Economists, political economists, sociologists and historians
have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and
have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include laissez-faire or free market capitalism, welfare capitalism and state capitalism. Different forms of capitalism feature varying degrees of free markets, public ownership, obstacles to free competition and state-sanctioned social policies. The degree of competition in markets, the role of intervention and regulation, and the scope of state ownership vary across different models of capitalism. The extent to which different markets are free as well as the rules defining private property are matters of politics and policy. Most existing capitalist economies are mixed economies, which combine elements of free markets with state intervention and in some cases economic planning.
Market economies have existed under many forms of government and in many different times, places and cultures. Modern capitalist societies—marked by a universalization of money-based social relations, a consistently large and system-wide class of workers who must work for wages, and a capitalist class which owns the means of production—developed in Western Europe in a process that led to the Industrial Revolution. Capitalist systems with varying degrees of direct government intervention have since become dominant in the Western world and continue to spread. Over time, capitalist countries have experienced consistent economic growth and an increase in the standard of living.
Critics of capitalism argue that it establishes power in the hands of a minority capitalist class that exists through the exploitation of the majority working class and their labor; prioritizes profit over social good, natural resources and the environment; and is an engine of inequality, corruption and economic instabilities. Supporters argue that it provides better products and innovation through competition, disperses wealth to all productive people, promotes pluralism and decentralization of power, creates strong economic growth, and yields productivity and prosperity that greatly benefit society.
Market economies have existed under many forms of government and in many different times, places and cultures. Modern capitalist societies—marked by a universalization of money-based social relations, a consistently large and system-wide class of workers who must work for wages, and a capitalist class which owns the means of production—developed in Western Europe in a process that led to the Industrial Revolution. Capitalist systems with varying degrees of direct government intervention have since become dominant in the Western world and continue to spread. Over time, capitalist countries have experienced consistent economic growth and an increase in the standard of living.
Critics of capitalism argue that it establishes power in the hands of a minority capitalist class that exists through the exploitation of the majority working class and their labor; prioritizes profit over social good, natural resources and the environment; and is an engine of inequality, corruption and economic instabilities. Supporters argue that it provides better products and innovation through competition, disperses wealth to all productive people, promotes pluralism and decentralization of power, creates strong economic growth, and yields productivity and prosperity that greatly benefit society.
Etymology
The term "capitalist", meaning an owner of capital, appears earlier than the term "capitalism" and it dates back to the mid-17th century. "Capitalism" is derived from capital, which evolved from capitale, a late Latin word based on caput, meaning "head"—also the origin of "chattel" and "cattle" in the sense of movable property (only much later to refer only to livestock). Capitale
emerged in the 12th to 13th centuries in the sense of referring to
funds, stock of merchandise, sum of money or money carrying interest.
By 1283, it was used in the sense of the capital assets of a trading
firm and it was frequently interchanged with a number of other
words—wealth, money, funds, goods, assets, property and so on.
The Hollandische Mercurius uses "capitalists" in 1633 and 1654 to refer to owners of capital. In French, Étienne Clavier referred to capitalistes in 1788, six years before its first recorded English usage by Arthur Young in his work Travels in France (1792). In his Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1817), David Ricardo referred to "the capitalist" many times. Samuel Taylor Coleridge, an English poet, used "capitalist" in his work Table Talk (1823). Pierre-Joseph Proudhon used the term "capitalist" in his first work, What is Property? (1840), to refer to the owners of capital. Benjamin Disraeli used the term "capitalist" in his 1845 work Sybil.
The initial usage of the term "capitalism" in its modern sense has been attributed to Louis Blanc
in 1850 ("What I call 'capitalism' that is to say the appropriation of
capital by some to the exclusion of others") and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
in 1861 ("Economic and social regime in which capital, the source of
income, does not generally belong to those who make it work through
their labour"). Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels referred to the "capitalistic system" and to the "capitalist mode of production" in Capital (1867). The use of the word "capitalism" in reference to an economic system appears twice in Volume I of Capital, p. 124 (German edition) and in Theories of Surplus Value,
tome II, p. 493 (German edition). Marx did not extensively use the form
capitalism, but instead those of capitalist and capitalist mode of
production, which appear more than 2,600 times in the trilogy The Capital. According to the Oxford English Dictionary (OED), the term "capitalism" first appeared in English in 1854 in the novel The Newcomes by novelist William Makepeace Thackeray, where he meant "having ownership of capital". Also according to the OED, Carl Adolph Douai, a German American socialist and abolitionist, used the phrase "private capitalism" in 1863.
History
Capitalism in its modern form can be traced to the emergence of agrarian capitalism and mercantilism in the early Renaissance, in city states like Florence.
Capital has existed incipiently on a small scale for centuries in the form of merchant, renting and lending activities and occasionally as small-scale industry with some wage labour. Simple commodity
exchange and consequently simple commodity production, which are the
initial basis for the growth of capital from trade, have a very long
history. Classical Islam promulgated capitalist economic policies such as free trade and banking. Their use of Indo-Arabic numerals facilitated bookkeeping. These innovations migrated to Europe through trade partners in cities such as Venice and Pisa. The Italian mathematician Fibonacci traveled the Mediterranean talking to Arab traders, and returned to popularize the use of Indo-Arabic numerals in Europe.
Capital and commercial trade thus existed for much of history,
but it did not lead to industrialisation or dominate the production
process of society. That required a set of conditions, including
specific technologies of mass production, the ability to independently
and privately own and trade in means of production, a class of workers
willing to sell their labour power for a living, a legal
framework promoting commerce, a physical infrastructure allowing the
circulation of goods on a large scale and security for private
accumulation. Many of these conditions do not currently exist in many Third World
countries, although there is plenty of capital and labour. The
obstacles for the development of capitalist markets are therefore less
technical and more social, cultural and political.
Agrarian capitalism
The economic foundations of the feudal agricultural system began to shift substantially in 16th-century England as the manorial system
had broken down and land began to become concentrated in the hands of
fewer landlords with increasingly large estates. Instead of a serf-based
system of labor, workers were increasingly employed as part of a
broader and expanding money-based economy. The system put pressure on
both landlords and tenants to increase the productivity of agriculture
to make profit; the weakened coercive power of the aristocracy to extract peasant surpluses
encouraged them to try better methods; and the tenants also had
incentive to improve their methods in order to flourish in a competitive
labor market.
Terms of rent for land were becoming subject to economic market forces
rather than to the previous stagnant system of custom and feudal
obligation.
By the early 17th century, England was a centralized state in which much of the feudal order of Medieval Europe
had been swept away. This centralization was strengthened by a good
system of roads and by a disproportionately large capital city, London.
The capital acted as a central market hub for the entire country,
creating a very large internal market for goods, contrasting with the
fragmented feudal holdings that prevailed in most parts of the Continent.
Mercantilism
A painting of a French seaport from 1638 at the height of mercantilism
The economic doctrine prevailing from the 16th to the 18th centuries is commonly called mercantilism. This period, the Age of Discovery, was associated with the geographic exploration of the foreign lands by merchant traders, especially from England and the Low Countries. Mercantilism was a system of trade for profit, although commodities were still largely produced by non-capitalist methods. Most scholars consider the era of merchant capitalism and mercantilism as the origin of modern capitalism, although Karl Polanyi
argued that the hallmark of capitalism is the establishment of
generalized markets for what he called the "fictitious commodities",
i.e. land, labor and money. Accordingly, he argued that "not until 1834
was a competitive labor market established in England, hence industrial
capitalism as a social system cannot be said to have existed before that
date".
Robert Clive after the Battle of Plassey, which began East India Company rule in India
England began a large-scale and integrative approach to mercantilism during the Elizabethan Era (1558–1603). A systematic and coherent explanation of balance of trade was made public through Thomas Mun's argument England's Treasure by Forraign Trade, or the Balance of our Forraign Trade is The Rule of Our Treasure. It was written in the 1620s and published in 1664.
