Gautama Buddha
| |
|---|---|

A statue of the Buddha from Sarnath, Uttar Pradesh, India, 4th century CE. The Buddha is depicted teaching in the lotus position, while making the Dharmacakra mudrā.
| |
| Other names | Siddhartha Gautama, Siddhattha Gotama, Shakyamuni |
| Personal | |
| Born |
Siddhartha Gautama
c. 563 or c. 480 BCE
Lumbini, Shakya Republic (according to Buddhist tradition)
|
| Died | c. 483 or c. 400 BCE (aged 80)
Kushinagar, Malla Republic (according to Buddhist tradition)
|
| Religion | Buddhism |
| Spouse | Yasodharā |
| Children | |
| Parents |
|
| Known for | Founder of Buddhism |
| Other names | Siddhartha Gautama, Siddhattha Gotama, Shakyamuni |
| Senior posting | |
| Predecessor | Kassapa Buddha |
| Successor | Maitreya |
Gautama Buddha (c. 563/480 – c. 483/400 BCE), also known as Siddhārtha Gautama (सिद्धार्थ गौतम) in Sanskrit or Siddhattha Gotama (शिद्धत्थ गोतम) in Pali , Shakyamuni (i.e. "Sage of the Shakyas") Buddha, or simply the Buddha, after the title of Buddha, was a monk (śramaṇa), mendicant, sage, philosopher, teacher and religious leader on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. He is believed to have lived and taught mostly in the northeastern part of ancient India sometime between the 6th and 4th centuries BCE.
Gautama taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and the severe asceticism found in the śramaṇa movement common in his region. He later taught throughout other regions of eastern India such as Magadha and Kosala.
Gautama is the primary figure in Buddhism. He is believed by Buddhists to be an enlightened teacher who attained full Buddhahood and shared his insights to help sentient beings end rebirth and suffering. Accounts of his life, discourses and monastic rules are believed by Buddhists to have been summarised after his death and memorized by his followers. Various collections of teachings attributed to him were passed down by oral tradition and first committed to writing about 400 years later.
Historical Siddhārtha Gautama
Scholars are hesitant to make unqualified claims about the historical facts of the Buddha's life. Most people accept that the Buddha lived, taught, and founded a monastic order during the Mahajanapada era during the reign of Bimbisara (c. 558 – c. 491 BCE, or c. 400 BCE), the ruler of the Magadha empire, and died during the early years of the reign of Ajatasatru, who was the successor of Bimbisara, thus making him a younger contemporary of Mahavira, the Jain tirthankara. While the general sequence of "birth, maturity, renunciation, search, awakening and liberation, teaching, death" is widely accepted, there is less consensus on the veracity of many details contained in traditional biographies.The times of Gautama's birth and death are uncertain. Most historians in the early 20th century dated his lifetime as c. 563 BCE to 483 BCE. More recently his death is dated later, between 411 and 400 BCE, while at a symposium on this question held in 1988, the majority of those who presented definite opinions gave dates within 20 years either side of 400 BCE for the Buddha's death. These alternative chronologies, however, have not been accepted by all historians.
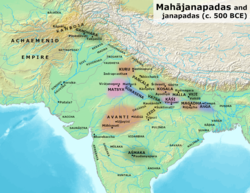
Historical context
Ancient kingdoms and cities of India during the time of the Buddha (circa 500 BCE).
The evidence of the early texts suggests that Siddhārtha Gautama was born into the Shakya
clan, a community that was on the periphery, both geographically and
culturally, of the eastern Indian subcontinent in the 5th century BCE. One of his usual names was "Sakamuni" or "Sakyamunī" ("Sage of the Shakyas"). It was either a small republic, or an oligarchy, and his father was an elected chieftain, or oligarch. According to the Buddhist tradition, Gautama was born in Lumbini, now in modern-day Nepal, and raised in the Shakya capital of Kapilvastu, which may have been either in what is present day Tilaurakot, Nepal or Piprahwa, India. According to Buddhist tradition, he obtained his enlightenment in Bodh Gaya, gave his first sermon in Sarnath, and died in Kushinagar.
Apart from the Vedic Brahmins, the Buddha's lifetime coincided with the flourishing of influential Śramaṇa schools of thought like Ājīvika, Cārvāka, Jainism, and Ajñana. Brahmajala Sutta
records sixty-two such schools of thought. In this context, a śramaṇa
refers to one who labors, toils, or exerts themselves (for some higher
or religious purpose). It was also the age of influential thinkers like Mahavira, Pūraṇa Kassapa, Makkhali Gosāla, Ajita Kesakambalī, Pakudha Kaccāyana, and Sañjaya Belaṭṭhaputta, as recorded in Samaññaphala Sutta, whose viewpoints the Buddha most certainly must have been acquainted with. Indeed, Sariputta and Moggallāna, two of the foremost disciples of the Buddha, were formerly the foremost disciples of Sañjaya Belaṭṭhaputta, the sceptic;
and the Pali canon frequently depicts Buddha engaging in debate with
the adherents of rival schools of thought. There is also philological
evidence to suggest that the two masters, Alara Kalama and Uddaka Ramaputta, were indeed historical figures and they most probably taught Buddha two different forms of meditative techniques. Thus, Buddha was just one of the many śramaṇa philosophers of that time. In an era where holiness of person was judged by their level of asceticism, Buddha was a reformist within the śramaṇa movement, rather than a reactionary against Vedic Brahminism.
