minor problems: to use it we first need to represent a Lie group as a group of matrices, but not all Lie groups can be represented in this way, and it is not obvious that the Lie algebra is independent of the representation we use. To get around these problems we give the general definition of the Lie algebra of a Lie group (in 4 steps):
- Vector fields on any smooth manifold M can be thought of as derivations X of the ring of smooth functions on the manifold, and therefore form a Lie algebra under the Lie bracket [X, Y] = XY − YX, because the Lie bracket of any two derivations is a derivation.
- If G is any group acting smoothly on the manifold M, then it acts on the vector fields, and the vector space of vector fields fixed by the group is closed under the Lie bracket and therefore also forms a Lie algebra.
- We apply this construction to the case when the manifold M is the underlying space of a Lie group G, with G acting on G = M by left translations Lg(h) = gh. This shows that the space of left invariant vector fields (vector fields satisfying Lg*Xh = Xgh for every h in G, where Lg* denotes the differential of Lg) on a Lie group is a Lie algebra under the Lie bracket of vector fields.
- Any tangent vector at the identity of a Lie group can be extended to a left invariant vector field by left translating the tangent vector to other points of the manifold. Specifically, the left invariant extension of an element v of the tangent space at the identity is the vector field defined by v^g = Lg*v. This identifies the tangent space TeG at the identity with the space of left invariant vector fields, and therefore makes the tangent space at the identity into a Lie algebra, called the Lie algebra of G, usually denoted by a Fraktur
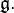 Thus the Lie bracket on
Thus the Lie bracket on  is given explicitly by [v, w] = [v^, w^]e.
is given explicitly by [v, w] = [v^, w^]e.
This Lie algebra

is finite-dimensional and it has the same dimension as the manifold
G. The Lie algebra of
G determines
G up to "local isomorphism", where two Lie groups are called
locally isomorphic if they look the same near the identity element. Problems about Lie groups are often solved by first solving the corresponding problem for the Lie algebras, and the result for groups then usually follows easily. For example, simple Lie groups are usually classified by first classifying the corresponding Lie algebras.
We could also define a Lie algebra structure on
Te using right invariant vector fields instead of left invariant vector fields. This leads to the same Lie algebra, because the inverse map on
G can be used to identify left invariant vector fields with right invariant vector fields, and acts as −1 on the tangent space
Te.
The Lie algebra structure on
Te can also be described as follows: the commutator operation
- (x, y) → xyx−1y−1
on
G ×
G sends (
e,
e) to
e, so its derivative yields a
bilinear operation on
TeG. This bilinear operation is actually the zero map, but the second derivative, under the proper identification of tangent spaces, yields an operation that satisfies the axioms of a
Lie bracket, and it is equal to twice the one defined through left-invariant vector fields.
Homomorphisms and isomorphisms
If
G and
H are Lie groups, then a Lie group homomorphism
f :
G →
H is a smooth
group homomorphism. In the case of complex Lie groups, such a homomorphism is required to be a
holomorphic map. However, these requirements are a bit stringent; over real or complex numbers, every continuous homomorphism between Lie groups turns out to be (real or complex)
analytic.
The composition of two Lie homomorphisms is again a homomorphism, and the class of all Lie groups, together with these morphisms, forms a
category. Moreover, every Lie group homomorphism induces a homomorphism between the corresponding Lie algebras. Let

be a Lie group homomorphism and let
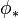
be its
derivative at the identity. If we identify the
Lie algebras of
G and
H with their
tangent spaces at the identity elements then
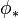
is a map between the corresponding Lie algebras:

One can show that
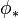
is actually a
Lie algebra homomorphism (meaning that it is a
linear map which preserves the
Lie bracket). In the language of
category theory, we then have a covariant
functor from the category of Lie groups to the category of Lie algebras which sends a Lie group to its Lie algebra and a Lie group homomorphism to its derivative at the identity.
Two Lie groups are called
isomorphic if there exists a
bijective homomorphism between them whose inverse is also a Lie group homomorphism. Equivalently, it is a
diffeomorphism which is also a group homomorphism.
Ado's theorem says every finite-dimensional Lie algebra is isomorphic to a matrix Lie algebra. For every finite-dimensional matrix Lie algebra, there is a linear group (matrix Lie group) with this algebra as its Lie algebra. So every abstract Lie algebra is the Lie algebra of some (linear) Lie group.
The
global structure of a Lie group is not determined by its Lie algebra; for example, if
Z is any discrete subgroup of the center of
G then
G and
G/
Z have the same Lie algebra (see the
table of Lie groups for examples). A
connected Lie group is
simple,
semisimple,
solvable,
nilpotent, or
abelian if and only if its Lie algebra has the corresponding property.
If we require that the Lie group be
simply connected, then the global structure is determined by its Lie algebra: for every finite-dimensional Lie algebra

over
F there is a simply connected Lie group
G with

as Lie algebra, unique up to isomorphism. Moreover every homomorphism between Lie algebras lifts to a unique homomorphism between the corresponding simply connected Lie groups.
The exponential map
The
exponential map from the Lie algebra M(
n,
R) of the
general linear group GL(
n,
R) to GL(
n,
R) is defined by the usual power series:
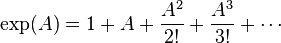
for matrices
A. If
G is any subgroup of GL(
n,
R), then the exponential map takes the Lie algebra of
G into
G, so we have an exponential map for all matrix groups.
The definition above is easy to use, but it is not defined for Lie groups that are not matrix groups, and it is not clear that the exponential map of a Lie group does not depend on its representation as a matrix group. We can solve both problems using a more abstract definition of the exponential map that works for all Lie groups, as follows.
Every vector
v in

determines a linear map from
R to

taking 1 to
v, which can be thought of as a Lie algebra homomorphism. Because
R is the Lie algebra of the simply connected Lie group
R, this induces a Lie group homomorphism
c :
R →
G so that
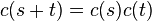
for all
s and
t. The operation on the right hand side is the group multiplication in
G. The formal similarity of this formula with the one valid for the
exponential function justifies the definition

This is called the
exponential map, and it maps the Lie algebra

into the Lie group
G. It provides a
diffeomorphism between a
neighborhood of 0 in

and a neighborhood of
e in
G. This exponential map is a generalization of the exponential function for real numbers (because
R is the Lie algebra of the Lie group of positive real numbers with multiplication), for complex numbers (because
C is the Lie algebra of the Lie group of non-zero complex numbers with multiplication) and for
matrices (because M(
n,
R) with the regular commutator is the Lie algebra of the Lie group GL(
n,
R) of all invertible matrices).
Because the exponential map is surjective on some neighbourhood
N of
e, it is common to call elements of the Lie algebra
infinitesimal generators of the group
G. The subgroup of
G generated by
N is the identity component of
G.
The exponential map and the Lie algebra determine the
local group structure of every connected Lie group, because of the
Baker–Campbell–Hausdorff formula: there exists a neighborhood
U of the zero element of

, such that for
u,
v in
U we have
![\exp(u)\,\exp(v) = \exp\left(u + v + \tfrac{1}{2}[u,v] + \tfrac{1}{12}[\,[u,v],v] - \tfrac{1}{12}[\,[u,v],u] - \cdots \right),](//upload.wikimedia.org/math/b/0/d/b0dd542c9dadf93bc17ce3af7b953ff6.png)
where the omitted terms are known and involve Lie brackets of four or more elements. In case
u and
v commute, this formula reduces to the familiar exponential law
exp(u) exp(v) = exp(u + v).
The exponential map relates Lie group homomorphisms. That is, if

is a Lie group homomorphism and

the induced map on the corresponding Lie algebras, then for all
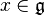
we have

