Soyuz spacecraft (TMA version)
| |
| Manufacturer | RKK Energia |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union, Russian Federation |
| Operator | Soviet space program (1967–91) Roscosmos (1991 onwards) |
| Applications | Carry cosmonauts to orbit and back; originally intended for Soviet Moonshot and Salyut space station transportation. |
| Specifications | |
| Design life | Up to six months docked to station |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit (circumlunar spaceflight during early program) |
| Production | |
| Status | In service |
| First launch | (Unmanned) November 28, 1966 (Manned) Soyuz 1 April 23, 1967 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derivatives | Shenzhou, Progress |
Soyuz (Russian: Сою́з, IPA: [sɐˈjus], lit. Union) is a series of spacecraft designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now RKK Energia) in the 1960s that remains in service today. The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet manned lunar programs. The Soyuz spacecraft is launched on a Soyuz rocket, the most reliable launch vehicle in the world to date. The Soyuz rocket design is based on the Vostok launcher, which in turn was based on the 8K74 or R-7A Semyorka, a Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile. All Soyuz spacecraft are launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Soyuz is currently the only means for manned space flights in the world and is heavily used in the International Space Station program.
History
The first Soyuz flight was unmanned and started on November 28, 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was unmanned. Soyuz 3,
launched on October 26, 1968, became the program's first successful
manned mission. The only other flight to suffer a fatal accident, Soyuz 11,
killed its crew of three when the cabin depressurized prematurely just
before reentry. These were the only humans to date to have died above
the Kármán line. Despite these early incidents, Soyuz is widely considered the world's safest, most cost-effective human spaceflight vehicle, established by its unparalleled length of operational history. Soyuz spacecraft were used to carry cosmonauts to and from Salyut and later Mir Soviet space stations, and are now used for transport to and from the International Space Station
(ISS). At least one Soyuz spacecraft is docked to ISS at all times for
use as an escape craft in the event of an emergency. The spacecraft is
intended to be replaced by the six-person Federation spacecraft.
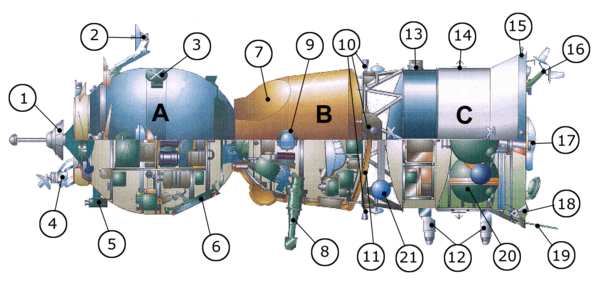
Design
Diagram showing the three elements of the Soyuz TMA spacecraft.
A Soyuz spacecraft consists of three parts (from front to back):
- A spheroid orbital module, which provides accommodation for the crew during their mission;
- A small aerodynamic reentry module, which returns the crew to Earth;
- A cylindrical service module with solar panels attached, which contains the instruments and engines.
The orbital and service modules are single-use and are destroyed upon
reentry in the atmosphere. Though this might seem wasteful, it reduces
the amount of heat shielding required for reentry, saving mass compared
to designs containing all of the living space and life support in a
single capsule. This allows smaller rockets to launch the spacecraft or
can be used to increase the habitable space available to the crew (6.2 m3 in Apollo CM vs 7.5 m3
in Soyuz) in the mass budget. The orbital and reentry portions are
habitable living space, with the service module containing the fuel,
main engines and instrumentation.
Soyuz can carry up to three crew members and provide life support
for about 30 person days. The life support system provides a
nitrogen/oxygen atmosphere at sea level partial pressures. The
atmosphere is regenerated through potassium superoxide (KO2) cylinders, which absorb most of the carbon dioxide (CO2) and water produced by the crew and regenerates the oxygen, and lithium hydroxide (LiOH) cylinders which absorb leftover CO2.
The vehicle is protected during launch by a payload fairing, which is jettisoned along with the SAS at 2 1⁄2
minutes into launch. It has an automatic docking system. The ship can
be operated automatically, or by a pilot independently of ground
control.
