| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uranium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /jʊəˈreɪniəm/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery gray metallic; corrodes to a spalling black oxide coat in air | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(U) | 238.02891(3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uranium in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group n/a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | f-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | actinide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f3 6d1 7s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell
| 2, 8, 18, 32, 21, 9, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 1405.3 K (1132.2 °C, 2070 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 4404 K (4131 °C, 7468 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 19.1 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 17.3 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 9.14 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 417.1 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 27.665 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6 (a weakly basic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.38 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 156 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 196±7 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 186 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of uranium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 3155 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 13.9 µm/(m·K) (at 25 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 27.5 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 0.280 µΩ·m (at 0 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 208 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 111 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 100 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vickers hardness | 1960–2500 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 2350–3850 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-61-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naming | after planet Uranus, itself named after Greek god of the sky Uranus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1789) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Eugène-Melchior Péligot (1841) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of uranium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uranium is a chemical element with symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable, with half-lives varying between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99%) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite.
In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2739–99.2752%), uranium-235 (0.7198–0.7202%), and a very small amount of uranium-234 (0.0050–0.0059%). Uranium decays slowly by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.47 billion years and that of uranium-235 is 704 million years, making them useful in dating the age of the Earth.
Many contemporary uses of uranium exploit its unique nuclear properties. Uranium-235 is the only naturally occurring fissile isotope, which makes it widely used in nuclear power plants and nuclear weapons. However, because of the tiny amounts found in nature, uranium needs to undergo enrichment so that enough uranium-235 is present. Uranium-238 is fissionable by fast neutrons, and is fertile, meaning it can be transmuted to fissile plutonium-239 in a nuclear reactor. Another fissile isotope, uranium-233, can be produced from natural thorium and is also important in nuclear technology. Uranium-238 has a small probability for spontaneous fission or even induced fission with fast neutrons; uranium-235 and to a lesser degree uranium-233 have a much higher fission cross-section for slow neutrons. In sufficient concentration, these isotopes maintain a sustained nuclear chain reaction. This generates the heat in nuclear power reactors, and produces the fissile material for nuclear weapons. Depleted uranium (238U) is used in kinetic energy penetrators and armor plating. Uranium is used as a colorant in uranium glass, producing lemon yellow to green colors. Uranium glass fluoresces green in ultraviolet light. It was also used for tinting and shading in early photography.
The 1789 discovery of uranium in the mineral pitchblende is credited to Martin Heinrich Klaproth, who named the new element after the recently discovered planet Uranus. Eugène-Melchior Péligot was the first person to isolate the metal and its radioactive properties were discovered in 1896 by Henri Becquerel. Research by Otto Hahn, Lise Meitner, Enrico Fermi and others, such as J. Robert Oppenheimer starting in 1934 led to its use as a fuel in the nuclear power industry and in Little Boy, the first nuclear weapon used in war. An ensuing arms race during the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union produced tens of thousands of nuclear weapons that used uranium metal and uranium-derived plutonium-239. The security of those weapons and their fissile material following the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991 is an ongoing concern for public health and safety.
Characteristics
A neutron-induced nuclear fission event involving uranium-235
When refined, uranium is a silvery white, weakly radioactive metal. It has a Mohs hardness of 6, sufficient to scratch glass and approximately equal to that of titanium, rhodium, manganese and niobium. It is malleable, ductile, slightly paramagnetic, strongly electropositive and a poor electrical conductor. Uranium metal has a very high density of 19.1 g/cm3, denser than lead (11.3 g/cm3),[12] but slightly less dense than tungsten and gold (19.3 g/cm3).
Uranium metal reacts with almost all non-metal elements (with the exception of the noble gases) and their compounds, with reactivity increasing with temperature. Hydrochloric and nitric acids dissolve uranium, but non-oxidizing acids other than hydrochloric acid attack the element very slowly. When finely divided, it can react with cold water; in air, uranium metal becomes coated with a dark layer of uranium oxide. Uranium in ores is extracted chemically and converted into uranium dioxide or other chemical forms usable in industry.
Uranium-235 was the first isotope that was found to be fissile. Other naturally occurring isotopes are fissionable, but not fissile. On bombardment with slow neutrons, its uranium-235 isotope will most of the time divide into two smaller nuclei, releasing nuclear binding energy and more neutrons. If too many of these neutrons are absorbed by other uranium-235 nuclei, a nuclear chain reaction
occurs that results in a burst of heat or (in special circumstances) an
explosion. In a nuclear reactor, such a chain reaction is slowed and
controlled by a neutron poison, absorbing some of the free neutrons. Such neutron absorbent materials are often part of reactor control rods.
As little as 15 lb (7 kg) of uranium-235 can be used to make an atomic bomb. The first nuclear bomb used in war, Little Boy, relied on uranium fission, but the very first nuclear explosive (the Gadget used at Trinity) and the bomb that destroyed Nagasaki (Fat Man) were both plutonium bombs.
Uranium metal has three allotropic forms:
- α (orthorhombic) stable up to 668 °C. Orthorhombic, space group No. 63, Cmcm, lattice parameters a = 285.4 pm, b = 587 pm, c = 495.5 pm.
- β (tetragonal) stable from 668 °C to 775 °C. Tetragonal, space group P42/mnm, P42nm, or P4n2, lattice parameters a = 565.6 pm, b = c = 1075.9 pm.
- γ (body-centered cubic) from 775 °C to melting point—this is the most malleable and ductile state. Body-centered cubic, lattice parameter a = 352.4 pm.
Applications
Military
Various militaries use depleted uranium as high-density penetrators.
The major application of uranium in the military sector is in high-density penetrators. This ammunition consists of depleted uranium (DU) alloyed with 1–2% other elements, such as titanium or molybdenum. At high impact speed, the density, hardness, and pyrophoricity of the projectile enable the destruction of heavily armored targets. Tank armor and other removable vehicle armor
can also be hardened with depleted uranium plates. The use of depleted
uranium became politically and environmentally contentious after the use
of such munitions by the US, UK and other countries during wars in the
Persian Gulf and the Balkans raised questions concerning uranium
compounds left in the soil.
