 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | L-ascorbic acid, ascorbic acid, ascorbate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682583 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, IM, IV, subQ |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | rapid & complete |
| Protein binding | negligible |
| Elimination half-life | varies according to plasma concentration |
| Excretion | kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| E number | E300 (antioxidants, ...) |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.061 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H8O6 |
| Molar mass | 176.12 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.694 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 190–192 °C (374–378 °F) (some decomposition) |
| Boiling point | 553 °C (1,027 °F) |
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid and L-ascorbic acid, is a vitamin found in various foods and sold as a dietary supplement. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant.
Current evidence does not support its use for the prevention of the common cold. There is, however, some evidence that regular use may shorten the length of colds. It is unclear whether supplementation affects the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, or dementia. It may be taken by mouth or by injection.
Vitamin C is generally well tolerated. Large doses may cause gastrointestinal discomfort, headache, trouble sleeping, and flushing of the skin. Normal doses are safe during pregnancy. The United States Institute of Medicine recommends against taking large doses.
Vitamin C was discovered in 1912, isolated in 1928, and in 1933 was the first vitamin to be chemically produced. It is on the World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines, which lists the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. Vitamin C is available as an inexpensive generic and over-the-counter medication. Partly for its discovery, Albert Szent-Györgyi and Walter Norman Haworth were awarded the 1937 Nobel Prizes in Physiology and Medicine and Chemistry, respectively. Foods containing vitamin C include citrus fruits, kiwifruit, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, raw bell peppers, and strawberries. Prolonged storage or cooking may reduce vitamin C content in foods.
Biology
Significance
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for certain animals including humans. The term vitamin C encompasses several vitamers
that have vitamin C activity in animals. Ascorbate salts such as sodium
ascorbate and calcium ascorbate are used in some dietary supplements.
These release ascorbate upon digestion. Ascorbate and ascorbic acid are
both naturally present in the body, since the forms interconvert
according to pH. Oxidized forms of the molecule such as dehydroascorbic acid are converted back to ascorbic acid by reducing agents.
Vitamin C functions as a cofactor in many enzymatic reactions in animals (and humans) that mediate a variety of essential biological functions, including wound healing and collagen synthesis. In humans, vitamin C deficiency leads to impaired collagen synthesis, contributing to the more severe symptoms of scurvy. Another biochemical role of vitamin C is to act as an antioxidant (a reducing agent) by donating electrons to various enzymatic and non-enzymatic reactions. Doing so converts vitamin C to an oxidized state - either as semidehydroascorbic acid or dehydroascorbic acid. These compounds can be restored to a reduced state by glutathione and NADPH-dependent enzymatic mechanisms.
In plants, vitamin C is a substrate for ascorbate peroxidase. This enzyme utilizes ascorbate to neutralize toxic hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by converting it to water (H2O).
Deficiency
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, since without this vitamin, collagen made by the body is too unstable to perform its function.
Scurvy leads to the formation of brown spots on the skin, spongy gums, and bleeding from all mucous membranes.
The spots are most abundant on the thighs and legs, and a person with
the ailment looks pale, feels depressed, and is partially immobilized.
In advanced scurvy there are open, suppurating wounds and loss of teeth and, eventually, death. The human body can store only a certain amount of vitamin C,
and so the body stores are depleted if fresh supplies are not consumed.
The time frame for onset of symptoms of scurvy in unstressed adults on a
completely vitamin C free diet, however, may range from one month to
more than six months, depending on previous loading of vitamin C.
Notable human dietary studies of experimentally induced scurvy have been conducted on conscientious objectors
during World War II in Britain and on Iowa state prisoners in the late
1960s to the 1980s. These studies both found that all obvious symptoms
of scurvy previously induced by an experimental scorbutic
diet with extremely low vitamin C content could be completely reversed
by additional vitamin C supplementation of only 10 mg a day. In these
experiments, there was no clinical difference noted between men given
70 mg vitamin C per day (which produced a blood level of vitamin C of
about 0.55 mg/dl, about 1/3 of tissue saturation levels) and those given
10 mg per day. Men in the prison study developed the first signs of
scurvy about four weeks after starting the vitamin C-free diet, whereas
in the British study, six to eight months were required, possibly due to
the pre-loading of this group with a 70 mg/day supplement for six weeks
before the scorbutic diet was fed.
Men in both studies on a diet devoid, or nearly devoid, of
vitamin C had blood levels of vitamin C too low to be accurately
measured when they developed signs of scurvy and, in the Iowa study, at
this time were estimated (by labeled vitamin C dilution) to have a body
pool of less than 300 mg, with daily turnover of only 2.5 mg/day,
implying an instantaneous half-life of 83 days by this time (elimination
constant of 4 months).
Uses
Vitamin C supplements at a drug store.
Vitamin C has a definitive role in treating scurvy, which is a
disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Beyond that, a role for vitamin C
as prevention or treatment for various diseases is disputed, with
reviews reporting conflicting results. A 2012 Cochrane review reported no effect of vitamin C supplementation on overall mortality. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as one of the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.
Scurvy
The disease scurvy is caused by vitamin C deficiency and can be prevented and treated with vitamin C-containing foods or dietary supplements. It takes at least a month of little to no vitamin C before symptoms occur.
