| Fibromyalgia | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) |
 | |
| The location of the nine paired tender points that constitute the 1990 American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology, neurology[2] |
| Symptoms | Widespread pain, feeling tired, sleep problems[3][4] |
| Usual onset | Middle age[5] |
| Duration | Long term[3] |
| Causes | Unknown[4][5] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms after ruling out other potential causes[4][5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, thyroid disease[6] |
| Treatment | Sufficient sleep and exercise, healthy diet[5] |
| Medication | Duloxetine, milnacipran, pregabalin, gabapentin[5][7] |
| Prognosis | Normal life expectancy[5] |
| Frequency | 2–8%[4] |
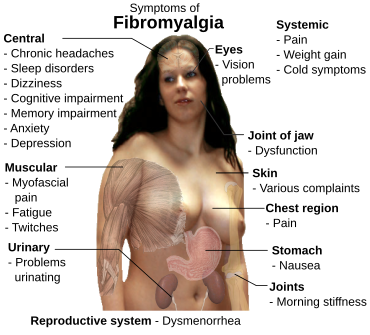
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a medical condition characterised by chronic widespread pain and a heightened pain response to pressure. Other symptoms include tiredness to a degree that normal activities are affected, sleep problems and troubles with memory. Some people also report restless legs syndrome, bowel or bladder problems, numbness and tingling and sensitivity to noise, lights or temperature. Fibromyalgia is frequently associated with depression, anxiety and posttraumatic stress disorder. Other types of chronic pain are also frequently present.
The cause of fibromyalgia is unknown; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors, with each playing a substantial role.[4][5] The condition runs in families, and many genes are believed to be involved.[8] Environmental factors may include psychological stress, trauma and certain infections.[4] The pain appears to result from processes in the central nervous system, and the condition is referred to as a "central sensitization syndrome".[3][4]
Fibromyalgia is recognized as a disorder by the US National Institutes of Health and the American College of Rheumatology.[5][9] There is no specific diagnostic test.[5] Diagnosis involves first ruling out other potential causes and verifying that a set number of symptoms are present.[4][5]
The treatment of fibromyalgia can be difficult.[5] Recommendations often include getting enough sleep, exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet.[5] Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may also be helpful.[4] The medications duloxetine, milnacipran or pregabalin may be used.[5] Use of opioid pain medication is controversial, with some stating their use is poorly supported by evidence[5][10] and others saying that weak opioids may be reasonable if other medications are not effective.[11] Dietary supplements also lack evidence to support their use.[5] While fibromyalgia can last a long time, it does not result in death or tissue damage.[5]
Fibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2–8% of the population.[4] Women are affected about twice as often as men.[4] Rates appear similar in different areas of the world and among different cultures.[4] Fibromyalgia was first defined in 1990, with updated criteria in 2011.[4] There is controversy about the classification, diagnosis and treatment of fibromyalgia.[12][13] While some feel the diagnosis of fibromyalgia may negatively affect a person, other research finds it to be beneficial.[4] The term "fibromyalgia" is from New Latin fibro-, meaning "fibrous tissues", Greek μυώ myo-, "muscle", and Greek άλγος algos, "pain"; thus, the term literally means "muscle and fibrous connective tissue pain".[14]
Classification
Differences in psychological and autonomic nervous system profiles among affected individuals may indicate the existence of fibromyalgia subtypes. A 2007 review divides individuals with fibromyalgia into four groups as well as "mixed types":[16]
- "extreme sensitivity to pain but no associated psychiatric conditions" (may respond to medications that block the 5-HT3 receptor)
- "fibromyalgia and comorbid, pain-related depression" (may respond to antidepressants)
- "depression with concomitant fibromyalgia syndrome" (may respond to antidepressants)
- "fibromyalgia due to somatization" (may respond to psychotherapy)
Signs and symptoms
The defining symptoms of fibromyalgia are chronic widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbance, and heightened pain in response to tactile pressure (allodynia).[17] Other symptoms may include tingling of the skin (paresthesias),[17] prolonged muscle spasms, weakness in the limbs, nerve pain, muscle twitching, palpitations,[18] and functional bowel disturbances.[19][20]
Many people experience cognitive dysfunction[17][21] (known as "fibrofog"), which may be characterized by impaired concentration,[22] problems with short[22][23] and long-term memory, short-term memory consolidation,[23] impaired speed of performance,[22][23] inability to multi-task, cognitive overload,[22][23] and diminished attention span. Fibromyalgia is often associated with anxiety and depressive symptoms.[23]
