The id, ego, and super-ego are three distinct, yet interacting agents in the psychic apparatus defined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche.
The three parts are the theoretical constructs in terms of whose activity and interaction our mental life is described. According to this Freudian model of the psyche, the id is the set of uncoordinated instinctual trends; the super-ego plays the critical and moralizing role; and the ego is the organized, realistic part that mediates between the desires of the id and the super-ego.[1]
As Freud explained:
The functional importance of the ego is manifested in the fact that normally control over the approaches to motility devolves upon it. Thus in its relation to the id it is like a man on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with his own strength while the ego uses borrowed forces. The analogy may be carried a little further. Often a rider, if he is not to be parted from his horse, is obliged to guide it where it wants to go; so in the same way the ego is in the habit of transforming the id's will into action as if it were its own. (p. 19).[2]Although the model is structural and makes reference to an apparatus, the id, ego and super-ego are purely psychological concepts and do not correspond to (somatic) structures of the brain such as the kind dealt with by neuroscience. The super-ego is observable in how someone can view themselves as guilty, bad, shameful, weak, and feel compelled to do certain things. Freud in The Ego and the Id discusses "the general character of harshness and cruelty exhibited by the [ego] ideal – its dictatorial 'Thou shalt.'"
Freud (1933) hypothesizes different levels of ego ideal or superego development with increasingly greater ideals:
...nor must it be forgotten that a child has a different estimate of [their] parents at different periods of [their] life. At the time at which the Oedipus complex gives place to the super-ego they are something quite magnificent; but later they lose much of this. Identifications then come about with these later parents as well, and indeed they regularly make important contributions to the formation of character; but in that case they only affect the ego, they no longer influence the super-ego, which has been determined by the earliest parental images.The earlier in development, the greater the estimate of parental power. When one defuses into rivalry with the parental imago, then one feels the 'dictatorial thou shalt' to manifest the power the imago represents. Four general levels are found in Freud's work: the auto-erotic, the narcissistic, the anal, and the phallic.[3] These different levels of development and the relations to parental imagos correspond to specific id forms of aggression and affection. For example, aggressive desires to decapitate, to dismember, to cannibalize, to swallow whole, to suck dry, to make disappear, to blow away, etc. animate myths, are enjoyed in fantasy and horror movies, and are observable in the fantasies and repressions of patients across cultures.
— New Introductory Lectures on Psychoanalysis, p. 64
The concepts themselves arose at a late stage in the development of Freud's thought as the "structural model" (which succeeded his "economic model" and "topographical model") and was first discussed in his 1920 essay Beyond the Pleasure Principle and was formalized and elaborated upon three years later in his The Ego and the Id. Freud's proposal was influenced by the ambiguity of the term "unconscious" and its many conflicting uses.
Id
The id (Latin for "it",[4] German: Es)[5] is the disorganized part of the personality structure that contains a human's basic, instinctual drives. Id is the only component of personality that is present from birth.[6] It is the source of our bodily needs, wants, desires, and impulses, particularly our sexual and aggressive drives. The id contains the libido, which is the primary source of instinctual force that is unresponsive to the demands of reality.[7] The id acts according to the "pleasure principle"—the psychic force that motivates the tendency to seek immediate gratification of any impulse[8]—defined as seeking to avoid pain or unpleasure (not "displeasure") aroused by increases in instinctual tension.[9] According to Freud the id is unconscious by definition:It is the dark, inaccessible part of our personality, what little we know of it we have learned from our study of the dreamwork and of course the construction of neurotic symptoms, and most of that is of a negative character and can be described only as a contrast to the ego. We approach the id with analogies: we call it a chaos, a cauldron full of seething excitations. ...It is filled with energy reaching it from the instincts, but it has no organization, produces no collective will, but only a striving to bring about the satisfaction of the instinctual needs subject to the observance of the pleasure principle.[10]In the id:
...contrary impulses exist side by side, without cancelling each other out. ...There is nothing in the id that could be compared with negation...nothing in the id which corresponds to the idea of time.[11]Developmentally, the id precedes the ego; i.e., the psychic apparatus begins, at birth, as an undifferentiated id, part of which then develops into a structured ego. Thus, the id:
...contains everything that is inherited, that is present at birth, is laid down in the constitution—above all, therefore, the instincts, which originate from the somatic organization, and which find a first psychical expression here (in the id) in forms unknown to us.[12]The mind of a newborn child is regarded as completely "id-ridden", in the sense that it is a mass of instinctive drives and impulses, and needs immediate satisfaction.