Depleted uranium is also used as a shielding material in some
containers used to store and transport radioactive materials. While the
metal itself is radioactive, its high density makes it more effective
than lead in halting radiation from strong sources such as radium. Other uses of depleted uranium include counterweights for aircraft control surfaces, as ballast for missile re-entry vehicles and as a shielding material. Due to its high density, this material is found in inertial guidance systems and in gyroscopic compasses.
Depleted uranium is preferred over similarly dense metals due to its
ability to be easily machined and cast as well as its relatively low
cost. The main risk of exposure to depleted uranium is chemical poisoning by uranium oxide rather than radioactivity (uranium being only a weak alpha emitter).
During the later stages of World War II, the entire Cold War,
and to a lesser extent afterwards, uranium-235 has been used as the
fissile explosive material to produce nuclear weapons. Initially, two
major types of fission bombs were built: a relatively simple device that
uses uranium-235 and a more complicated mechanism that uses plutonium-239 derived from uranium-238. Later, a much more complicated and far more powerful type of fission/fusion bomb (thermonuclear weapon) was built, that uses a plutonium-based device to cause a mixture of tritium and deuterium to undergo nuclear fusion.
Such bombs are jacketed in a non-fissile (unenriched) uranium case, and
they derive more than half their power from the fission of this
material by fast neutrons from the nuclear fusion process.
Civilian
The most visible civilian use of uranium is as the thermal power source used in nuclear power plants.
The main use of uranium in the civilian sector is to fuel nuclear power plants. One kilogram of uranium-235 can theoretically produce about 20 terajoules of energy (2×1013 joules), assuming complete fission; as much energy as 1500 tonnes of coal.
Commercial nuclear power plants use fuel that is typically enriched to around 3% uranium-235. The CANDU and Magnox designs are the only commercial reactors capable of using unenriched uranium fuel. Fuel used for United States Navy reactors is typically highly enriched in uranium-235 (the exact values are classified). In a breeder reactor, uranium-238 can also be converted into plutonium through the following reaction:
Uranium glass glowing under UV light
Before (and, occasionally, after) the discovery of radioactivity,
uranium was primarily used in small amounts for yellow glass and pottery
glazes, such as uranium glass and in Fiestaware.
The discovery and isolation of radium in uranium ore (pitchblende) by Marie Curie
sparked the development of uranium mining to extract the radium, which
was used to make glow-in-the-dark paints for clock and aircraft dials. This left a prodigious quantity of uranium as a waste product, since it takes three tonnes of uranium to extract one gram
of radium. This waste product was diverted to the glazing industry,
making uranium glazes very inexpensive and abundant. Besides the pottery
glazes, uranium tile glazes accounted for the bulk of the use, including common bathroom and kitchen tiles which can be produced in green, yellow, mauve, black, blue, red and other colors.
Uranium glass used as lead-in seals in a vacuum capacitor
Uranium was also used in photographic chemicals (especially uranium nitrate as a toner), in lamp filaments for stage lighting bulbs, to improve the appearance of dentures, and in the leather and wood industries for stains and dyes. Uranium salts are mordants of silk or wool. Uranyl acetate and uranyl formate are used as electron-dense "stains" in transmission electron microscopy, to increase the contrast of biological specimens in ultrathin sections and in negative staining of viruses, isolated cell organelles and macromolecules.
The discovery of the radioactivity of uranium ushered in additional scientific and practical uses of the element. The long half-life of the isotope uranium-238 (4.51×109 years) makes it well-suited for use in estimating the age of the earliest igneous rocks and for other types of radiometric dating, including uranium–thorium dating, uranium–lead dating and uranium–uranium dating. Uranium metal is used for X-ray targets in the making of high-energy X-rays.
History
Pre-discovery use
The planet Uranus, which uranium is named after
The use of uranium in its natural oxide form dates back to at least the year 79 CE, when it was used to add a yellow color to ceramic glazes. Yellow glass with 1% uranium oxide was found in a Roman villa on Cape Posillipo in the Bay of Naples, Italy, by R. T. Gunther of the University of Oxford in 1912. Starting in the late Middle Ages, pitchblende was extracted from the Habsburg silver mines in Joachimsthal, Bohemia (now Jáchymov in the Czech Republic), and was used as a coloring agent in the local glassmaking industry. In the early 19th century, the world's only known sources of uranium ore were these mines.
Discovery
Antoine Henri Becquerel discovered the phenomenon of radioactivity by exposing a photographic plate to uranium in 1896.
The discovery of the element is credited to the German chemist Martin Heinrich Klaproth. While he was working in his experimental laboratory in Berlin in 1789, Klaproth was able to precipitate a yellow compound (likely sodium diuranate) by dissolving pitchblende in nitric acid and neutralizing the solution with sodium hydroxide. Klaproth assumed the yellow substance was the oxide of a yet-undiscovered element and heated it with charcoal
to obtain a black powder, which he thought was the newly discovered
metal itself (in fact, that powder was an oxide of uranium). He named the newly discovered element after the planet Uranus (named after the primordial Greek god of the sky), which had been discovered eight years earlier by William Herschel.
In 1841, Eugène-Melchior Péligot, Professor of Analytical Chemistry at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers (Central School of Arts and Manufactures) in Paris, isolated the first sample of uranium metal by heating uranium tetrachloride with potassium.
Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity by using uranium in 1896. Becquerel made the discovery in Paris by leaving a sample of a uranium salt, K2UO2(SO4)2 (potassium uranyl sulfate), on top of an unexposed photographic plate in a drawer and noting that the plate had become "fogged". He determined that a form of invisible light or rays emitted by uranium had exposed the plate.
Fission research
Cubes and cuboids of uranium produced during the Manhattan project
A team led by Enrico Fermi in 1934 observed that bombarding uranium with neutrons produces the emission of beta rays (electrons or positrons from the elements produced; see beta particle).