Other symptoms often attributed to fibromyalgia that may be due to a comorbid disorder include myofascial pain syndrome, also referred to as chronic myofascial pain, diffuse non-dermatomal paresthesias, functional bowel disturbances and irritable bowel syndrome, genitourinary symptoms and interstitial cystitis, dermatological disorders, headaches, myoclonic twitches, and symptomatic hypoglycemia. Although fibromyalgia is classified based on the presence of chronic widespread pain, pain may also be localized in areas such as the shoulders, neck, low back, hips, or other areas. Many sufferers also experience varying degrees of myofascial pain and have high rates of comorbid temporomandibular joint dysfunction. 20–30% of people with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus may also have fibromyalgia.[24]
Cause
The cause of fibromyalgia is unknown. However, several hypotheses have been developed including "central sensitization".[17] This theory proposes that people with fibromyalgia have a lower threshold for pain because of increased reactivity of pain-sensitive nerve cells in the spinal cord or brain.[3] Neuropathic pain and major depressive disorder often co-occur with fibromyalgia – the reason for this comorbidity appears to be due to shared genetic abnormalities, which leads to impairments in monoaminergic, glutamatergic, neurotrophic, opioid and proinflammatory cytokine signaling. In these vulnerable individuals, psychological stress or illness can cause abnormalities in inflammatory and stress pathways which regulate mood and pain. Eventually, a sensitization and kindling effect occur in certain neurons leading to the establishment of fibromyalgia and sometimes a mood disorder.[25] The evidence suggests that the pain in fibromyalgia results primarily from pain processing pathways functioning abnormally. In simple terms, it can be described as the volume of the neurons being set too high and this hyper-excitability of pain processing pathways and under-activity of inhibitory pain pathways in the brain results in the affected individual experiencing pain. Some neurochemical abnormalities that occur in fibromyalgia also regulate mood, sleep, and energy, thus explaining why mood, sleep, and fatigue problems are commonly co-morbid with fibromyalgia.[15]Genetics
A mode of inheritance is currently unknown, but it is most probably polygenic.[8] Research has also demonstrated that fibromyalgia is potentially associated with polymorphisms of genes in the serotoninergic,[26] dopaminergic[27] and catecholaminergic systems.[28] However, these polymorphisms are not specific for fibromyalgia and are associated with a variety of allied disorders (e.g. chronic fatigue syndrome,[29] irritable bowel syndrome[30]) and with depression.[31] Individuals with the 5-HT2A receptor 102T/C polymorphism have been found to be at increased risk of developing fibromyalgia.[32]Lifestyle
Stress may be an important precipitating factor in the development of fibromyalgia.[33] Fibromyalgia is frequently comorbid with stress-related disorders such as chronic fatigue syndrome, posttraumatic stress disorder, irritable bowel syndrome and depression.[34] A systematic review found significant association between fibromyalgia and physical and sexual abuse in both childhood and adulthood, although the quality of studies was poor.[35] Poor lifestyles including being a smoker, obesity and lack of physical activity may increase the risk of an individual developing fibromyalgia.[36] A meta analysis found psychological trauma to be associated with FM, although not as strongly as in chronic fatigue syndrome.[37]Two studies that employed single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) reported metabolic abnormalities within the hippocampal complex in people with fibromyalgia. As the hippocampus plays crucial roles in maintenance of cognitive functions, sleep regulation, and pain perception, it was suggested that metabolic dysfunction of the hippocampus may be implicated in the appearance of these symptoms.[38] /[39]
Some authors have proposed that, because exposure to stressful conditions can alter the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, the development of fibromyalgia may stem from stress-induced disruption of the HPA axis.[40]
Sleep disturbances
In 1975, Moldofsky and colleagues reported the presence of anomalous alpha wave activity (typically associated with arousal states) measured by electroencephalogram (EEG) during non-rapid eye movement sleep of "fibrositis syndrome".[20] By disrupting stage IV sleep consistently in young, healthy subjects, the researchers reproduced a significant increase in muscle tenderness similar to that experienced in "neurasthenic musculoskeletal pain syndrome" but which resolved when the subjects were able to resume their normal sleep patterns.[41]Psychological factors