The id "knows no judgements of value: no good and evil, no morality. ...Instinctual cathexes seeking discharge—that, in our view, is all there is in the id."[13] It is regarded as "the great reservoir of libido",[14] the instinctive drive to create—the life instincts that are crucial to pleasurable survival. Alongside the life instincts came the death instincts—the death drive which Freud articulated relatively late in his career in "the hypothesis of a death instinct, the task of which is to lead organic life back into the inanimate state."[15] For Freud, "the death instinct would thus seem to express itself—though probably only in part—as an instinct of destruction directed against the external world and other organisms"[16] through aggression. Freud considered that "the id, the whole person...originally includes all the instinctual impulses...the destructive instinct as well",[17] as eros or the life instincts.
Ego
The ego (Latin for "I",[18] German: Ich)[19] acts according to the reality principle; i.e., it seeks to please the id's drive in realistic ways that will benefit in the long term rather than bring grief.[20] At the same time, Freud concedes that as the ego "attempts to mediate between id and reality, it is often obliged to cloak the [unconscious] commands of the id with its own preconscious rationalizations, to conceal the id's conflicts with reality, to profess...to be taking notice of reality even when the id has remained rigid and unyielding."[21] The reality principle that operates the ego is a regulating mechanism that enables the individual to delay gratifying immediate needs and function effectively in the real world. An example would be to resist the urge to grab other people's belongings, but instead to purchase those items.[22]The ego is the organized part of the personality structure that includes defensive, perceptual, intellectual-cognitive, and executive functions. Conscious awareness resides in the ego, although not all of the operations of the ego are conscious. Originally, Freud used the word ego to mean a sense of self, but later revised it to mean a set of psychic functions such as judgment, tolerance, reality testing, control, planning, defense, synthesis of information, intellectual functioning, and memory.[23] The ego separates out what is real. It helps us to organize our thoughts and make sense of them and the world around us.[23] "The ego is that part of the id which has been modified by the direct influence of the external world. ...The ego represents what may be called reason and common sense, in contrast to the id, which contains the passions...in its relation to the id it is like a person on horseback, who has to hold in check the superior strength of the horse; with this difference, that the rider tries to do so with their own strength, while the ego uses borrowed forces."[24] Still worse, "it serves three severe masters...the external world, the super-ego and the id."[21] Its task is to find a balance between primitive drives and reality while satisfying the id and super-ego. Its main concern is with the individual's safety and allows some of the id's desires to be expressed, but only when consequences of these actions are marginal. "Thus the ego, driven by the id, confined by the super-ego, repulsed by reality, struggles...[in] bringing about harmony among the forces and influences working in and upon it," and readily "breaks out in anxiety—realistic anxiety regarding the external world, moral anxiety regarding the super-ego, and neurotic anxiety regarding the strength of the passions in the id."[25] It has to do its best to suit all three, thus is constantly feeling hemmed by the danger of causing discontent on two other sides. It is said, however, that the ego seems to be more loyal to the id, preferring to gloss over the finer details of reality to minimize conflicts while pretending to have a regard for reality. But the super-ego is constantly watching every one of the ego's moves and punishes it with feelings of guilt, anxiety, and inferiority.