In other words the following diagram
commutes,
[Note 2]
(In short, exp is a
natural transformation from the functor Lie to the identity functor on the category of Lie groups.)
The exponential map from the Lie algebra to the Lie group is not always
onto, even if the group is connected (though it does map onto the Lie group for connected groups that are either compact or nilpotent). For example, the exponential map of
SL(2, R) is not surjective. Also, exponential map is not surjective nor injective for infinite-dimensional (see below) Lie groups modelled on
C∞ Fréchet space, even from arbitrary small neighborhood of 0 to corresponding neighborhood of 1.
Lie subgroup
A
Lie subgroup H of a Lie group
G is a Lie group that is a
subset of
G and such that the
inclusion map from
H to
G is an
injective immersion and
group homomorphism. According to
Cartan's theorem, a closed
subgroup of
G admits a unique
smooth structure which makes it an
embedded Lie subgroup of
G—i.e. a Lie subgroup such that the inclusion map is a smooth embedding.
Examples of non-closed subgroups are plentiful; for example take
G to be a
torus of dimension ≥ 2, and let
H be a
one-parameter subgroup of
irrational slope, i.e. one that winds around in
G. Then there is a Lie group
homomorphism φ :
R →
G with
H as its image. The
closure of
H will be a sub-torus in
G.
In terms of the
exponential map of
G, in general, only some of the Lie subalgebras of the Lie algebra
g of
G correspond to closed Lie subgroups
H of
G. There is no criterion solely based on the structure of
g which determines which those are.
Early history
According to the most authoritative source on the early history of Lie groups (Hawkins, p. 1),
Sophus Lie himself considered the winter of 1873–1874 as the birth date of his theory of continuous groups. Hawkins, however, suggests that it was "Lie's prodigious research activity during the four-year period from the fall of 1869 to the fall of 1873" that led to the theory's creation (
ibid). Some of Lie's early ideas were developed in close collaboration with
Felix Klein. Lie met with Klein every day from October 1869 through 1872: in Berlin from the end of October 1869 to the end of February 1870, and in Paris, Göttingen and Erlangen in the subsequent two years (
ibid, p. 2). Lie stated that all of the principal results were obtained by 1884. But during the 1870s all his papers (except the very first note) were published in Norwegian journals, which impeded recognition of the work throughout the rest of Europe (
ibid, p. 76). In 1884 a young German mathematician,
Friedrich Engel, came to work with Lie on a systematic treatise to expose his theory of continuous groups. From this effort resulted the three-volume
Theorie der Transformationsgruppen, published in 1888, 1890, and 1893.
Lie's ideas did not stand in isolation from the rest of mathematics. In fact, his interest in the geometry of differential equations was first motivated by the work of
Carl Gustav Jacobi, on the theory of
partial differential equations of first order and on the equations of
classical mechanics. Much of Jacobi's work was published posthumously in the 1860s, generating enormous interest in France and Germany (Hawkins, p. 43). Lie's
idée fixe was to develop a theory of symmetries of differential equations that would accomplish for them what
Évariste Galois had done for algebraic equations: namely, to classify them in terms of group theory. Lie and other mathematicians showed that the most important equations for
special functions and
orthogonal polynomials tend to arise from group theoretical symmetries. In Lie's early work, the idea was to construct a theory of
continuous groups, to complement the theory of
discrete groups that had developed in the theory of
modular forms, in the hands of
Felix Klein and
Henri Poincaré. The initial application that Lie had in mind was to the theory of
differential equations. On the model of
Galois theory and
polynomial equations, the driving conception was of a theory capable of unifying, by the study of
symmetry, the whole area of
ordinary differential equations. However, the hope that Lie Theory would unify the entire field of ordinary differential equations was not fulfilled. Symmetry methods for ODEs continue to be studied, but do not dominate the subject. There is a
differential Galois theory, but it was developed by others, such as Picard and Vessiot, and it provides a theory of