European merchants, backed by state controls, subsidies and monopolies, made most of their profits by buying and selling goods. In the words of Francis Bacon,
the purpose of mercantilism was "the opening and well-balancing of
trade; the cherishing of manufacturers; the banishing of idleness; the
repressing of waste and excess by sumptuary laws; the improvement and
husbanding of the soil; the regulation of prices...".
The British East India Company and the Dutch East India Company inaugurated an expansive era of commerce and trade. These companies were characterized by their colonial and expansionary powers given to them by nation-states.
During this era, merchants, who had traded under the previous stage of
mercantilism, invested capital in the East India Companies and other
colonies, seeking a return on investment.
Industrial capitalism
A Watt steam engine: the steam engine fuelled primarily by coal propelled the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain
In the mid-18th century, a new group of economic theorists, led by David Hume and Adam Smith,
challenged fundamental mercantilist doctrines such as the belief that
the world's wealth remained constant and that a state could only
increase its wealth at the expense of another state.
During the Industrial Revolution,
industrialists replaced merchants as a dominant factor in the
capitalist system and affected the decline of the traditional handicraft
skills of artisans, guilds and journeymen.
Also during this period, the surplus generated by the rise of
commercial agriculture encouraged increased mechanization of
agriculture. Industrial capitalism marked the development of the factory system of manufacturing, characterized by a complex division of labor
between and within work process and the routine of work tasks; and
finally established the global domination of the capitalist mode of
production.
Britain also abandoned its protectionist policy as embraced by mercantilism. In the 19th century, Richard Cobden and John Bright, who based their beliefs on the Manchester School, initiated a movement to lower tariffs. In the 1840s, Britain adopted a less protectionist policy, with the repeal of the Corn Laws and the Navigation Acts. Britain reduced tariffs and quotas, in line with David Ricardo's advocacy for free trade.
Modern capitalism
The gold standard formed the financial basis of the international economy from 1870 to 1914
Capitalism was carried across the world by broader processes of globalization
and by the beginning of the nineteenth century a series of loosely
connected market systems had come together as a relatively integrated
global system, in turn intensifying processes of economic and other
globalization. Later in the 20th century, capitalism overcame a challenge by centrally-planned economies and is now the encompassing system worldwide, with the mixed economy being its dominant form in the industrialized Western world.
Industrialization allowed cheap production of household items using economies of scale
while rapid population growth created sustained demand for commodities.
Globalization in this period was decisively shaped by 18th-century imperialism.
After the First and Second Opium Wars
and the completion of British conquest of India, vast populations of
these regions became ready consumers of European exports. Also in this
period, areas of sub-Saharan Africa and the Pacific islands were
colonised. The conquest of new parts of the globe, notably sub-Saharan
Africa, by Europeans yielded valuable natural resources such as rubber, diamonds and coal and helped fuel trade and investment between the European imperial powers, their colonies and the United States:
The inhabitant of London could order by telephone, sipping his morning tea, the various products of the whole earth, and reasonably expect their early delivery upon his doorstep. Militarism and imperialism of racial and cultural rivalries were little more than the amusements of his daily newspaper. What an extraordinary episode in the economic progress of man was that age which came to an end in August 1914.
In this period, the global financial system was mainly tied to the gold standard. The United Kingdom first formally adopted this standard in 1821. Soon to follow were Canada in 1853, Newfoundland in 1865, the United States and Germany (de jure) in 1873. New technologies, such as the telegraph, the transatlantic cable, the radiotelephone, the steamship and railway allowed goods and information to move around the world at an unprecedented degree.
The New York stock exchange traders' floor (1963)
In the period following the global depression of the 1930s, the state
played an increasingly prominent role in the capitalistic system
throughout much of the world. The postwar boom ended in the late 1960s
and early 1970s and the situation was worsened by the rise of stagflation. Monetarism, a modification of Keynesianism that is more compatible with laissez-faire, gained increasing prominence in the capitalist world, especially under the leadership of Ronald Reagan in the United States and Margaret Thatcher in the United Kingdom in the 1980s. Public and political interest began shifting away from the so-called collectivist concerns of Keynes's managed capitalism to a focus on individual choice, called "remarketized capitalism".
According to Harvard academic Shoshana Zuboff, a new genus of capitalism, surveillance capitalism, monetizes data acquired through surveillance. She states it was first discovered and consolidated at Google, emerged due to the "coupling of the vast powers of the digital with the radical indifference and intrinsic narcissism of the financial capitalism and its neoliberal vision that have dominated commerce for at least three decades, especially in the Anglo economies"
and depends on the global architecture of computer mediation which
produces a distributed and largely uncontested new expression of power
she calls "Big Other".
Relationship to democracy
Many analysts assert that China is one of the main examples of state capitalism in the 21st century
The relationship between democracy and capitalism is a contentious area in theory and in popular political movements. The extension of universal adult male suffrage
in 19th-century Britain occurred along with the development of
industrial capitalism and democracy became widespread at the same time
as capitalism, leading capitalists to posit a causal or mutual
relationship between them.
However, according to some authors in the 20th-century capitalism also
accompanied a variety of political formations quite distinct from
liberal democracies, including fascist regimes, absolute monarchies and single-party states.
Democratic peace theory asserts that democracies seldom fight other
democracies, but critics of that theory suggest that this may be because
of political similarity or stability rather than because they are
democratic or capitalist. Moderate critics argue that though economic
growth under capitalism has led to democracy in the past, it may not do
so in the future as authoritarian regimes have been able to manage economic growth without making concessions to greater political freedom.
One of the biggest supporters of the idea that capitalism promotes political freedom, Milton Friedman,
argued that competitive capitalism allows economic and political power
to be separate, ensuring that they do not clash with one another.
Moderate critics have recently challenged this, stating that the current
influence lobbying groups have had on policy in the United States is a
contradiction, given the approval of Citizens United.
This has led people to question the idea that competitive capitalism
promotes political freedom. The ruling on Citizens United allows
corporations to spend undisclosed and unregulated amounts of money on
political campaigns, shifting outcomes to the interests and undermining
true democracy. As explained in Robin Hahnel’s
writings, the centerpiece of the ideological defense of the free market
system is the concept of economic freedom and that supporters equate
economic democracy with economic freedom and claim that only the free
market system can provide economic freedom. According to Hahnel, there
are a few objections to the premise that capitalism offers freedom
through economic freedom. These objections are guided by critical
questions about who or what decides whose freedoms are more protected.
Often, the question of inequality is brought up when discussing how well
capitalism promotes democracy. An argument that could stand is that
economic growth can lead to inequality given that capital can be
acquired at different rates by different people. In Capital in the Twenty-First Century, Thomas Piketty of the Paris School of Economics asserts that inequality is the inevitable consequence of economic growth in a capitalist economy and the resulting concentration of wealth can destabilize democratic societies and undermine the ideals of social justice upon which they are built. Marxists, anarchists (except for anarcho-capitalists) and other leftists argue that capitalism is incompatible with democracy since capitalism according to Marx entails "dictatorship of the bourgeoisie" (owners of the means of production) while democracy entails rule by the people.
States with capitalistic economic systems have thrived under
political regimes deemed to be authoritarian or oppressive. Singapore
has a successful open market economy as a result of its competitive,
business-friendly climate and robust rule of law. Nonetheless, it often
comes under fire for its brand of government which though democratic and
consistently one of the least corrupt
also operates largely under a one-party rule and does not vigorously
defend freedom of expression given its government-regulated press as
well as penchant for upholding laws protecting ethnic and religious
harmony, judicial dignity and personal reputation. The private
(capitalist) sector in the People's Republic of China has grown
exponentially and thrived since its inception, despite having an
authoritarian government. Augusto Pinochet's rule in Chile led to economic growth and high levels of inequality by using authoritarian means to create a safe environment for investment and capitalism. Similarly, Suharto's authoritarian reign and extirpation of the Communist Party of Indonesia allowed for the expansion of capitalism in Indonesia.
