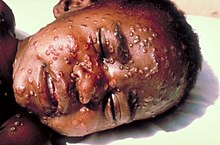
A child suffering from smallpox. In 1979, the World Health Organization announced the global eradication of smallpox. It is the only human disease to be eradicated worldwide.
Eradication is the reduction of an infectious disease's prevalence in the global host population to zero.
It is sometimes confused with elimination, which describes either the
reduction of an infectious disease's prevalence in a regional population
to zero, or the reduction of the global prevalence to a negligible
amount. Further confusion arises from the use of the term eradication to
refer to the total removal of a given pathogen from an individual (also known as clearance of an infection), particularly in the context of HIV and certain other viruses where such cures are sought.
Selection of infectious diseases for eradication is based on
rigorous criteria, as both biological and technical features determine
whether a pathogenic organism is (at least potentially) eradicable. The
targeted organism must not have a non-human reservoir (or, in the case of animal diseases, the infection reservoir must be an easily identifiable species, as in the case of rinderpest),
and/or amplify in the environment. This implies that sufficient
information on the life cycle and transmission dynamics is available at
the time an eradication initiative is programmed. An efficient and
practical intervention (such as a vaccine or antibiotic) must be
available to interrupt transmission of the infectious agent. Studies of
measles in the pre-vaccination era led to the concept of the critical community size, the size of the population below which a pathogen ceases to circulate.
Use of vaccination programs before the introduction of an eradication
campaign can reduce the susceptible population. The disease to be
eradicated should be clearly identifiable, and an accurate diagnostic
tool should exist. Economic considerations, as well as societal and
political support and commitment, are other crucial factors that
determine eradication feasibility.
Two infectious diseases have successfully been eradicated: smallpox and rinderpest. There are also four ongoing programs, targeting poliomyelitis, yaws, dracunculiasis, and malaria. Five more infectious diseases have been identified as of April 2008 as potentially eradicable with current technology by the Carter Center International Task Force for Disease Eradication—measles, mumps, rubella, lymphatic filariasis and cysticercosis.
Eradicated diseases
So far, two diseases have been successfully eradicated—one specifically affecting humans (smallpox), and one affecting a wide range of ruminants (rinderpest).
Smallpox
Boy with smallpox (1969). The last natural smallpox case was of Ali Maow Maalin, in Merca, Somalia, on 26 October 1977.
Smallpox was the first disease, and so far the only infectious disease of humans, to be eradicated by deliberate intervention. It became the first disease for which there was an effective vaccine in 1798 when Edward Jenner showed the protective effect of inoculation (vaccination) of humans with material from cowpox lesions.
Smallpox (variola) occurred in two clinical varieties: variola major, with a mortality rate of up to 40 percent, and variola minor, also known as alastrim, with a mortality rate less than one percent. The last naturally occurring case of Variola major was diagnosed in October 1975 in Bangladesh. The last naturally occurring case of smallpox (Variola minor) was diagnosed on 26 October 1977, on Ali Maow Maalin, in the Merca District, of Somalia.
The source of this case was a known outbreak in the nearby district of
Kurtuware. All 211 contacts were traced, revaccinated, and kept under
surveillance.
After two years' detailed analysis of national records the global
eradication of smallpox was certified by an international commission of
smallpox clinicians and medical scientists on 9 December 1979, and
endorsed by the General Assembly of the World Health Organization on 8
May 1980. However, there is an ongoing controversy
regarding the continued storage of the smallpox virus by labs in the US
and Russia, as any accidental or deliberate release could create a new
epidemic for persons born after or in the late 1980s due to the
cessation of vaccinations against the smallpox virus.
Rinderpest
During the 20th century, there were a series of campaigns to eradicate rinderpest, a viral disease which infected cattle and other ruminants and belonged to the same family as measles, primarily through the use of a live attenuated vaccine. The final, successful campaign was led by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. On 14 October 2010, with no diagnoses for nine years, the Food and Agriculture Organization announced that the disease had been completely eradicated, making this the first (and so far the only) disease of livestock to have been eradicated by human undertakings.
