The extended evolutionary synthesis consists of a set of theoretical concepts more comprehensive than the earlier modern synthesis of evolutionary biology that took place between 1918 and 1942. The extended evolutionary synthesis was called for in the 1950s by C. H. Waddington, argued for on the basis of punctuated equilibrium by Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge in the 1980s, and was reconceptualized in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller.
The extended evolutionary synthesis revisits the relative importance of different factors at play, examining several assumptions of the earlier synthesis, and augmenting it with additional causative factors. It includes multilevel selection, transgenerational epigenetic inheritance, niche construction, evolvability, and several concepts from evo-devo.
Not all biologists have agreed on the need for, or the scope of, an extended synthesis. Many have collaborated on another synthesis in evolutionary developmental biology, which concetrates on developmental molecular genetics and evolution to understand how natural selection operated on developmental processes and deep homologies between organisms at the level of highly conserved genes.
The preceding "modern synthesis"
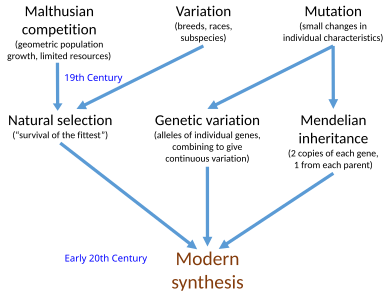
Several major ideas about evolution came together in the population genetics of the early 20th century to form the modern synthesis, including genetic variation, natural selection, and particulate (Mendelian) inheritance. This ended the eclipse of Darwinism and supplanted a variety of non-Darwinian theories of evolution. However, it did not unify all of biology, omitting sciences such as developmental biology.
The modern synthesis was the widely accepted early-20th-century synthesis reconciling Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection and Gregor Mendel's theory of genetics in a joint mathematical framework. It established evolution as biology's central paradigm. The 19th-century ideas of natural selection by Darwin and Mendelian genetics were united by researchers who included Ronald Fisher, one of the three founders of population genetics, and J. B. S. Haldane and Sewall Wright, between 1918 and 1932. Julian Huxley introduced the phrase "modern synthesis" in his 1942 book, Evolution: The Modern Synthesis.
Early history
During the 1950s, the English biologist C. H. Waddington called for an extended synthesis based on his research on epigenetics and genetic assimilation. An extended synthesis was also proposed by the Austrian zoologist Rupert Riedl, with the study of evolvability. In 1978, Michael J. D. White wrote about an extension of the modern synthesis based on new research from speciation.1980s: punctuated equilibrium
In the 1980s, the American palaeontologists Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge argued for an extended synthesis based on their idea of punctuated equilibrium, the role of species selection shaping large scale evolutionary patterns and natural selection working on multiple levels extending from genes to species. The ethologist John Endler wrote a paper in 1988 discussing processes of evolution that he felt had been neglected.Contributions from evolutionary developmental biology
Some researchers in the field of evolutionary developmental biology proposed another synthesis. They argue that the modern and extended syntheses should mostly center on genes and suggest an integration of embryology with molecular genetics an evolution, aiming to understand how natural selection operates on gene regulation and deep homologies between organisms at the level of highly conserved genes, transcription factors and signalling pathways. By contrast, a different strand of evo-devo following an organismal approach contributes to the extended synthesis by emphasizing (amongst others) developmental bias (both through facilitation and constraint), evolvability, and inherency of form as primary factors in the evolution of complex structures and phenotypic novelties.Recent history
Massimo Pigliucci, a leading proponent of the extended evolutionary synthesis in its 2007 form
The idea of an extended synthesis was relaunched in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci, and Gerd B. Müller with a book in 2010 titled Evolution: The Extended Synthesis, which has served as a launching point for work on the extended synthesis. This includes:
- The role of prior configurations, genomic structures, and other traits in the organism in generating evolutionary variations.
- How increasing dimensionality of fitness landscapes affects our view of speciation.
- The role of multilevel selection in the major evolutionary transitions.
- New types of inheritance, including cultural and epigenetic inheritance.
- The way that organismal development and developmental plasticity channel evolutionary pathways and generates phenotypic novelty
- How organisms modify the environments they belong to through niche construction.
Predictions
The extended synthesis is characterized by its additional set of predictions that differ from the standard modern synthesis theory:- change in phenotype can precede change in genotype
- changes in phenotype are predominantly positive, rather than neutral
- changes in phenotype are induced in many organisms, rather than one organism
- revolutionary change in phenotype can occur through mutation, facilitated variation or threshold events
- repeated evolution in isolated populations can be by convergent evolution or developmental bias
- adaptation can be caused by natural selection, environmental induction, non-genetic inheritance, learning and cultural transmission (see: Baldwin effect, meme, transgenerational epigenetic inheritance, ecological inheritance, non-Mendelian inheritance)
- rapid evolution can result from simultaneous induction, natural selection and developmental dynamics
- biodiversity can be affected by features of developmental systems such as differences in evolvability
- heritable variation is directed towards variants that are adaptive and integrated with phenotype
- niche construction is biased towards environmental changes that suit the constructor's phenotype, or that of its descendants, and enhance their fitness
- kin selection
- multilevel selection
- self-organization
Testing
The extended evolutionary synthesis is currently being tested by a group of scientists from eight institutions in Britain, Sweden and the United States. The £7.7 million project is supported by a £5.7 million grant from the John Templeton Foundation.The project is headed by Kevin N. Laland at the University of St Andrews and Tobias Uller at Lund University. According to Laland what the extended synthesis "really boils down to is recognition that, in addition to selection, drift, mutation and other established evolutionary processes, other factors, particularly developmental influences, shape the evolutionary process in important ways."