Launch escape system
The Vostok
spacecraft utilized an ejector seat to bail out the cosmonaut in the
event of a low-altitude launch failure, as well as during reentry,
however it would probably have been ineffective in the first 20 seconds
after liftoff when the altitude would be too low for the parachute to
deploy. Inspired by the Mercury
LES, Soviet designers began work on a similar system in 1962. This
included developing a complex sensing system to monitor various launch
vehicle parameters and trigger an abort if a booster malfunction
occurred. Based on data from R-7 launches over the years, engineers
developed a list of the most likely failure modes for the vehicle and
could narrow down abort conditions to premature separation of a strap-on
booster, low engine thrust, loss of combustion chamber pressure, or
loss of booster guidance. The Spacecraft Abort System (SAS; Russian: Система Аварийного Спасения, translit. Sistema Avarijnogo Spaseniya)
could also be manually activated from the ground, but unlike American
spacecraft, there was no way for the cosmonauts to trigger it
themselves.
Since it turned out to be almost impossible to separate the
entire payload shroud from the Soyuz service module cleanly, the
decision was made to have the shroud split between the service module
and descent module during an abort. Four folding stabilizers were added
to improve aerodynamic stability during ascent. Two test runs of the SAS
were carried out in 1966-67.
The basic design of the SAS has remained almost unchanged in 50
years of use and all Soyuz launches carry it. The only modification was
in 1972 when the aerodynamic fairing over the SAS motor nozzles was
removed for weight-saving reasons as the redesigned Soyuz 7K-T
spacecraft carried extra life support equipment. The unmanned Progress
resupply ferry has a dummy escape tower and removes the stabilizer fins
from the payload shroud. There have been three failed launches of a
manned Soyuz vehicle, Soyuz 18-1 in 1975, Soyuz T-10-1 in 1983 and Soyuz MS-10 in October 2018. The 1975 failure was aborted after escape tower jettison. In 1983, Soyuz T-10-1's SAS successfully rescued the cosmonauts from an on-pad fire and explosion of the launch vehicle. Most recently in 2018, the SAS sub-system in the payload shroud of Soyuz MS-10
successfully rescued the cosmonauts from a rocket failure 2 minutes and
45 second after liftoff after the escape tower had already been
jettisoned.
Orbital module
Soyuz spacecraft's Orbital Module
The forepart of the spacecraft is the Orbital Module (Russian: бытовой отсек, translit. bytovoi otsek),
also known as habitation section. It houses all the equipment that will
not be needed for reentry, such as experiments, cameras or cargo. The
module also contains a toilet, docking avionics and communications gear.
Internal volume is 6 m3 (212 cu ft), living space 5 m3
(177 cu ft). On the latest Soyuz versions (since Soyuz TM), a small
window was introduced, providing the crew with a forward view.
A hatch between it and the Descent Module can be closed so as to
isolate it to act as an airlock if needed, crew members exiting through
its side port (near the descent module). On the launch pad, the crew
enter the spacecraft through this port.
This separation also lets the Orbital Module be customized to the
mission with less risk to the life-critical descent module. The
convention of orientation in a micro-g environment
differs from that of the Descent Module, as crew members stand or sit
with their heads to the docking port. Also the rescue of the crew whilst
on the launch pad or with the SAS system is complicated because of the
orbital module.
Separation of the Orbital Module is critical for a safe landing;
without separation of the Orbital Module, it is not possible for the
crew to survive landing in the Descent Module. This is because the
Orbital Module would interfere with proper deployment of the Descent
Module's parachutes, and the extra mass exceeds the capability of the
main parachute and braking engines to provide a safe soft landing speed.
In view of this, the Orbital Module was separated before the ignition
of the return engine until the late 1980s. This guaranteed that the
Descent Module and Orbital Module would be separated before the Descent
Module was placed in a reentry trajectory. However, after the
problematic landing of Soyuz TM-5
in September 1988 this procedure was changed and the Orbital Module is
now separated after the return maneuver. This change was made as the
TM-5 crew could not deorbit for 24 hours after they jettisoned their
Orbital Module, which contained their sanitation facilities and the
docking collar needed to attach to MIR. The risk of not being able to
separate the Orbital Module is effectively judged to be less than the
risk of needing the facilities in it, following a failed deorbit.
