Chlorophyll at different scales
Seen through a microscope, chlorophyll is concentrated within organisms in structures called chloroplasts.
Plants are perceived as green because chlorophyll absorbs mainly the blue and red wavelenght and reflects the green.
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρός, chloros ("green") and φύλλον, phyllon ("leaf"). Chlorophyll is essential in photosynthesis, allowing plants to absorb energy from light.
Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum, which it reflects, producing the green color of chlorophyll-containing tissues. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll a and b.
History
Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817.
The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was the first time that magnesium had been detected in living tissue.
After initial work done by German chemist Richard Willstätter spanning from 1905 to 1915, the general structure of chlorophyll a was elucidated by Hans Fischer in 1940. By 1960, when most of the stereochemistry of chlorophyll a was known, Robert Burns Woodward published a total synthesis of the molecule. In 1967, the last remaining stereochemical elucidation was completed by Ian Fleming, and in 1990 Woodward and co-authors published an updated synthesis. Chlorophyll f was announced to be present in cyanobacteria and other oxygenic microorganisms that form stromatolites in 2010; a molecular formula of C55H70O6N4Mg and a structure of (2-formyl)-chlorophyll a were deduced based on NMR, optical and mass spectra.
Photosynthesis
Absorbance spectra of free chlorophyll a (blue) and b (red) in a solvent. The spectra of chlorophyll molecules are slightly modified in vivo depending on specific pigment-protein interactions.
Chlorophyll is vital for photosynthesis, which allows plants to absorb energy from light.
Chlorophyll molecules are arranged in and around photosystems that are embedded in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts.
In these complexes, chlorophyll serves three functions. The function of
the vast majority of chlorophyll (up to several hundred molecules per
photosystem) is to absorb light. Having done so, these same centers
execute their second function: the transfer of that light energy by resonance energy transfer to a specific chlorophyll pair in the reaction center of the photosystems. This pair effects the final function of chlorophylls, charge separation, leading to biosynthesis.
The two currently accepted photosystem units are photosystem II and photosystem I, which have their own distinct reaction centers, named P680 and P700, respectively. These centres are named after the wavelength (in nanometers)
of their red-peak absorption maximum. The identity, function and
spectral properties of the types of chlorophyll in each photosystem are
distinct and determined by each other and the protein structure
surrounding them. Once extracted from the protein into a solvent (such
as acetone or methanol), these chlorophyll pigments can be separated into chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
The function of the reaction center of chlorophyll is to absorb
light energy and transfer it to other parts of the photosystem. The
absorbed energy of the photon is transferred to an electron in a process
called charge separation. The removal of the electron from the
chlorophyll is an oxidation reaction. The chlorophyll donates the high
energy electron to a series of molecular intermediates called an electron transport chain. The charged reaction center of chlorophyll (P680+) is then reduced back to its ground state by accepting an electron stripped from water. The electron that reduces P680+ ultimately comes from the oxidation of water into O2 and H+ through several intermediates. This reaction is how photosynthetic organisms such as plants produce O2 gas, and is the source for practically all the O2 in Earth's atmosphere. Photosystem I typically works in series with Photosystem II; thus the P700+
of Photosystem I is usually reduced as it accepts the electron, via
many intermediates in the thylakoid membrane, by electrons coming,
ultimately, from Photosystem II. Electron transfer reactions in the
thylakoid membranes are complex, however, and the source of electrons
used to reduce P700+ can vary.
The electron flow produced by the reaction center chlorophyll pigments is used to pump H+ ions across the thylakoid membrane, setting up a chemiosmotic potential used mainly in the production of ATP (stored chemical energy) or to reduce NADP+ to NADPH. NADPH is a universal agent used to reduce CO2 into sugars as well as other biosynthetic reactions.
Reaction center chlorophyll–protein complexes are capable of
directly absorbing light and performing charge separation events without
the assistance of other chlorophyll pigments, but the probability of
that happening under a given light intensity is small. Thus, the other
chlorophylls in the photosystem and antenna pigment proteins all
cooperatively absorb and funnel light energy to the reaction center.
Besides chlorophyll a, there are other pigments, called accessory pigments, which occur in these pigment–protein antenna complexes.
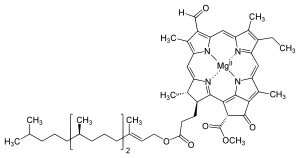
Chemical structure
Space-filling model of the chlorophyll a molecule
Chlorophylls are numerous in types, but all are defined by the
presence of a fifth ring beyond the four pyrrole-like rings. Most
chlorophylls are classified as chlorins, which are reduced relatives to porphyrins (found in hemoglobin). They share a common biosynthetic pathway as porphyrins, including the precursor uroporphyrinogen III. Unlike hemes, which feature iron at the center of the tetrapyrrole ring, chlorophylls bind magnesium. For the structures depicted in this article, some of the ligands attached to the Mg2+ center are omitted for clarity. The chlorin ring can have various side chains, usually including a long phytol chain. The most widely distributed form in terrestrial plants is chlorophyll a.
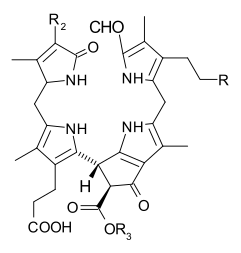
When leaves degreen in the process of plant senescence, chlorophyll is converted to a group of colorless tetrapyrroles known as nonfluorescent chlorophyll catabolites (NCC's) with the general structure:
These compounds have also been identified in several ripening fruits.