The fission products were at first mistaken for new elements with
atomic numbers 93 and 94, which the Dean of the Faculty of Rome, Orso
Mario Corbino, christened ausonium and hesperium, respectively. The experiments leading to the discovery of uranium's ability to fission (break apart) into lighter elements and release binding energy were conducted by Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann in Hahn's laboratory in Berlin. Lise Meitner and her nephew, the physicist Otto Robert Frisch, published the physical explanation in February 1939 and named the process "nuclear fission".
Soon after, Fermi hypothesized that the fission of uranium might
release enough neutrons to sustain a fission reaction. Confirmation of
this hypothesis came in 1939, and later work found that on average about
2.5 neutrons are released by each fission of the rare uranium isotope
uranium-235. Fermi urged Alfred O. C. Nier
to separate uranium isotopes for determination of the fissile
component, and on February 29, 1940, Nier used an instrument he built at
the University of Minnesota to separate the world's first uranium-235 sample in the Tate Laboratory. After mailed to Columbia University's cyclotron, John Dunning confirmed the sample to be the isolated fissile material on March 1. Further work found that the far more common uranium-238 isotope can be transmuted
into plutonium, which, like uranium-235, is also fissile by thermal
neutrons. These discoveries led numerous countries to begin working on
the development of nuclear weapons and nuclear power.
On 2 December 1942, as part of the Manhattan Project, another team led by Enrico Fermi was able to initiate the first artificial self-sustained nuclear chain reaction, Chicago Pile-1. An initial plan using enriched uranium-235 was abandoned as it was as yet unavailable in sufficient quantities. Working in a lab below the stands of Stagg Field at the University of Chicago, the team created the conditions needed for such a reaction by piling together 400 short tons (360 metric tons) of graphite, 58 short tons (53 metric tons) of uranium oxide, and six short tons (5.5 metric tons) of uranium metal, a majority of which was supplied by Westinghouse Lamp Plant in a makeshift production process.
Nuclear weaponry
The mushroom cloud over Hiroshima after the dropping of the uranium-based atomic bomb nicknamed 'Little Boy'
Two major types of atomic bombs were developed by the United States during World War II: a uranium-based device (codenamed "Little Boy") whose fissile material was highly enriched uranium, and a plutonium-based device (see Trinity test and "Fat Man")
whose plutonium was derived from uranium-238. The uranium-based Little
Boy device became the first nuclear weapon used in war when it was
detonated over the Japanese city of Hiroshima on 6 August 1945. Exploding with a yield equivalent to 12,500 tonnes of TNT, the blast and thermal wave of the bomb destroyed nearly 50,000 buildings and killed approximately 75,000 people (see Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki). Initially it was believed that uranium was relatively rare, and that nuclear proliferation
could be avoided by simply buying up all known uranium stocks, but
within a decade large deposits of it were discovered in many places
around the world.
Reactors
Four light bulbs lit with electricity generated from the first artificial electricity-producing nuclear reactor, EBR-I (1951)
The X-10 Graphite Reactor at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
(ORNL) in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, formerly known as the Clinton Pile and
X-10 Pile, was the world's second artificial nuclear reactor (after
Enrico Fermi's Chicago Pile) and was the first reactor designed and
built for continuous operation. Argonne National Laboratory's Experimental Breeder Reactor I, located at the Atomic Energy Commission's National Reactor Testing Station near Arco, Idaho, became the first nuclear reactor to create electricity on 20 December 1951.
Initially, four 150-watt light bulbs were lit by the reactor, but
improvements eventually enabled it to power the whole facility (later,
the town of Arco became the first in the world to have all its electricity come from nuclear power generated by BORAX-III, another reactor designed and operated by Argonne National Laboratory). The world's first commercial scale nuclear power station, Obninsk in the Soviet Union, began generation with its reactor AM-1 on 27 June 1954. Other early nuclear power plants were Calder Hall in England, which began generation on 17 October 1956, and the Shippingport Atomic Power Station in Pennsylvania, which began on 26 May 1958. Nuclear power was used for the first time for propulsion by a submarine, the USS Nautilus, in 1954.
Prehistoric naturally occurring fission
In 1972, the French physicist Francis Perrin discovered fifteen ancient and no longer active natural nuclear fission reactors in three separate ore deposits at the Oklo mine in Gabon, West Africa, collectively known as the Oklo Fossil Reactors. The ore deposit is 1.7 billion years old; then, uranium-235 constituted about 3% of the total uranium on Earth.
This is high enough to permit a sustained nuclear fission chain
reaction to occur, provided other supporting conditions exist. The
capacity of the surrounding sediment to contain the nuclear waste
products has been cited by the U.S. federal government as supporting
evidence for the feasibility to store spent nuclear fuel at the Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository.
Contamination and the Cold War legacy
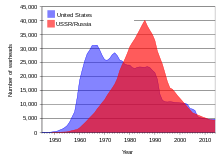
U.S. and USSR/Russian nuclear weapons stockpiles, 1945–2005
Above-ground nuclear tests by the Soviet Union and the United States in the 1950s and early 1960s and by France into the 1970s and 1980s spread a significant amount of fallout from uranium daughter isotopes around the world. Additional fallout and pollution occurred from several nuclear accidents.
Uranium miners have a higher incidence of cancer. An excess risk of lung cancer among Navajo uranium miners, for example, has been documented and linked to their occupation. The Radiation Exposure Compensation Act,
a 1990 law in the US, required $100,000 in "compassion payments" to
uranium miners diagnosed with cancer or other respiratory ailments.
During the Cold War
between the Soviet Union and the United States, huge stockpiles of
uranium were amassed and tens of thousands of nuclear weapons were
created using enriched uranium and plutonium made from uranium. Since
the break-up of the Soviet Union
in 1991, an estimated 600 short tons (540 metric tons) of highly
enriched weapons grade uranium (enough to make 40,000 nuclear warheads)
have been stored in often inadequately guarded facilities in the Russian Federation and several other former Soviet states. Police in Asia, Europe, and South America on at least 16 occasions from 1993 to 2005 have intercepted shipments of smuggled bomb-grade uranium or plutonium, most of which was from ex-Soviet sources. From 1993 to 2005 the Material Protection, Control, and Accounting Program, operated by the federal government of the United States, spent approximately US $550 million to help safeguard uranium and plutonium stockpiles in Russia. This money was used for improvements and security enhancements at research and storage facilities. Scientific American
reported in February 2006 that in some of the facilities security
consisted of chain link fences which were in severe states of disrepair.