Varieties of capitalism
Peter A. Hall and David Soskice
argued that modern economies have developed two different forms of
capitalism: liberal market economies (or LME) (e.g. the United States,
the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand and Ireland) and coordinated
market economies (CME) (e.g. Germany, Japan, Sweden and Austria). Those
two types can be distinguished by the primary way in which firms
coordinate with each other and other actors, such as trade unions.
In LMEs, firms primarily coordinate their endeavors by way of
hierarchies and market mechanisms. Coordinated market economies more
heavily rely on non-market forms of interaction in the coordination of
their relationship with other actors. These two forms of capitalisms developed different industrial relations, vocational training and education, corporate governance,
inter-firm relations and relations with employees. The existence of
these different forms of capitalism has important societal effects,
especially in periods of crisis and instability. Since the early 2000s,
the number of labor market outsiders has rapidly grown in Europe,
especially among the youth, potentially influencing social and political
participation. Using varieties of capitalism theory, it is possible to
disentangle the different effects on social and political participation
that an increase of labor market outsiders has in liberal and
coordinated market economies (Ferragina et al., 2016).
The social and political disaffection, especially among the youth,
seems to be more pronounced in liberal than coordinated market
economies. This signals an important problem for liberal market
economies in a period of crisis. If the market does not provide
consistent job opportunities (as it has in previous decades), the
shortcomings of liberal social security systems may depress social and
political participation even further than in other capitalist economies.
Characteristics
In general, capitalism as an economic system and mode of production can be summarised by the following:
- Capital accumulation: production for profit and accumulation as the implicit purpose of all or most of production, constriction or elimination of production formerly carried out on a common social or private household basis.
- Commodity production: production for exchange on a market; to maximize exchange-value instead of use-value.
- Private ownership of the means of production.
- High levels of wage labour.
- The investment of money to make a profit.
- The use of the price mechanism to allocate resources between competing uses.
- Economically efficient use of the factors of production and raw materials due to maximization of value added in the production process.
- Freedom of capitalists to act in their self-interest in managing their business and investments.
The market
The
price (P) of a product is determined by a balance between production at
each price (supply, S) and the desires of those with purchasing power
at each price (demand, D): this results in a market equilibrium, with a
given quantity (Q) sold of the product, whereas a rise in demand would
result in an increase in price and an increase in output
In free market and laissez-faire
forms of capitalism, markets are used most extensively with minimal or
no regulation over the pricing mechanism. In mixed economies, which are
almost universal today, markets continue to play a dominant role, but they are regulated to some extent by the state in order to correct market failures, promote social welfare, conserve natural resources, fund defense and public safety or other rationale. In state capitalist systems, markets are relied upon the least, with the state relying heavily on state-owned enterprises or indirect economic planning to accumulate capital.
Supply is the amount of a good or service that is available for
purchase or sale. Demand is the measure of value for a good that people
are willing to buy at a given time. Prices tend to rise when demand for
an available resource increases or its supply diminishes and fall with
demand or when supply increases.
Competition arises when more than one producer is trying to sell
the same or similar products to the same buyers. In capitalist theory,
competition leads to innovation and more affordable prices. Without
competition, a monopoly or cartel may develop. A monopoly occurs when a firm is granted exclusivity over a market. Hence the firm can engage in rent seeking
behaviors such as limiting output and raising prices because it has no
fear of competition. A cartel is a group of firms that act together in a
monopolistic manner to control output and prices.
Governments have implemented legislation for the purpose of
preventing the creation of monopolies and cartels. In 1890, the Sherman
Anti-Trust Act became the first legislation passed by the United States
Congress to limit monopolies.
Profit motive
The profit motive,
in the theory in capitalism, is the desire to earn income in the form
of profit. Stated differently, the reason for a business's existence is
to turn a profit. The profit motive functions according to rational choice theory,
or the theory that individuals tend to pursue what is in their own best
interests. Accordingly, businesses seek to benefit themselves and/or
their shareholders by maximizing profit.
In capitalist theoretics, the profit motive is said to ensure that resources are being allocated efficiently. For instance, Austrian economist Henry Hazlitt
explains: "If there is no profit in making an article, it is a sign
that the labor and capital devoted to its production are misdirected:
the value of the resources that must be used up in making the article is
greater than the value of the article itself".
In other words, profits let companies know whether an item is worth
producing. Theoretically, in free and competitive markets maximising
profit ensures that resources are not wasted.
Private property
The relationship between the state,
its formal mechanisms and capitalist societies has been debated in many
fields of social and political theory, with active discussion since the
19th century. Hernando de Soto
is a contemporary Peruvian economist who has argued that an important
characteristic of capitalism is the functioning state protection of
property rights in a formal property system where ownership and
transactions are clearly recorded.
According to de Soto, this is the process by which physical
assets are transformed into capital, which in turn may be used in many
more ways and much more efficiently in the market economy. A number of
Marxian economists have argued that the Enclosure Acts in England and similar legislation elsewhere were an integral part of capitalist primitive accumulation and that specific legal frameworks of private land ownership have been integral to the development of capitalism.
Market competition
In capitalist economics, market competition is the rivalry among
sellers trying to achieve such goals as increasing profits, market share
and sales volume by varying the elements of the marketing mix:
price, product, distribution and promotion. Merriam-Webster defines
competition in business as "the effort of two or more parties acting
independently to secure the business of a third party by offering the
most favourable terms". It was described by Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) and later economists as allocating productive resources to their most highly valued uses and encouraging efficiency. Smith and other classical economists before Antoine Augustine Cournot
were referring to price and non-price rivalry among producers to sell
their goods on best terms by bidding of buyers, not necessarily to a
large number of sellers nor to a market in final equilibrium. Competition is widespread throughout the market process. It is a condition where "buyers tend to compete with other buyers, and sellers tend to compete with other sellers".
In offering goods for exchange, buyers competitively bid to purchase
specific quantities of specific goods which are available, or might be
available if sellers were to choose to offer such goods. Similarly,
sellers bid against other sellers in offering goods on the market,
competing for the attention and exchange resources of buyers.
Competition results from scarcity—there
is never enough to satisfy all conceivable human wants—and occurs "when
people strive to meet the criteria that are being used to determine who
gets what".
Economic growth
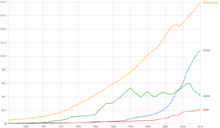
World's GDP per capita shows exponential growth since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution
Capitalism and the economy of the People's Republic of China
Historically, capitalism has an ability to promote economic growth as measured by gross domestic product (GDP), capacity utilization or standard of living.
This argument was central, for example, to Adam Smith's advocacy of
letting a free market control production and price and allocate
resources. Many theorists have noted that this increase in global GDP
over time coincides with the emergence of the modern world capitalist
system.
Between 1000 and 1820, the world economy grew sixfold, a faster
rate than the population growth, so individuals enjoyed, on average, a
50% increase in income. Between 1820 and 1998, world economy grew
50-fold, a much faster rate than the population growth, so individuals
enjoyed on average a 9-fold increase in income.
Over this period, in Europe, North America and Australasia the economy
grew 19-fold per person, even though these regions already had a higher
starting level; and in Japan, which was poor in 1820, the increase per
person was 31-fold. In the Third World, there was an increase, but only 5-fold per person.
As a mode of production
The capitalist mode of production refers to the systems of organising production and distribution within capitalist societies.