Descent module
Replica of the Soyuz spacecraft's Entry Module at the Euro Space Center In Belgium
Soyuz spacecraft's Descent Module
The Descent Module (Russian: Спуска́емый Аппара́т, tr. Spuskáyemy Apparát),
also known as a reentry capsule, is used for launch and the journey
back to Earth. Half of the Descent Module is covered by a heat-resistant
covering to protect it during reentry;
this half faces the Earth during reentry. It is slowed initially by the
atmosphere, then by a braking parachute, followed by the main parachute
which slows the craft for landing. At one meter above the ground,
solid-fuel braking engines mounted behind the heat shield
are fired to give a soft landing. One of the design requirements for
the Descent Module was for it to have the highest possible volumetric
efficiency (internal volume divided by hull area). The best shape for
this is a sphere — as the pioneering Vostok spacecraft's Descent Module used — but such a shape can provide no lift, which results in a purely ballistic reentry.
Ballistic reentries are hard on the occupants due to high deceleration
and cannot be steered beyond their initial deorbit burn. That is why it
was decided to go with the "headlight" shape that the Soyuz uses – a
hemispherical forward area joined by a barely angled (seven degrees)
conical section to a classic spherical section heat shield. This shape
allows a small amount of lift to be generated due to the unequal weight
distribution. The nickname was thought up at a time when nearly every
headlight was circular. The small dimensions of the Descent Module led
to it having only two-man crews after the death of the Soyuz 11 crew. The later Soyuz T spacecraft solved this issue. Internal volume of Soyuz SA is 4 m3 (141 cu ft); 2.5 m3 (88 cu ft) is usable for crew (living space).
Service module
Soyuz spacecraft's Instrumentation/Propulsion Module
At the back of the vehicle is the Service Module (Russian: прибо́рно-агрега́тный отсе́к, tr. pribórno-agregátny otsék). It has a pressurized container shaped like a bulging can (instrumentation compartment, priborniy otsek) that contains systems for temperature control, electric power supply, long-range radio
communications, radio telemetry, and instruments for orientation and
control. A non-pressurized part of the Service Module (propulsion
compartment, agregatniy otsek) contains the main engine and a liquid-fuelled propulsion system
for maneuvering in orbit and initiating the descent back to Earth. The
ship also has a system of low-thrust engines for orientation, attached
to the intermediate compartment (perekhodnoi otsek).
Outside the Service Module are the sensors for the orientation system
and the solar array, which is oriented towards the Sun by rotating the
ship. An incomplete separation between the Service and Reentry Modules
led to emergency situations during Soyuz 5, Soyuz TMA-10 and Soyuz TMA-11,
which led to an incorrect reentry orientation (crew ingress hatch
first). The failure of several explosive bolts did not cut the
connection between the Service/Reentry Modules on the latter two
flights.
Reentry procedure
The Soyuz uses a method similar to the US Apollo command and service module
to deorbit itself. The spacecraft is turned engine-forward and the main
engine is fired for deorbiting on the far side of Earth ahead of its
planned landing site. This requires the least propellant for reentry; the spacecraft travels on an elliptical Hohmann transfer orbit to the entry interface point where atmospheric drag slows it enough to fall out of orbit.
Early Soyuz spacecraft would then have the Service and Orbital
Modules detach simultaneously from the Descent Module. As they are
connected by tubing and electrical cables to the Descent Module, this
would aid in their separation and avoid having the Descent Module alter
its orientation.[citation needed] Later Soyuz spacecraft detached the Orbital Module before firing the main engine, which saved propellant. Since the Soyuz TM-5
landing issue, the Orbital Module is once again detached only after the
reentry firing, which led to (but did not cause) emergency situations
of Soyuz TMA-10 and TMA-11.
The Orbital Module cannot remain in orbit as an addition to a space
station, as the airlock hatch between the Orbital and Reentry Modules is
a part of the Reentry Module, and the Orbital Module therefore
depressurizes after separation.
Reentry firing is usually done on the "dawn" side of the Earth,
so that the spacecraft can be seen by recovery helicopters as it
descends in the evening twilight, illuminated by the Sun when it is
above the shadow of the Earth.