quadratures, the
indefinite integrals required to express solutions.
Additional impetus to consider continuous groups came from ideas of
Bernhard Riemann, on the foundations of geometry, and their further development in the hands of Klein. Thus three major themes in 19th century mathematics were combined by Lie in creating his new theory: the idea of symmetry, as exemplified by Galois through the algebraic notion of a
group; geometric theory and the explicit solutions of
differential equations of mechanics, worked out by
Poisson and Jacobi; and the new understanding of
geometry that emerged in the works of
Plücker,
Möbius,
Grassmann and others, and culminated in Riemann's revolutionary vision of the subject.
Although today Sophus Lie is rightfully recognized as the creator of the theory of continuous groups, a major stride in the development of their structure theory, which was to have a profound influence on subsequent development of mathematics, was made by
Wilhelm Killing, who in 1888 published the first paper in a series entitled
Die Zusammensetzung der stetigen endlichen Transformationsgruppen (
The composition of continuous finite transformation groups) (Hawkins, p. 100). The work of Killing, later refined and generalized by
Élie Cartan, led to classification of
semisimple Lie algebras, Cartan's theory of
symmetric spaces, and
Hermann Weyl's description of
representations of compact and semisimple Lie groups using
highest weights.
In 1900
David Hilbert challenged Lie theorists with his
Fifth Problem presented at the
International Congress of Mathematicians in Paris.
Weyl brought the early period of the development of the theory of Lie groups to fruition, for not only did he classify irreducible representations of semisimple Lie groups and connect the theory of groups with quantum mechanics, but he also put Lie's theory itself on firmer footing by clearly enunciating the distinction between Lie's
infinitesimal groups (i.e., Lie algebras) and the Lie groups proper, and began investigations of topology of Lie groups. The theory of Lie groups was systematically reworked in modern mathematical language in a monograph by
Claude Chevalley.
The concept of a Lie group, and possibilities of classification
Lie groups may be thought of as smoothly varying families of symmetries. Examples of symmetries include rotation about an axis. What must be understood is the nature of 'small' transformations, e.g., rotations through tiny angles, that link nearby transformations. The mathematical object capturing this structure is called a
Lie algebra (
Lie himself called them "infinitesimal groups"). It can be defined because Lie groups are manifolds, so have
tangent spaces at each point.
The Lie algebra of any
compact Lie group (very roughly: one for which the symmetries form a bounded set) can be decomposed as a
direct sum of an
abelian Lie algebra and some number of
simple ones. The structure of an abelian Lie algebra is mathematically uninteresting (since the Lie bracket is identically zero); the interest is in the simple summands. Hence the question arises: what are the
simple Lie algebras of compact groups? It turns out that they mostly fall into four infinite families, the "classical Lie algebras" A
n, B
n, C
n and D
n, which have simple descriptions in terms of symmetries of Euclidean space. But there are also just five "exceptional Lie algebras" that do not fall into any of these families. E
8 is the largest of these.
Lie groups are classified according to their algebraic properties (
simple,
semisimple,
solvable,
nilpotent,
abelian), their
connectedness (
connected or
simply connected) and their
compactness.
- Compact Lie groups are all known: they are finite central quotients of a product of copies of the circle group S1 and simple compact Lie groups (which correspond to connected Dynkin diagrams).
- Any simply connected solvable Lie group is isomorphic to a closed subgroup of the group of invertible upper triangular matrices of some rank, and any finite-dimensional irreducible representation of such a group is 1-dimensional. Solvable groups are too messy to classify except in a few small dimensions.
- Any simply connected nilpotent Lie group is isomorphic to a closed subgroup of the group of invertible upper triangular matrices with 1's on the diagonal of some rank, and any finite-dimensional irreducible representation of such a group is 1-dimensional. Like solvable groups, nilpotent groups are too messy to classify except in a few small dimensions.
