Environmental economics is a sub-field of economics that is concerned with environmental issues. It has become a widely studied topic due to growing concerns in regards to the environment in the twentyfirst century. Quoting from the National Bureau of Economic Research Environmental Economics program:
... Environmental Economics ... undertakes theoretical or empirical studies of the economic effects of national or local environmental policies around the world ... . Particular issues include the costs and benefits of alternative environmental policies to deal with air pollution, water quality, toxic substances, solid waste, and global warming.Environmental economics is distinguished from ecological economics in that ecological economics emphasizes the economy as a subsystem of the ecosystem with its focus upon preserving natural capital. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing "strong" sustainability and rejecting the proposition that natural capital can be substituted by human-made capital.
Topics and concepts
Market failure
Central to environmental economics is the concept of market failure. Market failure means that markets fail to allocate resources efficiently. As stated by Hanley, Shogren, and White (2007) in their textbook Environmental Economics: "A market failure occurs when the market does not allocate scarce resources to generate the greatest social welfare. A wedge exists between what a private person does given market prices and what society might want him or her to do to protect the environment. Such a wedge implies wastefulness or economic inefficiency; resources can be reallocated to make at least one person better off without making anyone else worse off." Common forms of market failure include externalities, non-excludability and non-rivalry.Externality
An externality exists when a person makes a choice that affects other people in a way that is not accounted for in the market price. An externality can be positive or negative, but is usually associated with negative externalities in environmental economics. For instance, water seepage in residential buildings happen in upper floor affect the lower floor. Another example concerns how the sale of Amazon timber disregards the amount of carbon dioxide released in the cutting. Or a firm emitting pollution will typically not take into account the costs that its pollution imposes on others. As a result, pollution may occur in excess of the 'socially efficient' level, which is the level that would exist if the market was required to account for the pollution. A classic definition influenced by Kenneth Arrow and James Meade is provided by Heller and Starrett (1976), who define an externality as "a situation in which the private economy lacks sufficient incentives to create a potential market in some good and the nonexistence of this market results in losses of Pareto efficiency". In economic terminology, externalities are examples of market failures, in which the unfettered market does not lead to an efficient outcome.Common goods and public goods
When it is too costly to exclude some people from access to an environmental resource, the resource is either called a common property resource (when there is rivalry for the resource, such that one person's use of the resource reduces others' opportunity to use the resource) or a public good (when use of the resource is non-rivalrous). In either case of non-exclusion, market allocation is likely to be inefficient.These challenges have long been recognized. Hardin's (1968) concept of the tragedy of the commons popularized the challenges involved in non-exclusion and common property. "Commons" refers to the environmental asset itself, "common property resource" or "common pool resource" refers to a property right regime that allows for some collective body to devise schemes to exclude others, thereby allowing the capture of future benefit streams; and "open-access" implies no ownership in the sense that property everyone owns nobody owns.
The basic problem is that if people ignore the scarcity value of the commons, they can end up expending too much effort, over harvesting a resource (e.g., a fishery). Hardin theorizes that in the absence of restrictions, users of an open-access resource will use it more than if they had to pay for it and had exclusive rights, leading to environmental degradation. See, however, Ostrom's (1990) work on how people using real common property resources have worked to establish self-governing rules to reduce the risk of the tragedy of the commons.
The mitigation of climate change effects is an example of a public good, where the social benefits are not reflected completely in the market price. This is a public good since the risks of climate change are both non-rival and non-excludable. Such efforts are non-rival since climate mitigation provided to one does not reduce the level of mitigation that anyone else enjoys. They are non-excludable actions as they will have global consequences from which no one can be excluded. A country's incentive to invest in carbon abatement is reduced because it can "free ride" off the efforts of other countries. Over a century ago, Swedish economist Knut Wicksell (1896) first discussed how public goods can be under-provided by the market because people might conceal their preferences for the good, but still enjoy the benefits without paying for them.