The Soyuz craft is designed to come down on land, usually somewhere in
the deserts of Kazakhstan in central Asia. This is in contrast to early
US manned spacecraft, which splashed down in the ocean.
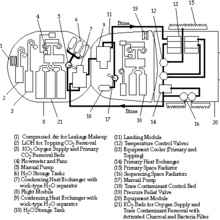
Spacecraft systems
Soyuz diagram
Exploded plan of the Soyuz MS spacecraft.
- Thermal control system – Sistema Obespecheniya Teplovogo Rezhima, SOTR
- Life support system – Kompleks Sredstv Obespecheniya Zhiznideyatelnosti, KSOZh
- Power supply system – Sistema Elektropitaniya, SEP
- Communication and tracking systems – Rassvet (Dawn) radio communications system, onboard measurement system (SBI), Kvant-V spacecraft control, Klyost-M television system, orbit radio tracking (RKO)
- Onboard complex control system – Sistema Upravleniya Bortovym Kompleksom, SUBK
- Combined propulsion system – Kompleksnaya Dvigatelnaya Ustanovka, KDU
- Chaika-3 motion control system (SUD)
- Optical/visual devices (OVP) – VSK-4 (Vizir Spetsialniy Kosmicheskiy-4), night vision device (VNUK-K, Visir Nochnogo Upravleniya po Kursu), docking light, pilot's sight (VP-1, Vizir Pilota-1), laser rangefinder (LPR-1, Lazerniy Dalnomer-1)
- Kurs rendezvous system
- Docking system – Sistema Stykovki i Vnutrennego Perekhoda, SSVP
- Teleoperator control mode – Teleoperatorniy Rezhim Upravleniya, TORU
- Entry actuators system – Sistema Ispolnitelnikh Organov Spuska, SIO-S
- Landing aids kit – Kompleks Sredstv Prizemleniya, KSP
- Portable survival kit – Nosimiy Avariyniy Zapas, NAZ, containing a TP-82 Cosmonaut survival pistol or Makarov pistol
- Soyuz launch escape system – Sistema Avariynogo Spaseniya, SAS
|
|
|
Variants
The
Soyuz spacecraft has been the subject of continuous evolution since the
early 1960s. Thus several different versions, proposals and projects
exist.
Specifications
Soyuz 7K (part of the 7K-9K-11K circumlunar complex) (1963)
Soyuz 7K manned spacecraft concept (1963).
Sergei Korolev initially promoted the Soyuz A-B-V circumlunar complex (7K-9K-11K)
concept (also known as L1) in which a two-man craft Soyuz 7K would
rendezvous with other components (9K and 11K) in Earth orbit to assemble
a lunar excursion vehicle, the components being delivered by the proven
R-7 rocket.
First generation
Soyuz 7K-OK(A) spacecraft with an active docking unit.
Soyuz 7K-OKS for Salyut space stations.
The manned Soyuz spacecraft can be classified into design generations. Soyuz 1 through Soyuz 11 (1967–1971) were first-generation vehicles, carrying a crew of up to three without spacesuits and distinguished from those following by their bent solar panels and their use of the Igla automatic docking navigation system, which required special radar antennas. This first generation encompassed the original Soyuz 7K-OK and the Soyuz 7K-OKS for docking with the Salyut 1 space station. The probe and drogue docking system permitted internal transfer of cosmonauts from the Soyuz to the station.
The Soyuz 7K-L1
was designed to launch a crew from the Earth to circle the moon, and
was the primary hope for a Soviet circumlunar flight. It had several
test flights in the Zond program from 1967–1970 (Zond 4 to Zond 8), which produced multiple failures in the 7K-L1's reentry systems. The remaining 7K-L1s were scrapped. The Soyuz 7K-L3 was designed and developed in parallel to the Soyuz 7K-L1, but was also scrapped. Soyuz 1 was plagued with technical issues, and cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov was killed when the spacecraft crashed during its return to Earth. This was the first in-flight fatality in the history of spaceflight.
The next manned version of the Soyuz was the Soyuz 7K-OKS. It was designed for space station
flights and had a docking port that allowed internal transfer between
spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-OKS had two manned flights, both in 1971. Soyuz 11, the second flight, depressurized upon reentry, killing its three-man crew.