To overcome this the ego employs defense mechanisms. The defense mechanisms are not done so directly or consciously. They lessen the tension by covering up our impulses that are threatening.[26] Ego defense mechanisms are often used by the ego when id behavior conflicts with reality and either society's morals, norms, and taboos or the individual's expectations as a result of the internalization of these morals, norms, and their taboos.
Denial, displacement, intellectualisation, fantasy, compensation, projection, rationalization, reaction formation, regression, repression, and sublimation were the defense mechanisms Freud identified. However, his daughter Anna Freud clarified and identified the concepts of undoing, suppression, dissociation, idealization, identification, introjection, inversion, somatisation, splitting, and substitution.
"The ego is not sharply separated from the id; its lower portion merges
into it.... But the repressed merges into the id as well, and is merely a
part of it. The repressed is only cut off sharply from the ego by the
resistances of repression; it can communicate with the ego through the
id." (Sigmund Freud, 1923)
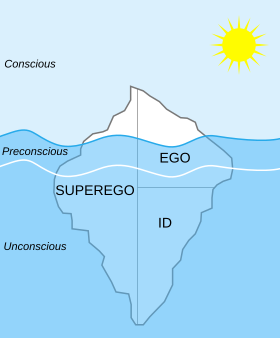
In a diagram of the Structural and Topographical Models of Mind, the ego is depicted to be half in the consciousness, while a quarter is in the preconscious and the other quarter lies in the unconscious.
In modern English, ego has many meanings. It could mean one’s self-esteem; an inflated sense of self-worth; the conscious-thinking self;[27] or in philosophical terms, one’s self. Ego development is known as the development of multiple processes, cognitive function, defenses, and interpersonal skills or to early adolescence when ego processes are emerged.[20]
Super-ego
The super-ego[28] (German: Über-Ich)[29] reflects the internalization of cultural rules, mainly taught by parents applying their guidance and influence.[8] Freud developed his concept of the super-ego from an earlier combination of the ego ideal and the "special psychical agency which performs the task of seeing that narcissistic satisfaction from the ego ideal is ensured...what we call our 'conscience'."[30] For him "the installation of the super-ego can be described as a successful instance of identification with the parental agency," while as development proceeds "the super-ego also takes on the influence of those who have stepped into the place of parents — educators, teachers, people chosen as ideal models".Thus a child's super-ego is in fact constructed on the model not of its parents but of its parents' super-ego; the contents which fill it are the same and it becomes the vehicle of tradition and of all the time-resisting judgments of value which have propagated themselves in this manner from generation to generation.[31]The super-ego aims for perfection.[26] It forms the organized part of the personality structure, mainly but not entirely unconscious, that includes the individual's ego ideals, spiritual goals, and the psychic agency (commonly called "conscience") that criticizes and prohibits their drives, fantasies, feelings, and actions. "The Super-ego can be thought of as a type of conscience that punishes misbehavior with feelings of guilt. For example, for having extra-marital affairs."[32] Taken in this sense, the super-ego is the precedent for the conceptualization of the inner critic as it appears in contemporary therapies such as IFS.[33]
The super-ego works in contradiction to the id. The super-ego strives to act in a socially appropriate manner, whereas the id just wants instant self-gratification. The super-ego controls our sense of right and wrong and guilt. It helps us fit into society by getting us to act in socially acceptable ways.[23]
The super-ego's demands often oppose the id's, so the ego sometimes has a hard time in reconciling the two.[26]
Freud's theory implies that the super-ego is a symbolic internalisation of the father figure and cultural regulations. The super-ego tends to stand in opposition to the desires of the id because of their conflicting objectives, and its aggressiveness towards the ego. The super-ego acts as the conscience, maintaining our sense of morality and proscription from taboos. The super-ego and the ego are the product of two key factors: the state of helplessness of the child and the Oedipus complex.[34] Its formation takes place during the dissolution of the Oedipus complex and is formed by an identification with and internalisation of the father figure after the little boy cannot successfully hold the mother as a love-object out of fear of castration. Freud described the super-ego and its relationship to the father figure and Oedipus complex thus:
The super-ego retains the character of the father, while the more powerful the Oedipus complex was and the more rapidly it succumbed to repression (under the influence of authority, religious teaching, schooling and reading), the stricter will be the domination of the super-ego over the ego later on—in the form of conscience or perhaps of an unconscious sense of guilt.[35]The concept of super-ego and the Oedipus complex is subject to criticism for its perceived sexism. Women, who are considered to be already castrated, do not identify with the father, and therefore, for Freud, "their super-ego is never so inexorable, so impersonal, so independent of its emotional origins as we require it to be in men...they are often more influenced in their judgements by feelings of affection or hostility."[36] However, Freud went on to modify his position to the effect "that the majority of men are also far behind the masculine ideal and that all human individuals, as a result of their human identity, combine in themselves both masculine and feminine characteristics, otherwise known as human characteristics."[37]
Advantages of the structural model
The iceberg metaphor is often used to explain the psyche's parts in relation to one another.