Historically, the life of the Buddha also coincided with the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley during the rule of Darius I from about 517/516 BCE. This Achaemenid occupation of the areas of Gandhara and Sindh, which was to last for about two centuries, was accompanied by the introduction of Achaemenid religions, reformed Mazdaism or early Zoroastrianism, to which Buddhism might have in part reacted.
In particular, the ideas of the Buddha may have partly consisted of a
rejection of the "absolutist" or "perfectionist" ideas contained in
these Achaemenid religions.
Earliest sources
The words "Bu-dha" (𑀩𑀼𑀥, the Buddha) and "Sa-kya-mu-nī " ( 𑀲𑀓𑁆𑀬𑀫𑀼𑀦𑀻, "Sage of the Shakyas") in Brahmi script, on Ashoka's Rummindei Minor Pillar Edict (circa 250 BCE).
No written records about Gautama were found from his lifetime or from
the one or two centuries thereafter. In the middle of the 3rd century
BCE, several Edicts of Ashoka (reigned c. 269–232 BCE) mention the Buddha, and particularly Ashoka's Rummindei Minor Pillar Edict commemorates the Emperor's pilgrimage to Lumbini as the Buddha's birthplace. Another one of his edicts (Minor Rock Edict No. 3) mentions the titles of several Dhamma texts, establishing the existence of a written Buddhist tradition at least by the time of the Maurya era. These texts may be the precursor of the Pāli Canon.
Bharhut inscription: Bhagavato Sakamunino Bodho (𑀪𑀕𑀯𑀢𑁄 𑀲𑀓𑀫𑀼𑀦𑀺𑀦𑁄 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑁄 "The illumination of the Blessed Sakamuni"), circa 100 BCE.
"Sakamuni" in also mentioned in the reliefs of Bharhut, dated to circa 100 BCE, in relation with his illumination and the Bodhi tree, with the inscription Bhagavato Sakamunino Bodho ("The illumination of the Blessed Sakamuni").
The oldest surviving Buddhist manuscripts are the Gandhāran Buddhist texts, reported to have been found in or around Haḍḍa near Jalalabad in eastern Afghanistan and now preserved in the British Library. They are written in the Gāndhārī language using the Kharosthi script on twenty-seven birch bark manuscripts and date from the first century BCE to the third century CE.
On the basis of philological evidence, Indologist and Pali expert Oskar von Hinüber
says that some of the Pali suttas have retained very archaic
place-names, syntax, and historical data from close to the Buddha's
lifetime, including the Mahāparinibbāṇa Sutta
which contains a detailed account of the Buddha's final days. Hinüber
proposes a composition date of no later than 350–320 BCE for this text,
which would allow for a "true historical memory" of the events
approximately 60 years prior if the Short Chronology for the Buddha's
lifetime is accepted (but also reminds that such a text was originally
intended more as hagiography than as an exact historical record of events).
Traditional biographies
The first known anthropomorphic representation of the Buddha, here surrounded by Brahma (left) and Śakra (right). Bimaran Casket, mid-1st century CE, British Museum.
Biographical sources
The sources for the life of Siddhārtha Gautama are a variety of
different, and sometimes conflicting, traditional biographies. These
include the Buddhacarita, Lalitavistara Sūtra, Mahāvastu, and the Nidānakathā. Of these, the Buddhacarita is the earliest full biography, an epic poem written by the poet Aśvaghoṣa in the first century CE. The Lalitavistara Sūtra is the next oldest biography, a Mahāyāna/Sarvāstivāda biography dating to the 3rd century CE. The Mahāvastu from the Mahāsāṃghika Lokottaravāda tradition is another major biography, composed incrementally until perhaps the 4th century CE. The Dharmaguptaka biography of the Buddha is the most exhaustive, and is entitled the Abhiniṣkramaṇa Sūtra, and various Chinese translations of this date between the 3rd and 6th century CE. The Nidānakathā is from the Theravada tradition in Sri Lanka and was composed in the 5th century by Buddhaghoṣa.
From canonical sources come the Jataka tales, the Mahapadana Sutta (DN 14), and the Achariyabhuta Sutta
(MN 123), which include selective accounts that may be older, but are
not full biographies. The Jātakas retell previous lives of Gautama as a bodhisattva, and the first collection of these can be dated among the earliest Buddhist texts. The Mahāpadāna Sutta and Achariyabhuta Sutta both recount miraculous events surrounding Gautama's birth, such as the bodhisattva's descent from the Tuṣita Heaven into his mother's womb.