Global eradication underway
Poliomyelitis (polio)
| Year | Estimated | Recorded |
|---|---|---|
| 1975 | — | 49,293 |
| 1980 | 400,000 | 52,552 |
| 1985 | — | 38,637 |
| 1988 | 350,000 | 35,251 |
| 1990 | — | 23,484 |
| 1993 | 100,000 | 10,487 |
| 1995 | — | 7,035 |
| 2000 | — | 2,971 |
| 2005 | — | 1,998 |
| 2010 | — | 1,352 |
| 2011 | — | 650 |
| 2012 | — | 222 |
| 2013 | — | 385 |
| 2014 | — | 359 |
| 2015 | — | 74 |
| 2016 | — | 37 |
| 2017 | — | 22 |
| 2018 | — | 33 |
A dramatic reduction of the incidence of poliomyelitis in industrialized countries followed the development of a vaccine in the 1950s. In 1960, Czechoslovakia became the first country certified to have eliminated polio.
In 1988, the World Health Organization (WHO), Rotary International, the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) passed the Global Polio Eradication Initiative.
Its goal was to eradicate polio by the year 2000. The updated strategic
plan for 2004–2008 expects to achieve global eradication by
interrupting poliovirus transmission, using the strategies of routine immunization,
supplementary immunization campaigns, and surveillance of possible
outbreaks. The WHO estimates that global savings from eradication, due
to forgone treatment and disability costs, could exceed one billion U.S. dollars per year.
The following world regions have been declared polio-free:
- The Americas (1994)
- Indo-West Pacific region (1997)
- Europe (1998)
- Western Pacific region, including China (2000)
- Southeast Asia region (2014), including India
The lowest annual wild polio prevalence seen so far was in 2017, with
only 22 reported cases, although there were more total reported cases
(including circulated vaccine-derived cases) than in 2016, mainly due to
reporting of circulated vaccine-derived cases in Syria, where it likely
had already been circulating,
but gone unreported, presumably due to the civil war. Only two or three
countries remain in which poliovirus transmission may never have been
interrupted: Pakistan, Afghanistan, and perhaps Nigeria. (There have been no cases caused by wild strains of poliovirus in Nigeria since August 2016, though cVDPV2 was detected in environmental samples in 2017.)
Nigeria was removed from the WHO list of polio-endemic countries in
September 2015 but added back in 2016, and India was removed in 2014 after no new cases were reported for one year.
On 20 September 2015, the World Health Organization announced
that wild poliovirus type 2 had been eradicated worldwide, as it has not
been seen since 1999. Wild poliovirus type 3 may also be eradicated as
it has not been seen since 2012, leaving only wild poliovirus type 1 and
circulating vaccine-derived polio circulating in a few isolated
pockets, with all wild polio cases after August 2016 in Afghanistan and
Pakistan.
Dracunculiasis
| Year | Reported cases | Countries |
|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 892,055 | 16 |
| 1995 | 129,852 | 19 |
| 2000 | 75,223 | 16 |
| 2005 | 10,674 | 12 |
| 2010 | 1,797 | 6 |
| 2011 | 1,060 | 4 |
| 2012 | 542 | 4 |
| 2013 | 148 | 5 |
| 2014 | 126 | 4 |
| 2015 | 22 | 4 |
| 2016 | 25 | 3 |
| 2017 | 30 | 2 |
| 2018 | 28 | 3 |
Dracunculiasis, also called Guinea worm disease, is a painful and disabling parasitic disease caused by a worm, Dracunculus medinensis. It is spread through consumption of drinking water infested with copepods hosting Dracunculus larvae. The Carter Center has led the effort to eradicate the disease, along with the CDC, the WHO, UNICEF, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Unlike diseases such as smallpox and polio, there is no vaccine or drug therapy for guinea worm. Eradication efforts have been based on making drinking water
supplies safer (e.g. by provision of borehole wells, or through
treating the water with larvicide), on containment of infection and on
education for safe drinking water practices. These strategies have
produced many successes: two decades of eradication efforts have reduced
guinea worm's global incidence
to 22 cases in 2015, after which cases rose to 25 cases in 2016, and 30
cases in 2017, but this is still down from an estimated 3.5 million in
1986. Success has been slower than was hoped—the original goal for
eradication was 1995. The WHO has certified 180 countries free of the
disease, and only three countries—South Sudan, Ethiopia, and Chad—reported cases of guinea worm in 2016, and only two—Ethiopia and Chad—in 2017. As of 2010,
the WHO predicted it would be "a few years yet" before eradication is
achieved, on the basis that it took 6–12 years for the countries that
have so far eliminated guinea worm transmission to do so after reporting
a similar number of cases to that reported by Sudan in 2009.