Early symptoms are malaise and lethargy, progressing to shortness of
breath, bone pain, bleeding gums, susceptibility to bruising, poor wound
healing, and finally fever, convulsions and eventual death.
Until quite late in the disease the damage is reversible, as healthy
collagen replaces the defective collagen with vitamin C repletion.
Treatment can be orally or by intramuscular or intravenous injection. Scurvy was known to Hippocrates in the classical era. The disease was shown to be prevented by citrus fruit in an early controlled trial by a Royal Navy surgeon, James Lind, in 1747, and from 1796 lemon juice was issued to all Royal Navy crewmen.
Infection
The Nobel prizewinner Linus Pauling advocated taking vitamin C for the common cold in a 1970 book.
The effect of vitamin C on the common cold has been extensively researched. The earliest publication of a controlled clinical trial appears to be from 1945. Researchers continued to work on this question, but research interest and public interest spiked after Linus Pauling,
two-time awardee of the Nobel Prize (Chemistry Prize, 1954, Peace Prize
1962), started publishing research on the topic and also published a
book "Vitamin C and the Common Cold" in 1970. A revised and expanded edition "Vitamin C, the Common Cold and the Flu" was published in 1976.
Research on vitamin C in the common cold has been divided into
effects on prevention, duration, and severity. A Cochrane review which
looked at at least 200 mg/day concluded that vitamin C taken on a
regular basis was not effective in prevention of the common cold. At
least 1000 mg/day also made no difference. However, taking vitamin C on a
regular basis did reduce the average duration by 8% in adults and 14%
in children, and also reduced severity of colds.
A subset of trials reported that supplementation reduced the incidence
of colds by half in marathon runners, skiers, or soldiers in subarctic
conditions.
Another subset of trials looked at therapeutic use, meaning that
vitamin C was not started unless the people started to feel the
beginnings of a cold. In these, vitamin C did not impact duration or
severity. An earlier review stated that vitamin C did not prevent colds, did reduce duration, did not reduce severity.
The authors of the Cochrane review concluded that "...given the
consistent effect of vitamin C on the duration and severity of colds in
the regular supplementation studies, and the low cost and safety, it may
be worthwhile for common cold patients to test on an individual basis
whether therapeutic vitamin C is beneficial for them."
Vitamin C distributes readily in high concentrations into immune cells, has antimicrobial and natural killer cell activities, promotes lymphocyte proliferation, and is consumed quickly during infections, effects indicating a prominent role in immune system regulation. The European Food Safety Authority found a cause and effect relationship
exists between the dietary intake of vitamin C and functioning of a
normal immune system in adults and in children under three years of age.
Cancer
There are
two approaches to the question of whether vitamin C has an impact on
cancer. First, within the normal range of dietary intake without
additional dietary supplementation, are people who consume more vitamin C
at lower risk for developing cancer, and if so, does an orally consumed
supplement have the same benefit? Second, for people diagnosed with
cancer, will large amounts of ascorbic acid administered intravenously
treat the cancer, reduce the adverse effects of other treatments, and so
prolong survival and improve quality of life? A 2013 Cochrane review
found no evidence that vitamin C supplementation reduces the risk of
lung cancer in healthy people or those at high risk due to smoking or
asbestos exposure. A second meta-analysis found no effect on the risk of prostate cancer.
Two meta-analyses evaluated the effect of vitamin C supplementation on
the risk of colorectal cancer. One found a weak association between
vitamin C consumption and reduced risk, and the other found no effect
from supplementation. A 2011 meta-analysis failed to find support for the prevention of breast cancer with vitamin C supplementation, but a second study concluded that vitamin C may be associated with increased survival in those already diagnosed.
Under the rubric of orthomolecular medicine,
"Intravenous vitamin C is a contentious adjunctive cancer therapy,
widely used in naturopathic and integrative oncology settings." With oral administration absorption efficiency decreases as amounts increase. Intravenous administration bypasses this.
Doing so makes it possible to achieve plasma concentrations of 5 to 10
millimoles/liter (mmol/L), which far exceed the approximately 0.2 mmol/L
limit from oral consumption.
The theories of mechanism are contradictory. At high tissue
concentrations ascorbic acid is described as acting as a pro-oxidant,
generating hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to kill tumor
cells. The same literature claims that ascorbic acid acts as an
antioxidant, thereby reducing the adverse effects of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Research continues in this field, but a 2014 review concluded:
"Currently, the use of high-dose intravenous vitamin C [as an anticancer
agent] cannot be recommended outside of a clinical trial."
A 2015 review added: "There is no high-quality evidence to suggest that
ascorbate supplementation in cancer patients either enhances the
antitumor effects of chemotherapy or reduces its toxicity. Evidence for
ascorbate's anti-tumor effects was limited to case reports and
observational and uncontrolled studies."
Cardiovascular disease
A 2013 meta-analysis found no evidence that vitamin C supplementation reduces the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, cardiovascular mortality, or all-cause mortality.
However, a second analysis found an inverse relationship between
circulating vitamin C levels or dietary vitamin C and the risk of
stroke.
