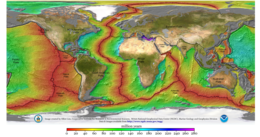
Age of the sea floor. Much of the dating information comes from magnetic anomalies.
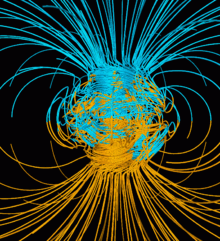
Computer simulation of the Earth's magnetic field in a period of normal polarity between reversals.
Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.
Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline
in the 19th century, its origins date back to ancient times. The first
magnetic compasses were made from lodestones,
while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the
history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 AD.
Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox;
and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density
and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the
20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration
of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential
role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.
Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. In Exploration Geophysics, Geophysical survey
data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral
deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the
thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.
Physical phenomena
Geophysics is a highly interdisciplinary subject, and geophysicists contribute to every area of the Earth sciences. To provide a clearer idea of what constitutes geophysics, this section describes phenomena that are studied in physics and how they relate to the Earth and its surroundings.
Gravity
A map of deviations in gravity from a perfectly smooth, idealized Earth.
The gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun give rise to two high
tides and two low tides every lunar day, or every 24 hours and 50
minutes. Therefore, there is a gap of 12 hours and 25 minutes between
every high tide and between every low tide.
Gravitational forces make rocks press down on deeper rocks, increasing their density as the depth increases. Measurements of gravitational acceleration and gravitational potential at the Earth's surface and above it can be used to look for mineral deposits. The surface gravitational field provides information on the dynamics of tectonic plates. The geopotential surface called the geoid
is one definition of the shape of the Earth. The geoid would be the
global mean sea level if the oceans were in equilibrium and could be
extended through the continents (such as with very narrow canals).
Heat flow
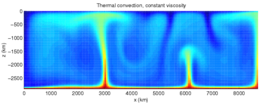
A model of thermal convection in the Earth's mantle. The thin red columns are mantle plumes.
The Earth is cooling, and the resulting heat flow generates the Earth's magnetic field through the geodynamo and plate tectonics through mantle convection. The main sources of heat are the primordial heat and radioactivity, although there are also contributions from phase transitions. Heat is mostly carried to the surface by thermal convection, although there are two thermal boundary layers – the core-mantle boundary and the lithosphere – in which heat is transported by conduction. Some heat is carried up from the bottom of the mantle by mantle plumes. The heat flow at the Earth's surface is about 4.2 × 1013 W, and it is a potential source of geothermal energy.
Vibrations
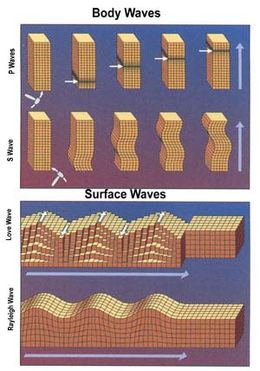
Illustration of the deformations of a block by body waves and surface waves (see seismic wave).
Seismic waves
are vibrations that travel through the Earth's interior or along its
surface. The entire Earth can also oscillate in forms that are called normal modes or free oscillations of the Earth. Ground motions from waves or normal modes are measured using seismographs.
If the waves come from a localized source such as an earthquake or
explosion, measurements at more than one location can be used to locate
the source. The locations of earthquakes provide information on plate
tectonics and mantle convection.
Recording of seismic waves from controlled sources provide
information on the region that the waves travel through. If the density
or composition of the rock changes, waves are reflected. Reflections
recorded using Reflection Seismology
can provide a wealth of information on the structure of the earth up to
several kilometers deep and are used to increase our understanding of
the geology as well as to explore for oil and gas. Changes in the travel direction, called refraction, can be used to infer the deep structure of the Earth.
Earthquakes pose a risk to humans. Understanding their mechanisms, which depend on the type of earthquake (e.g., intraplate or deep focus), can lead to better estimates of earthquake risk and improvements in earthquake engineering.
Electricity
Although we mainly notice electricity during thunderstorms, there is always a downward electric field near the surface that averages 120 volts per meter. Relative to the solid Earth, the atmosphere has a net positive charge due to bombardment by cosmic rays. A current of about 1800 amperes flows in the global circuit.
It flows downward from the ionosphere over most of the Earth and back
upwards through thunderstorms. The flow is manifested by lightning below
the clouds and sprites above.