Freud's earlier, topographical model of the mind had divided the mind into the three elements of conscious, preconscious, and unconscious. The conscious contains events that we are aware of, preconscious is events that are in the process of becoming conscious, and unconscious include events that we are not aware of.[38] At its heart was "the dialectic of unconscious traumatic memory versus consciousness...which soon became a conflict between System Ucs versus System Cs."[39] With what Freud called the "disagreeable discovery that on the one hand (super-)ego and conscious and on the other hand repressed and unconscious are far from coinciding,"[40] Freud took the step in the structural model to "no longer use the term 'unconscious' in the systematic sense," and to rename "the mental region that is foreign to the ego...[and] in future call it the 'id'."[41] The partition of the psyche defined in the structural model is thus one that cuts across the topographical model's partition of "conscious vs. unconscious".
"The new terminology which he introduced has a highly clarifying effect and so made further clinical advances possible."[42] Its value lies in the increased degree of precision and diversification made possible: Although the id is unconscious by definition, the ego and the super-ego are both partly conscious and partly unconscious. What is more, with this new model Freud achieved a more systematic classification of mental disorder than had been available previously:
Transference neuroses correspond to a conflict between the ego and the id; narcissistic neuroses, to a conflict between the ego and the superego; and psychoses, to one between the ego and the external world.[43]It is important to realise however, that "the three newly presented entities, the id, the ego and the superego, all had lengthy past histories (two of them under other names)"[44]—the id as the systematic unconscious, the super-ego as conscience/ego ideal. Equally, Freud never abandoned the topographical division of conscious, preconscious, and unconscious, though as he noted ruefully "the three qualities of consciousness and the three provinces of the mental apparatus do not fall together into three peaceful couples...we had no right to expect any such smooth arrangement."[45]
The iceberg metaphor is a commonly used visual metaphor when attempting to relate the ego, id and superego with the conscious and unconscious mind. In the iceberg metaphor the entire id and part of both the superego and the ego would be submerged in the underwater portion representing the unconscious mind. The remaining portions of the ego and superego would be displayed above water in the conscious mind area.[7]
Translation
The terms "id", "ego", and "super-ego" are not Freud's own. They are latinisations by his translator James Strachey. Freud himself wrote of "das Es",[5] "das Ich",[19] and "das Über-Ich"[29]—respectively, "the It", "the I", and "the Over-I" (or "I above"); thus to the German reader, Freud's original terms are more or less self-explanatory. Freud borrowed the term "das Es" from Georg Groddeck, a German physician to whose unconventional ideas Freud was much attracted (Groddeck's translators render the term in English as "the It").[46] The word ego is taken directly from Latin, where it is the nominative of the first person singular personal pronoun and is translated as "I myself" to express emphasis.Figures like Bruno Bettelheim have criticized the way "the English translations impeded students' efforts to gain a true understanding of Freud."[47] by substituting the formalised language of the elaborated code for the quotidian immediacy of Freud's own language.