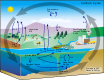
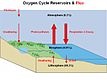
- GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES CRITICAL FOR LIFE
Valuation
Assessing the economic value of the environment is a major topic within the field. Use and indirect use are tangible benefits accruing from natural resources or ecosystem services. Non-use values include existence, option, and bequest values. For example, some people may value the existence of a diverse set of species, regardless of the effect of the loss of a species on ecosystem services. The existence of these species may have an option value, as there may be the possibility of using it for some human purpose. For example, certain plants may be researched for drugs. Individuals may value the ability to leave a pristine environment to their children.Use and indirect use values can often be inferred from revealed behavior, such as the cost of taking recreational trips or using hedonic methods in which values are estimated based on observed prices. Non-use values are usually estimated using stated preference methods such as contingent valuation or choice modelling. Contingent valuation typically takes the form of surveys in which people are asked how much they would pay to observe and recreate in the environment (willingness to pay) or their willingness to accept (WTA) compensation for the destruction of the environmental good. Hedonic pricing examines the effect the environment has on economic decisions through housing prices, traveling expenses, and payments to visit parks.
Solutions
Solutions advocated to correct such externalities include:- Environmental regulations. Under this plan, the economic impact has to be estimated by the regulator. Usually this is done using cost-benefit analysis. There is a growing realization that regulations (also known as "command and control" instruments) are not so distinct from economic instruments as is commonly asserted by proponents of environmental economics. E.g.1 regulations are enforced by fines, which operate as a form of tax if pollution rises above the threshold prescribed. E.g.2 pollution must be monitored and laws enforced, whether under a pollution tax regime or a regulatory regime. The main difference an environmental economist would argue exists between the two methods, however, is the total cost of the regulation. "Command and control" regulation often applies uniform emissions limits on polluters, even though each firm has different costs for emissions reductions. Some firms, in this system, can abate inexpensively, while others can only abate at high cost. Because of this, the total abatement has some expensive and some inexpensive efforts to abate. Consequently, modern "Command and control" regulations are oftentimes designed in a way, which addresses these issues by incorporating utility parameters. For instance, CO2 emission standards for specific manufacturers in the automotive industry are either linked to the average vehicle footprint (US system) or average vehicle weight (EU system) of their entire vehicle fleet. Environmental economic regulations find the cheapest emission abatement efforts first, then the more expensive methods second. E.g. as said earlier, trading, in the quota system, means a firm only abates if doing so would cost less than paying someone else to make the same reduction. This leads to a lower cost for the total abatement effort as a whole.
- Quotas on pollution. Often it is advocated that pollution reductions should be achieved by way of tradeable emissions permits, which if freely traded may ensure that reductions in pollution are achieved at least cost. In theory, if such tradeable quotas are allowed, then a firm would reduce its own pollution load only if doing so would cost less than paying someone else to make the same reduction. In practice, tradeable permits approaches have had some success, such as the U.S.'s sulphur dioxide trading program or the EU Emissions Trading Scheme, and interest in its application is spreading to other environmental problems.
- Taxes and tariffs on pollution. Increasing the costs of polluting will discourage polluting, and will provide a "dynamic incentive," that is, the disincentive continues to operate even as pollution levels fall. A pollution tax that reduces pollution to the socially "optimal" level would be set at such a level that pollution occurs only if the benefits to society (for example, in form of greater production) exceeds the costs. Some advocate a major shift from taxation from income and sales taxes to tax on pollution - the so-called "green tax shift."
