Technological change (TC), technological development, technological achievement, or technological progress is the overall process of invention, innovation and diffusion of technology or processes. In essence, technological change covers the invention of technologies (including processes) and their commercialization or release as open source via research and development (producing emerging technologies), the continual improvement
of technologies (in which they often become less expensive), and the
diffusion of technologies throughout industry or society (which
sometimes involves disruption and convergence). In short, technological change is based on both better and more technology.
Original model of three phases of the process of
Technological Change
Modeling technological change
In its earlier days, technological change was illustrated with the 'Linear Model of Innovation', which has now been largely discarded to be replaced with a model of technological change that involves innovation at all stages of research, development, diffusion, and use. When speaking about "modeling technological change," this often means the process of innovation. This process of continuous improvement is often modeled as a curve depicting decreasing costs over time (for instance fuel cell which have become cheaper every year). TC is also often modelled using a learning curve, ex.: Ct=C0 * Xt^-b.Technological change itself is often included in other models (e.g. climate change models) and was often taken as an exogenous factor. These days TC is more often included as an endogenous factor. This means that it is taken as something you can influence. Today, there are sectors that maintain policy can influence the speed and direction of technological change. For instance, proponents of the Induced Technological Change hypothesis state that policy makers can steer the direction of technological advances by influencing relative factor prices and this can be demonstrated in the way climate policies impact the use of fossil fuel energy, specifically how it becomes relatively more expensive. Until now, the empirical evidence about the existence of policy induced innovation effects is still lacking and this may be attributed to a variety of reasons outside the sparsity of models (e.g. long-term policy uncertainty and exogenous drivers of (directed) innovation). A related concept is the notion of Directed Technical Change with more emphasis on price induced directional rather than policy induced scale effects.
Invention
The creation of something new, or a "breakthrough" technology. This is often included in the process of product development and relies on research. This can be demonstrated in the invention of the spreadsheet software. Newly invented technologies are conventionally patented.Diffusion
Diffusion pertains to the spread of a technology through a society or industry. The diffusion of a technology theory generally follows an S-shaped curve as early versions of technology are rather unsuccessful, followed by a period of successful innovation with high levels of adoption, and finally a dropping off in adoption as a technology reaches its maximum potential in a market. In the case of a personal computer, it has made way beyond homes and into business settings, such as office workstations and server machines to host websites.Technological change as a social process
Underpinning the idea of technological change as a social process is general agreement on the importance of social context and communication. According to this model, technological change is seen as a social process involving producers and adopters and others (such as government) who are profoundly affected by cultural setting, political institutions and marketing strategies.In free market economies, the maximization of profits is a powerful driver of technological change. Generally, only those technologies that promise to maximize profits for the owners of incoming producing capital are developed and reach the market. Any technological product that fails to meet this criterion - even though they may satisfy very important societal needs - are eliminated. Therefore, technological change is a social process strongly biased in favor of the financial interests of capital. There are currently no well established democratic processes, such as voting on the social or environmental desirability of a new technology prior to development and marketing, that would allow average citizens to direct the course of technological change.
Elements of diffusion
Emphasis has been on four key elements of the technological change process: (1) an innovative technology (2) communicated through certain channels (3) to members of a social system (4) who adopt it over a period of time. These elements are derived from Everett M. Rogers Diffusion of innovations theory using a communications-type approach.Innovation
Rogers proposed that there are five main attributes of innovative technologies which influence acceptance. He called these criteria ACCTO, which stands for Advantage, Compatibility, Complexity, Trialability, and Observability. Relative advantage may be economic or non-economic, and is the degree to which an innovation is seen as superior to prior innovations fulfilling the same needs. It is positively related to acceptance (e.g. the higher the relative advantage, the higher the adoption level, and vice versa). Compatibility is the degree to which an innovation appears consistent with existing values, past experiences, habits and needs to the potential adopter; a low level of compatibility will slow acceptance. Complexity is the degree to which an innovation appears difficult to understand and use; the more complex an innovation, the slower its acceptance. Trialability is the perceived degree to which an innovation may be tried on a limited basis, and is positively related to acceptance. Trialability can accelerate acceptance because small-scale testing reduces risk. Observability is the perceived degree to which results of innovating are visible to others and is positively related to acceptance.Communication channels
Communication channels are the means by which a source conveys a message to a receiver. Information may be exchanged through two fundamentally different, yet complementary, channels of communication. Awareness is more often obtained through the mass media, while uncertainty reduction that leads to acceptance mostly results from face-to-face communication.Social system
The social system provides a medium through which and boundaries within which, innovation is adopted. The structure of the social system affects technological change in several ways. Social norms, opinion leaders, change agents, government and the consequences of innovations are all involved. Also involved are cultural setting, nature of political institutions, laws, policies and administrative structures.Time
Time enters into the acceptance process in many ways. The time dimension relates to the innovativeness of an individual or other adopter, which is the relative earlyness or lateness with which an innovation is adopted.
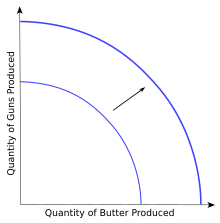
Technological change can cause the production-possibility frontier to shift outward, allowing economic growth.