- Simple Lie groups are sometimes defined to be those that are simple as abstract groups, and sometimes defined to be connected Lie groups with a simple Lie algebra. For example, SL(2, R) is simple according to the second definition but not according to the first. They have all been classified (for either definition).
- Semisimple Lie groups are Lie groups whose Lie algebra is a product of simple Lie algebras.[3] They are central extensions of products of simple Lie groups.
The
identity component of any Lie group is an open
normal subgroup, and the
quotient group is a
discrete group. The universal cover of any connected Lie group is a simply connected Lie group, and conversely any connected Lie group is a quotient of a simply connected Lie group by a discrete normal subgroup of the center. Any Lie group
G can be decomposed into discrete, simple, and abelian groups in a canonical way as follows. Write
- Gcon for the connected component of the identity
- Gsol for the largest connected normal solvable subgroup
- Gnil for the largest connected normal nilpotent subgroup
so that we have a sequence of normal subgroups
- 1 ⊆ Gnil ⊆ Gsol ⊆ Gcon ⊆ G.
Then
- G/Gcon is discrete
- Gcon/Gsol is a central extension of a product of simple connected Lie groups.
- Gsol/Gnil is abelian. A connected abelian Lie group is isomorphic to a product of copies of R and the circle group S1.
- Gnil/1 is nilpotent, and therefore its ascending central series has all quotients abelian.
This can be used to reduce some problems about Lie groups (such as finding their unitary representations) to the same problems for connected simple groups and nilpotent and solvable subgroups of smaller dimension.
Infinite-dimensional Lie groups
Lie groups are often defined to be finite-dimensional, but there are many groups that resemble Lie groups, except for being infinite-dimensional. The simplest way to define infinite-dimensional Lie groups is to model them on
Banach spaces, and in this case much of the basic theory is similar to that of finite-dimensional Lie groups.
However this is inadequate for many applications, because many natural examples of infinite-dimensional Lie groups are not Banach manifolds. Instead one needs to define Lie groups modeled on more general locally convex topological vector spaces. In this case the relation between the Lie algebra and the Lie group becomes rather subtle, and several results about finite-dimensional Lie groups no longer hold.
Some of the examples that have been studied include:
The diffeomorphism group of spacetime sometimes appears in attempts to
quantize gravity.
- The group of smooth maps from a manifold to a finite-dimensional Lie group is an example of a gauge group (with operation of pointwise multiplication), and is used in quantum field theory and Donaldson theory. If the manifold is a circle these are called loop groups, and have central extensions whose Lie algebras are (more or less) Kac–Moody algebras.
- There are infinite-dimensional analogues of general linear groups, orthogonal groups, and so on. One important aspect is that these may have simpler topological properties: see for example Kuiper's theorem. In M-Theory theory, for example, a 10 dimensional SU(N) gauge theory becomes an 11 dimensional theory when N becomes infinite.
- A specific example is that
 is equal to the group of area preserving diffeomorphisms of a torus.
is equal to the group of area preserving diffeomorphisms of a torus.




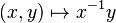
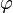 as a parameter, this group can be
as a parameter, this group can be 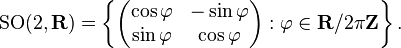
 Thus the Lie bracket on
Thus the Lie bracket on  is given explicitly by [v, w] = [v^, w^]e.
is given explicitly by [v, w] = [v^, w^]e. be a Lie group homomorphism and let
be a Lie group homomorphism and let  be its
be its 
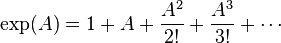
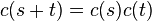

 is a Lie group homomorphism and
is a Lie group homomorphism and  the induced map on the corresponding Lie algebras, then for all
the induced map on the corresponding Lie algebras, then for all 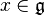 we have
we have

 is equal to the group of area preserving diffeomorphisms of a torus.
is equal to the group of area preserving diffeomorphisms of a torus.