A meta-analysis of 44 clinical trials has shown a significant positive effect of vitamin C on endothelial
function when taken at doses greater than 500 mg per day. The
endothelium is a layer of cells that line the interior surface of blood
vessels. Endothelial dysfunction
is implicated in many aspects of vascular diseases. The researchers
noted that the effect of vitamin C supplementation appeared to be
dependent on health status, with stronger effects in those at higher
risk of cardiovascular disease.
Brain function
A 2017 systematic review found lower vitamin C concentrations in people with cognitive impairment, including Alzheimer's disease and dementia, compared to people with normal cognition. The cognitive testing, however, relied on the Mini-Mental State Examination,
which is only a general test of cognition, indicating an overall low
quality of research assessing the potential importance of vitamin C on
cognition in normal and impaired people. A review of nutrient status in people with Alzheimer's disease reported low plasma vitamin C, but also low blood levels of folate, vitamin B12, and vitamin E.
Other diseases
Studies examining the effects of vitamin C intake on the risk of Alzheimer's disease have reached conflicting conclusions. Maintaining a healthy dietary intake is probably more important than supplementation for achieving any potential benefit. A 2010 review found no role for vitamin C supplementation in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Vitamin C supplementation does not prevent or slow the progression of age-related cataract.
Side effects
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin,
with dietary excesses not absorbed, and excesses in the blood rapidly
excreted in the urine, so it exhibits remarkably low acute toxicity.
More than two to three grams may cause indigestion, particularly when
taken on an empty stomach. However, taking vitamin C in the form of sodium ascorbate and calcium ascorbate may minimize this effect.
Other symptoms reported for large doses include nausea, abdominal
cramps and diarrhea. These effects are attributed to the osmotic effect
of unabsorbed vitamin C passing through the intestine.
In theory, high vitamin C intake may cause excessive absorption of
iron. A summary of reviews of supplementation in healthy subjects did
not report this problem but left as untested the possibility that
individuals with hereditary hemochromatosis might be adversely affected.
There is a longstanding belief among the mainstream medical community that vitamin C increases risk of kidney stones. "Reports of kidney stone formation associated with excess ascorbic acid intake are limited to individuals with renal disease".
Reviews state that "data from epidemiological studies do not support an
association between excess ascorbic acid intake and kidney stone
formation in apparently healthy individuals",
although one large, multi-year trial did report a nearly two-fold
increase in kidney stones in men who regularly consumed a vitamin C
supplement.
Diet
Recommended levels
| US vitamin C recommendations (mg per day) | |
|---|---|
| RDA (children ages 1–3 years) | 15 |
| RDA (children ages 4–8 years) | 25 |
| RDA (children ages 9–13 years) | 45 |
| RDA (girls ages 14–18 years) | 65 |
| RDA (boys ages 14–18 years) | 75 |
| RDA (adult female) | 75 |
| RDA (adult male) | 90 |
| RDA (pregnancy) | 85 |
| RDA (lactation) | 120 |
| UL (adult female) | 2,000 |
| UL (adult male) | 2,000 |
Recommendations for vitamin C intake by adults have been set by various national agencies:
- 40 milligrams per day: India National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad
- 45 milligrams per day or 300 milligrams per week: the World Health Organization
- 80 milligrams per day: the European Commission Council on nutrition labeling
- 90 mg/day (males) and 75 mg/day (females): Health Canada 2007
- 90 mg/day (males) and 75 mg/day (females): United States National Academy of Sciences.
- 100 milligrams per day: Japan National Institute of Health and Nutrition.
- 110 mg/day (males) and 95 mg/day (females): European Food Safety Authority
In 2000 the North American Dietary Reference Intake chapter on vitamin C updated the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) to 90 milligrams per day for adult men and 75 mg/day for adult women, and set a Tolerable upper intake level (UL) for adults of 2,000 mg/day. The table shows RDAs for the United States and Canada for children, and for pregnant and lactating women.
For the European Union, the EFSA set higher recommendations for adults,
and also for children: 20 mg/day for ages 1–3, 30 mg/day for ages 4–6,
45 mg/day for ages 7–10, 70 mg/day for ages 11–14, 100 mg/day for males
ages 15–17, 90 mg/day for females ages 15–17. For pregnancy 100 mg/day;
for lactation 155 mg/day.
India, on the other hand, has set recommendations much lower: 40 mg/day
for ages 1 through adult, 60 mg/day for pregnancy, and 80 mg/day for
lactation. Clearly, there is not consensus among countries.
Cigarette smokers and people exposed to secondhand smoke have
lower plasma vitamin C levels than nonsmokers. The thinking is that
inhalation of smoke causes oxidative damage, depleting this antioxidant
vitamin.
The U.S. Institute of Medicine estimated that smokers need 35 mg more
vitamin C per day than nonsmokers, but did not formally establish a
higher RDA for smokers.
One meta-analysis showed an inverse relationship between vitamin C
intake and lung cancer, although it concluded that more research is
needed to confirm this observation.
The U.S. National Center for Health Statistics conducts biannual
National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to assess the
health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United
States. Some results are reported as What We Eat In America. The
2013-2014 survey reported that for adults ages 20 years and older, men
consumed on average 83.3 mg/d and women 75.1 mg/d. This means that half
the women and more than half the men are not consuming the RDA for
vitamin C.