The number of cases in 2016 (25) was less than 1% of the number in
2009, so real progress has been made towards this prediction.
Nonetheless, the last 1% may be the hardest, and cases have increased from 2015 (22) to 2017 (30). The worm is able to infect dogs, domestic cats and baboons as well as humans, complicating eradication efforts.
Yaws
Yaws is a rarely fatal but highly disfiguring disease caused by the spiral-shaped bacterium (spirochete) Treponema pallidum pertenue, a close relative of the syphilis bacteria Treponema pallidum pallidum,
spread through skin to skin contact with infectious lesions. The
global prevalence of this disease and the other endemic treponematoses, bejel and pinta,
was reduced by the Global Control of Treponematoses (TCP) program
between 1952 and 1964 from about 50 million cases to about 2.5 million
(a 95% reduction). However, following the cessation of this program
these diseases remained at a low prevalence in parts of Asia, Africa and
the Americas with sporadic outbreaks. According to a 2012 official WHO
roadmap, the elimination should be achievable by 2020.
Yaws is currently targeted by the South-East Asian Regional Office of
the WHO for elimination from the remaining endemic countries in this
region (India, Indonesia and East Timor) by 2010, and so far, this appears to have met with some success, since no cases have been seen in India since 2004. The discovery that oral antibiotic azithromycin can be used instead of the previous standard, injected penicillin, was tested on Lihir Island from 2013 to 2014; a single oral dose of the macrolide antibiotic reduced disease prevalence from 2.4% to 0.3% at 12 months.
The campaign was in an early stage in 2013, still gathering data on
disease incidence and planning initial large-scale treatment campaigns
in Cameroon, Ghana, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands,
and Vanuatu.
Malaria
Malaria has been eliminated from most of Europe, North America, Australia, North Africa and the Caribbean, and parts of South America, Asia and Southern Africa.
The WHO defines elimination as having no domestic transmission for the
past three years. They also define an "elimination stage" when a country
is on the verge of eliminating malaria, as being less than one case per
1000 people at risk per year. According to the 2011 WHO World Malaria
Report,
28 countries are certified as having eliminated malaria. Eight
countries appear to be malaria free but steps still need to be taken to
ensure they do not re-establish transmission. Nine countries are in the
elimination stage and eight the pre-elimination stage (fewer than 5
cases per 1000 people at risk per year).
In 1955 the WHO launched the Global Malaria Eradication Program (GMEP). Support waned, and the program was suspended in 1969.
Since 2000, support for eradication has increased. According to the
WHO's World Malaria Report 2015, the global mortality rate for malaria
fell by 60% between 2000 and 2015. The WHO aims to achieve a further 90%
reduction between 2015 and 2030. Bill Gates believes that global eradication is possible by 2040.
Regional elimination established or underway
Some
diseases have already been eliminated from large regions of the world,
and/or are currently being targeted for regional elimination. This is
sometimes described as "eradication", although technically the term only
applies when this is achieved on a global scale.
Even after regional elimination is successful, interventions often
need to continue to prevent a disease becoming re-established. Three of
the diseases here listed (lymphatic filariasis, measles, and rubella)
are among the diseases believed to be potentially eradicable by the
International Task Force for Disease Eradication, and if successful,
regional elimination programs may yet prove a stepping stone to later
global eradication programs.This section does not cover elimination
where it is used to mean control programs sufficiently tight to reduce
the burden of an infectious disease or other health problem to a level
where they may be deemed to have little impact on public health, such as the leprosy, neonatal tetanus, or obstetric fistula campaigns.
Hookworm
In North American countries, such as the United States, elimination of hookworm
had been attained due to scientific advances (Despite the United States
declaring that it had eliminated Hookworm decades ago, a 2017 study
showed that it has re-emerged in poor rural black communities). The Rockefeller Foundation's hookworm campaign in the 1920s was supposed to focus on the eradication of hookworm infections for those living in Mexico and other rural areas. However, the campaign was politically influenced, causing it to be less successful, and regions such as Mexico still deal with these infections from parasitic worms.
This use of health campaigns by political leaders for political and
economic advantages has been termed the science-politics paradox.
Lymphatic filariasis
Lymphatic filariasis is an infection of the lymph system by mosquito-borne microfilarial worms which can cause elephantiasis.