There is strong evidence that major depression is associated with fibromyalgia as with other chronic pain conditions (1999),[42] although it is unclear the direction of the causal relationship.[43] A comprehensive review into the relationship between fibromyalgia and major depressive disorder (MDD) found substantial similarities in neuroendocrine abnormalities, psychological characteristics, physical symptoms and treatments between fibromyalgia and MDD, but currently available findings do not support the assumption that MDD and fibromyalgia refer to the same underlying construct or can be seen as subsidiaries of one disease concept.[44] Indeed, the sensation of pain has at least two dimensions: a sensory dimension which processes the magnitude and location of the pain, and an affective-motivational dimension which processes the unpleasantness. Accordingly, a study that employed functional magnetic resonance imaging to evaluate brain responses to experimental pain among people with fibromyalgia found that depressive symptoms were associated with the magnitude of clinically induced pain response specifically in areas of the brain that participate in affective pain processing, but not in areas involved in sensory processing which indicates that the amplification of the sensory dimension of pain in fibromyalgia occurs independently of mood or emotional processes.[45] Fibromyalgia has also been linked with bipolar disorder, particularly the hypomania component.[46]Non-celiac gluten sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) may be an underlying cause of fibromyalgia symptoms but further research is needed.[47][48]Pathophysiology
Pain processing abnormalities
Abnormalities in the ascending and descending pathways involved in processing pain have been observed in fibromyalgia. 50% less stimulus is needed to evoke pain in those with fibromyalgia.[49] A proposed mechanism for chronic pain is sensitization of secondary pain neurons mediated by increased release of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide by glial cells.[50] Inconsistent reports of decreased serum and CSF values of serotonin have been observed. There is also some data that suggests altered dopaminergic and noradrenergic signaling in fibromyalgia.[51] Supporting the monoamine related theories is the efficacy of monoaminergic antidepressants in fibromyalgia.[52][53]Neuroendocrine system
Studies on the neuroendocrine system and HPA axis in fibromyalgia have been inconsistent. One study found fibromyalgia patients exhibited higher plasma cortisol, more extreme peaks and troughs, and higher rates of dexamethasone non suppression. However, other studies have only found correlations between a higher Cortisol awakening response and pain, and not any other abnormalities in cortisol.[49] Increased baseline ACTH and increase in response to stress have been observed, hypothesized to be a result of decreased negative feedback.[51]Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system abnormalities have been observed in fibromyalgia, including decreased vasoconstriction response, increased drop in blood pressure and worsening of symptoms in response to tilt table test, and decreased heart rate variability. Heart rate variabilities observed were different in males and females.[49]Sleep
Disrupted sleep, insomnia, and poor quality sleep occur frequently in FM, and may contribute to pain by decreased release of IGF-1 and human growth hormone, leading to decreased tissue repair. Restorative sleep was correlated with improvement in pain related symptoms.[49]Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging studies have observed decreased levels of NAA in the hippocampus of people with fibromyalgia, indicating decreased neuron functionality in this region. Altered connectivity and decreased grey matter of the default mode network,[54] the insula, and executive attention network have been found in fibromyalgia. Increased levels of glutamate and glutamine have been observed in the amygdala, parts of the prefrontal cortex, the posterior cingulate cortex, and the insula, correlating with pain levels in FM. Decreased GABA has been observed in the anterior insular in fibromyalgia. However, neuroimaging studies, in particular neurochemical imaging studies, are limited by methodology and interpretation.[55] Increased cerebral blood flow in response to pain was found in one fMRI study.[50] Findings of decreased blood flow in the thalamus and other regions of the basal ganglia correlating with treatment have been relatively consistent over three studies. Decreased binding of μ-opioid receptor have been observed; however, it is unknown if this is a result of increased endogenous binding in response to pain, or down regulation.[51]Inflammation and immune system
Overlaps have been drawn between sickness behavior, chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia. One study found increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in fibromyalgia, which may increase sensitivity to pain, and contribute to mood problems.[56] Increased levels of IL-1RA, Interleukin 6 and Interleukin 8 have been found.[57] Neurogenic inflammation has been proposed as a contributing factor to fibromyalgia.[58] A systematic review found most cytokines levels were similar in patients and controls, except for IL-1 receptor antagonist, IL-6 and IL-8[59]Diagnosis
The location of the nine paired tender points that comprise the 1990 American College of Rheumatology criteria for fibromyalgia.