The same survey stated that about 30% of adults reported they consumed a
vitamin C dietary supplement or a multi-vitamin/mineral supplement that
included vitamin C, and that for these people total consumption was
between 300 and 400 mg/d.
In 2000 the Institute of Medicine of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences set a Tolerable upper intake level
(UL) for adults of 2,000 mg/day. The amount was chosen because human
trials had reported diarrhea and other gastrointestinal disturbances at
intakes of greater than 3,000 mg/day. This was the
Lowest-Observed-Adverse-Effect Level (LOAEL), meaning that other adverse
effects were observed at higher intakes. The European Food Safety Authority
(EFSA) reviewed the safety question in 2006 and reached the conclusion
that there was not sufficient evidence to set a UL for vitamin C.[66]
The Japan National Institute of Health and Nutrition reviewed the same
question in 2010 and also reached the conclusion that there was not
sufficient evidence to set a UL.
Food labeling
For
U.S. food and dietary supplement labeling purposes, the amount in a
serving is expressed as a percent of Daily Value (%DV). For vitamin C
labeling purposes, 100% of the Daily Value was 60 mg, but as of May 27,
2016 it was revised to 90 mg to bring it into agreement with the RDA. A table of the old and new adult Daily Values is provided at Reference Daily Intake.
The original deadline to be in compliance was July 28, 2018, but on
September 29, 2017 the FDA released a proposed rule that extended the
deadline to January 1, 2020 for large companies and January 1, 2021 for
small companies.
European Union regulations require that labels declare energy, protein,
fat, saturated fat, carbohydrates, sugars, and salt. Voluntary
nutrients may be shown if present in significant amounts. Instead of
Daily Values, amounts are shown as percent of Reference Intakes (RIs).
For vitamin C, 100% RI was set at 80 mg in 2011.
Sources
The richest natural sources are fruits and vegetables. Vitamin C is the most widely taken nutritional supplement and is available in a variety of forms, including tablets, drink mixes, and in capsules.
Plant sources
While
plant foods are generally a good source of vitamin C, the amount in
foods of plant origin depends on the variety of the plant, soil
condition, climate where it grew, length of time since it was picked,
storage conditions, and method of preparation. The following table is approximate and shows the relative abundance in different raw plant sources.
As some plants were analyzed fresh while others were dried (thus,
artificially increasing concentration of individual constituents like
vitamin C), the data are subject to potential variation and difficulties
for comparison. The amount is given in milligrams per 100 grams of the
edible portion of the fruit or vegetable:
| Plant source | Amount (mg / 100g) |
|---|---|
| Kakadu plum | 1000–5300 |
| Camu camu | 2800 |
| Acerola | 1677 |
| Seabuckthorn | 695 |
| Indian gooseberry | 445 |
| Rose hip | 426 |
| Guava | 228 |
| Blackcurrant | 200 |
| Yellow bell pepper/capsicum | 183 |
| Red bell pepper/capsicum | 128 |
| Kale | 120 |
| Kiwifruit, broccoli | 90 |
| Plant source | Amount (mg / 100g) |
|---|---|
| Green bell pepper/capsicum | 80 |
| Loganberry, redcurrant, Brussels sprouts | 80 |
| Cloudberry, elderberry | 60 |
| Papaya, strawberry | 60 |
| Orange, lemon | 53 |
| Pineapple, cauliflower | 48 |
| Cantaloupe | 40 |
| Grapefruit, raspberry | 30 |
| Passion fruit, spinach | 30 |
| Cabbage, lime | 30 |
| Mango | 28 |
| Blackberry | 21 |
| Plant source | Amount (mg / 100g) |
|---|---|
| Potato, honeydew melon | 20 |
| Tomato | 14 |
| Cranberry | 13 |
| Blueberry, grape | 10 |
| Apricot, plum, watermelon | 10 |
| Avocado | 8.8 |
| Onion | 7.4 |
| Cherry, peach | 7 |
| Carrot, apple, asparagus | 6 |
Goats,
like many animals but not humans, make their own vitamin C. An adult
goat, weighing approx. 70 kg, will manufacture more than 13,300 mg of
vitamin C per day in normal health, and levels manyfold higher when
faced with stress.
Animal-sourced foods do not provide much vitamin C, and what there
is, is largely destroyed by the heat of cooking. For example, raw
chicken liver contains 17.9 mg/100 g, but fried, the content is reduced
to 2.7 mg/100 g. Chicken eggs contain no vitamin C, raw or cooked. Vitamin C is present in human breast milk at 5.0 mg/100 g and 6.1 mg/100 g in one tested sample of infant formula, but cow's milk contains only 1.0 mg/ 100 g.
Food preparation
Vitamin C chemically decomposes
under certain conditions, many of which may occur during the cooking of
food. Vitamin C concentrations in various food substances decrease with
time in proportion to the temperature at which they are stored
and cooking can reduce the vitamin C content of vegetables by around
60% possibly partly due to increased enzymatic destruction as it may be
more significant at sub-boiling temperatures. Longer cooking times also add to this effect, as will copper food vessels, which catalyse the decomposition.