Nature of traditional depictions
Māyā miraculously giving birth to Siddhārtha. Sanskrit, palm-leaf manuscript. Nālandā, Bihar, India. Pāla period
In the earliest Buddhist texts, the nikāyas and āgamas, the Buddha is not depicted as possessing omniscience (sabbaññu) nor is he depicted as being an eternal transcendent (lokottara) being. According to Bhikkhu Analayo,
ideas of the Buddha's omniscience (along with an increasing tendency to
deify him and his biography) are found only later, in the Mahayana sutras and later Pali commentaries or texts such as the Mahāvastu. In the Sandaka Sutta, the Buddha's disciple Ananda outlines an argument against the claims of teachers who say they are all knowing while in the Tevijjavacchagotta Sutta
the Buddha himself states that he has never made a claim to being
omniscient, instead he claimed to have the "higher knowledges" (abhijñā). The earliest biographical material from the Pali Nikayas focuses on the Buddha's life as a śramaṇa, his search for enlightenment under various teachers such as Alara Kalama and his forty-five-year career as a teacher.
Traditional biographies of Gautama generally include numerous
miracles, omens, and supernatural events. The character of the Buddha in
these traditional biographies is often that of a fully transcendent
(Skt. lokottara) and perfected being who is unencumbered by the mundane world. In the Mahāvastu,
over the course of many lives, Gautama is said to have developed
supramundane abilities including: a painless birth conceived without
intercourse; no need for sleep, food, medicine, or bathing, although
engaging in such "in conformity with the world"; omniscience, and the
ability to "suppress karma".
Nevertheless, some of the more ordinary details of his life have been
gathered from these traditional sources. In modern times there has been
an attempt to form a secular understanding of Siddhārtha Gautama's life by omitting the traditional supernatural elements of his early biographies.
Andrew Skilton writes that the Buddha was never historically regarded by Buddhist traditions as being merely human:
It is important to stress that, despite modern Theravada teachings to the contrary (often a sop to skeptical Western pupils), he was never seen as being merely human. For instance, he is often described as having the thirty-two major and eighty minor marks or signs of a mahāpuruṣa, "superman"; the Buddha himself denied that he was either a man or a god; and in the Mahāparinibbāna Sutta he states that he could live for an aeon were he asked to do so.
The ancient Indians were generally unconcerned with chronologies,
being more focused on philosophy. Buddhist texts reflect this tendency,
providing a clearer picture of what Gautama may have taught than of the
dates of the events in his life. These texts contain descriptions of the
culture and daily life of ancient India which can be corroborated from
the Jain scriptures, and make the Buddha's time the earliest period in Indian history for which significant accounts exist. British author Karen Armstrong
writes that although there is very little information that can be
considered historically sound, we can be reasonably confident that
Siddhārtha Gautama did exist as a historical figure.
Michael Carrithers goes a bit further by stating that the most general
outline of "birth, maturity, renunciation, search, awakening and
liberation, teaching, death" must be true.
Biography
Conception and birth
Maya's dream of the Birth of Gautama Siddhartha.
Birthplace of Gautama Buddha in Lumbini, Nepal, a holy shrine also for many non-Buddhists.
The Buddhist tradition regards Lumbini, in present-day Nepal to be the birthplace of the Buddha. He grew up in Kapilavastu. The exact site of ancient Kapilavastu is unknown. It may have been either Piprahwa, Uttar Pradesh, in present-day India, or Tilaurakot, in present-day Nepal. Both places belonged to the Sakya territory, and are located only 15 miles (24 km) apart.
Gautama was born to a Hindu
Kshatriya family, the son of Śuddhodana, "an elected chief of the Shakya clan", whose capital was Kapilavastu, and who were later annexed by the growing Kingdom of Kosala during the Buddha's lifetime. Gautama was the family name. His mother, Maya (Māyādevī), Suddhodana's wife, was a Koliyan princess. Legend has it that, on the night Siddhartha was conceived, Queen Maya dreamt that a white elephant with six white tusks entered her right side, and ten months later
Siddhartha was born. As was the Shakya tradition, when his mother Queen
Maya became pregnant, she left Kapilavastu for her father's kingdom to
give birth. However, her son is said to have been born on the way, at
Lumbini, in a garden beneath a sal tree.
The day of the Buddha's birth is widely celebrated in Theravada countries as Vesak. Buddha's Birthday is called Buddha Purnima
in Nepal, Bangladesh, and India as he is believed to have been born on a
full moon day. Various sources hold that the Buddha's mother died at
his birth, a few days or seven days later. The infant was given the name
Siddhartha (Pāli: Siddhattha), meaning "he who achieves his aim".
During the birth celebrations, the hermit seer Asita journeyed from his mountain abode and announced that the child would either become a great king (chakravartin) or a great sadhu. By traditional account,
this occurred after Siddhartha placed his feet in Asita's hair and
Asita examined the birthmarks. Suddhodana held a naming ceremony on the
fifth day, and invited eight Brahmin scholars to read the future. All gave a dual prediction that the baby would either become a great king or a great holy man. Kondañña, the youngest, and later to be the first arhat other than the Buddha, was reputed to be the only one who unequivocally predicted that Siddhartha would become a Buddha.
While later tradition and legend characterised Śuddhodana as a hereditary monarch, the descendant of the Suryavansha (Solar dynasty) of Ikṣvāku (Pāli: Okkāka), many scholars think that Śuddhodana was the elected chief of a tribal confederacy.
Early texts suggest that Gautama was not familiar with the
dominant religious teachings of his time until he left on his religious
quest, which is said to have been motivated by existential concern for
the human condition. The state of the Shakya clan was not a monarchy and seems to have been structured either as an oligarchy, or as a form of republic.
