From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The term harmonic in its strictest sense is any member of the harmonic series. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music and acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, etc. It is typically applied when considering the frequencies of repeating signals, such as sinusoidal waves, that happen to relate as whole-numbered multiples. In that case, a harmonic is a signal whose frequency is a whole-numbered multiple of the frequency of some other given signal. For example, in alternating current of 60 cycles per second, "fifth-harmonic distortion" would produce an unwanted additional signal at 300 cycles per second, exactly five times the original frequency.
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental frequency, therefore the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. As multiples of the fundamental frequency, successive harmonics can be found by repeatedly adding the fundamental frequency. For example, if the fundamental frequency (first harmonic) is 25 Hz, the frequencies of the next harmonics are: 50 Hz (2nd harmonic), 75 Hz (3rd harmonic), 100 Hz (4th harmonic) etc.
Characteristics
Most acoustic instruments emit complex tones containing many individual partials (component simple tones or sinusoidal waves), but the untrained human ear typically does not perceive those partials as separate phenomena. Rather, a musical note is perceived as one sound, the quality or timbre of that sound being a result of the relative strengths of the individual partials.Many acoustic oscillators, such as the human voice or a bowed violin string, produce complex tones that are more or less periodic, and thus are composed of partials that are near matches to integer multiples of the fundamental frequency and therefore resemble the ideal harmonics and are called "harmonic partials" or simply "harmonics" for convenience (although it's not strictly accurate to call a partial a harmonic, the first being real and the second being ideal). Oscillators that produce harmonic partials behave somewhat like 1-dimensional resonators, and are often long and thin, such as a guitar string or a column of air open at both ends (as with the modern orchestral transverse flute). Wind instruments whose air column is open at only one end, such as trumpets and clarinets, also produce partials resembling harmonics. However they only produce partials matching the odd harmonics, at least in theory. The reality of acoustic instruments is such that none of them behaves as perfectly as the somewhat simplified theoretical models would predict.
Partials whose frequencies are not integer multiples of the fundamental are referred to as inharmonic partials.
Some acoustic instruments emit a mix of harmonic and inharmonic partials but still produce an effect on the ear of having a definite fundamental pitch, such as pianos, strings plucked pizzicato, vibraphones, marimbas, and certain pure-sounding bells or chimes. Antique singing bowls are known for producing multiple harmonic partials or multiphonics. [1] [2]
Other oscillators, such as cymbals, drum heads, and other percussion instruments, naturally produce an abundance of inharmonic partials and do not imply any particular pitch, and therefore cannot be used melodically or harmonically in the same way other instruments can.
Harmonics and overtones
An overtone is any frequency higher than the fundamental. The tight relation between overtones and harmonics in music often leads to their being used synonymously in a strictly musical context, but they are counted differently leading to some possible confusion. This chart demonstrates how they are counted:| Frequency | Order | Name 1 | Name 2 | Wave Representation | Molecular Representation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 · f = 440 Hz | n = 1 | fundamental tone | 1st harmonic | 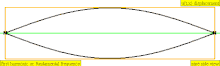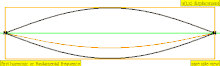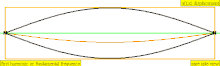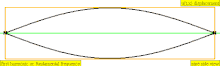 |
 |
| 2 · f = 880 Hz | n = 2 | 1st overtone | 2nd harmonic |  |
 |
| 3 · f = 1320 Hz | n = 3 | 2nd overtone | 3rd harmonic | 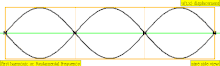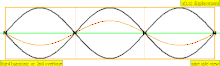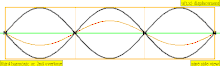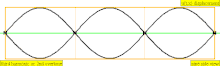 |
 |
| 4 · f = 1760 Hz | n = 4 | 3rd overtone | 4th harmonic |  |
 |
In a simple case (e.g., recorder) this has the effect of making the note go up in pitch by an octave, but in more complex cases many other pitch variations are obtained. In some cases it also changes the timbre of the note. This is part of the normal method of obtaining higher notes in wind instruments, where it is called overblowing. The extended technique of playing multiphonics also produces harmonics. On string instruments it is possible to produce very pure sounding notes, called harmonics or flageolets by string players, which have an eerie quality, as well as being high in pitch. Harmonics may be used to check at a unison the tuning of strings that are not tuned to the unison. For example, lightly fingering the node found halfway down the highest string of a cello produces the same pitch as lightly fingering the node 1/3 of the way down the second highest string. For the human voice see Overtone singing, which uses harmonics.