Another cause of vitamin C being lost from food is leaching,
where the water-soluble vitamin dissolves into the cooking water, which
is later poured away and not consumed. However, vitamin C does not
leach in all vegetables at the same rate; research shows broccoli seems to retain more than any other.
Research has also shown that freshly cut fruits do not lose significant
nutrients when stored in the refrigerator for a few days.
Supplements
Vitamin
C dietary supplements are available as tablets, capsules, drink mix
packets, in multi-vitamin/mineral formulations, in antioxidant
formulations, and as crystalline powder.
Vitamin C is also added to some fruit juices and juice drinks. Tablet
and capsule content ranges from 25 mg to 1500 mg per serving. The most
commonly used supplement compounds are ascorbic acid, sodium ascorbate
and calcium ascorbate. Vitamin C molecules can also be bound to the fatty acid palmitate, creating ascorbyl palmitate, or else incorporated into liposomes.
Food fortification
In 2014, the Canadian Food Inspection Agency evaluated the effect of fortification of foods with ascorbate in the guidance document, Foods to Which Vitamins, Mineral Nutrients and Amino Acids May or Must be Added.
Voluntary and mandatory fortification was described for various classes
of foods. Among foods classified for mandatory fortification with
vitamin C were fruit-flavored drinks, mixes, and concentrates, foods for
a low-energy diet, meal replacement products, and evaporated milk.
Food additives
Ascorbic acid and some of its salts and esters are common additives added to various foods, mostly to retard oxidation. The relevant European food additive E numbers are:
- E300 ascorbic acid (approved for use as a food additive in the EU, U.S. and Australia and New Zealand)
- E301 sodium ascorbate (approved for use as a food additive in the EU, U.S. and Australia and New Zealand)
- E302 calcium ascorbate (approved for use as a food additive in the EU, U.S. and Australia and New Zealand)
- E303 potassium ascorbate (approved in Australia and New Zealand, but not in U.S.)
- E304 fatty acid esters of ascorbic acid such as ascorbyl palmitate (approved for use as a food additive in the EU, U.S. and Australia and New Zealand)
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Vitamin C – specifically, in the form of ascorbate – performs numerous physiological functions in the human body by serving as an enzyme substrate and/or cofactor and an electron donor. These functions include the synthesis of collagen, carnitine, and neurotransmitters; the synthesis and catabolism of tyrosine; and the metabolism of microsome.
During biosynthesis, ascorbate acts as a reducing agent, donating
electrons and preventing oxidation to keep iron and copper atoms in
their reduced states.
Vitamin C functions as a cofactor for the following enzymes:
- Three groups of enzymes (prolyl-3-hydroxylases, prolyl-4-hydroxylases, and lysyl hydroxylases) that are required for the hydroxylation of proline and lysine in the synthesis of collagen. These reactions add hydroxyl groups to the amino acids proline or lysine in the collagen molecule via prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase, both requiring vitamin C as a cofactor. The role of vitamin C as a cofactor is to oxidize prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase from Fe2+ to Fe3+ and to reduce it from Fe3+ to Fe2+. Hydroxylation allows the collagen molecule to assume its triple helix structure, and thus vitamin C is essential to the development and maintenance of scar tissue, blood vessels, and cartilage.
- Two enzymes (ε-N-trimethyl-L-lysine hydroxylase and γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase) that are necessary for synthesis of carnitine. Carnitine is essential for the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria for ATP generation.
- Hypoxia-inducible factor-proline dioxygenase enzymes (isoforms: EGLN1, EGLN2, and EGLN3)
- Dopamine beta-hydroxylase participates in the biosynthesis of norepinephrine from dopamine.
- Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase amidates peptide hormones by removing the glyoxylate residue from their c-terminal glycine residues. This increases peptide hormone stability and activity.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
From
the U.S. National Institutes of Health: [In humans] "Approximately
70%–90% of vitamin C is absorbed at moderate intakes of 30–180 mg/day.
However, at doses above 1,000 mg/day, absorption falls to less than
50%."
It is transported through the intestine via both glucose-sensitive and
glucose-insensitive mechanisms, so the presence of large quantities of
sugar in the intestine can slow absorption.
Ascorbic acid is absorbed in the body by both active transport
and simple diffusion. Sodium-Dependent Active Transport—Sodium-Ascorbate
Co-Transporters (SVCTs) and Hexose transporters (GLUTs)—are the two
transporter proteins required for active absorption. SVCT1 and SVCT2 import the reduced form of ascorbate across plasma membranes. GLUT1 and GLUT3 are glucose transporters, and transfer only the dehydroascorbic acid (DHA) form of vitamin C.
Although dehydroascorbic acid is absorbed in higher rate than
ascorbate, the amount of dehydroascorbic acid found in plasma and
tissues under normal conditions is low, as cells rapidly reduce
dehydroascorbic acid to ascorbate.
Transport
SVCTs appear to be the predominant system for vitamin C transport in the body, the notable exception being red blood cells, which lose SVCT proteins during maturation.
In both vitamin C synthesizers (example: rat) and non-synthesizers
(example: human) cells with few exceptions maintain ascorbic acid
concentrations much higher than the approximately 50 micromoles/liter
(µmol/L) found in plasma. For example, the ascorbic acid content of
pituitary and adrenal glands can exceed 2,000 µmol/L, and muscle is at
200-300 µmol/L.