The more egalitarian gana-sangha form of government, as a political
alternative to the strongly hierarchical kingdoms, may have influenced
the development of the śramanic Jain and Buddhist sanghas, where monarchies tended toward Vedic Brahmanism.
| Birth and childhood of the Buddha |
|
Early life and marriage
Departure of Prince Siddhartha
Siddhartha was brought up by his mother's younger sister, Maha Pajapati.
By tradition, he is said to have been destined by birth to the life of a
prince and had three palaces (for seasonal occupation) built for him.
His father, said to be King Śuddhodana, wishing for his son to be a
great king, is said to have shielded him from religious teachings and
from knowledge of human suffering.
While Śuddhodana has traditionally been depicted as a king, and
Siddhartha as his prince, more recent scholarship suggests the Shakya were in-fact organised as a semi-republican oligarchy rather than a monarchy.
When he reached the age of 16, his father reputedly arranged his marriage to a cousin of the same age named Yaśodharā (Pāli: Yasodharā). According to the early Buddhist Texts of several schools, and numerous post-canonical accounts, she gave birth to a son, named Rāhula. Siddhartha is said to have spent 29 years as a prince in Kapilavastu.
Although his father ensured that Siddhartha was provided with
everything he could want or need, Buddhist scriptures say that the
future Buddha felt that material wealth was not life's ultimate goal.
Renunciation and ascetic life
The Victory of Buddha
The "Great Departure" of Siddhartha Gautama, surrounded by a halo, he is accompanied by numerous guards, maithuna loving couples, and devata who have come to pay homage; Gandhara, Kushan period
At the age of 29, Siddhartha left his palace to meet his subjects.
Despite his father's efforts to hide from him the sick, aged and
suffering, Siddhartha was said to have seen an old man. When his
charioteer Channa
explained to him that all people grew old, the prince went on further
trips beyond the palace. On these he encountered a diseased man, a
decaying corpse, and an ascetic. These depressed him, and he initially strove to overcome ageing, sickness, and death by living the life of an ascetic.
Accompanied by Channa and riding his horse Kanthaka, Gautama quit his palace for the life of a mendicant. It's said that "the horse's hooves were muffled by the gods" to prevent guards from knowing of his departure.
Gautama initially went to Rajagaha
and began his ascetic life by begging for alms in the street. After
King Bimbisara's men recognised Siddhartha and the king learned of his
quest, Bimbisara offered Siddhartha the throne. Siddhartha rejected the
offer but promised to visit his kingdom of Magadha first, upon attaining enlightenment.
He left Rajagaha and practised under two hermit teachers of yogic meditation. After mastering the teachings of Alara Kalama
(Skr. Ārāḍa Kālāma), he was asked by Kalama to succeed him. However,
Gautama felt unsatisfied by the practice, and moved on to become a
student of yoga with Udaka Ramaputta (Skr. Udraka Rāmaputra).
With him, he achieved high levels of meditative consciousness and was
again asked to succeed his teacher. But, once more, he was not
satisfied, and again moved on.
Awakening
The Buddha surrounded by the demons of Māra. Sanskrit palm leaf manuscript. Nālandā, Bihar, India. Pāla period
Mahabodhi Temple in Bodh Gaya, India, where Gautama Buddha attained nirvana under the Bodhi Tree (left)
According to the early Buddhist texts, after realising that meditative dhyana was the right path to awakening, but that extreme asceticism didn't work, Gautama discovered what Buddhists know as being, the Middle Way—a path of moderation away from the extremes of self-indulgence and self-mortification, or the Noble Eightfold Path, as described in the Dhammacakkappavattana Sutta, which is regarded as the first discourse of the Buddha. In a famous incident, after becoming starved and weakened, he is said to have accepted milk and rice pudding from a village girl named Sujata. Such was his emaciated appearance that she wrongly believed him to be a spirit that had granted her a wish.
The gilded "Emaciated Buddha statue" in an Ubosoth in Bangkok representing the stage of his asceticism
Following this incident, Gautama was famously seated under a pipal tree—now known as the Bodhi tree—in Bodh Gaya, India, when he vowed never to arise until he had found the truth. Kaundinya
and four other companions, believing that he had abandoned his search
and become undisciplined, ceased to stay with him, and went to somewhere
else. After a reputed 49 days of meditation, at the age of 35, he is
said to have attained Enlightenment, and became known as the Buddha or "Awakened One" ("Buddha" is also sometimes translated as "The Enlightened One").
According to some sutras of the Pali canon, at the time of his awakening he realised complete insight into the Four Noble Truths, thereby attaining liberation from samsara, the endless cycle of rebirth, suffering and dying again.
According to scholars, this story of the awakening and the stress on
"liberating insight" is a later development in the Buddhist tradition,
where the Buddha may have regarded the practice of dhyana as leading to nirvana and moksha.
Nirvana is the extinguishing of the "fires" of desire, hatred,
and ignorance, that keep the cycle of suffering and rebirth going. Nirvana is also regarded as the "end of the world", in that no personal identity or boundaries of the mind remain. In such a state, a being is said to possess the Ten Characteristics, belonging to every Buddha.