A variety of electric methods are used in geophysical survey. Some measure spontaneous potential, a potential that arises in the ground because of man-made or natural disturbances. Telluric currents flow in Earth and the oceans. They have two causes: electromagnetic induction by the time-varying, external-origin geomagnetic field and motion of conducting bodies (such as seawater) across the Earth's permanent magnetic field. The distribution of telluric current density can be used to detect variations in electrical resistivity of underground structures. Geophysicists can also provide the electric current themselves.
Electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves occur in the ionosphere and magnetosphere as well as in Earth's outer core. Dawn chorus is believed to be caused by high-energy electrons that get caught in the Van Allen radiation belt. Whistlers are produced by lightning strikes. Hiss may be generated by both. Electromagnetic waves may also be generated by earthquakes.
In the highly conductive liquid iron of the outer core, magnetic
fields are generated by electric currents through electromagnetic
induction. Alfvén waves are magnetohydrodynamic
waves in the magnetosphere or the Earth's core. In the core, they
probably have little observable effect on the Earth's magnetic field,
but slower waves such as magnetic Rossby waves may be one source of geomagnetic secular variation.
Electromagnetic methods that are used for geophysical survey include transient electromagnetics, magnetotellurics, surface nuclear magnetic resonance and electromagnetic seabed logging.
Magnetism
The Earth's magnetic field protects the Earth from the deadly solar wind and has long been used for navigation. It originates in the fluid motions of the outer core. The magnetic field in the upper atmosphere gives rise to the auroras.
Earth's dipole axis (pink line) is tilted away from the rotational axis (blue line).
The Earth's field is roughly like a tilted dipole, but it changes over time (a phenomenon called geomagnetic secular variation). Mostly the geomagnetic pole stays near the geographic pole, but at random intervals averaging 440,000 to a million years or so, the polarity of the Earth's field reverses. These geomagnetic reversals, analyzed within a Geomagnetic Polarity Time Scale,
contain 184 polarity intervals in the last 83 million years, with
change in frequency over time, with the most recent brief complete
reversal of the Laschamp event occurring 41,000 years ago during the last glacial period. Geologists observed geomagnetic reversal recorded in volcanic rocks, through magnetostratigraphy correlation
and their signature can be seen as parallel linear magnetic anomaly
stripes on the seafloor. These stripes provide quantitative information
on seafloor spreading, a part of plate tectonics. They are the basis of magnetostratigraphy, which correlates magnetic reversals with other stratigraphies to construct geologic time scales. In addition, the magnetization in rocks can be used to measure the motion of continents.
Radioactivity
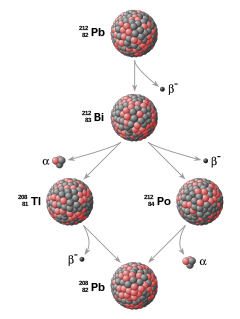
Example of a radioactive decay chain
Radioactive decay accounts for about 80% of the Earth's internal heat, powering the geodynamo and plate tectonics. The main heat-producing isotopes are potassium-40, uranium-238, uranium-235, and thorium-232.
Radioactive elements are used for radiometric dating, the primary method for establishing an absolute time scale in geochronology.
Unstable isotopes decay at predictable rates, and the decay rates
of different isotopes cover several orders of magnitude, so radioactive
decay can be used to accurately date both recent events and events in
past geologic eras. Radiometric mapping using ground and airborne gamma spectrometry
can be used to map the concentration and distribution of radioisotopes
near the Earth's surface, which is useful for mapping lithology and
alteration.
Fluid dynamics
Fluid motions occur in the magnetosphere, atmosphere, ocean, mantle and core. Even the mantle, though it has an enormous viscosity, flows like a fluid over long time intervals. This flow is reflected in phenomena such as isostasy, post-glacial rebound and mantle plumes. The mantle flow drives plate tectonics and the flow in the Earth's core drives the geodynamo.
Geophysical fluid dynamics is a primary tool in physical oceanography and meteorology. The rotation of the Earth has profound effects on the Earth's fluid dynamics, often due to the Coriolis effect. In the atmosphere it gives rise to large-scale patterns like Rossby waves and determines the basic circulation patterns of storms. In the ocean they drive large-scale circulation patterns as well as Kelvin waves and Ekman spirals at the ocean surface. In the Earth's core, the circulation of the molten iron is structured by Taylor columns.