According to an interview from the article, one facility had been
storing samples of enriched (weapons grade) uranium in a broom closet
before the improvement project; another had been keeping track of its
stock of nuclear warheads using index cards kept in a shoe box.
Occurrence
Origin
Along with all elements having atomic weights higher than that of iron, uranium is only naturally formed in supernovae. Primordial thorium and uranium are only produced in the r-process (rapid neutron capture), because the s-process (slow neutron capture) is too slow and cannot pass the gap of instability after bismuth. Besides the two extant primordial uranium isotopes, 235U and 238U, the r-process also produced significant quantities of 236U, which has a shorter half-life and has long since decayed completely to 232Th, which was itself enriched by the decay of 244Pu, accounting for the observed higher-than-expected abundance of thorium and lower-than-expected abundance of uranium. While the natural abundance of uranium has been supplemented by the decay of extinct 242Pu (half-life 0.375 million years) and 247Cm (half-life 16 million years), producing 238U and 235U
respectively, this occurred to an almost negligible extent due to the
shorter half-lives of these parents and their lower production than 236U and 244Pu, the parents of thorium: the 247Cm:235U ratio at the formation of the Solar System was (7.0±1.6)×10−5.
Biotic and abiotic
Uraninite, also known as pitchblende, is the most common ore mined to extract uranium.
The evolution of Earth's radiogenic heat flow over time: contribution from 235U in red and from 238U in green
Uranium is a naturally occurring element that can be found in low levels within all rock, soil, and water. Uranium is the 51st element in order of abundance
in the Earth's crust. Uranium is also the highest-numbered element to
be found naturally in significant quantities on Earth and is almost
always found combined with other elements. The decay of uranium, thorium, and potassium-40 in the Earth's mantle is thought to be the main source of heat that keeps the outer core liquid and drives mantle convection, which in turn drives plate tectonics.
Uranium's average concentration in the Earth's crust is (depending on the reference) 2 to 4 parts per million, or about 40 times as abundant as silver. The Earth's crust from the surface to 25 km (15 mi) down is calculated to contain 1017 kg (2×1017 lb) of uranium while the oceans may contain 1013 kg (2×1013 lb).
The concentration of uranium in soil ranges from 0.7 to 11 parts per
million (up to 15 parts per million in farmland soil due to use of
phosphate fertilizers), and its concentration in sea water is 3 parts per billion.
Uranium is more plentiful than antimony, tin, cadmium, mercury, or silver, and it is about as abundant as arsenic or molybdenum. Uranium is found in hundreds of minerals, including uraninite (the most common uranium ore), carnotite, autunite, uranophane, torbernite, and coffinite. Significant concentrations of uranium occur in some substances such as phosphate rock deposits, and minerals such as lignite, and monazite sands in uranium-rich ores (it is recovered commercially from sources with as little as 0.1% uranium).
Citrobacter species can have concentrations of uranium in their cells 300 times the level of the surrounding environment.
Some bacteria, such as Shewanella putrefaciens, Geobacter metallireducens and some strains of Burkholderia fungorum, use uranium for their growth and convert U(VI) to U(IV).
Other organisms, such as the lichen Trapelia involuta or microorganisms such as the bacterium Citrobacter, can absorb concentrations of uranium that are up to 300 times the level of their environment. Citrobacter species absorb uranyl ions when given glycerol phosphate
(or other similar organic phosphates). After one day, one gram of
bacteria can encrust themselves with nine grams of uranyl phosphate
crystals; this creates the possibility that these organisms could be
used in bioremediation to decontaminate uranium-polluted water.
The proteobacterium Geobacter has also been shown to bioremediate uranium in ground water. The mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices increases uranium content in the roots of its symbiotic plant.
In nature, uranium(VI) forms highly soluble carbonate complexes
at alkaline pH. This leads to an increase in mobility and availability
of uranium to groundwater and soil from nuclear wastes which leads to
health hazards. However, it is difficult to precipitate uranium as
phosphate in the presence of excess carbonate at alkaline pH. A Sphingomonas
sp. strain BSAR-1 has been found to express a high activity alkaline
phosphatase (PhoK) that has been applied for bioprecipitation of uranium
as uranyl phosphate species from alkaline solutions. The precipitation
ability was enhanced by overexpressing PhoK protein in E. coli.
Plants
absorb some uranium from soil. Dry weight concentrations of uranium in
plants range from 5 to 60 parts per billion, and ash from burnt wood can
have concentrations up to 4 parts per million. Dry weight concentrations of uranium in food plants are typically lower with one to two micrograms per day ingested through the food people eat.
Production and mining
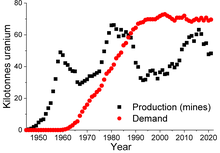
World uranium production (mines) and demand
Yellowcake is a concentrated mixture of uranium oxides that is further refined to extract pure uranium.
Worldwide production of U3O8 (yellowcake) in 2013 amounted to 70,015 tonnes, of which 22,451 t (32%) was mined in Kazakhstan. Other important uranium mining countries are Canada (9,331 t), Australia (6,350 t), Niger (4,518 t), Namibia (4,323 t) and Russia (3,135 t).
Uranium ore is mined in several ways: by open pit, underground, in-situ leaching, and borehole mining.
Low-grade uranium ore mined typically contains 0.01 to 0.25% uranium
oxides. Extensive measures must be employed to extract the metal from
its ore. High-grade ores found in Athabasca Basin deposits in Saskatchewan, Canada can contain up to 23% uranium oxides on average. Uranium ore is crushed and rendered into a fine powder and then leached with either an acid or alkali. The leachate is subjected to one of several sequences of precipitation, solvent extraction, and ion exchange. The resulting mixture, called yellowcake, contains at least 75% uranium oxides U3O8. Yellowcake is then calcined to remove impurities from the milling process before refining and conversion.