According to a story in the Āyācana Sutta (Samyutta Nikaya VI.1)—a scripture found in the Pāli and other canons—immediately after his awakening, the Buddha debated whether or not he should teach the Dharma
to others. He was concerned that humans were so overpowered by
ignorance, greed, and hatred that they could never recognise the path,
which is subtle, deep and hard to grasp. However, in the story, Brahmā Sahampati convinced him, arguing that at least some will understand it. The Buddha relented and agreed to teach.
Formation of the sangha
Dhamek Stupa in Sarnath, India, site of the first teaching of the Buddha in which he taught the Four Noble Truths to his first five disciples
After his awakening, the Buddha met Taphussa and Bhallika—two merchant brothers from the city of Balkh
in what is currently Afghanistan—who became his first lay disciples. It
is said that each was given hairs from his head, which are now claimed
to be enshrined as relics in the Shwe Dagon Temple in Rangoon, Burma. The Buddha intended to visit Asita, and his former teachers, Alara Kalama and Udaka Ramaputta, to explain his findings, but they had already died.
He then traveled to the Deer Park near Varanasi (Benares) in northern India, where he set in motion what Buddhists call the Wheel of Dharma
by delivering his first sermon to the five companions with whom he had
sought enlightenment. Together with him, they formed the first saṅgha: the company of Buddhist monks.
All five become arahants, and within the first two months, with the conversion of Yasa
and fifty-four of his friends, the number of such arahants is said to
have grown to 60. The conversion of three brothers named Kassapa
followed, with their reputed 200, 300 and 500 disciples, respectively.
This swelled the sangha to more than 1,000.
Travels and teaching
For the remaining 45 years of his life, the Buddha is said to have traveled in the Gangetic Plain, in what is now Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and southern Nepal, teaching a diverse range of people: from nobles to servants, murderers such as Angulimala, and cannibals such as Alavaka.
Although the Buddha's language remains unknown, it's likely that he
taught in one or more of a variety of closely related Middle Indo-Aryan
dialects, of which Pali may be a standardisation.
The sangha traveled through the subcontinent, expounding the
dharma. This continued throughout the year, except during the four
months of the Vassa
rainy season when ascetics of all religions rarely traveled. One reason
was that it was more difficult to do so without causing harm to animal
life. At this time of year, the sangha would retreat to monasteries,
public parks or forests, where people would come to them.
A view of Vulture Peak, Rajgir, India where the Atanatiya Sutta was held
The first vassana was spent at Varanasi when the sangha was formed. After this, the Buddha kept a promise to travel to Rajagaha, capital of Magadha, to visit King Bimbisara. During this visit, Sariputta and Maudgalyayana were converted by Assaji,
one of the first five disciples, after which they were to become the
Buddha's two foremost followers. The Buddha spent the next three seasons
at Veluvana Bamboo Grove monastery in Rajagaha, the capital of Magadha.
Upon hearing of his son's awakening, Suddhodana sent, over a
period, ten delegations to ask him to return to Kapilavastu. On the
first nine occasions, the delegates failed to deliver the message and
instead joined the sangha to become arahants. The tenth delegation, led
by Kaludayi, a childhood friend of Gautama's (who also became an
arahant), however, delivered the message.
Now two years after his awakening, the Buddha agreed to return,
and made a two-month journey by foot to Kapilavastu, teaching the dharma
as he went. At his return, the royal palace prepared a midday meal, but
the sangha was making an alms round in Kapilavastu. Hearing this,
Suddhodana approached his son, the Buddha, saying:
Ours is the warrior lineage of Mahamassata, and not a single warrior has gone seeking alms.
The Buddha is said to have replied:
That is not the custom of your royal lineage. But it is the custom of my Buddha lineage. Several thousands of Buddhas have gone by seeking alms.
Buddhist texts say that Suddhodana invited the sangha into the palace
for the meal, followed by a dharma talk. After this he is said to have
become a sotapanna. During the visit, many members of the royal family joined the sangha. The Buddha's cousins Ananda and Anuruddha became two of his five chief disciples. At the age of seven, his son Rahula also joined, and became one of his ten chief disciples. His half-brother Nanda also joined and became an arahant.
Of the Buddha's disciples, Sariputta, Maudgalyayana, Mahakasyapa,
Ananda and Anuruddha are believed to have been the five closest to him.
His ten foremost disciples were reputedly completed by the quintet of Upali, Subhoti, Rahula, Mahakaccana and Punna.
In the fifth vassana, the Buddha was staying at Mahavana near Vesali
when he heard news of the impending death of his father. He is said to
have gone to Suddhodana and taught the dharma, after which his father
became an arahant.
The last days of Buddha teachings
The king's death and cremation were to inspire the creation of an
order of nuns. Buddhist texts record that the Buddha was reluctant to
ordain women. His foster mother Maha Pajapati,
for example, approached him, asking to join the sangha, but he refused.
Maha Pajapati, however, was so intent on the path of awakening that she
led a group of royal Sakyan and Koliyan ladies, which followed the
sangha on a long journey to Rajagaha. In time, after Ananda championed
their cause, the Buddha is said to have reconsidered and, five years
after the formation of the sangha agreed to the ordination of women as
nuns. He reasoned that males and females had an equal capacity for
awakening. But he gave women additional rules (Vinaya) to follow.