There is no single test that can fully diagnose fibromyalgia and there is debate over what should be considered essential diagnostic criteria and whether an objective diagnosis is possible. In most cases, people with fibromyalgia symptoms may also have laboratory test results that appear normal and many of their symptoms may mimic those of other rheumatic conditions such as arthritis or osteoporosis. The most widely accepted set of classification criteria for research purposes was elaborated in 1990 by the Multicenter Criteria Committee of the American College of Rheumatology. These criteria, which are known informally as "the ACR 1990", define fibromyalgia according to the presence of the following criteria:
- A history of widespread pain lasting more than three months – affecting all four quadrants of the body, i.e., both sides, and above and below the waist.
- Tender points – there are 18 designated possible tender points (although a person with the disorder may feel pain in other areas as well). Diagnosis is no longer based on the number of tender points.[60][61]
2010 provisional criteria
Widespread Pain Index (WPI) Areas
In 2010, the American College of Rheumatology approved provisional revised diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia that eliminated the 1990 criteria's reliance on tender point testing.[63] The revised criteria use a widespread pain index (WPI) and symptom severity scale (SS) in place of tender point testing under the 1990 criteria. The WPI counts up to 19 general body areas[a] in which the person has experienced pain in the preceding two weeks. The SS rates the severity of the person's fatigue, unrefreshed waking, cognitive symptoms, and general somatic symptoms,[b] each on a scale from 0 to 3, for a composite score ranging from 0 to 12. The revised criteria for diagnosis are:
- WPI ≥ 7 and SS ≥ 5 OR WPI 3–6 and SS ≥ 9,
- Symptoms have been present at a similar level for at least three months, and
- No other diagnosable disorder otherwise explains the pain.[63]:607
Multidimensional assessment
Some research has suggested not to categorise fibromyalgia as a somatic disease or a mental disorder, but to use a multidimensional approach taking into consideration somatic symptoms, psychological factors, psychosocial stressors and subjective belief regarding fibromyalgia.[64] A review has looked at self-report questionnaires assessing fibromyalgia on multiple dimensions, including:[64]- Revised Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire[65]
- Widespread Pain Index[66]
- Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
- Multiple Ability Self-Report Questionnaire[67]
- Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory
- Medical Outcomes Study Sleep Scale
Differential diagnosis
People referred to rheumatologists may incorrectly receive a diagnosis of fibromyalgia in up to two thirds of cases.[68] Certain systemic, inflammatory, endocrine, rheumatic, infectious, and neurologic disorders may cause fibromyalgia-like symptoms, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, hypothyroidism, ankylosing spondylitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic-related polyenthesitis, hepatitis C, peripheral neuropathies, entrapment syndromes (such as carpal tunnel syndrome), multiple sclerosis and myasthenia gravis. The differential diagnosis is made during the evaluation on the basis of the person's medical history, physical examination, and laboratory investigations.[47][68][69][70]Management
As with many other medically unexplained syndromes, there is no universally accepted treatment or cure for fibromyalgia, and treatment typically consists of symptom management. Developments in the understanding of the pathophysiology of the disorder have led to improvements in treatment, which include prescription medication, behavioral intervention, and exercise. Indeed, integrated treatment plans that incorporate medication, patient education, aerobic exercise and cognitive behavioral therapy have been shown to be effective in alleviating pain and other fibromyalgia-related symptoms.[71]The Association of the Scientific Medical Societies in Germany,[72] the European League Against Rheumatism[73] and the Canadian Pain Society[74] currently publish guidelines for the diagnosis and management of FMS.