Private money-making in various forms (renting, banking, merchant
trade, production for profit and so on) preceded the development of the
capitalist mode of production as such. The capitalist mode of production
proper based on wage-labour and private ownership of the means of
production and on industrial technology began to grow rapidly in Western
Europe from the Industrial Revolution, later extending to most of the world.
The term capitalist mode of production is defined by private ownership of the means of production, extraction of surplus value by the owning class for the purpose of capital accumulation, wage-based labour and at least as far as commodities are concerned being market-based.
Capitalism in the form of money-making activity has existed in
the shape of merchants and money-lenders who acted as intermediaries
between consumers and producers engaging in simple commodity production (hence the reference to "merchant capitalism")
since the beginnings of civilisation. What is specific about the
"capitalist mode of production" is that most of the inputs and outputs
of production are supplied through the market (i.e. they are commodities) and essentially all production is in this mode.
For example, in flourishing feudalism most or all of the factors of
production including labour are owned by the feudal ruling class
outright and the products may also be consumed without a market of any
kind, it is production for use within the feudal social unit and for
limited trade.
This has the important consequence that the whole organisation of the
production process is reshaped and re-organised to conform with economic
rationality as bounded
by capitalism, which is expressed in price relationships between inputs
and outputs (wages, non-labour factor costs, sales and profits) rather
than the larger rational context faced by society overall—that is, the
whole process is organised and re-shaped in order to conform to
"commercial logic". Essentially, capital accumulation comes to define
economic rationality in capitalist production.
A society, region or nation
is capitalist if the predominant source of incomes and products being
distributed is capitalist activity, but even so this does not yet mean
necessarily that the capitalist mode of production is dominant in that
society.
Supply and demand
The price P of a product is determined by a balance between production at each price (supply S) and the desires of those with purchasing power at each price (demand D): the diagram shows a positive shift in demand from D1 to D2, resulting in an increase in price (P) and quantity sold (Q) of the product
In capitalist economic structures, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good
will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by
consumers (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied by
producers (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity.
- If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, then a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.
- If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, then a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price.
- If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), then a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price.
- If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), then a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.
Graphical representation of supply and demand
Although it is normal to regard the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied as functions of the price of the goods, the standard graphical representation, usually attributed to Alfred Marshall,
has price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis, the
opposite of the standard convention for the representation of a
mathematical function.
Since determinants of supply and demand other than the price of
the goods in question are not explicitly represented in the
supply-demand diagram, changes in the values of these variables are
represented by moving the supply and demand curves (often described as
"shifts" in the curves). By contrast, responses to changes in the price
of the good are represented as movements along unchanged supply and
demand curves.
Supply schedule
A
supply schedule is a table that shows the relationship between the
price of a good and the quantity supplied. Under the assumption of perfect competition, supply is determined by marginal cost.
That is: firms will produce additional output while the cost of
producing an extra unit of output is less than the price they would
receive.
A hike in the cost of raw goods would decrease supply and
shifting costs up while a discount would increase supply, shifting costs
down and hurting producers as producer surplus decreases.
By its very nature, conceptualising a supply curve requires the
firm to be a perfect competitor (i.e. to have no influence over the
market price). This is true because each point on the supply curve is
the answer to the question "If this firm is faced with this
potential price, how much output will it be able to and willing to
sell?". If a firm has market power, its decision of how much output to
provide to the market influences the market price, therefore the firm is
not "faced with" any price and the question becomes less relevant.
Economists distinguish between the supply curve of an individual
firm and between the market supply curve. The market supply curve is
obtained by summing the quantities supplied by all suppliers at each
potential price, thus in the graph of the supply curve individual firms'
supply curves are added horizontally to obtain the market supply curve.
Economists also distinguish the short-run market supply curve
from the long-run market supply curve. In this context, two things are
assumed constant by definition of the short run: the availability of one
or more fixed inputs (typically physical capital)
and the number of firms in the industry. In the long-run, firms can
adjust their holdings of physical capital, enabling them to better
adjust their quantity supplied at any given price. Furthermore, in the
long-run potential competitors can enter
or exit the industry in response to market conditions. For both of
these reasons, long-run market supply curves are generally flatter than
their short-run counterparts.
The determinants of supply are:
- Production costs: how much a goods costs to be produced. Production costs are the cost of the inputs; primarily labor, capital, energy and materials. They depend on the technology used in production and/or technological advances. See productivity.
- Firms' expectations about future prices.
- Number of suppliers.
Demand schedule
A demand schedule, depicted graphically as the demand curve, represents the amount of some goods
that buyers are willing and able to purchase at various prices,
assuming all determinants of demand other than the price of the good in
question, such as income, tastes and preferences, the price of substitute goods and the price of complementary goods, remain the same. Following the law of demand,
the demand curve is almost always represented as downward-sloping,
meaning that as price decreases, consumers will buy more of the good.
Just like the supply curves reflect marginal cost curves, demand curves are determined by marginal utility curves.
Consumers will be willing to buy a given quantity of a good at a given
price, if the marginal utility of additional consumption is equal to the
opportunity cost
determined by the price—that is, the marginal utility of alternative
consumption choices. The demand schedule is defined as the willingness
and ability of a consumer to purchase a given product in a given frame
of time.
While the aforementioned demand curve is generally
downward-sloping, there may be rare examples of goods that have
upward-sloping demand curves. Two different hypothetical types of goods
with upward-sloping demand curves are Giffen goods (an inferior, but staple good) and Veblen goods (goods made more fashionable by a higher price).
By its very nature, conceptualising a demand curve requires that
the purchaser be a perfect competitor—that is, that the purchaser has no
influence over the market price. This is true because each point on the
demand curve is the answer to the question "If this buyer is faced with
this potential price, how much of the product will it purchase?". If a
buyer has market power, so its decision of how much to buy influences
the market price, then the buyer is not "faced with" any price and the
question is meaningless.
Like with supply curves, economists distinguish between the
demand curve of an individual and the market demand curve. The market
demand curve is obtained by summing the quantities demanded by all
consumers at each potential price, thus in the graph of the demand curve
individuals' demand curves are added horizontally to obtain the market
demand curve.
The determinants of demand are:
- Income.
- Tastes and preferences.
- Prices of related goods and services.
- Consumers' expectations about future prices and incomes that can be checked.
- Number of potential consumers.
Equilibrium
In the context of supply and demand, economic equilibrium refers to a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market
price is established through competition such that the amount of goods
or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing
price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and
the quantity is called "competitive quantity" or market clearing
quantity.
Partial equilibrium
Partial equilibrium, as the name suggests, takes into consideration only a part of the market to attain equilibrium.
Jain proposes (attributed to George Stigler):
"A partial equilibrium is one which is based on only a restricted range
of data, a standard example is price of a single product, the prices of
all other products being held fixed during the analysis".
The supply and demand model is a partial equilibrium model of economic equilibrium, where the clearance on the market of some specific goods is obtained independently from prices and quantities in other markets. In other words, the prices of all substitutes and complements as well as income levels of consumers are constant. This makes analysis much simpler than in a general equilibrium model which includes an entire economy.
Here the dynamic process is that prices adjust until supply
equals demand. It is a powerfully simple technique that allows one to
study equilibrium, efficiency and comparative statics.
The stringency of the simplifying assumptions inherent in this approach
make the model considerably more tractable, but it may produce results
which while seemingly precise do not effectively model real world
economic phenomena.
Partial equilibrium analysis examines the effects of policy
action in creating equilibrium only in that particular sector or market
which is directly affected, ignoring its effect in any other market or
industry assuming that they being small will have little impact if any.
Hence this analysis is considered to be useful in constricted markets.