Mahaparinirvana (Death)
The Buddha's entry into parinirvana. Sanskrit palm leaf manuscript. Nālandā, Bihar, India. Pāla period
According to the Mahaparinibbana Sutta of the Pali canon, at the age of 80, the Buddha announced that he would soon reach parinirvana,
or the final deathless state, and abandon his earthly body. After this,
the Buddha ate his last meal, which he had received as an offering from
a blacksmith named Cunda. Falling violently ill, Buddha instructed his attendant Ānanda
to convince Cunda that the meal eaten at his place had nothing to do
with his passing and that his meal would be a source of the greatest
merit as it provided the last meal for a Buddha. Mettanando and von Hinüber argue that the Buddha died of mesenteric infarction, a symptom of old age, rather than food poisoning.
The precise contents of the Buddha's final meal are not clear,
due to variant scriptural traditions and ambiguity over the translation
of certain significant terms; the Theravada tradition generally believes that the Buddha was offered some kind of pork, while the Mahayana
tradition believes that the Buddha consumed some sort of truffle or
other mushroom. These may reflect the different traditional views on Buddhist vegetarianism and the precepts for monks and nuns.
Buddha's cremation stupa, Kushinagar (Kushinara).
Waley suggests that Theravadins would take suukaramaddava (the contents of the Buddha's last meal), which can translate literally as pig-soft, to mean "soft flesh of a pig" or "pig's soft-food", that is, after Neumann, a soft food favoured by pigs, assumed to be a truffle.
He argues (also after Neumann) that as "(p)lant names tend to be local
and dialectical", as there are several plants known to have suukara- (pig) as part of their names, and as Pali Buddhism developed in an area remote from the Buddha's death, suukaramaddava
could easily have been a type of plant whose local name was unknown to
those in Pali regions. Specifically, local writers writing soon after
the Buddha's death knew more about their flora than Theravadin
commentator Buddhaghosa
who lived hundreds of years and hundreds of kilometers remote in time
and space from the events described. Unaware that it may have been a
local plant name and with no Theravadin prohibition against eating
animal flesh, Theravadins would not have questioned the Buddha eating
meat and interpreted the term accordingly.
The sharing of the relics of the Buddha, Zenyōmitsu-Temple Museum, Tokyo
According to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha died at Kuśināra (present-day Kushinagar, India), which became a pilgrimage centre. Ananda protested the Buddha's decision to enter parinirvana in the abandoned jungles of Kuśināra of the Malla
kingdom. The Buddha, however, is said to have reminded Ananda how
Kushinara was a land once ruled by a righteous wheel-turning king and
the appropriate place for him to die.
The Buddha then asked all the attendant Bhikkhus
to clarify any doubts or questions they had and cleared them all in a
way which others could not do. They had none. According to Buddhist
scriptures, he then finally entered parinirvana. The Buddha's final words are reported to have been: "All composite things (Saṅkhāra)
are perishable. Strive for your own liberation with diligence" (Pali:
'vayadhammā saṅkhārā appamādena sampādethā'). His body was cremated and
the relics were placed in monuments or stupas, some of which are believed to have survived until the present. For example, the Temple of the Tooth or "Dalada Maligawa" in Sri Lanka is the place where what some believe to be the relic of the right tooth of Buddha is kept at present.
Life scenes of Buddha, sandstone: Birth, Enlightenment, Descent from Heaven, First Sermon, Passing Away, c. 2nd century CE, Government Museum, Mathura.
According to the Pāli historical chronicles of Sri Lanka, the Dīpavaṃsa and Mahāvaṃsa, the coronation of Emperor Aśoka (Pāli: Asoka) is 218 years after the death of the Buddha. According to two textual records in Chinese (十八部論 and 部執異論),
the coronation of Emperor Aśoka is 116 years after the death of the
Buddha. Therefore, the time of Buddha's passing is either 486 BCE
according to Theravāda record or 383 BCE according to Mahayana record.
However, the actual date traditionally accepted as the date of the
Buddha's death in Theravāda countries is 544 or 545 BCE, because the
reign of Emperor Aśoka was traditionally reckoned to be about 60 years
earlier than current estimates. In Burmese Buddhist tradition, the date
of the Buddha's death is 13 May 544 BCE. whereas in Thai tradition it is 11 March 545 BCE.
At his death, the Buddha is famously believed to have told his disciples to follow no leader. Mahakasyapa was chosen by the sangha to be the chairman of the First Buddhist Council, with the two chief disciples Maudgalyayana and Sariputta having died before the Buddha.
Hair Relics of Buddha on display at Gangaramaya Temple (Colombo).
While in the Buddha's days he was addressed by the very respected
titles Buddha, Shākyamuni, Shākyasimha, Bhante and Bho, he was known
after his parinirvana nirvana as Arihant, Bhagavā/Bhagavat/Bhagwān, Mahāvira, Jina/Jinendra, Sāstr, Sugata, and most popularly in scriptures as Tathāgata.