Waves and other phenomena in the magnetosphere can be modeled using magnetohydrodynamics.
Mineral physics
The physical properties of minerals must be understood to infer the composition of the Earth's interior from seismology, the geothermal gradient and other sources of information. Mineral physicists study the elastic properties of minerals; their high-pressure phase diagrams, melting points and equations of state at high pressure; and the rheological properties of rocks, or their ability to flow. Deformation of rocks by creep make flow possible, although over short times the rocks are brittle. The viscosity of rocks is affected by temperature and pressure, and in turn determines the rates at which tectonic plates move.
Water is a very complex substance and its unique properties are essential for life. Its physical properties shape the hydrosphere and are an essential part of the water cycle and climate. Its thermodynamic properties determine evaporation and the thermal gradient in the atmosphere. The many types of precipitation involve a complex mixture of processes such as coalescence, supercooling and supersaturation. Some precipitated water becomes groundwater, and groundwater flow includes phenomena such as percolation, while the conductivity
of water makes electrical and electromagnetic methods useful for
tracking groundwater flow. Physical properties of water such as salinity have a large effect on its motion in the oceans.
The many phases of ice form the cryosphere and come in forms like ice sheets, glaciers, sea ice, freshwater ice, snow, and frozen ground (or permafrost).
Regions of the Earth
Size and form of the Earth
The Earth is roughly spherical, but it bulges towards the Equator, so it is roughly in the shape of an ellipsoid (see Earth ellipsoid). This bulge is due to its rotation and is nearly consistent with an Earth in hydrostatic equilibrium. The detailed shape of the Earth, however, is also affected by the distribution of continents and ocean basins, and to some extent by the dynamics of the plates.
Structure of the interior
Seismic velocities and boundaries in the interior of the Earth sampled by seismic waves.
Evidence from seismology, heat flow at the surface, and mineral physics
is combined with the Earth's mass and moment of inertia to infer models
of the Earth's interior – its composition, density, temperature,
pressure. For example, the Earth's mean specific gravity (5.515) is far higher than the typical specific gravity of rocks at the surface (2.7–3.3), implying that the deeper material is denser. This is also implied by its low moment of inertia ( 0.33 M R2, compared to 0.4 M R2
for a sphere of constant density). However, some of the density
increase is compression under the enormous pressures inside the Earth.
The effect of pressure can be calculated using the Adams–Williamson equation.
The conclusion is that pressure alone cannot account for the increase
in density. Instead, we know that the Earth's core is composed of an
alloy of iron and other minerals.
Reconstructions of seismic waves in the deep interior of the Earth show that there are no S-waves
in the outer core. This indicates that the outer core is liquid,
because liquids cannot support shear. The outer core is liquid, and the
motion of this highly conductive fluid generates the Earth's field. Earth's inner core, however, is solid because of the enormous pressure.
Reconstruction of seismic reflections in the deep interior
indicate some major discontinuities in seismic velocities that demarcate
the major zones of the Earth: inner core, outer core, mantle,
lithosphere and crust. The mantle itself is divided into the upper mantle, transition zone, lower mantle and D′′ layer. Between the crust and the mantle is the Mohorovičić discontinuity.
The seismic model of the Earth does not by itself determine the
composition of the layers. For a complete model of the Earth, mineral
physics is needed to interpret seismic velocities in terms of
composition. The mineral properties are temperature-dependent, so the geotherm must also be determined. This requires physical theory for thermal conduction and convection and the heat contribution of radioactive elements. The main model for the radial structure of the interior of the Earth is the preliminary reference Earth model (PREM). Some parts of this model have been updated by recent findings in mineral physics (see post-perovskite) and supplemented by seismic tomography. The mantle is mainly composed of silicates, and the boundaries between layers of the mantle are consistent with phase transitions.
The mantle acts as a solid for seismic waves, but under high
pressures and temperatures it deforms so that over millions of years it
acts like a liquid. This makes plate tectonics possible.
Magnetosphere
Schematic of Earth's magnetosphere. The solar wind flows from left to right.