Studies have demonstrated that transmission of the infection can be
broken when a single dose of combined oral medicines is consistently
maintained annually for approximately seven years. The strategy for eliminating transmission of lymphatic filariasis is mass distribution of medicines that kill the microfilariae and stop transmission of the parasite by mosquitoes in endemic communities. In sub-Saharan Africa, albendazole is being used with ivermectin to treat the disease, whereas elsewhere in the world albendazole is used with diethylcarbamazine. Using a combination of treatments better reduces the number of microfilariae in blood. Avoiding mosquito bites, such as by using insecticide-treated mosquito bed nets, also reduces the transmission of lymphatic filariasis. In the Americas, more than 90% of the burden of lymphatic filariasis is on the island of Hispaniola
(comprising Haiti and the Dominican Republic). An elimination effort
to address this is currently under way alongside the malaria effort
described above; the Dominican Republic expects to eliminate its seven
remaining foci by 2010, but lymphatic filariasis is still endemic to 110
of 140 communes in Haiti.
As of October 2008, the efforts of the Global Programme to
Eliminate LF are estimated to have already prevented 6.6 million new
filariasis cases from developing in children, and to have stopped the
progression of the disease in another 9.5 million people who have
already contracted it. Overall, of 83 endemic countries, mass treatment
has been rolled out in 48, and elimination of transmission reportedly
achieved in 21.
Measles
Five out of six WHO regions have goals to eliminate measles, and at the 63rd World Health Assembly
in May 2010, delegates agreed to move towards eventual eradication,
although no specific global target date has yet been agreed. The Americas
set a goal in 1994 to eliminate measles and rubella transmission by
2000, and successfully achieved regional measles elimination in 2002,
although there have been occasional small outbreaks from imported cases
since then. Europe had set a goal to eliminate measles transmission by 2010, but were hindered by the MMR vaccine controversy
and by low uptake in certain groups, and despite achieving low levels
by 2008, European countries have since experienced a small resurgence in
cases. They have set a new target of 2015. The Eastern Mediterranean also had goals to eliminate measles by 2010
(later revised to 2015), the Western Pacific aims to eliminate the
disease by 2012, and in 2009 the regional committee for Africa agreed a
goal of measles elimination by 2020. As of May 2010, only the South-East Asian region has yet to set a target date for elimination of measles transmission.
In 2005, a global target was agreed for a 90% reduction in
measles deaths by 2010 from the 757,000 deaths in 2000; estimates for
2008 show a 78% decline so far to 164,000 deaths. However, some have been pushing to attempt global eradication.
This was updated at the 2010 World Health Assembly to a targeted 95%
reduction in mortality by 2015, alongside specific vaccination and
structural targets,
and in a meeting in November 2010, the Strategic Advisory Group of
Experts on Immunization "concluded that measles can and should be
eradicated".
A study of the costs of eradicating measles compared to the costs of
maintaining indefinite control was commissioned in 2009 by the WHO and
the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. In 2013, measles deaths globally were down to 145,700.
As of mid-2013, measles elimination in many areas is stalling.
"This year, measles and rubella outbreaks are occurring in many areas of
the world where people have no immunity to these viruses. The reasons
people are unvaccinated range from lack of access to vaccines in areas
of insecurity, to poor performing health systems, to vaccine refusals.
We need to address each of these challenges if we’re going to meet
global measles and rubella elimination goals," said Dr. Myrna Charles of
the American Red Cross, as reported in a post in the Measles and Rubella Initiative's blog.
A look at the WHO's epidemiological graph of measles over time from
2008-2013 show that, with little more of two years to go to 2015,
measles cases in 2013 are moving in the wrong direction, with more cases
this year than at the same point in 2012 or 2011.
During 2014 there were 23 outbreaks of measles in the United
States and over 600 individual cases, which is the highest seen in
decades. In 2015 the US has had one major outbreak of measles
originating from an amusement park in California of a variant of the
virus circulating in the Philippines in 2014. From this there have been
113 individual measles cases and one death (out of the total of 189
cases in the U.S. in 2015).