Léon Walras first formalised the idea of a one-period economic equilibrium of the general economic system, but it was French economist Antoine Augustin Cournot and English political economist Alfred Marshall who developed tractable models to analyse an economic system.
Empirical estimation
Demand and supply relations in a market can be statistically estimated from price, quantity and other data with sufficient information in the model. This can be done with simultaneous-equation methods of estimation in econometrics.
Such methods allow solving for the model-relevant "structural
coefficients", the estimated algebraic counterparts of the theory. The parameter identification problem is a common issue in "structural estimation". Typically, data on exogenous variables (that is, variables other than price and quantity, both of which are endogenous variables) are needed to perform such an estimation. An alternative to "structural estimation" is reduced-form estimation, which regresses each of the endogenous variables on the respective exogenous variables.
Macroeconomic uses of demand and supply
Demand and supply have also been generalised to explain macroeconomic variables in a market economy, including the quantity of total output and the general price level. The Aggregate Demand–Aggregate Supply model
may be the most direct application of supply and demand to
macroeconomics, but other macroeconomic models also use supply and
demand. Compared to microeconomic uses of demand and supply, different (and more controversial) theoretical considerations apply to such macroeconomic counterparts as aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Demand and supply are also used in macroeconomic theory to relate money supply and money demand to interest rates and to relate labor supply and labor demand to wage rates.
History
According
to Hamid S. Hosseini, the power of supply and demand was understood to
some extent by several early Muslim scholars, such as fourteenth-century
Mamluk scholar Ibn Taymiyyah,
who wrote: "If desire for goods increases while its availability
decreases, its price rises. On the other hand, if availability of the
good increases and the desire for it decreases, the price comes down".
John Locke's 1691 work Some Considerations on the Consequences of the Lowering of Interest and the Raising of the Value of Money includes an early and clear description of supply and demand and their relationship. In this description, demand is rent:
"The price of any commodity rises or falls by the proportion of the
number of buyer and sellers" and "that which regulates the price... [of
goods] is nothing else but their quantity in proportion to their rent".
The phrase "supply and demand" was first used by James Denham-Steuart in his Inquiry into the Principles of Political Economy, published in 1767. Adam Smith used the phrase in his 1776 book The Wealth of Nations, and David Ricardo titled one chapter of his 1817 work Principles of Political Economy and Taxation "On the Influence of Demand and Supply on Price".
In The Wealth of Nations, Smith generally assumed that the
supply price was fixed, but that its "merit" (value) would decrease as
its "scarcity" increased, in effect what was later called the law of
demand also. In Principles of Political Economy and Taxation, Ricardo more rigorously laid down the idea of the assumptions that were used to build his ideas of supply and demand. Antoine Augustin Cournot first developed a mathematical model of supply and demand in his 1838 Researches into the Mathematical Principles of Wealth, including diagrams.
During the late 19th century, the marginalist school of thought emerged. This field mainly was started by Stanley Jevons, Carl Menger and Léon Walras.
The key idea was that the price was set by the most expensive
price—that is, the price at the margin. This was a substantial change
from Adam Smith's thoughts on determining the supply price.
In his 1870 essay "On the Graphical Representation of Supply and Demand", Fleeming Jenkin
in the course of "introduc[ing] the diagrammatic method into the
English economic literature" published the first drawing of supply and
demand curves therein, including comparative statics from a shift of supply or demand and application to the labor market. The model was further developed and popularized by Alfred Marshall in the 1890 textbook Principles of Economics.
Role of government
In a capitalist system, the government does not prohibit private
property or prevent individuals from working where they please. The
government does not prevent firms from determining what wages they will
pay and what prices they will charge for their products. However, many
countries have minimum wage laws and minimum safety standards.
Under some versions of capitalism, the government carries out a
number of economic functions, such as issuing money, supervising public
utilities and enforcing private contracts. Many countries have competition laws
that prohibit monopolies and cartels from forming. Despite
anti-monopoly laws, large corporations can form near-monopolies in some
industries. Such firms can temporarily drop prices and accept losses to
prevent competition from entering the market and then raise them again
once the threat of entry is reduced. In many countries, public utilities
(e.g. electricity, heating fuel and communications) are able to operate
as a monopoly under government regulation due to high economies of
scale.
Government agencies regulate the standards of service in many
industries, such as airlines and broadcasting as well as financing a
wide range of programs. In addition, the government regulates the flow
of capital and uses financial tools such as the interest rate to control
factors such as inflation and unemployment.
Relationship to political freedom
In his book The Road to Serfdom, Friedrich Hayek asserts that the economic freedom of capitalism is a requisite of political freedom.
He argues that the market mechanism is the only way of deciding what to
produce and how to distribute the items without using coercion. Milton Friedman, Andrew Brennan and Ronald Reagan also promoted this view. Friedman claimed that centralized economic operations are always accompanied by political repression.
In his view, transactions in a market economy are voluntary and that
the wide diversity that voluntary activity permits is a fundamental
threat to repressive political leaders and greatly diminish their power
to coerce. Some of Friedman's views were shared by John Maynard Keynes, who believed that capitalism is vital for freedom to survive and thrive. Freedom House,
an American think tank that conducts international research on and
advocates for, democracy, political freedom and human rights, has argued
"there is a high and statistically significant correlation between the
level of political freedom as measured by Freedom House and economic freedom as measured by the Wall Street Journal/Heritage Foundation survey".
Types of capitalism
There
are many variants of capitalism in existence that differ according to
country and region. They vary in their institutional makeup and by their
economic policies. The common features among all the different forms of
capitalism is that they are based on the production of goods and
services for profit, predominantly market-based allocation of resources
and they are structured upon the accumulation of capital. The major
forms of capitalism are listed hereafter:
Advanced capitalism
Advanced capitalism is the situation that pertains to a society in which the capitalist model has been integrated and developed deeply and extensively for a prolonged period. Various writers identify Antonio Gramsci
as an influential early theorist of advanced capitalism, even if he did
not use the term himself. In his writings, Gramsci sought to explain
how capitalism had adapted to avoid the revolutionary overthrow that had
seemed inevitable in the 19th century. At the heart of his explanation
was the decline of raw coercion as a tool of class power, replaced by
use of civil society institutions to manipulate public ideology in the capitalists' favour.
Jürgen Habermas
has been a major contributor to the analysis of advanced-capitalistic
societies. Habermas observed four general features that characterise
advanced capitalism:
- Concentration of industrial activity in a few large firms.
- Constant reliance on the state to stabilise the economic system.
- A formally democratic government that legitimises the activities of the state and dissipates opposition to the system.
- The use of nominal wage increases to pacify the most restless segments of the work force.
Finance capitalism
In their critique of capitalism, Marxism and Leninism both emphasise the role of "finance capital" as the determining and ruling-class interest in capitalist society, particularly in the latter stages.
Rudolf Hilferding is credited with first bringing the term "finance capitalism" into prominence through Finance Capital, his 1910 study of the links between German trusts, banks and monopolies—a study subsumed by Vladimir Lenin into Imperialism, the Highest Stage of Capitalism (1917), his analysis of the imperialist relations of the great world powers.
Lenin concluded that the banks at that time operated as "the chief
nerve centres of the whole capitalist system of national economy". For the Comintern (founded in 1919), the phrase "dictatorship of finance capitalism" became a regular one.
Fernnand Braudel
would later point to two earlier periods when finance capitalism had
emerged in human history—with the Genoese in the 16th century and with
the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries—although at those points it
developed from commercial capitalism. Giovanni Arrighi
extended Braudel's analysis to suggest that a predominance of finance
capitalism is a recurring, long-term phenomenon, whenever a previous
phase of commercial/industrial capitalist expansion reaches a plateau.