If a planet's magnetic field is strong enough, its interaction with the solar wind forms a magnetosphere. Early space probes mapped out the gross dimensions of the Earth's magnetic field, which extends about 10 Earth radii
towards the Sun. The solar wind, a stream of charged particles, streams
out and around the terrestrial magnetic field, and continues behind the
magnetic tail,
hundreds of Earth radii downstream. Inside the magnetosphere, there are
relatively dense regions of solar wind particles called the Van Allen
radiation belts.
Methods
Geodesy
Geophysical measurements are generally at a particular time and
place. Accurate measurements of position, along with earth deformation
and gravity, are the province of geodesy.
While geodesy and geophysics are separate fields, the two are so
closely connected that many scientific organizations such as the American Geophysical Union, the Canadian Geophysical Union and the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics encompass both.
Absolute positions are most frequently determined using the global positioning system (GPS). A three-dimensional position is calculated using messages from four or more visible satellites and referred to the 1980 Geodetic Reference System. An alternative, optical astronomy,
combines astronomical coordinates and the local gravity vector to get
geodetic coordinates. This method only provides the position in two
coordinates and is more difficult to use than GPS. However, it is useful
for measuring motions of the Earth such as nutation and Chandler wobble. Relative positions of two or more points can be determined using very-long-baseline interferometry.
Gravity measurements became part of geodesy because they were
needed to related measurements at the surface of the Earth to the
reference coordinate system. Gravity measurements on land can be made
using gravimeters
deployed either on the surface or in helicopter flyovers. Since the
1960s, the Earth's gravity field has been measured by analyzing the
motion of satellites. Sea level can also be measured by satellites using
radar altimetry, contributing to a more accurate geoid. In 2002, NASA launched the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment
(GRACE), wherein two twin satellites map variations in Earth's gravity
field by making measurements of the distance between the two satellites
using GPS and a microwave ranging system. Gravity variations detected
by GRACE include those caused by changes in ocean currents; runoff and
ground water depletion; melting ice sheets and glaciers.
Satellites and space probes
Satellites in space have made it possible to collect data from not only the visible light region, but in other areas of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The planets can be characterized by their force fields: gravity and
their magnetic fields, which are studied through geophysics and space
physics.
Measuring the changes in acceleration experienced by spacecraft as they orbit has allowed fine details of the gravity fields of the planets to be mapped. For example, in the 1970s, the gravity field disturbances above lunar maria were measured through lunar orbiters, which led to the discovery of concentrations of mass, mascons, beneath the Imbrium, Serenitatis, Crisium, Nectaris and Humorum basins.
History
Geophysics emerged as a separate discipline only in the 19th century, from the intersection of physical geography, geology, astronomy, meteorology, and physics. However, many geophysical phenomena – such as the Earth's magnetic field and earthquakes – have been investigated since the ancient era.
Ancient and classical eras
Replica of Zhang Heng's seismoscope, possibly the first contribution to seismology.
The magnetic compass existed in China back as far as the fourth century BC. It was used as much for feng shui
as for navigation on land. It was not until good steel needles could be
forged that compasses were used for navigation at sea; before that,
they could not retain their magnetism long enough to be useful. The
first mention of a compass in Europe was in 1190 AD.
In circa 240 BC, Eratosthenes of Cyrene deduced that the Earth was round and measured the circumference of the Earth, using trigonometry and the angle of the Sun at more than one latitude in Egypt. He developed a system of latitude and longitude.
Perhaps the earliest contribution to seismology was the invention of a seismoscope by the prolific inventor Zhang Heng in 132 AD.
This instrument was designed to drop a bronze ball from the mouth of a
dragon into the mouth of a toad. By looking at which of eight toads had
the ball, one could determine the direction of the earthquake. It was
1571 years before the first design for a seismoscope was published in
Europe, by Jean de la Hautefeuille. It was never built.
Beginnings of modern science
One of the publications that marked the beginning of modern science was William Gilbert's De Magnete
(1600), a report of a series of meticulous experiments in magnetism.
Gilbert deduced that compasses point north because the Earth itself is
magnetic.
In 1687 Isaac Newton published his Principia, which not only laid the foundations for classical mechanics and gravitation but also explained a variety of geophysical phenomena such as the tides and the precession of the equinox.
The first seismometer, an instrument capable of keeping a continuous record of seismic activity, was built by James Forbes in 1844.