Medications
Health Canada and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have approved pregabalin[75] and duloxetine, for the management of fibromyalgia. The FDA also approved milnacipran, but the European Medicines Agency refused marketing authority.[76]Antidepressants
Antidepressants are "associated with improvements in pain, depression, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and health-related quality of life in people with FMS."[77] The goal of antidepressants should be symptom reduction and if used long term, their effects should be evaluated against side effects. A small number of people benefit significantly from the SNRIs duloxetine and milnacipran and the tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), such as amitriptyline. However, many people experience more adverse effects than benefits.[78][79] While amitriptyline has been used as a first line treatment, the quality of evidence to support this use is poor.[80]It can take up to three months to derive benefit from the antidepressant amitriptyline and between three and six months to gain the maximal response from duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin. Some medications have the potential to cause withdrawal symptoms when stopping so gradual discontinuation may be warranted particularly for antidepressants and pregabalin.[12]
There is tentative evidence that the benefits and harms of SSRIs appear to be about similar.[81]
Anti-seizure medication
The anti-convulsant drugs gabapentin and pregabalin may be used to reduce pain.[82][7] There is tentative evidence that gabapentin may be of benefit for pain in about 18% of people with fibromyalgia.[7] It is not possible to predict who will benefit, and a short trial may be recommended to test the effectiveness of this type of medication. Approximately 6/10 people who take gabapentin to treat pain related to fibromyalgia experience unpleasant side effects such as dizziness, abnormal walking, or swelling from fluid accumulation.[83][needs update] Pregabalin demonstrates a benefit in about 9% of people.[84] Pregabalin reduced time off work by 0.2 days per week.[85]Opioids
The use of opioids is controversial. As of 2015, no opioid is approved for use in this condition by the FDA.[86] The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) in 2014 stated that there was a lack of evidence for opioids for most people.[5] The Association of the Scientific Medical Societies in Germany in 2012 made no recommendation either for or against the use of weak opioids because of the limited amount of scientific research addressing their use in the treatment of FM. They strongly advise against using strong opioids.[72] The Canadian Pain Society in 2012 said that opioids, starting with a weak opioid like tramadol, can be tried but only for people with moderate to severe pain that is not well-controlled by non-opioid painkillers. They discourage the use of strong opioids and only recommend using them while they continue to provide improved pain and functioning. Healthcare providers should monitor people on opioids for ongoing effectiveness, side effects and possible unwanted drug behaviors.[74]The European League Against Rheumatism in 2008 recommends tramadol and other weak opioids may be used for pain but not strong opioids.[73] A 2015 review found fair evidence to support tramadol use if other medications do not work.[86] A 2018 review found little evidence to support the combination of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and tramadol over a single medication.[87] Goldenberg et al suggest that tramadol works via its serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition, rather than via its action as a weak opioid receptor agonist.[10]
A large study of US people with fibromyalgia found that between 2005 and 2007 37.4% were prescribed short-acting opioids and 8.3% were prescribed long-acting opioids,[88] with around 10% of those prescribed short-acting opioids using tramadol;[89] and a 2011 Canadian study of 457 people with FM found 32% used opioids and two thirds of those used strong opioids.[74]
Others
A 2007 review concluded that a period of nine months of growth hormone was required to reduce fibromyalgia symptoms and normalize IGF-1.[90] A 2014 also found some evidence support its use.[91] Sodium oxybate increases growth hormone production levels through increased slow-wave sleep patterns. However, this medication was not approved by the FDA for the indication for use in people with fibromyalgia due to the concern for abuse.[92]The muscle relaxants cyclobenzaprine, carisoprodol with acetaminophen and caffeine and tizanidine are sometimes used to treat fibromyalgia; however as of 2015 they are not approved for this use in the United States.[93][94] The use of NSAIDs is not recommended as first line therapy.[95] Moreover, NSAIDs cannot be considered as useful in the management of fibromyalgia.[96]