Second generation
Upgraded Soyuz 7K-T version.
The second generation, called Soyuz Ferry or Soyuz 7K-T, comprised Soyuz 12 through Soyuz 40 (1973–1981).
It was developed out of the military Soyuz concepts studied in previous years and was capable of carrying 2 cosmonauts with Sokol space suits (after the Soyuz 11 accident). Several models were planned, but none actually flew in space. These versions were named Soyuz P, Soyuz PPK, Soyuz R, Soyuz 7K-VI, and Soyuz OIS (Orbital Research Station).
The Soyuz 7K-T/A9 version was used for the flights to the military Almaz space station.
Soyuz 7K-TM was the spacecraft used in the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975, which saw the first and only docking of a Soyuz spacecraft with an Apollo Command/Service Module. It was also flown in 1976 for the Earth-science mission, Soyuz 22. Soyuz 7K-TM served as a technological bridge to the third generation.
Third generation
Soyuz-T spacecraft.
The third generation Soyuz-T (T: Russian: транспортный, translit. transportnyi, lit. 'transport')
spacecraft (1976–1986) featured solar panels allowing longer missions, a
revised Igla rendezvous system and new translation/attitude thruster
system on the Service module. It could carry a crew of three, now
wearing spacesuits.
Fourth generation
Soyuz-TM (1986–2003)
Soyuz-TM
spacecraft. Compare the antennas on the orbital module to those on
Soyuz-T. Differences reflect the change from the Igla rendezvous system
used on Soyuz-T to the Kurs rendezvous system used on Soyuz-TM.
The Soyuz-TM crew transports (M: Russian: модифицированный, translit. modifitsirovannyi, lit. 'modified') were fourth generation Soyuz spacecraft, and were used from 1986 to 2003 for ferry flights to Mir and the International Space Station.
Soyuz-TMA (2003–2012)
The Soyuz TMA-6
Soyuz TMA (A: Russian: антропометрический, translit. antropometricheskii, lit. 'anthropometric') features several changes to accommodate requirements requested by NASA in order to service the International Space Station,
including more latitude in the height and weight of the crew and
improved parachute systems. It is also the first expendable vehicle to
feature "glass cockpit"
technology. Soyuz-TMA looks identical to a Soyuz-TM spacecraft on the
outside, but interior differences allow it to accommodate taller
occupants with new adjustable crew couches.
Soyuz TMA-M (2010–2016)
The Soyuz TMA-M was an upgrade of the baseline Soyuz-TMA, using a new
computer, digital interior displays, updated docking equipment, and the
vehicle's total mass was reduced by 70 kilograms. The new version
debuted on 7 October 2010 with the launch of TMA-01M, carrying the ISS Expedition 25 crew.
The Soyuz TMA-08M
mission set a new record for the fastest manned docking with a space
station. The mission used a new six-hour rendezvous, faster than the
previous Soyuz launches, which had, since 1986, taken two days.
Soyuz MS (since 2016)
Soyuz MS-01 docked to the ISS
Soyuz MS is the final planned upgrade of the Soyuz spacecraft. Its maiden flight was in July 2016 with mission MS-01.
Major changes include:
- more efficient solar panels
- modified docking and attitude control engine positions for redundancy during docking and de-orbit burns
- new Kurs NA approach and docking system which weighs half as much and consumes a third of the power of previous system
- new TsVM-101 computer, about one eighth the weight (8.3 kg vs. 70 kg) and much smaller than the previous Argon-16 computer
- unified digital command/telemetry system (MBITS) to relay telemetry via satellite, and control spacecraft when out of sight of ground stations; also provides the crew with position data when out of ground tracking range
- GLONASS/GPS and Cospas-Sarsat satellite systems for more accurate location during search/rescue operations after landing
Related craft
The unmanned Progress spacecraft were derived from Soyuz and are used for servicing space stations.
While not being direct derivatives of Soyuz, the Chinese Shenzhou spacecraft uses Soyuz TM technology sold in 1984 and the Indian Orbital Vehicle follow the same general layout as that pioneered by Soyuz.