Commercial-grade uranium can be produced through the reduction of uranium halides with alkali or alkaline earth metals. Uranium metal can also be prepared through electrolysis of KUF
5 or UF
4, dissolved in molten calcium chloride (CaCl
2) and sodium chloride (NaCl) solution. Very pure uranium is produced through the thermal decomposition of uranium halides on a hot filament.
5 or UF
4, dissolved in molten calcium chloride (CaCl
2) and sodium chloride (NaCl) solution. Very pure uranium is produced through the thermal decomposition of uranium halides on a hot filament.
Resources and reserves
It is estimated that 5.5 million tonnes of uranium exists in ore
reserves that are economically viable at US$59 per lb of uranium, while 35 million tonnes are classed as mineral resources (reasonable prospects for eventual economic extraction). Prices went from about $10/lb in May 2003 to $138/lb in July 2007. This has caused a big increase in spending on exploration, with US$200 million being spent worldwide in 2005, a 54% increase on the previous year.
This trend continued through 2006, when expenditure on exploration
rocketed to over $774 million, an increase of over 250% compared to
2004. The OECD Nuclear Energy Agency said exploration figures for 2007 would likely match those for 2006.
Australia has 31% of the world's known uranium ore reserves and the world's largest single uranium deposit, located at the Olympic Dam Mine in South Australia. There is a significant reserve of uranium
in Bakouma a sub-prefecture in the prefecture of Mbomou in Central African Republic.
Some nuclear fuel comes from nuclear weapons being dismantled, such as from the Megatons to Megawatts Program.
An additional 4.6 billion tonnes of uranium are estimated to be in sea water (Japanese scientists in the 1980s showed that extraction of uranium from sea water using ion exchangers was technically feasible). There have been experiments to extract uranium from sea water, but the yield has been low due to the carbonate present in the water. In 2012, ORNL
researchers announced the successful development of a new absorbent
material dubbed HiCap which performs surface retention of solid or gas
molecules, atoms or ions and also effectively removes toxic metals from
water, according to results verified by researchers at Pacific Northwest
National Laboratory.
Supplies
Monthly uranium spot price in US$ per pound. The 2007 price peak is clearly visible.
In 2005, seventeen countries produced concentrated uranium oxides: Canada (27.9% of world production), Australia (22.8%), Kazakhstan (10.5%), Russia (8.0%), Namibia (7.5%), Niger (7.4%), Uzbekistan (5.5%), the United States (2.5%), Argentina (2.1%), Ukraine (1.9%) and China (1.7%).
Kazakhstan continues to increase production and may have become the
world's largest producer of uranium by 2009 with an expected production
of 12,826 tonnes, compared to Canada with 11,100 t and Australia with
9,430 t. In the late 1960s, UN geologists also discovered major uranium deposits and other rare mineral reserves in Somalia.
The find was the largest of its kind, with industry experts estimating
the deposits at over 25% of the world's then known uranium reserves of
800,000 tons.
The ultimate available supply is believed to be sufficient for at least the next 85 years, although some studies indicate underinvestment in the late twentieth century may produce supply problems in the 21st century.
Uranium deposits seem to be log-normal distributed. There is a 300-fold
increase in the amount of uranium recoverable for each tenfold decrease
in ore grade.
In other words, there is little high grade ore and proportionately much more low grade ore available.
Compounds
Reactions of uranium metal
Oxidation states and oxides
Oxides
Calcined uranium yellowcake, as produced in many large mills,
contains a distribution of uranium oxidation species in various forms
ranging from most oxidized to least oxidized. Particles with short
residence times in a calciner will generally be less oxidized than those
with long retention times or particles recovered in the stack scrubber.
Uranium content is usually referenced to U
3O
8, which dates to the days of the Manhattan Project when U
3O
8 was used as an analytical chemistry reporting standard.
3O
8, which dates to the days of the Manhattan Project when U
3O
8 was used as an analytical chemistry reporting standard.
Phase relationships
in the uranium-oxygen system are complex. The most important oxidation
states of uranium are uranium(IV) and uranium(VI), and their two
corresponding oxides are, respectively, uranium dioxide (UO
2) and uranium trioxide (UO
3). Other uranium oxides such as uranium monoxide (UO), diuranium pentoxide (U
2O
5), and uranium peroxide (UO
4·2H
2O) also exist.
2) and uranium trioxide (UO
3). Other uranium oxides such as uranium monoxide (UO), diuranium pentoxide (U
2O
5), and uranium peroxide (UO
4·2H
2O) also exist.
The most common forms of uranium oxide are triuranium octoxide (U
3O
8) and UO
2. Both oxide forms are solids that have low solubility in water and are relatively stable over a wide range of environmental conditions. Triuranium octoxide is (depending on conditions) the most stable compound of uranium and is the form most commonly found in nature. Uranium dioxide is the form in which uranium is most commonly used as a nuclear reactor fuel. At ambient temperatures, UO
2 will gradually convert to U
3O
8. Because of their stability, uranium oxides are generally considered the preferred chemical form for storage or disposal.
3O
8) and UO
2. Both oxide forms are solids that have low solubility in water and are relatively stable over a wide range of environmental conditions. Triuranium octoxide is (depending on conditions) the most stable compound of uranium and is the form most commonly found in nature. Uranium dioxide is the form in which uranium is most commonly used as a nuclear reactor fuel. At ambient temperatures, UO
2 will gradually convert to U
3O
8. Because of their stability, uranium oxides are generally considered the preferred chemical form for storage or disposal.
Aqueous chemistry
Uranium in its oxidation states III, IV, V, VI
Salts of many oxidation states of uranium are water-soluble and may be studied in aqueous solutions. The most common ionic forms are U3+ (brown-red), U4+ (green), UO+
2 (unstable), and UO2+
2 (yellow), for U(III), U(IV), U(V), and U(VI), respectively. A few solid and semi-metallic compounds such as UO and US exist for the formal oxidation state uranium(II), but no simple ions are known to exist in solution for that state. Ions of U3+ liberate hydrogen from water and are therefore considered to be highly unstable. The UO2+
2 ion represents the uranium(VI) state and is known to form compounds such as uranyl carbonate, uranyl chloride and uranyl sulfate. UO2+
2 also forms complexes with various organic chelating agents, the most commonly encountered of which is uranyl acetate.