Dopamine agonists (e.g. pramipexole and ropinirole) resulted in some improvement in a minority of people,[97] but side effects, including the onset of impulse control disorders like compulsive gambling and shopping, might be a concern for some people.[98]
There is some evidence that 5HT3 antagonists may be beneficial.[99] Preliminary clinical data finds that low-dose naltrexone (LDN) may provide symptomatic improvement.[100]
Very low quality evidence suggests quetiapine may be effective in fibromyalgia.[101]
No high quality evidence exists that suggests synthetic THC (nabilone) helps with fibromyalgia.[102]
Therapy
Due to the uncertainty about the pathogenesis of FM, current treatment approaches focus on management of symptoms to improve quality of life,[103] using integrated pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches.[104] There is no single intervention shown to be effective for all patients [105] and no gold treatment standard exists for FM.[106] Multimodal/multidisciplinary therapy is recommended to target multiple underlying factors of FM.[107] A meta-analysis of 1,119 subjects found "strong evidence that multicomponent treatment has beneficial short-term effects on key symptoms of FMS." [108]Cognitive behavioural therapy
Non-pharmacological components include cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), exercise and psychoeducation (specifically, sleep hygiene).[109][110][111][112] CBT and related psychological and behavioural therapies have a small to moderate effect in reducing symptoms of fibromyalgia.[113][110] Effect sizes tend to be small when CBT is used as a stand-alone treatment for FM patients, but these improve significantly when CBT is part of a wider multidisciplinary treatment program.[114] The greatest benefit occurs when CBT is used along with exercise.[71][115]A 2010 systematic review of 14 studies reported that CBT improves self-efficacy or coping with pain and reduces the number of physician visits at post-treatment, but has no significant effect on pain, fatigue, sleep or health-related quality of life at post-treatment or follow-up. Depressed mood was also improved but this could not be distinguished from some risks of bias.[116]
Mind-body therapy
Mind-body therapies focus on interactions among the brain, mind, body and behaviour. The National Centre for Complementary and Alternative Medicine defines the treatments under holistic principle that mind-body are interconnected and through treatment there is improvement in psychological and physical well-being, and allow patient to have an active role in their treatment.[117] There are several therapies such as mindfulness, movement therapy (yoga, tai chi), psychological (including CBT) and biofeedback (use of technology to give audio/visual feedback on physiological processes like heart rate). There is only weak evidence that psychological intervention is effective in the treatment of fibromyalgia and no good evidence for the benefit of other mind-body therapies.[117]Exercise
There is strong evidence indicating that exercise improves fitness and sleep and may reduce pain and fatigue in some people with fibromyalgia.[118][119] In particular, there is strong evidence that cardiovascular exercise is effective for some people.[120] Studies of different forms of aerobic exercise for adults with fibromyalgia indicate that aerobic exercise improves quality of life, decreases pain, slightly improves physical function and makes no difference in fatigue and stiffness.[121] Long-term effects are uncertain.[121]A recommended approach to a graded exercise program begins with small, frequent exercise periods and builds up from there.[122] In children, fibromyalgia is often treated with an intense physical and occupational therapy program for musculoskeletal pain syndromes. These programs also employ counseling, art therapy, and music therapy. These programs are evidence-based and report long-term total pain resolution rates as high as 88%.[123]
Prognosis