Mercantilism
The subscription room at Lloyd's of London in the early 19th century
Mercantilism is a nationalist form of early capitalism that came into
existence approximately in the late 16th century. It is characterized
by the intertwining of national business interests to state-interest and
imperialism; and consequently, the state apparatus is utilized to
advance national business interests abroad. An example of this is
colonists living in America who were only allowed to trade with and
purchase goods from their respective mother countries (e.g. Britain,
Portugal and France). Mercantilism was driven by the belief that the
wealth of a nation is increased through a positive balance of trade with
other nations—it corresponds to the phase of capitalist development
sometimes called the primitive accumulation of capital.
Free market economy
Free market economy refers to a capitalist economic system where
prices for goods and services are set freely by the forces of supply and
demand and are allowed to reach their point of equilibrium without
intervention by government policy. It typically entails support for
highly competitive markets and private ownership of productive
enterprises. Laissez-faire is a more extensive form of free market economy where the role of the state is limited to protecting property rights, or for plumbline anarcho-capitalists, property rights are protected by private firms and market-generated law.
Social market economy
A social market economy is a nominally free market system where
government intervention in price formation is kept to a minimum, but the
state provides significant services in the area of social security,
unemployment benefits and recognition of labor rights through national collective bargaining
arrangements. This model is prominent in Western and Northern European
countries as well as Japan, albeit in slightly different configurations.
The vast majority of enterprises are privately owned in this economic
model.
Rhine capitalism
refers to the contemporary model of capitalism and adaptation of the
social market model that exists in continental Western Europe today.
State capitalism
State capitalism is a capitalist market economy dominated by
state-owned enterprises, where the state enterprises are organized as
commercial, profit-seeking businesses. The designation has been used
broadly throughout the 20th century to designate a number of different
economic forms, ranging from state-ownership in market economies to the
command economies of the former Eastern Bloc. According to Aldo Musacchio, a professor at Harvard Business School,
state capitalism is a system in which governments, whether democratic or
autocratic, exercise a widespread influence on the economy either
through direct ownership or various subsidies. Musacchio notes a number
of differences between today's state capitalism and its predecessors. In
his opinion, gone are the days when governments appointed bureaucrats
to run companies: the world's largest state-owned enterprises are now
traded on the public markets and kept in good health by large
institutional investors. Contemporary state capitalism is associated
with the East Asian model of capitalism, dirigisme and the economy of Norway. Alternatively, Merriam-Webster
defines state capitalism as "an economic system in which private
capitalism is modified by a varying degree of government ownership and
control".
In Socialism: Utopian and Scientific, Friedrich Engels
argued that state-owned enterprises would characterize the final stage
of capitalism, consisting of ownership and management of large-scale
production and communication by the bourgeois state. In his writings, Vladimir Lenin
characterized the economy of Soviet Russia as state capitalist,
believing state capitalism to be an early step toward the development of
socialism.
Some economists and left-wing academics including Richard D. Wolff and Noam Chomsky argue that the economies of the former Soviet Union
and Eastern bloc represented a form of state capitalism because their
internal organization within enterprises and the system of wage labor
remained intact.
The term is not used by Austrian School economists to describe state ownership of the means of production. The economist Ludwig von Mises
argued that the designation of "state capitalism" was simply a new
label for the old labels of "state socialism" and "planned economy" and
differed only in non-essentials from these earlier designations.
The debate between proponents of private versus state capitalism
is centered around questions of managerial efficacy, productive
efficiency and fair distribution of wealth.
Corporate capitalism
Corporate capitalism is a free or mixed-market economy characterized
by the dominance of hierarchical, bureaucratic corporations.
Mixed economy
A mixed economy is a largely market-based economy consisting of both
private and public ownership of the means of production and economic interventionism through macroeconomic policies intended to correct market failures,
reduce unemployment and keep inflation low. The degree of intervention
in markets varies among different countries. Some mixed economies, such
as France under dirigisme, also featured a degree of indirect economic planning over a largely capitalist-based economy.
Most [DJS -- all?] modern capitalist economies are defined as "mixed economies" to some degree.
Others
Other variants of capitalism include:
|
|
|
Capital accumulation
The accumulation of capital
is the process of "making money", or growing an initial sum of money
through investment in production. Capitalism is based on the
accumulation of capital, whereby financial capital
is invested in order to make a profit and then reinvested into further
production in a continuous process of accumulation. In Marxian economic
theory, this dynamic is called the law of value. Capital accumulation forms the basis of capitalism, where economic activity is structured around the accumulation of capital, defined as investment in order to realize a financial profit.
In this context, "capital" is defined as money or a financial asset
invested for the purpose of making more money (whether in the form of
profit, rent, interest, royalties, capital gain or some other kind of
return).
In mainstream economics, accounting and Marxian economics, capital accumulation is often equated with investment of profit income or saving, especially in real capital goods. The concentration and centralisation of capital are two of the results of such accumulation. In modern macroeconomics and econometrics, the phrase "capital formation" is often used in preference to "accumulation", though the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) refers nowadays to "accumulation". The term “accumulation” is occasionally used in national accounts.
Background
Accumulation
can be measured as the monetary value of investments, the amount of
income that is reinvested, or as the change in the value of assets owned
(the increase in the value of the capital stock). Using company balance sheets, tax data and direct surveys as a basis, government statisticians estimate total investments and assets for the purpose of national accounts, national balance of payments and flow of funds statistics. The Reserve Banks and the Treasury usually provide interpretations and analysis of this data. Standard indicators include capital formation, gross fixed capital formation, fixed capital, household asset wealth and foreign direct investment.
Organisations such as the International Monetary Fund, the UNCTAD, the World Bank Group, the OECD and the Bank for International Settlements used national investment data to estimate world trends. The Bureau of Economic Analysis, Eurostat
and the Japan Statistical Office provide data on the United States,
Europe and Japan respectively. Other useful sources of investment
information are business magazines such as Fortune, Forbes, The Economist, Business Week and so on as well as various corporate "watchdog" organisations and non-governmental organisation publications. A reputable scientific journal is the Review of Income & Wealth.
In the case of the United States, the "Analytical Perspectives"
document (an annex to the yearly budget) provides useful wealth and
capital estimates applying to the whole country.
In Karl Marx'
economic theory, capital accumulation refers to the operation whereby
profits are reinvested increasing the total quantity of capital. Capital
is viewed by Marx as expanding value, that is, in other terms, as a sum
of capital, usually expressed in money, that is transformed through
human labor into a larger value, extracted as profits and expressed as
money. Here, capital is defined essentially as economic or commercial
asset value in search of additional value or surplus-value.
This requires property relations which enable objects of value to be
appropriated and owned, and trading rights to be established. Capital
accumulation has a double origin, namely in trade and in expropriation,
both of a legal or illegal kind. The reason is that a stock of capital
can be increased through a process of exchange or "trading up", but also
through directly taking an asset or resource from someone else without
compensation. David Harvey calls this accumulation by dispossession.
The continuation and progress of capital accumulation depends on
the removal of obstacles to the expansion of trade and this has
historically often been a violent process. As markets expand, more and
more new opportunities develop for accumulating capital because more and
more types of goods and services can be traded in. However, capital
accumulation may also confront resistance when people refuse to sell, or
refuse to buy (for example a strike by investors or workers, or consumer resistance).
Concentration and centralisation
According
to Marx, capital has the tendency for concentration and centralization
in the hands of the wealthy. Marx explains: "It is concentration of
capitals already formed, destruction of their individual independence,
expropriation of capitalist by capitalist, transformation of many small
into few large capitals. [...] Capital grows in one place to a huge mass
in a single hand, because it has in another place been lost by many.
[...] The battle of competition is fought by cheapening of commodities.
The cheapness of commodities demands, caeteris paribus, on the
productiveness of labour, and this again on the scale of production.