2 (unstable), and UO2+
2 (yellow), for U(III), U(IV), U(V), and U(VI), respectively. A few solid and semi-metallic compounds such as UO and US exist for the formal oxidation state uranium(II), but no simple ions are known to exist in solution for that state. Ions of U3+ liberate hydrogen from water and are therefore considered to be highly unstable. The UO2+
2 ion represents the uranium(VI) state and is known to form compounds such as uranyl carbonate, uranyl chloride and uranyl sulfate. UO2+
2 also forms complexes with various organic chelating agents, the most commonly encountered of which is uranyl acetate.
Unlike the uranyl salts of uranium and polyatomic ion uranium-oxide cationic forms, the uranates, salts containing a polyatomic uranium-oxide anion, are generally not water-soluble.
Carbonates
The interactions of carbonate anions with uranium(VI) cause the Pourbaix diagram
to change greatly when the medium is changed from water to a carbonate
containing solution. While the vast majority of carbonates are insoluble
in water (students are often taught that all carbonates other than
those of alkali metals are insoluble in water), uranium carbonates are
often soluble in water. This is because a U(VI) cation is able to bind
two terminal oxides and three or more carbonates to form anionic
complexes.
Effects of pH
The uranium fraction diagrams in the presence of carbonate illustrate
this further: when the pH of a uranium(VI) solution increases, the
uranium is converted to a hydrated uranium oxide hydroxide and at high
pHs it becomes an anionic hydroxide complex.
When carbonate is added, uranium is converted to a series of
carbonate complexes if the pH is increased. One effect of these
reactions is increased solubility of uranium in the pH range 6 to 8, a
fact that has a direct bearing on the long term stability of spent
uranium dioxide nuclear fuels.
Hydrides, carbides and nitrides
Uranium metal heated to 250 to 300 °C (482 to 572 °F) reacts with hydrogen to form uranium hydride.
Even higher temperatures will reversibly remove the hydrogen. This
property makes uranium hydrides convenient starting materials to create
reactive uranium powder along with various uranium carbide, nitride, and halide compounds.
Two crystal modifications of uranium hydride exist: an α form that is
obtained at low temperatures and a β form that is created when the
formation temperature is above 250 °C.
Uranium carbides and uranium nitrides are both relatively inert semimetallic compounds that are minimally soluble in acids, react with water, and can ignite in air to form U
3O
8. Carbides of uranium include uranium monocarbide (UC), uranium dicarbide (UC
2), and diuranium tricarbide (U
2C
3). Both UC and UC
2 are formed by adding carbon to molten uranium or by exposing the metal to carbon monoxide at high temperatures. Stable below 1800 °C, U
2C
3 is prepared by subjecting a heated mixture of UC and UC
2 to mechanical stress. Uranium nitrides obtained by direct exposure of the metal to nitrogen include uranium mononitride (UN), uranium dinitride (UN
2), and diuranium trinitride (U
2N
3).
3O
8. Carbides of uranium include uranium monocarbide (UC), uranium dicarbide (UC
2), and diuranium tricarbide (U
2C
3). Both UC and UC
2 are formed by adding carbon to molten uranium or by exposing the metal to carbon monoxide at high temperatures. Stable below 1800 °C, U
2C
3 is prepared by subjecting a heated mixture of UC and UC
2 to mechanical stress. Uranium nitrides obtained by direct exposure of the metal to nitrogen include uranium mononitride (UN), uranium dinitride (UN
2), and diuranium trinitride (U
2N
3).
Halides
Uranium hexafluoride is the feedstock used to separate uranium-235 from natural uranium.
All uranium fluorides are created using uranium tetrafluoride (UF
4); UF
4 itself is prepared by hydrofluorination of uranium dioxide. Reduction of UF
4 with hydrogen at 1000 °C produces uranium trifluoride (UF
3). Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction of solid UF
4 with gaseous uranium hexafluoride (UF
6) can form the intermediate fluorides of U
2F
9, U
4F
17, and UF
5.
4); UF
4 itself is prepared by hydrofluorination of uranium dioxide. Reduction of UF
4 with hydrogen at 1000 °C produces uranium trifluoride (UF
3). Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction of solid UF
4 with gaseous uranium hexafluoride (UF
6) can form the intermediate fluorides of U
2F
9, U
4F
17, and UF
5.
At room temperatures, UF
6 has a high vapor pressure, making it useful in the gaseous diffusion process to separate the rare uranium-235 from the common uranium-238 isotope. This compound can be prepared from uranium dioxide and uranium hydride by the following process:
6 has a high vapor pressure, making it useful in the gaseous diffusion process to separate the rare uranium-235 from the common uranium-238 isotope. This compound can be prepared from uranium dioxide and uranium hydride by the following process:
- UO
2 + 4 HF → UF
4 + 2 H
2O (500 °C, endothermic) - UF
4 + F
2 → UF
6 (350 °C, endothermic)
The resulting UF
6, a white solid, is highly reactive (by fluorination), easily sublimes (emitting a vapor that behaves as a nearly ideal gas), and is the most volatile compound of uranium known to exist.
6, a white solid, is highly reactive (by fluorination), easily sublimes (emitting a vapor that behaves as a nearly ideal gas), and is the most volatile compound of uranium known to exist.
One method of preparing uranium tetrachloride (UCl
4) is to directly combine chlorine with either uranium metal or uranium hydride. The reduction of UCl
4 by hydrogen produces uranium trichloride (UCl
3) while the higher chlorides of uranium are prepared by reaction with additional chlorine. All uranium chlorides react with water and air.
4) is to directly combine chlorine with either uranium metal or uranium hydride. The reduction of UCl
4 by hydrogen produces uranium trichloride (UCl
3) while the higher chlorides of uranium are prepared by reaction with additional chlorine. All uranium chlorides react with water and air.