The known coenzymatic functions of ascorbic acid do not require such
high concentrations, so there may be other, as yet unknown functions.
Consequences of all this organ content is that plasma vitamin C is not a
good indicator of whole-body status, and people may vary in the amount
of time needed to show symptoms of deficiency when consuming a diet very
low in vitamin C.
Excretion
Excretion
can be as ascorbic acid, via urine. In humans, during times of low
dietary intake, vitamin C is reabsorbed by the kidneys rather than
excreted. Only when plasma concentrations are 1.4 mg/dL or higher does
re-absorption decline and the excess amounts pass freely into the urine.
This salvage process delays onset of deficiency.
Ascorbic acid also converts (reversibly) to dehydroascorbate (DHA) and
from that compound non-reversibly to 2,3-diketogluonate and then
oxalate. These three compounds are also excreted via urine. Humans are
better than guinea pigs at converting DHA back to ascorbate, and thus
take much longer to become vitamin C deficient.
Chemistry
The name "vitamin C" always refers to the L-enantiomer of ascorbic acid and its oxidized
forms, such as dehydroascorbate (DHA). Therefore, unless written
otherwise, "ascorbate" and "ascorbic acid" refer in the nutritional
literature to L-ascorbate and L-ascorbic acid respectively. Ascorbic acid is a weak sugar acid structurally related to glucose. In biological systems, ascorbic acid can be found only at low pH, but in solutions above pH 5 is predominantly found in the ionized
form, ascorbate. All of these molecules have vitamin C activity and
thus are used synonymously with vitamin C, unless otherwise specified.
Numerous analytical methods have been developed for ascorbic acid
detection. For example, vitamin C content of a food sample such as
fruit juice can be calculated by measuring the volume of the sample
required to decolorize a solution of dichlorophenolindophenol (DCPIP) and then calibrating the results by comparison with a known concentration of vitamin C.
Testing for levels
Simple tests are available to measure the levels of vitamin C in the urine and in serum or blood plasma. However these reflect recent dietary intake rather than total body content. It has been observed that while serum or blood plasma concentrations follow a circadian rhythm
or reflect short-term dietary impact, content within tissues is more
stable and can give a better view of the availability of ascorbate
within the entire organism. However, very few hospital laboratories are
adequately equipped and trained to carry out such detailed analyses.
Biosynthesis
The vast majority of animals and plants are able to synthesize vitamin C, through a sequence of enzyme-driven steps, which convert monosaccharides to vitamin C. Yeasts do not make L-ascorbic acid but rather its stereoisomer, erythorbic acid.
In animals, the starting material is glucose. In some species that synthesize ascorbate in the liver (including mammals and perching birds), the glucose is extracted from glycogen; ascorbate synthesis is a glycogenolysis-dependent process. In animals that cannot synthesize vitamin C, the enzyme L-gulonolactone oxidase (GULO), that catalyses the last step in the biosynthesis, is highly mutated and non-functional.
Animal pathway
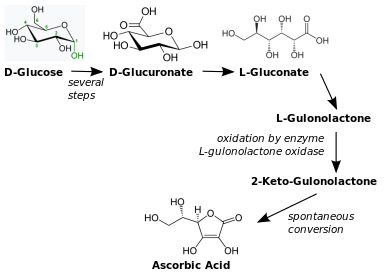
Vitamin C biosynthesis in vertebrates
The biosynthesis of ascorbic acid in vertebrates
starts with the formation of UDP-glucuronic acid. UDP-glucuronic acid
is formed when UDP-glucose undergoes two oxidations catalyzed by the
enzyme UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase. UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase uses the
co-factor NAD+ as the electron acceptor. The transferase UDP-glucuronate pyrophosphorylase removes a UMP and glucuronokinase, with the cofactor ADP, removes the final phosphate leading to D-glucuronic acid. The aldehyde group of this compound is reduced to a primary alcohol using the enzyme glucuronate reductase and the cofactor NADPH, yielding L-gulonic acid. This is followed by lactone formation with the hydrolase gluconolactonase between the carbonyl on C1 and hydroxyl group on C4. L-Gulonolactone then reacts with oxygen, catalyzed by the enzyme L-gulonolactone oxidase (which is nonfunctional in humans and other Haplorrhini primates) and the cofactor FAD+. This reaction produces 2-oxogulonolactone (2-keto-gulonolactone), which spontaneously undergoes enolization to form ascorbic acid.
Some mammals have lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C, including simians and tarsiers, which together make up one of two major primate suborders, Haplorrhini. This group includes humans. The other more primitive primates (Strepsirrhini) have the ability to make vitamin C. Synthesis does not occur in most bats nor in species in the rodent family Caviidae, that includes guinea pigs and capybaras, but does occur in other rodents, including rats and mice.
Reptiles and older orders of birds make ascorbic acid in their kidneys. Recent orders of birds and most mammals make ascorbic acid in their liver. A number of species of passerine
birds also do not synthesize, but not all of them, and those that do
not are not clearly related; there is a theory that the ability was lost
separately a number of times in birds.