While it is true that electronically produced periodic tones (e.g. square waves or other non-sinusoidal waves) have "harmonics" that are whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency, practical instruments do not all have this characteristic. For example higher "harmonics"' of piano notes are not true harmonics but are "overtones" and can be very sharp, i.e. a higher frequency than given by a pure harmonic series. This is especially true of instruments other than stringed or brass/woodwind ones, e.g., xylophone, drums, bells etc., where not all the overtones have a simple whole number ratio with the fundamental frequency.
The fundamental frequency is the reciprocal of the period of the periodic phenomenon.
Harmonics on stringed instruments
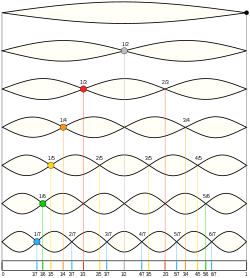
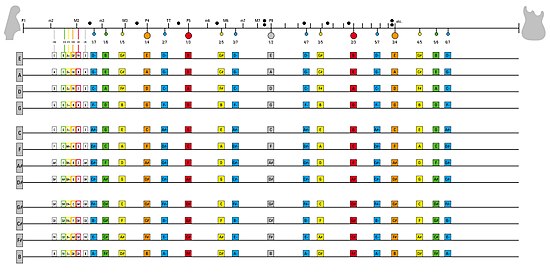
The following table displays the stop points on a stringed instrument, such as the guitar (guitar harmonics), at which gentle touching of a string will force it into a harmonic mode when vibrated. String harmonics (flageolet tones) are described as having a "flutelike, silvery quality that can be highly effective as a special color" when used and heard in orchestration.[3] It is unusual to encounter natural harmonics higher than the fifth partial on any stringed instrument except the double bass, on account of its much longer strings.[4]
Composer Arnold Dreyblatt is able to bring out different harmonics on the single string of his modified double bass by slightly altering his unique bowing technique halfway between hitting and bowing the strings.
Composer Lawrence Ball uses harmonics to generate music electronically.
The following table displays the stop points on a stringed instrument, such as the guitar (guitar harmonics), at which gentle touching of a string will force it into a harmonic mode when vibrated. String harmonics (flageolet tones) are described as having a "flutelike, silvery quality that can be highly effective as a special color" when used and heard in orchestration.[3] It is unusual to encounter natural harmonics higher than the fifth partial on any stringed instrument except the double bass, on account of its much longer strings.[4]
| Harmonic | Stop note | Sounded note relative to open string | Cents above open string | Cents reduced to one octave | Audio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | octave | octave (P8) | 1,200.0 | 0.0 | |
| 3 | just perfect fifth | P8 + just perfect fifth (P5) | 1,902.0 | 702.0 | |
| 4 | second octave | 2P8 | 2,400.0 | 0.0 | |
| 5 | just major third | 2P8 + just major third (M3) | 2,786.3 | 386.3 | |
| 6 | just minor third | 2P8 + P5 | 3,102.0 | 702.0 | |
| 7 | septimal minor third | 2P8 + septimal minor seventh (m7) | 3,368.8 | 968.8 | |
| 8 | septimal major second | 3P8 | 3,600.0 | 0.0 | |
| 9 | Pythagorean major second | 3P8 + Pythagorean major second (M2) | 3,803.9 | 203.9 | |
| 10 | just minor whole tone | 3P8 + just M3 | 3,986.3 | 386.3 | |
| 11 | greater undecimal neutral second | 3P8 + lesser undecimal tritone | 4,151.3 | 551.3 | |
| 12 | lesser undecimal neutral second | 3P8 + P5 | 4,302.0 | 702.0 | |
| 13 | tridecimal 2/3-tone | 3P8 + tridecimal neutral sixth (n6) | 4,440.5 | 840.5 | |
| 14 | 2/3-tone | 3P8 + P5 + septimal minor third (m3) | 4,568.8 | 968.8 | |
| 15 | septimal (or major) diatonic semitone | 3P8 + just major seventh (M7) | 4,688.3 | 1,088.3 | |
| 16 | just (or minor) diatonic semitone | 4P8 | 4,800.0 | 0.0 |
Table

Table of harmonics of a stringed instrument with colored dots indicating which positions can be lightly fingered to generate just intervals up to the 7th harmonic
Artificial harmonics
Although harmonics are most often used on open strings, occasionally a score will call for an artificial harmonic, produced by playing an overtone on a stopped string. As a performance technique, it is accomplished by using two fingers on the fingerboard, the first to shorten the string to the desired fundamental, with the second touching the node corresponding to the appropriate harmonic.Other information
Harmonics may be either used or considered as the basis of just intonation systems.Composer Arnold Dreyblatt is able to bring out different harmonics on the single string of his modified double bass by slightly altering his unique bowing technique halfway between hitting and bowing the strings.
Composer Lawrence Ball uses harmonics to generate music electronically.