Bromides and iodides of uranium are formed by direct reaction of, respectively, bromine and iodine with uranium or by adding UH
3 to those element's acids. Known examples include: UBr
3, UBr
4, UI
3, and UI
4. Uranium oxyhalides are water-soluble and include UO
2F
2, UOCl
2, UO
2Cl
2, and UO
2Br
2. Stability of the oxyhalides decrease as the atomic weight of the component halide increases.
3 to those element's acids. Known examples include: UBr
3, UBr
4, UI
3, and UI
4. Uranium oxyhalides are water-soluble and include UO
2F
2, UOCl
2, UO
2Cl
2, and UO
2Br
2. Stability of the oxyhalides decrease as the atomic weight of the component halide increases.
Isotopes
Natural concentrations
Natural uranium consists of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (99.28% natural abundance), uranium-235 (0.71%), and uranium-234 (0.0054%). All three are radioactive, emitting alpha particles, with the exception that all three of these isotopes have small probabilities of undergoing spontaneous fission, rather than alpha emission. There are also five other trace isotopes: uranium-239, which is formed when 238U undergoes spontaneous fission, releasing neutrons that are captured by another 238U atom; uranium-237, which is formed when 238U captures a neutron but emits two more, which then decays to neptunium-237; and finally, uranium-233, which is formed in the decay chain of that neptunium-237. It is also expected that thorium-232 should be able to undergo double beta decay, which would produce uranium-232, but this has not yet been observed experimentally.
Uranium-238 is the most stable isotope of uranium, with a half-life of about 4.468×109 years, roughly the age of the Earth. Uranium-235 has a half-life of about 7.13×108 years, and uranium-234 has a half-life of about 2.48×105 years.
For natural uranium, about 49% of its alpha rays are emitted by each of 238U atom, and also 49% by 234U (since the latter is formed from the former) and about 2.0% of them by the 235U. When the Earth was young, probably about one-fifth of its uranium was uranium-235, but the percentage of 234U was probably much lower than this.
Uranium-238 is usually an α emitter (occasionally, it undergoes spontaneous fission), decaying through the uranium series, which has 18 members, into lead-206, by a variety of different decay paths.
The decay chain of 235U, which is called the actinium series, has 15 members and eventually decays into lead-207. The constant rates of decay in these decay series makes the comparison of the ratios of parent to daughter elements useful in radiometric dating.
Uranium-234, which is a member of the uranium series (the decay
chain of uranium-238), decays to lead-206 through a series of relatively
short-lived isotopes.
Uranium-233 is made from thorium-232 by neutron bombardment, usually in a nuclear reactor, and 233U is also fissile. Its decay chain forms part of the neptunium series and ends at bismuth-209 and thallium-205.
Uranium-235 is important for both nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons, because it is the only uranium isotope existing in nature on Earth in any significant amount that is fissile. This means that it can be split into two or three fragments (fission products) by thermal neutrons.
Uranium-238 is not fissile, but is a fertile isotope, because after neutron activation it can produce plutonium-239, another fissile isotope. Indeed, the 238U nucleus can absorb one neutron to produce the radioactive isotope uranium-239. 239U decays by beta emission to neptunium-239, also a beta-emitter, that decays in its turn, within a few days into plutonium-239. 239Pu was used as fissile material in the first atomic bomb detonated in the "Trinity test" on 15 July 1945 in New Mexico.
Enrichment
Cascades of gas centrifuges are used to enrich uranium ore to concentrate its fissionable isotopes.
In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2742%) and uranium-235 (0.7204%). Isotope separation concentrates (enriches) the fissionable uranium-235 for nuclear weapons and most nuclear power plants, except for gas cooled reactors and pressurised heavy water reactors. Most neutrons released by a fissioning atom of uranium-235 must impact other uranium-235 atoms to sustain the nuclear chain reaction. The concentration and amount of uranium-235 needed to achieve this is called a 'critical mass'.
To be considered 'enriched', the uranium-235 fraction should be between 3% and 5%.
This process produces huge quantities of uranium that is depleted of
uranium-235 and with a correspondingly increased fraction of
uranium-238, called depleted uranium or 'DU'. To be considered
'depleted', the uranium-235 isotope concentration should be no more than
0.3%.
The price of uranium has risen since 2001, so enrichment tailings
containing more than 0.35% uranium-235 are being considered for
re-enrichment, driving the price of depleted uranium hexafluoride above
$130 per kilogram in July 2007 from $5 in 2001.
The gas centrifuge process, where gaseous uranium hexafluoride (UF
6) is separated by the difference in molecular weight between 235UF6 and 238UF6 using high-speed centrifuges, is the cheapest and leading enrichment process. The gaseous diffusion process had been the leading method for enrichment and was used in the Manhattan Project. In this process, uranium hexafluoride is repeatedly diffused through a silver-zinc membrane, and the different isotopes of uranium are separated by diffusion rate (since uranium 238 is heavier it diffuses slightly slower than uranium-235). The molecular laser isotope separation method employs a laser beam of precise energy to sever the bond between uranium-235 and fluorine. This leaves uranium-238 bonded to fluorine and allows uranium-235 metal to precipitate from the solution. An alternative laser method of enrichment is known as atomic vapor laser isotope separation (AVLIS) and employs visible tunable lasers such as dye lasers. Another method used is liquid thermal diffusion.
6) is separated by the difference in molecular weight between 235UF6 and 238UF6 using high-speed centrifuges, is the cheapest and leading enrichment process. The gaseous diffusion process had been the leading method for enrichment and was used in the Manhattan Project. In this process, uranium hexafluoride is repeatedly diffused through a silver-zinc membrane, and the different isotopes of uranium are separated by diffusion rate (since uranium 238 is heavier it diffuses slightly slower than uranium-235). The molecular laser isotope separation method employs a laser beam of precise energy to sever the bond between uranium-235 and fluorine. This leaves uranium-238 bonded to fluorine and allows uranium-235 metal to precipitate from the solution. An alternative laser method of enrichment is known as atomic vapor laser isotope separation (AVLIS) and employs visible tunable lasers such as dye lasers. Another method used is liquid thermal diffusion.