In particular, the ability to synthesize vitamin C is presumed to have
been lost and then later re-acquired in at least two cases. The ability to synthesize vitamin C has also been lost in about 96% of fish (the teleosts).
Most tested families of bats (order Chiroptera),
including major insect and fruit-eating bat families, cannot synthesize
vitamin C. A trace of gulonolactone oxidase was detected in only 1 of
34 bat species tested, across the range of 6 families of bats tested. There are at least two species of bats, frugivorous bat (Rousettus leschenaultii) and insectivorous bat (Hipposideros armiger), that retain (or regained) their ability of vitamin C production.
Some of these species (including humans) are able to make do with
the lower levels available from their diets by recycling oxidised
vitamin C.
Most simians consume the vitamin in amounts 10 to 20 times higher than that recommended by governments for humans.
This discrepancy constitutes much of the basis of the controversy on
current recommended dietary allowances. It is countered by arguments
that humans are very good at conserving dietary vitamin C, and are able
to maintain blood levels of vitamin C comparable with simians on a far
smaller dietary intake, perhaps by recycling oxidized vitamin C.
Plant pathways
Vitamin C biosynthesis in plants
There are many different biosynthesis pathways for ascorbic acid in
plants. Most of these pathways are derived from products found in
glycolysis and other pathways. For example, one pathway goes through the
plant cell wall polymers. The plant ascorbic acid biosynthesis pathway most principal seems to be L-galactose. L-Galactose reacts with the enzyme L-galactose
dehydrogenase, whereby the lactone ring opens and forms again but with
between the carbonyl on C1 and hydroxyl group on the C4, resulting in L-galactonolactone. L-Galactonolactone then reacts with the mitochondrial flavoenzyme L-galactonolactone dehydrogenase. to produce ascorbic acid. L-Ascorbic acid has a negative feedback on L-galactose dehydrogenase in spinach.
Ascorbic acid efflux by embryo of dicots plants is a well-established
mechanism of iron reduction, and a step obligatory for iron uptake.
All plants synthesize ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid functions as a
cofactor for enzymes involved in photosynthesis, synthesis of plant
hormones, as an antioxidant and also regenerator of other antioxidants. Plants use multiple pathways to synthesize vitamin C. The major pathway starts with glucose, fructose or mannose (all simple sugars) and proceeds to L-galactose, L-galactonolactone and ascorbic acid. There is feedback regulation in place, in that the presence of ascorbic acid inhibits enzymes in the synthesis pathway. This process follows a diurnal rhythm,
so that enzyme expression peaks in the morning to support biosynthesis
later on when mid-day sunlight intensity demands high ascorbic acid
concentrations.
Minor pathways may be specific to certain parts of plants; these can be
either identical to the vertebrate pathway (including the GLO enzyme),
or start with inositol and get to ascorbic acid via L-galactonic acid to
L-galactonolactone.
Evolution
Ascorbic acid is a common enzymatic cofactor in mammals used in the synthesis of collagen, as well as a powerful reducing agent capable of rapidly scavenging a number of reactive oxygen species
(ROS). Given that ascorbate has these important functions, it is
surprising that the ability to synthesize this molecule has not always
been conserved. In fact, anthropoid primates, Cavia porcellus (guinea pigs), teleost fishes, most bats, and some Passeriform birds have all independently lost the ability to internally synthesize Vitamin C in either the kidney or the liver. In all of the cases where genomic analysis was done on an ascorbic acid auxotroph,
the origin of the change was found to be a result of loss-of-function
mutations in the gene that codes for L-Gulono-γ-lactone oxidase, the
enzyme that catalyzes the last step of the ascorbic acid pathway
outlined above. One explanation for the repeated loss of the ability to synthesize vitamin C is that it was the result of genetic drift; assuming that the diet was rich in vitamin C, natural selection would not act to preserve it.
In the case of the simians, it is thought that the loss of the
ability to make vitamin C may have occurred much farther back in
evolutionary history than the emergence of humans or even apes, since it
evidently occurred soon after the appearance of the first primates, yet
sometime after the split of early primates into the two major suborders
Haplorrhini (which cannot make vitamin C) and its sister suborder of non-tarsier prosimians, the Strepsirrhini ("wet-nosed" primates), which retained the ability to make vitamin C. According to molecular clock dating, these two suborder primate branches parted ways about 63 to 60 million years ago.
Approximately three to five million years later (58 million years ago),
only a short time afterward from an evolutionary perspective, the
infraorder Tarsiiformes, whose only remaining family is that of the tarsier (Tarsiidae), branched off from the other haplorrhines.
Since tarsiers also cannot make vitamin C, this implies the mutation
had already occurred, and thus must have occurred between these two
marker points (63 to 58 million years ago).
It has also been noted that the loss of the ability to synthesize ascorbate strikingly parallels the inability to break down uric acid, also a characteristic of primates. Uric acid and ascorbate are both strong reducing agents. This has led to the suggestion that, in higher primates, uric acid has taken over some of the functions of ascorbate.