Therefore, the larger capitals beat the smaller. It will further be
remembered that, with the development of the capitalist mode of
production, there is an increase in the minimum amount of individual
capital necessary to carry on a business under its normal conditions.
The smaller capitals, therefore, crowd into spheres of production which
Modern Industry has only sporadically or incompletely got hold of. Here
competition rages [...] It always ends in the ruin of many small
capitalists, whose capitals partly pass into the hands of their
conquerors, partly vanish".
The rate of accumulation
In Marxian economics, the rate of accumulation is defined as (1) the value of the real net increase in the stock of capital in an accounting period; and (2) the proportion of realised surplus-value
or profit-income which is reinvested, rather than consumed. This rate
can be expressed by means of various ratios between the original capital
outlay, the realised turnover, surplus-value or profit and
reinvestments (e.g. the writings of the economist Michał Kalecki).
Other things being equal, the greater the amount of profit-income
that is disbursed as personal earnings and used for consumptive
purposes, the lower the savings rate and the lower the rate of
accumulation is likely to be. However, earnings spent on consumption can
also stimulate market demand and higher investment. This is the cause
of endless controversies in economic theory about "how much to spend,
and how much to save".
In a boom period of capitalism, the growth of investments is
cumulative, i.e. one investment leads to another, leading to a
constantly expanding market, an expanding labor force and an increase in the standard of living for the majority of the people.
In a stagnating, decadent capitalism, the accumulation process is
increasingly oriented towards investment on military and security
forces, real estate, financial speculation and luxury consumption. In
that case, income from value-adding
production will decline in favour of interest, rent and tax income,
with as a corollary an increase in the level of permanent unemployment.
The more capital one owns, the more capital one can also borrow. The
inverse is also true and this is one factor in the widening gap between
the rich and the poor.
Ernest Mandel
emphasised that the rhythm of capital accumulation and growth depended
critically on (1) the division of a society's social product between "necessary product" and "surplus product"; and (2) the division of the surplus product between investment and consumption. In turn, this allocation pattern reflected the outcome of competition
among capitalists, competition between capitalists and workers and
competition between workers. The pattern of capital accumulation can
therefore never be simply explained by commercial factors as it also
involved social factors and power relationships.
The circuit of capital accumulation from production
Strictly speaking, capital has accumulated only when realised profit income has been reinvested in capital assets. As suggested in the first volume of Marx' Das Kapital, the process of capital accumulation in production has at least seven distinct but linked moments:
- The initial investment of capital (which could be borrowed capital) in means of production and labor power.
- The command over surplus-labour and its appropriation.
- The valorisation (increase in value) of capital through production of new outputs.
- The appropriation of the new output produced by employees, containing the added value.
- The realisation of surplus-value through output sales.
- The appropriation of realised surplus-value as (profit) income after deduction of costs.
- The reinvestment of profit income in production.
All of these moments do not refer simply to an "economic" or
commercial process. Rather, they assume the existence of legal, social,
cultural and economic power conditions, without which creation,
distribution and circulation of the new wealth could not occur. This
becomes especially clear when the attempt is made to create a market
where none exists, or where people refuse to trade.
Simple and expanded reproduction
In the second volume of Das Kapital, Marx continues the story and shows that with the aid of bank credit
capital in search of growth can more or less smoothly mutate from one
form to another, alternately taking the form of money capital (liquid
deposits, securities and so on), commodity capital (tradable products,
real estate and the like), or production capital (means of production and labor power).
His discussion of the simple and expanded reproduction
of the conditions of production offers a more sophisticated model of
the parameters of the accumulation process as a whole. At simple
reproduction, a sufficient amount is produced to sustain society at the
given living standard;
the stock of capital stays constant. At expanded reproduction, more
product-value is produced than is necessary to sustain society at a
given living standard (a surplus product); the additional product-value is available for investments which enlarge the scale and variety of production.
The bourgeois claim there is no economic law
according to which capital is necessarily re-invested in the expansion
of production, that such depends on anticipated profitability, market
expectations and perceptions of investment risk. Such statements only
explain the subjective experiences of investors and ignore the objective
realities which would influence such opinions. As Marx states in the
second volume of Das Kapital, simple reproduction only exists if
the variable and surplus capital realised by Dept. 1—producers of means
of production—exactly equals that of the constant capital of Dept. 2,
producers of articles of consumption (p. 524). Such equilibrium rests on
various assumptions, such as a constant labor supply (no population
growth). Accumulation does not imply a necessary change in total
magnitude of value produced, but can simply refer to a change in the
composition of an industry (p. 514).
Ernest Mandel
introduced the additional concept of contracted economic reproduction,
i.e. reduced accumulation where business operating at a loss outnumbers
growing business, or economic reproduction on a decreasing scale, for
example due to wars, natural disasters or devalorisation.
Balanced economic growth
requires that different factors in the accumulation process expand in
appropriate proportions. However, markets themselves cannot
spontaneously create that balance and in fact what drives business
activity is precisely the imbalances between supply and demand:
inequality is the motor of growth. This partly explains why the
worldwide pattern of economic growth is very uneven and unequal, even
although markets have existed almost everywhere for a very long-time.
Some people argue that it also explains government regulation of market
trade and protectionism.
Capital accumulation as social relation
"Accumulation of capital" sometimes also refers in Marxist writings to the reproduction of capitalist social relations (institutions) on a larger scale over time, i.e. the expansion of the size of the proletariat and of the wealth owned by the bourgeoisie.
This interpretation emphasises that capital ownership, predicated on
command over labor, is a social relation: the growth of capital implies
the growth of the working class (a "law of accumulation"). In the first volume of Das Kapital, Marx had illustrated this idea with reference to Edward Gibbon Wakefield's theory of colonisation:
Wakefield discovered that in the Colonies, property in money, means of subsistence, machines, and other means of production, does not as yet stamp a man as a capitalist if there be wanting the correlative—the wage-worker, the other man who is compelled to sell himself of his own free-will. He discovered that capital is not a thing, but a social relation between persons, established by the instrumentality of things. Mr. Peel, he moans, took with him from England to Swan River, West Australia, means of subsistence and of production to the amount of £50,000. Mr. Peel had the foresight to bring with him, besides, 3,000 persons of the working-class, men, women, and children. Once arrived at his destination, 'Mr. Peel was left without a servant to make his bed or fetch him water from the river.' Unhappy Mr. Peel, who provided for everything except the export of English modes of production to Swan River!
— Das Kapital, vol. 1, ch. 33
In the third volume of Das Kapital,
Marx refers to the "fetishism of capital" reaching its highest point
with interest-bearing capital because now capital seems to grow of its
own accord without anybody doing anything:
The relations of capital assume their most externalised and most fetish-like form in interest-bearing capital. We have here , money creating more money, self-expanding value, without the process that effectuates these two extremes. In merchant's capital, , there is at least the general form of the capitalistic movement, although it confines itself solely to the sphere of circulation, so that profit appears merely as profit derived from alienation; but it is at least seen to be the product of a social relation, not the product of a mere thing. [...] This is obliterated in , the form of interest-bearing capital. [...] The thing (money, commodity, value) is now capital even as a mere thing, and capital appears as a mere thing. The result of the entire process of reproduction appears as a property inherent in the thing itself. It depends on the owner of the money, i.e., of the commodity in its continually exchangeable form, whether he wants to spend it as money or loan it out as capital. In interest-bearing capital, therefore, this automatic fetish, self-expanding value, money generating money, are brought out in their pure state and in this form it no longer bears the birth-marks of its origin. The social relation is consummated in the relation of a thing, of money, to itself. Instead of the actual transformation of money into capital, we see here only form without content.