Measurement of chlorophyll content
Pure chlorophyll has a strong green color.
Measurement of the absorption of light is complicated by the solvent
used to extract the chlorophyll from plant material, which affects the
values obtained,
- In diethyl ether, chlorophyll a has approximate absorbance maxima of 430 nm and 662 nm, while chlorophyll b has approximate maxima of 453 nm and 642 nm.
- The absorption peaks of chlorophyll a are at 465 nm and 665 nm. Chlorophyll a fluoresces at 673 nm (maximum) and 726 nm. The peak molar absorption coefficient of chlorophyll a exceeds 105 M−1 cm−1, which is among the highest for small-molecule organic compounds.
- In 90% acetone-water, the peak absorption wavelengths of chlorophyll a are 430 nm and 664 nm; peaks for chlorophyll b are 460 nm and 647 nm; peaks for chlorophyll c1 are 442 nm and 630 nm; peaks for chlorophyll c2 are 444 nm and 630 nm; peaks for chlorophyll d are 401 nm, 455 nm and 696 nm.
By measuring the absorption of light in the red and far red regions,
it is possible to estimate the concentration of chlorophyll within a
leaf.
Ratio fluorescence emission can be used to measure chlorophyll content. By exciting chlorophyll a fluorescence at a lower wavelength, the ratio of chlorophyll fluorescence emission at 705±10 nm and 735±10 nm can provide a linear relationship of chlorophyll content when compared to chemical testing. The ratio F735/F700 provided a correlation value of r2 0.96 compared to chemical testing in the range from 41 mg m−2 up to 675 mg m−2. Gitelson also developed a formula for direct readout of chlorophyll content in mg m−2. The formula provided a reliable method of measuring chlorophyll content from 41 mg m−2 up to 675 mg m−2 with a correlation r2 value of 0.95.
Biosynthesis
In plants, chlorophyll may be synthesized from succinyl-CoA and glycine, although the immediate precursor to chlorophyll a and b is protochlorophyllide. In Angiosperm plants, the last step, the conversion of protochlorophyllide to chlorophyll, is light-dependent and such plants are pale (etiolated) if grown in darkness. Non-vascular plants and green algae have an additional light-independent enzyme and grow green even in darkness.
Chlorophyll itself is bound to proteins and can transfer the
absorbed energy in the required direction. Protochlorophyllide occurs
mostly in the free form and, under light conditions, acts as a photosensitizer, forming highly toxic free radicals.
Hence, plants need an efficient mechanism of regulating the amount of
chlorophyll precursor. In angiosperms, this is done at the step of
aminolevulinic acid (ALA), one of the intermediate compounds in the
biosynthesis pathway. Plants that are fed by ALA accumulate high and
toxic levels of protochlorophyllide; so do the mutants with the damaged
regulatory system.
Chlorosis is a condition in which leaves produce insufficient chlorophyll, turning them yellow. Chlorosis can be caused by a nutrient deficiency of iron — called iron chlorosis — or by a shortage of magnesium or nitrogen.
Soil pH sometimes plays a role in nutrient-caused chlorosis; many
plants are adapted to grow in soils with specific pH levels and their
ability to absorb nutrients from the soil can be dependent on this. Chlorosis can also be caused by pathogens including viruses, bacteria and fungal infections, or sap-sucking insects.
Complementary light absorbance of anthocyanins with chlorophylls
Superposition of spectra of chlorophyll a and b with oenin (malvidin 3O glucoside), a typical anthocyanidin,
showing that, while chlorophylls absorb in the blue and yellow/red
parts of the visible spectrum, oenin absorbs mainly in the green part of
the spectrum, where chlorophylls don't absorb at all.
Anthocyanins are other plant pigments. The absorbance pattern responsible for the red color of anthocyanins may be complementary to that of green chlorophyll in photosynthetically active tissues such as young Quercus coccifera leaves. It may protect the leaves from attacks by plant eaters that may be attracted by green color.
Distribution
The
chlorophyll maps show milligrams of chlorophyll per cubic meter of
seawater each month. Places where chlorophyll amounts were very low,
indicating very low numbers of phytoplankton,
are blue. Places where chlorophyll concentrations were high, meaning
many phytoplankton were growing, are yellow. The observations come from
the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA's Aqua
satellite. Land is dark gray, and places where MODIS could not collect
data because of sea ice, polar darkness, or clouds are light gray.The
highest chlorophyll concentrations, where tiny surface-dwelling ocean
plants are thriving,
are in cold polar waters or in places where ocean currents bring cold
water to the surface, such as around the equator and along the shores of
continents. It is not the cold water itself that stimulates the
phytoplankton. Instead, the cool temperatures are often a sign that the
water has welled up to the surface from deeper in the ocean, carrying
nutrients that have built up over time. In polar waters, nutrients
accumulate in surface waters during the dark winter months when plants
cannot grow. When sunlight returns in the spring and summer, the plants
flourish in high concentrations.
Culinary use
Chlorophyll is registered as a food additive (colorant), and its E number is E140. Chefs use chlorophyll to color a variety of foods and beverages green, such as pasta and spirits. Absinthe gains its green color from the chlorophyll introduced through the large variety of herbs included in its production. Chlorophyll is not soluble in water, and it is first mixed with a small quantity of vegetable oil to obtain the desired solution.