Relics
After his death, Buddha's cremation relics were divided amongst 8
royal families and his disciples; centuries later they would be
enshrined by King Ashoka into 84,000 stupas.
Many supernatural legends surround the history of alleged relics as
they accompanied the spread of Buddhism and gave legitimacy to rulers.
War over the Buddha's Relics held by the city of Kushinagar, South Gate, Stupa no. 1, Sanchi.
Physical characteristics
An extensive and colourful physical description of the Buddha has been laid down in scriptures. A kshatriya
by birth, he had military training in his upbringing, and by Shakyan
tradition was required to pass tests to demonstrate his worthiness as a
warrior in order to marry. He had a strong enough body to be noticed by one of the kings and was asked to join his army as a general. He is also believed by Buddhists to have "the 32 Signs of the Great Man".
The Brahmin Sonadanda described him as "handsome, good-looking,
and pleasing to the eye, with a most beautiful complexion. He has a
godlike form and countenance, he is by no means unattractive." (D,
I:115)
"It is wonderful, truly marvellous, how serene is the good
Gotama's appearance, how clear and radiant his complexion, just as the
golden jujube in autumn is clear and radiant, just as a palm-tree fruit
just loosened from the stalk is clear and radiant, just as an adornment
of red gold wrought in a crucible by a skilled goldsmith, deftly beaten
and laid on a yellow-cloth shines, blazes and glitters, even so, the
good Gotama's senses are calmed, his complexion is clear and radiant."
(A, I:181)
A disciple named Vakkali, who later became an arahant, was so
obsessed by the Buddha's physical presence that the Buddha is said to
have felt impelled to tell him to desist, and to have reminded him that
he should know the Buddha through the Dhamma and not through physical
appearances.
Although there are no extant representations of the Buddha in human form until around the 1st century CE, descriptions of the physical characteristics of fully enlightened buddhas are attributed to the Buddha in the Digha Nikaya's Lakkhaṇa Sutta (D, I:142). In addition, the Buddha's physical appearance is described by Yasodhara to their son Rahula upon the Buddha's first post-Enlightenment return to his former princely palace in the non-canonical Pali devotional hymn, Narasīha Gāthā ("The Lion of Men").
Among the 32 main characteristics it is mentioned that Buddha has blue eyes.
Nine virtues
Recollection of nine virtues attributed to the Buddha is a common Buddhist meditation and devotional practice called Buddhānusmṛti. The nine virtues are also among the 40 Buddhist meditation subjects. The nine virtues of the Buddha appear throughout the Tipitaka, and include:
- Buddho – Awakened
- Sammasambuddho – Perfectly self-awakened
- Vijja-carana-sampano – Endowed with higher knowledge and ideal conduct.
- Sugato – Well-gone or Well-spoken.
- Lokavidu – Wise in the knowledge of the many worlds.
- Anuttaro Purisa-damma-sarathi – Unexcelled trainer of untrained people.
- Satthadeva-Manussanam – Teacher of gods and humans.
- Bhagavathi – The Blessed one
- Araham – Worthy of homage. An Arahant is "one with taints destroyed, who has lived the holy life, done what had to be done, laid down the burden, reached the true goal, destroyed the fetters of being, and is completely liberated through final knowledge."
Teachings
Lord Buddha at Pandavleni Caves, Nashik.
Use of Brahmanical motifs
In the Pali Canon, the Buddha uses many Brahmanical devices. For example, in Samyutta Nikaya 111, Majjhima Nikaya 92 and Vinaya i 246 of the Pali Canon, the Buddha praises the Agnihotra as the foremost sacrifice and the Gayatri mantra as the foremost meter:
aggihuttamukhā yaññā sāvittī chandaso mukham.
Sacrifices have the Agnihotra as foremost; of meter, the foremost is the Sāvitrī.
Tracing the oldest teachings
One method to obtain information on the oldest core of Buddhism is to compare the oldest versions of the Pali Canon and other texts, such as the surviving portions of Sarvastivada, Mulasarvastivada, Mahisasaka, Dharmaguptaka, and the Chinese Agamas. The reliability of these sources, and the possibility of drawing out a core of oldest teachings, is a matter of dispute. According to Vetter, inconsistencies remain, and other methods must be applied to resolve those inconsistencies.
According to Schmithausen, there are three positions held by scholars of Buddhism:
- "Stress on the fundamental homogeneity and substantial authenticity of at least a considerable part of the Nikayic materials."
- "Scepticism with regard to the possibility of retrieving the doctrine of earliest Buddhism."
- "Cautious optimism in this respect."
Dhyana and insight
The Buddha on a coin of Kanishka I, c. 130 CE.
A core problem in the study of early Buddhism is the relation between dhyana and insight.
Schmithausen notes that the mention of the four noble truths as
constituting "liberating insight", which is attained after mastering the
Rupa Jhanas, is a later addition to texts such as Majjhima Nikaya 36.
Earliest Buddhism
According to Tilmann Vetter, the core of earliest Buddhism is the practice of dhyāna, as a workable alternative to painful ascetic practices. Bronkhorst agrees that Dhyāna was a Buddhist invention, whereas Norman notes that "the Buddha's way to release [...] was by means of meditative practices." Discriminating insight into transiency as a separate path to liberation was a later development.