Although in itself neither degenerative nor fatal, the chronic pain of fibromyalgia is pervasive and persistent. Most people with fibromyalgia report that their symptoms do not improve over time. An evaluation of 332 consecutive new people with fibromyalgia found that disease-related factors such as pain and psychological factors such as work status, helplessness, education, and coping ability had an independent and significant relationship to FM symptom severity and function.[124]Epidemiology
Fibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2–8% of the population.[4][125] Females are affected about twice as often as males based on criteria as of 2014.[4]Fibromyalgia may not be diagnosed in up to 75% of affected people.[15]
History
Chronic widespread pain had already been described in the literature in the 19th century but the term fibromyalgia was not used until 1976 when Dr P.K. Hench used it to describe these symptoms.[12] Many names, including "muscular rheumatism", "fibrositis", "psychogenic rheumatism", and "neurasthenia" were applied historically to symptoms resembling those of fibromyalgia.[126] The term fibromyalgia was coined by researcher Mohammed Yunus as a synonym for fibrositis and was first used in a scientific publication in 1981.[127] Fibromyalgia is from the Latin fibra (fiber)[128] and the Greek words myo (muscle)[129] and algos (pain).[130]Historical perspectives on the development of the fibromyalgia concept note the "central importance" of a 1977 paper by Smythe and Moldofsky on fibrositis.[131][132] The first clinical, controlled study of the characteristics of fibromyalgia syndrome was published in 1981,[133] providing support for symptom associations. In 1984, an interconnection between fibromyalgia syndrome and other similar conditions was proposed,[134] and in 1986, trials of the first proposed medications for fibromyalgia were published.[134]
A 1987 article in the Journal of the American Medical Association used the term "fibromyalgia syndrome" while saying it was a "controversial condition".[135] The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) published its first classification criteria for fibromyalgia in 1990,[136] although these are not strictly diagnostic criteria.[16]
Society and culture
Economics
People with fibromyalgia generally have higher health-care costs and utilization rates. A study of almost 20,000 Humana members enrolled in Medicare Advantage and commercial plans compared costs and medical utilizations and found that people with fibromyalgia used twice as much pain-related medication as those without fibromyalgia. Furthermore, the use of medications and medical necessities increased markedly across many measures once diagnosis was made.[137]Controversies
Fibromyalgia was defined relatively recently. It continues to be a disputed diagnosis. Dr. Frederick Wolfe, lead author of the 1990 paper that first defined the diagnostic guidelines for fibromyalgia, stated in 2008, that he believed it "clearly" not to be a disease but instead a physical response to depression and stress,.[138] In 2013 Wolfe added that its causes "are controversial in a sense" and "there are many factors that produce these symptoms – some are psychological and some are physical and it does exist on a continuum".[139]Some members of the medical community do not consider fibromyalgia a disease because of a lack of abnormalities on physical examination and the absence of objective diagnostic tests.[131][140]
Neurologists and pain specialists tend to view fibromyalgia as a pathology due to dysfunction of muscles and connective tissue as well as functional abnormalities in the central nervous system. Rheumatologists define the syndrome in the context of "central sensitization" – heightened brain response to normal stimuli in the absence of disorders of the muscles, joints, or connective tissues. On the other hand, psychiatrists often view fibromyalgia as a type of affective disorder, whereas specialists in psychosomatic medicine tend to view fibromyalgia as being a somatic symptom disorder. These controversies do not engage healthcare specialists alone; some patients object to fibromyalgia being described in purely somatic terms. There is extensive research evidence to support the view that the central symptom of fibromyalgia, namely pain, has a neurogenic origin, though this is consistent in both views.[12][15]
The validity of fibromyalgia as a unique clinical entity is a matter of contention because "no discrete boundary separates syndromes such as FMS, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, or chronic muscular headaches".[120][141] Because of this symptomatic overlap, some researchers have proposed that fibromyalgia and other analogous syndromes be classified together as functional somatic syndromes for some purposes.[142]