— Das Kapital, vol. 1, ch. 24
Wage labour
An industrial worker amidst heavy steel semi-products (Kinex Bearings, Bytča, Slovakia, c. 1995–2000)
Wage labour refers to the sale of labour under a formal or informal employment contract to an employer. These transactions usually occur in a labour market where wages are market determined. Individuals who possess and supply financial capital or labor to productive ventures often become owners, either jointly (as shareholders)
or individually. In Marxist economics, these owners of the means of
production and suppliers of capital are generally called capitalists.
The description of the role of the capitalist has shifted, first
referring to a useless intermediary between producers to an employer of
producers and eventually came to refer to owners of the means of
production. Labor
includes all physical and mental human resources, including
entrepreneurial capacity and management skills, which are needed to
produce products and services. Production is the act of making goods or services by applying labor power.
Critics of the capitalist mode of production see wage labour as a
major, if not defining, aspect of hierarchical industrial systems. Most
opponents of the institution support worker self-management and economic democracy
as alternatives to both wage labour and to capitalism. While most
opponents of the wage system blame the capitalist owners of the means of
production for its existence, most anarchists and other libertarian socialists
also hold the state as equally responsible as it exists as a tool
utilised by capitalists to subsidise themselves and protect the
institution of private ownership of the means of production. As some opponents of wage labour take influence from Marxist propositions, many are opposed to private property, but maintain respect for personal property.
Types
The most
common form of wage labour currently is ordinary direct, or "full-time",
employment in which a free worker sells his or her labour for an
indeterminate time (from a few years to the entire career of the worker)
in return for a money-wage or salary and a continuing relationship with
the employer which it does not in general offer contractors or other
irregular staff. However, wage labour takes many other forms and
explicit as opposed to implicit (i.e. conditioned by local labour and
tax law) contracts are not uncommon. Economic history shows a great
variety of ways in which labour is traded and exchanged. The differences
show up in the form of:
- Employment status: a worker could be employed full-time, part-time, or on a casual basis. He or she could be employed for example temporarily for a specific project only, or on a permanent basis. Part-time wage labour could combine with part-time self-employment. The worker could be employed also as an apprentice.
- Civil (legal) status: the worker could for example be a free citizen, an indentured labourer, the subject of forced labour (including some prison or army labour); a worker could be assigned by the political authorities to a task, they could be a semi-slave or a serf bound to the land who is hired out part of the time. So the labour might be performed on a more or less voluntary basis, or on a more or less involuntary basis, in which there are many gradations.
- Method of payment (remuneration or compensation): the work done could be paid "in cash" (a money-wage) or "in kind" (through receiving goods and/or services), or in the form of "piece rates" where the wage is directly dependent on how much the worker produces. In some cases, the worker might be paid in the form of credit used to buy goods and services, or in the form of stock options or shares in an enterprise.
- Method of hiring: the worker might engage in a labour-contract on his or her own initiative, or he or she might hire out their labour as part of a group. However, he or she may also hire out their labour via an intermediary (such as an employment agency) to a third party. In this case, he or she is paid by the intermediary, but works for a third party which pays the intermediary. In some cases, labour is subcontracted several times, with several intermediaries. Another possibility is that the worker is assigned or posted to a job by a political authority, or that an agency hires out a worker to an enterprise together with the means of production.
Effects of war
The common view among economic historians is that the Great Depression ended with the advent of World War II (assembling the North American B-25 Mitchell at Kansas City, 1942)
War typically causes the diversion, destruction and creation of
capital assets as capital assets are both destroyed or consumed and
diverted to types of production needed to fight the war. Many assets are
wasted and in some few cases created specifically to fight a war. War
driven demands may be a powerful stimulus for the accumulation of
capital and production capability in limited areas and market expansion
outside the immediate theatre of war. Often this has induced laws
against perceived and real war profiteering.
The total hours worked in the United States rose by 34 percent
during World War II, even though the military draft reduced the civilian
labor force by 11 percent.
War destruction can be illustrated by looking at World War II.
Industrial war damage was heaviest in Japan, where 1/4 of factory
buildings and 1/3 of plant and equipment were destroyed; 1/7 of electric
power-generating capacity was destroyed and 6/7 of oil refining
capacity. The Japanese merchant fleet lost 80% of their ships. In
Germany in 1944, when air attacks were heaviest, 6.5% of machine tools
were damaged or destroyed, but around 90% were later repaired. About 10%
of steel production capacity was lost. In Europe, the United States and
the Soviet Union enormous resources were accumulated and ultimately
dissipated as planes, ships, tanks and so on were built and then lost or
destroyed.
Germany's total war damage was estimated at about 17.5% of the pre-war total capital stock by value, i.e. about 1/6. In the Berlin
area alone, there were 8 million refugees lacking basic necessities. In
1945, less than 10% of the railways were still operating. 2,395 rail
bridges were destroyed and a total of 7,500 bridges, 10,000 locomotives
and more than 100,000 goods wagons were destroyed. Less than 40% of the
remaining locomotives were operational.
However, by the first quarter of 1946 European rail traffic,
which was given assistance and preferences (by Western appointed
military governors) for resources and material as an essential asset,
regained its prewar operational level. At the end of the year, 90% of
Germany's railway lines were operating again. In retrospect, the
rapidity of infrastructure reconstruction appears astonishing.
Initially, in May 1945 newly installed United States president Harry S. Truman's
directive had been that no steps would be taken towards economic
rehabilitation of Germany. In fact, the initial industry plan of 1946
prohibited production in excess of half of the 1938 level; the iron and
steel industry was allowed to produce only less than a third of pre-war
output. These plans were rapidly revised and better plans were
instituted. In 1946, over 10% of Germany's physical capital stock (plant
and equipment) was also dismantled and confiscated, most of it going to
the Soviet Union. By 1947, industrial production in Germany was at 1/3
of the 1938 level and industrial investment at about 1/2 the 1938 level.
The first big strike-wave in the Ruhr
occurred in early 1947—it was about food rations and housing, but soon
there were demands for nationalisation. However, the United States
appointed military governor (Newman) stated at the time that he had the
power to break strikes by withholding food rations. The clear message
was "no work, no eat". As the military controls in Western Germany were
nearly all relinquished and the Germans were allowed to rebuild their
own economy with Marshall Plan
aid things rapidly improved. By 1951, German industrial production had
overtaken the prewar level. The Marshall Aid funds were important, but
after the currency reform (which permitted German capitalists to revalue
their assets) and the establishment of a new political system much more
important was the commitment of the United States to rebuilding German
capitalism and establishing a free market economy and government, rather
than keeping Germany in a weak position. Initially, average real wages
remained low, lower even than in 1938, until the early 1950s while
profitability was unusually high. So the total investment fund, aided by
credits, was also high, resulting in a high rate of capital
accumulation which was nearly all reinvested in new construction or new
tools. This was called the German economic miracle or Wirtschaftswunder.
In Italy, the victorious Allies did three things in 1945: they
imposed their absolute military authority; they quickly disarmed the
Italian partisans from a very large stock of weapons; and they agreed to
a state guarantee of wage payments as well as a veto on all sackings of
workers from their jobs.
Although the Italian Communist Party grew very large immediately after
the war ended—it achieved a membership of 1.7 million people in a
population of 45 million—it was outmaneuvered through a complicated
political battle by the Christian Democrats after three years. In the 1950s, an economic boom began in Italy, at first fueled by internal demand and then also by exports.
In modern times, it has often been possible to rebuild physical
capital assets destroyed in wars completely within the space of about 10
years, except in cases of severe pollution by chemical warfare or other kinds of irreparable devastation. However, damage to human capital
has been much more devastating in terms of fatalities (in the case of
World War II, about 55 million deaths), permanent physical disability,
enduring ethnic hostility and psychological injuries which have effects
for at least several generations.