The WHO region of the Americas declared on 27 September 2016 it had eliminated measles. The last confirmed endemic case of measles in the Americas was in Brazil in July 2015. May 2017 saw a return of measles to the US after an outbreak in Minnesota among unvaccinated children. Another outbreak occurred in the state of New York between 2018 and 2019, causing over 200 confirmed measles cases in mostly ultra-Orthodox Jewish communities. Subsequent outbreaks occurred in New Jersey and Washington state with over 30 cases reported in the Pacific Northwest.
Rubella
The WHO region of the Americas declared on 29 April 2015 it had eliminated rubella and congenital rubella syndrome. The last confirmed endemic case of rubella in the Americas was in Argentina in February 2009.
The WHO European region missed its elimination target of 2010 due to
undervaccination in Central and Western Europe; it has set a new goal of
2015. The disease remains problematic in other regions; in Japan, there were 15,000 cases in 2013.
Onchocerciasis
Onchocerciasis (river blindness) is the world's second leading cause of infectious blindness. It is caused by the nematode Onchocerca volvulus, which is transmitted to people via the bite of a black fly. Elimination of this disease is under way in the region of the Americas, where this disease is endemic to Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Mexico and Venezuela. The principal tool being used is mass ivermectin treatment. If successful, the only remaining endemic locations would be in Africa and Yemen.
In Africa, it is estimated that greater than 102 million people in 19
countries are at high risk of onchocerciasis infection, and in 2008,
56.7 million people in 15 of these countries received community-directed
treatment with ivermectin. Since adopting such treatment measures in
1997, the African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control reports a
reduction in the prevalence of onchocerciasis in the countries under its
mandate from a pre-intervention level of 46.5% in 1995 to 28.5% in
2008. Some African countries, such as Uganda, are also attempting elimination and successful elimination was reported in 2009 from two endemic foci in Mali and Senegal.
On 29 July 2013, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) announced that after 16 years of efforts, Colombia had become the first country in the world to eliminate the parasitic disease onchocerciasis.
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) and new variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD)
Following an epidemic of vCJD in the UK in the 1990s, there have been campaigns to eliminate BSE in cattle across the EU and beyond which appear to have achieved large reductions in the number of cattle with this disease.
Cases of vCJD have also fallen since then, for instance from an annual
peak of 29 cases in 2000 to 5 cases in 2008 and zero in 2012. However,
since then 2 cases have been reported in both 2013 and 2014: 2 in
France; 1 in the United Kingdom; and 1 in the United States.
Following the ongoing eradication effort, only 7 cases of BSE
were reported worldwide in 2013: 3 in the United Kingdom; 2 in France; 1
in Ireland; and 1 in Poland. This is the lowest number of cases since
at least 1988. In 2015 there were at least 6 reported cases (3 were of the atypical H-type).
Syphilis
In 2015, Cuba became the first country in the world to eliminate mother-to-child syphilis. In 2017 the WHO certified that Antigua And Barbuda, Saint Kitts And Nevis and four British Overseas Territories—Anguilla, Bermuda, Cayman Islands, and Montserrat—have been certified that they have ended transmission of mother-to-child syphilis and HIV. Nevertheless eradication of syphilis by all transmission methods remains unresolved and many questions about the eradication effort remain to be answered.
African trypanosomiasis
Early planning by the WHO for the eradication of African trypanosomiasis, also known as sleeping sickness,
is underway as the rate of reported cases continues to decline and
passive treatment is continued. The WHO aims to completely eliminate
transmission of the Trypanosoma brucei gambiense parasite by 2030, though it acknowledges that this goal "leaves no room for complacency."
Rabies
Rabies-free countries as of 2010
Because the rabies
virus is almost always caught from animals, rabies eradication has
focused on reducing the population of wild and stray animals, controls and compulsory quarantine on animals entering the country, and vaccination of pets and wild animals. Many island nations, including Iceland, Ireland, Japan, Malta, and the United Kingdom, managed to eliminate rabies during the twentieth century, and more recently much of continental Europe has been declared rabies-free.
Other eradicable diseases
As far as animal diseases are concerned, now that rinderpest has been stamped out, many experts believe peste des petits ruminants (PPR) is the next disease amenable to global eradication. Also known as goat plague or ovine rinderpest,
PPR is a highly contagious viral disease of goats and sheep
characterized by fever, painful sores in the mouth, tongue and feet,
diarrhea, pneumonia and death, especially in young animals. It is caused
by a virus of the genus Morbillivirus that is related to rinderpest, measles and canine distemper.