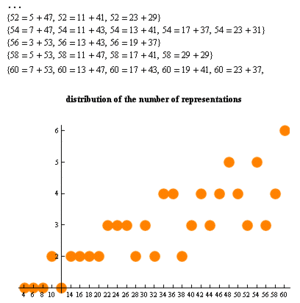
The
even integers from 4 to 28 as sums of two primes: Even integers
correspond to horizontal lines. For each prime, there are two oblique
lines, one red and one blue. The sums of two primes are the
intersections of one red and one blue line, marked by a circle. Thus the
circles on a given horizontal line give all partitions of the
corresponding even integer into the sum of two primes.
Goldbach's conjecture is one of the oldest and best-known unsolved problems in number theory and all of mathematics. It states:
The conjecture has been shown to hold for all integers less than 4 × 1018, but remains unproven despite considerable effort.
Goldbach number
The number of ways an even number can be represented as the sum of two primes.
A Goldbach number is a positive even integer that can be expressed as the sum of two odd primes. Since four is the only even number greater than two that requires the even prime 2 in order to be written as the sum of two primes, another form of the statement of Goldbach's conjecture is that all even integers greater than 4 are Goldbach numbers.
The expression of a given even number as a sum of two primes is called a Goldbach partition of that number. The following are examples of Goldbach partitions for some even numbers:
- 6 = 3 + 3
- 8 = 3 + 5
- 10 = 3 + 7 = 5 + 5
- 12 = 7 + 5
- ...
- 100 = 3 + 97 = 11 + 89 = 17 + 83 = 29 + 71 = 41 + 59 = 47 + 53
- ...
- 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 4, 4, 2, 3, 4, 3, 4, 5, 4, 3, 5, 3, 4, 6, 3, 5, 6, 2, 5, 6, 5, 5, 7, 4, 5, 8, 5, 4, 9, 4, 5, 7, 3, 6, 8, 5, 6, 8, 6, 7, 10, 6, 6, 12, 4, 5, 10, 3, ... (sequence A045917 in the OEIS).
Origins
Letter from Goldbach to Euler dated on 7. June 1742 (Latin-German).
- Every integer which can be written as the sum of two primes, can also be written as the sum of as many primes as one wishes, until all terms are units.
- Every integer greater than 2 can be written as the sum of three primes.
- Every integer greater than 5 can be written as the sum of three primes.
- Every even integer greater than 2 can be written as the sum of two primes,
"Dass … ein jeder numerus par eine summa duorum primorum sey, halte ich für ein ganz gewisses theorema, ungeachtet ich dasselbe nicht demonstriren kann." ("That … every even integer is a sum of two primes, I regard as a completely certain theorem, although I cannot prove it.")Goldbach's third version (equivalent to the two other versions) is the form in which the conjecture is usually expressed today. It is also known as the "strong", "even", or "binary" Goldbach conjecture, to distinguish it from a weaker conjecture, known today variously as the Goldbach's weak conjecture, the "odd" Goldbach conjecture, or the "ternary" Goldbach conjecture. This weak conjecture asserts that all odd numbers greater than 7 are the sum of three odd primes, and appears to have been proved in 2013. The weak conjecture is a corollary of the strong conjecture, as, if n – 3 is a sum of two primes, then n is a sum of three primes. The converse implication, and the strong Goldbach conjecture remain unproven.
Verified results
For small values of n, the strong Goldbach conjecture (and hence the weak Goldbach conjecture) can be verified directly. For instance, Nils Pipping in 1938 laboriously verified the conjecture up to n ≤ 105. With the advent of computers, many more values of n have been checked; T. Oliveira e Silva is running a distributed computer search that has verified the conjecture for n ≤ 4 × 1018 (and double-checked up to 4 × 1017) as of 2013. One record from this search is that 3,325,581,707,333,960,528 is the smallest number that has no Goldbach partition with a prime below 9781.Heuristic justification
Statistical considerations that focus on the probabilistic distribution of prime numbers present informal evidence in favour of the conjecture (in both the weak and strong forms) for sufficiently large integers: the greater the integer, the more ways there are available for that number to be represented as the sum of two or three other numbers, and the more "likely" it becomes that at least one of these representations consists entirely of primes.