According to the Mahāsaccakasutta, from the fourth jhana the Buddha gained bodhi. Yet, it is not clear what he was awakened to.
According to Schmithausen and Bronkhorst, "liberating insight" is a
later addition to this text, and reflects a later development and
understanding in early Buddhism.
The mentioning of the four truths as constituting "liberating insight"
introduces a logical problem, since the four truths depict a linear path
of practice, the knowledge of which is in itself not depicted as being
liberating:
[T]hey do not teach that one is released by knowing the four noble truths, but by practicing the fourth noble truth, the eightfold path, which culminates in right samadhi.
Although "Nibbāna" (Sanskrit: Nirvāna)
is the common term for the desired goal of this practice, many other
terms can be found throughout the Nikayas, which are not specified.
According to Vetter, the description of the Buddhist path may
initially have been as simple as the term "the middle way". In time,
this short description was elaborated, resulting in the description of
the eightfold path.
According to both Bronkhorst and Anderson, the four truths became a substitution for prajna, or "liberating insight", in the suttas in those texts where "liberating insight" was preceded by the four jhanas.
According to Bronkhorst, the four truths may not have been formulated
in earliest Buddhism, and did not serve in earliest Buddhism as a
description of "liberating insight". Gotama's teachings may have been personal, "adjusted to the need of each person."
The three marks of existence
may reflect Upanishadic or other influences. K.R. Norman supposes that
these terms were already in use at the Buddha's time, and were familiar
to his listeners.
The Brahma-vihara was in origin probably a brahmanic term; but its usage may have been common to the Sramana traditions.
Later developments
In time, "liberating insight" became an essential feature of the
Buddhist tradition. The following teachings, which are commonly seen as
essential to Buddhism, are later formulations which form part of the
explanatory framework of this "liberating insight":
- The Four Noble Truths: that suffering is an ingrained part of existence; that the origin of suffering is craving for sensuality, acquisition of identity, and fear of annihilation; that suffering can be ended; and that following the Noble Eightfold Path is the means to accomplish this;
- The Noble Eightfold Path: right view, right intention, right speech, right action, right livelihood, right effort, right mindfulness, and right concentration;
- Dependent origination: the mind creates suffering as a natural product of a complex process.
Other religions
Buddha as an avatar at Dwaraka Tirumala temple, Andhra Pradesh.
Some Hindus regard Gautama as the 9th avatar of Vishnu. However, Buddha's teachings deny the authority of the Vedas and the concepts of Brahman-Atman. Consequently Buddhism is generally classified as a nāstika school (heterodox, literally "It is not so") in contrast to the six orthodox schools of Hinduism.
The Buddha is regarded as a prophet by the minority Ahmadiyya sect of Muslims—a sect considered deviant and rejected as apostate by mainstream Islam. Some early Chinese Taoist-Buddhists thought the Buddha to be a reincarnation of Laozi.
Disciples of the Cao Đài religion worship the Buddha as a major religious teacher.
His image can be found in both their Holy See and on the home altar. He
is revealed during communication with Divine Beings as son of their
Supreme Being (God the Father) together with other major religious
teachers and founders like Jesus, Laozi, and Confucius.
The Christian Saint Josaphat is based on the Buddha. The name comes from the Sanskrit Bodhisattva via Arabic Būdhasaf and Georgian Iodasaph. The only story in which St. Josaphat appears, Barlaam and Josaphat, is based on the life of the Buddha.
Josaphat was included in earlier editions of the Roman Martyrology
(feast day 27 November)—though not in the Roman Missal—and in the
Eastern Orthodox Church liturgical calendar (26 August).
In the ancient Gnostic sect of Manichaeism, the Buddha is listed among the prophets who preached the word of God before Mani.
In Sikhism, Buddha is mentioned as the 23rd avatar of Vishnu in the Chaubis Avtar, a composition in Dasam Granth traditionally and historically attributed to Guru Gobind Singh.
In the Bahá'í Faith, Buddha is regarded as one of the Manifestations of God.
Depiction in arts and media
- Films
- Little Buddha, a 1994 film by Bernardo Bertolucci
- Prem Sanyas, a 1925 silent film, directed by Franz Osten and Himansu Rai
- Television
- Buddha, a 2013 mythological drama on Zee TV
- The Buddha 2010 PBS documentary by award-winning filmmaker David Grubin and narrated by Richard Gere
- Literature
- The Light of Asia, an 1879 epic poem by Edwin Arnold
- Buddha, a manga series that ran from 1972 to 1983 by Osamu Tezuka
- Siddhartha novel by Hermann Hesse, written in German in 1922
- Lord of Light, a novel by Roger Zelazny depicts a man in a far future Earth Colony who takes on the name and teachings of the Buddha
- Creation, a 1981 novel by Gore Vidal, includes the Buddha as one of the religious figures that the main character encounters
- Music
- Karuna Nadee, a 2010 oratorio by Dinesh Subasinghe
- The Light of Asia, an 1886 oratorio by Dudley Buck
Painting
- Shussan Shaka, a Zen painting motif
A panorama of scenes from the Buddha's life, from a Burmese parabaik or picture book.