Human exposure
A person can be exposed to uranium (or its radioactive daughters, such as radon)
by inhaling dust in air or by ingesting contaminated water and food.
The amount of uranium in air is usually very small; however, people who
work in factories that process phosphate fertilizers,
live near government facilities that made or tested nuclear weapons,
live or work near a modern battlefield where depleted uranium weapons have been used, or live or work near a coal-fired
power plant, facilities that mine or process uranium ore, or enrich
uranium for reactor fuel, may have increased exposure to uranium.
Houses or structures that are over uranium deposits (either natural or
man-made slag deposits) may have an increased incidence of exposure to
radon gas. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the permissible exposure limit for uranium exposure in the workplace as 0.25 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 0.2 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday and a short-term limit of 0.6 mg/m3. At levels of 10 mg/m3, uranium is immediately dangerous to life and health.
Most ingested uranium is excreted during digestion.
Only 0.5% is absorbed when insoluble forms of uranium, such as its
oxide, are ingested, whereas absorption of the more soluble uranyl ion can be up to 5%.
However, soluble uranium compounds tend to quickly pass through the
body, whereas insoluble uranium compounds, especially when inhaled by
way of dust into the lungs, pose a more serious exposure hazard. After entering the bloodstream, the absorbed uranium tends to bioaccumulate and stay for many years in bone tissue because of uranium's affinity for phosphates. Uranium is not absorbed through the skin, and alpha particles released by uranium cannot penetrate the skin.
Incorporated uranium becomes uranyl ions, which accumulate in bone, liver, kidney, and reproductive tissues. Uranium can be decontaminated from steel surfaces and aquifers.
Effects and precautions
Normal functioning of the kidney, brain, liver, heart, and other systems can be affected by uranium exposure, because, besides being weakly radioactive, uranium is a toxic metal. Uranium is also a reproductive toxicant. Radiological effects are generally local because alpha radiation, the primary form of 238U
decay, has a very short range, and will not penetrate skin. Alpha
radiation from inhaled uranium has been demonstrated to cause lung
cancer in exposed nuclear workers. Uranyl (UO2+
2) ions, such as from uranium trioxide or uranyl nitrate and other hexavalent uranium compounds, have been shown to cause birth defects and immune system damage in laboratory animals. While the CDC has published one study that no human cancer has been seen as a result of exposure to natural or depleted uranium, exposure to uranium and its decay products, especially radon, are widely known and significant health threats. Exposure to strontium-90, iodine-131, and other fission products is unrelated to uranium exposure, but may result from medical procedures or exposure to spent reactor fuel or fallout from nuclear weapons. Although accidental inhalation exposure to a high concentration of uranium hexafluoride has resulted in human fatalities, those deaths were associated with the generation of highly toxic hydrofluoric acid and uranyl fluoride rather than with uranium itself. Finely divided uranium metal presents a fire hazard because uranium is pyrophoric; small grains will ignite spontaneously in air at room temperature.
2) ions, such as from uranium trioxide or uranyl nitrate and other hexavalent uranium compounds, have been shown to cause birth defects and immune system damage in laboratory animals. While the CDC has published one study that no human cancer has been seen as a result of exposure to natural or depleted uranium, exposure to uranium and its decay products, especially radon, are widely known and significant health threats. Exposure to strontium-90, iodine-131, and other fission products is unrelated to uranium exposure, but may result from medical procedures or exposure to spent reactor fuel or fallout from nuclear weapons. Although accidental inhalation exposure to a high concentration of uranium hexafluoride has resulted in human fatalities, those deaths were associated with the generation of highly toxic hydrofluoric acid and uranyl fluoride rather than with uranium itself. Finely divided uranium metal presents a fire hazard because uranium is pyrophoric; small grains will ignite spontaneously in air at room temperature.
Uranium metal is commonly handled with gloves as a sufficient precaution. Uranium concentrate is handled and contained so as to ensure that people do not inhale or ingest it.
| Body system | Human studies | Animal studies | In vitro |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renal | Elevated levels of protein excretion, urinary catalase and diuresis | Damage to proximal convoluted tubules, necrotic cells cast from tubular epithelium, glomerular changes (renal failure) | No studies |
| Brain/CNS | Decreased performance on neurocognitive tests | Acute cholinergic toxicity; Dose-dependent accumulation in cortex, midbrain, and vermis; Electrophysiological changes in hippocampus | No studies |
| DNA | Increased reports of cancers | Increased mutagenicity (in mice) and induction of tumors | Binucleated cells with micronuclei, Inhibition of cell cycle kinetics and proliferation; Sister chromatid induction, tumorigenic phenotype |
| Bone/muscle | No studies | Inhibition of periodontal bone formation; and alveolar wound healing | No studies |
| Reproductive | Uranium miners have more first-born female children | Moderate to severe focal tubular atrophy; vacuolization of Leydig cells | No studies |
| Lungs/respiratory | No adverse health effects reported | Severe nasal congestion and hemorrhage, lung lesions and fibrosis, edema and swelling, lung cancer | No studies |
| Gastrointestinal | Vomiting, diarrhea, albuminuria | No studies | No studies |
| Liver | No effects seen at exposure dose | Fatty livers, focal necrosis | No studies |
| Skin | No exposure assessment data available | Swollen vacuolated epidermal cells, damage to hair follicles and sebaceous glands | No studies |
| Tissues surrounding embedded DU fragments | Elevated uranium urine concentrations | Elevated uranium urine concentrations, perturbations in biochemical and neuropsychological testing | No studies |
| Immune system | Chronic fatigue, rash, ear and eye infections, hair and weight loss, cough. May be due to combined chemical exposure rather than DU alone | No studies | No studies |
| Eyes | No studies | Conjunctivitis, irritation inflammation, edema, ulceration of conjunctival sacs | No studies |
| Blood | No studies | Decrease in RBC count and hemoglobin concentration | No studies |
| Cardiovascular | Myocarditis resulting from the uranium ingestion, which ended six months after ingestion | No effects | No studies |