- Better defined property rights. The Coase Theorem states that assigning property rights will lead to an optimal solution, regardless of who receives them, if transaction costs are trivial and the number of parties negotiating is limited. For example, if people living near a factory had a right to clean air and water, or the factory had the right to pollute, then either the factory could pay those affected by the pollution or the people could pay the factory not to pollute. Or, citizens could take action themselves as they would if other property rights were violated. The US River Keepers Law of the 1880s was an early example, giving citizens downstream the right to end pollution upstream themselves if government itself did not act (an early example of bioregional democracy). Many markets for "pollution rights" have been created in the late twentieth century—see emissions trading. According to the Coase Theorem, the involved parties will bargain with each other, which results in an efficient solution. However, modern economic theory has shown that the presence of asymmetric information may lead to inefficient bargaining outcomes. Specifically, Rob (1989) has shown that pollution claim settlements will not lead to the socially optimal outcome when the individuals that will be affected by pollution have learned private information about their disutility already before the negotiations take place. Goldlücke and Schmitz (2018) have shown that inefficiencies may also result if the parties learn their private information only after the negotiations, provided that the feasible transfer payments are bounded.
Relationship to other fields
Environmental economics is related to ecological economics but there are differences. Most environmental economists have been trained as economists. They apply the tools of economics to address environmental problems, many of which are related to so-called market failures—circumstances wherein the "invisible hand" of economics is unreliable. Most ecological economists have been trained as ecologists, but have expanded the scope of their work to consider the impacts of humans and their economic activity on ecological systems and services, and vice versa. This field takes as its premise that economics is a strict subfield of ecology. Ecological economics is sometimes described as taking a more pluralistic approach to environmental problems and focuses more explicitly on long-term environmental sustainability and issues of scale.Environmental economics is viewed as more pragmatic in a price system; ecological economics as more idealistic in its attempts not to use money as a primary arbiter of decisions. These two groups of specialists sometimes have conflicting views which may be traced to the different philosophical underpinnings.
Another context in which externalities apply is when globalization permits one player in a market who is unconcerned with biodiversity to undercut prices of another who is - creating a race to the bottom in regulations and conservation. This, in turn, may cause loss of natural capital with consequent erosion, water purity problems, diseases, desertification, and other outcomes which are not efficient in an economic sense. This concern is related to the subfield of sustainable development and its political relation, the anti-globalization movement.
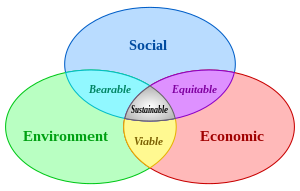
The three pillars of sustainability (clickable)
Environmental economics was once distinct from resource economics. Natural resource economics as a subfield began when the main concern of researchers was the optimal commercial exploitation of natural resource stocks. But resource managers and policy-makers eventually began to pay attention to the broader importance of natural resources (e.g. values of fish and trees beyond just their commercial exploitation). It is now difficult to distinguish "environmental" and "natural resource" economics as separate fields as the two became associated with sustainability. Many of the more radical green economists split off to work on an alternate political economy.
Environmental economics was a major influence on the theories of natural capitalism and environmental finance, which could be said to be two sub-branches of environmental economics concerned with resource conservation in production, and the value of biodiversity to humans, respectively. The theory of natural capitalism (Hawken, Lovins, Lovins) goes further than traditional environmental economics by envisioning a world where natural services are considered on par with physical capital.
The more radical Green economists reject neoclassical economics in favour of a new political economy beyond capitalism or communism that gives a greater emphasis to the interaction of the human economy and the natural environment, acknowledging that "economy is three-fifths of ecology" - Mike Nickerson.
These more radical approaches would imply changes to money supply and likely also a bioregional democracy so that political, economic, and ecological "environmental limits" were all aligned, and not subject to the arbitrage normally possible under capitalism.
An emerging sub-field of environmental economics studies its intersection with development economics. Dubbed "envirodevonomics" by Michael Greenstone and B. Kelsey Jack in their paper "Envirodevonomics: A Research Agenda for a Young Field," the sub-field is primarily interested in studying "why environmental quality [is] so poor in developing countries." A strategy for better understanding this correlation between a country's GDP and its environmental quality involves analyzing how many of the central concepts of environmental economics, including market failures, externalities, and willingness to pay, may be complicated by the particular problems facing developing countries, such as political issues, lack of infrastructure, or inadequate financing tools, among many others.