Number of ways to write an even number n as the sum of two primes (4 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000)
A very crude version of the heuristic probabilistic argument (for the strong form of the Goldbach conjecture) is as follows. The prime number theorem asserts that an integer m selected at random has roughly a
 chance of being prime. Thus if n is a large even integer and m is a number between 3 and n/2, then one might expect the probability of m and n − m simultaneously being prime to be
chance of being prime. Thus if n is a large even integer and m is a number between 3 and n/2, then one might expect the probability of m and n − m simultaneously being prime to be ![1{\big /}{\big [}\ln m\,\ln(n-m){\big ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ebd3400044de44f8fc6c9c4a5830d94c5719a92d) . If one pursues this heuristic, one might expect the total number of ways to write a large even integer n as the sum of two odd primes to be roughly
. If one pursues this heuristic, one might expect the total number of ways to write a large even integer n as the sum of two odd primes to be roughly
This heuristic argument is actually somewhat inaccurate, because it assumes that the events of m and n − m being prime are statistically independent of each other. For instance, if m is odd then n − m is also odd, and if m is even, then n − m is even, a non-trivial relation because, besides the number 2, only odd numbers can be prime. Similarly, if n is divisible by 3, and m was already a prime distinct from 3, then n − m would also be coprime to 3 and thus be slightly more likely to be prime than a general number. Pursuing this type of analysis more carefully, Hardy and Littlewood in 1923 conjectured (as part of their famous Hardy–Littlewood prime tuple conjecture) that for any fixed c ≥ 2, the number of representations of a large integer n as the sum of c primes
 with
with  should be asymptotically equal to
should be asymptotically equal to  is the number of solutions to the equation
is the number of solutions to the equation
 in modular arithmetic, subject to the constraints
in modular arithmetic, subject to the constraints  . This formula has been rigorously proven to be asymptotically valid for c ≥ 3 from the work of Vinogradov, but is still only a conjecture when
. This formula has been rigorously proven to be asymptotically valid for c ≥ 3 from the work of Vinogradov, but is still only a conjecture when  . In the latter case, the above formula simplifies to 0 when n is odd, and to
. In the latter case, the above formula simplifies to 0 when n is odd, and to
 is Hardy–Littlewood's twin prime constant
is Hardy–Littlewood's twin prime constant
The Goldbach partition functions shown here can be displayed as histograms which informatively illustrate the above equations. See Goldbach's comet.
Rigorous results
The strong Goldbach conjecture is much more difficult than the weak Goldbach conjecture. Using Vinogradov's method, Chudakov, Van der Corput, and Estermann showed that almost all even numbers can be written as the sum of two primes (in the sense that the fraction of even numbers which can be so written tends towards 1). In 1930, Lev Schnirelmann proved that any natural number greater than 1 can be written as the sum of not more than C prime numbers, where C is an effectively computable constant, see Schnirelmann density. Schnirelmann's constant is the lowest number C with this property. Schnirelmann himself obtained C < 800,000. This result was subsequently enhanced by many authors, such as Olivier Ramaré, who in 1995 showed that every even number n ≥ 4 is in fact the sum of at most six primes. The best known result currently stems from the proof of the weak Goldbach conjecture by Harald Helfgott, which directly implies that every even number n ≥ 4 is the sum of at most four primes.In 1924 Hardy and Littlewood showed under the assumption of the GRH that amount of even numbers up to X violating Goldbach conjecture is much less than
 for small c.
for small c.Chen Jingrun showed in 1973 using the methods of sieve theory that every sufficiently large even number can be written as the sum of either two primes, or a prime and a semiprime (the product of two primes).
In 1975, Hugh Montgomery and Robert Charles Vaughan showed that "most" even numbers are expressible as the sum of two primes. More precisely, they showed that there exist positive constants c and C such that for all sufficiently large numbers N, every even number less than N is the sum of two primes, with at most
 exceptions. In particular, the set of even integers which are not the sum of two primes has density zero.
exceptions. In particular, the set of even integers which are not the sum of two primes has density zero.Linnik proved in 1951 the existence of a constant K such that every sufficiently large even number is the sum of two primes and at most K powers of 2. Roger Heath-Brown and Jan-Christoph Schlage-Puchta in 2002 found that K = 13 works.
As with many famous conjectures in mathematics, there are a number of purported proofs of the Goldbach conjecture, none of which are accepted by the mathematical community.
Related problems
Although Goldbach's conjecture implies that every positive integer greater than one can be written as a sum of at most three primes, it is not always possible to find such a sum using a greedy algorithm that uses the largest possible prime at each step. The Pillai sequence tracks the numbers requiring the largest number of primes in their greedy representations.One can consider similar problems in which primes are replaced by other particular sets of numbers, such as the squares.
- It was proven by Lagrange that every positive integer is the sum of four squares.
- Hardy and Littlewood listed as their Conjecture I: "Every large odd number (n > 5) is the sum of a prime and the double of a prime." (Mathematics Magazine, 66.1 (1993): 45–47.) This conjecture is known as Lemoine's conjecture (also called Levy's conjecture).
- The Goldbach conjecture for practical numbers, a prime-like sequence of integers, was stated by Margenstern in 1984, and proved by Melfi in 1996: every even number is a sum of two practical numbers.