Industrial synthesis
Vitamin C is produced from glucose by two main routes. The Reichstein process, developed in the 1930s, uses a single pre-fermentation followed by a purely chemical route. The modern two-step fermentation process, originally developed in China
in the 1960s, uses additional fermentation to replace part of the later
chemical stages. The Reichstein process and the modern two-step
fermentation processes use sorbitol as the starting material and convert
it to sorbose using fermentation. The modern two-step fermentation
process then converts sorbose to KGA through another fermentation step,
avoiding an extra intermediate.
Both processes yield approximately 60% vitamin C from the glucose feed.
World production of synthesized vitamin C was estimated at
approximately 110,000 tonnes annually in 2000. Traditionally, the main
producers were BASF/Takeda, DSM, Merck and the China Pharmaceutical Group Ltd. of the People's Republic of China. By 2008 only the DSM plant in Scotland remained operational outside of China because of the strong price competition from China.
The world price of vitamin C rose sharply in 2008 partly as a
result of rises in basic food prices but also in anticipation of a
stoppage of the two Chinese plants, situated at Shijiazhuang near Beijing, as part of a general shutdown of polluting industry in China over the period of the Olympic games. Production resumed after the Olympics, but then five Chinese manufacturers met in 2010, among them Northeast Pharmaceutical Group and North China Pharmaceutical Group, and agreed to temporarily stop production in order to maintain prices.
In 2011 an American suit was filed against four Chinese companies that
allegedly colluded to limit production and fix prices of vitamin C in
the United States. The companies did not deny the accusation but say in
their defense that the Chinese government compelled them to act in this
way. In January 2012 a United States judge ruled that the Chinese companies can be sued in the U.S. by buyers acting as a group.
A verdict was reached in March 2013 imposing a $147.8 million fine.
This verdict was reversed by the 2nd U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in
New York, on the grounds that China formally advised the Court that its
laws required the vitamin C makers to violate the Sherman Act, a U.S.
antitrust law. In June 2017 the U.S. Supreme Court announced that it would consider an appeal filed to reverse the lower court decision.
History
Folk medicine
The
need to include fresh plant food or raw animal flesh in the diet to
prevent disease was known from ancient times. Native people living in
marginal areas incorporated this into their medicinal lore. For example,
spruce needles were used in temperate zones in infusions, or the leaves
from species of drought-resistant trees in desert areas. In 1536, the
French explorers Jacques Cartier and Daniel Knezevic, exploring the St. Lawrence River, used the local natives' knowledge to save his men who were dying of scurvy. He boiled the needles of the arbor vitae tree to make a tea that was later shown to contain 50 mg of vitamin C per 100 grams.
Scurvy at sea
Citrus fruits were among the first sources of vitamin C available to ships' surgeons.
In the 1497 expedition of Vasco da Gama, the curative effects of citrus fruit were known.
The Portuguese planted fruit trees and vegetables in Saint Helena, a
stopping point for homebound voyages from Asia, and left their sick to
be taken home by the next ship.
Authorities occasionally recommended plant food to prevent scurvy during long sea voyages. John Woodall, the first surgeon to the British East India Company, recommended the preventive and curative use of lemon juice in his 1617 book, The Surgeon's Mate. In 1734, the Dutch writer Johann Bachstrom gave the firm opinion that "scurvy is solely owing to a total abstinence from fresh vegetable food, and greens."
Scurvy had long been a principal killer of sailors during the long sea voyages.
According to Jonathan Lamb, "In 1499, Vasco da Gama lost 116 of his
crew of 170; In 1520, Magellan lost 208 out of 230;...all mainly to
scurvy."
James Lind, a British Royal Navy surgeon who, in 1747, identified that a quality in fruit prevented scurvy in one of the first recorded controlled experiments.
The first attempt to give scientific basis for the cause of this disease was by a ship's surgeon in the Royal Navy, James Lind.
While at sea in May 1747, Lind provided some crew members with two
oranges and one lemon per day, in addition to normal rations, while
others continued on cider, vinegar, sulfuric acid or seawater, along with their normal rations, in one of the world's first controlled experiments. The results showed that citrus fruits prevented the disease. Lind published his work in 1753 in his Treatise on the Scurvy.
Fresh fruit was expensive to keep on board, whereas boiling it
down to juice allowed easy storage but destroyed the vitamin (especially
if boiled in copper kettles). It was 1796 before the British navy adopted lemon
juice as standard issue at sea. In 1845, ships in the West Indies were
provided with lime juice instead, and in 1860 lime juice was used
throughout the Royal Navy, giving rise to the American use of the
nickname "limey" for the British. Captain James Cook had previously demonstrated the advantages of carrying "Sour krout" on board, by taking his crews to the Hawaiian Islands without losing any of his men to scurvy. For this, the British Admiralty awarded him a medal.
The name antiscorbutic was used in the eighteenth and
nineteenth centuries for foods known to prevent scurvy. These foods
included lemons, limes, oranges, sauerkraut, cabbage, malt, and portable soup. In 1928, the Canadian Arctic anthropologist Vilhjalmur Stefansson showed that the Inuit avoid scurvy on a diet of largely raw meat. Later studies on traditional food diets of the Yukon First Nations, Dene, Inuit, and Métis of Northern Canada showed that their daily intake of vitamin C averaged between 52 and 62 mg/day, comparable with the Estimated Average Requirement.
Discovery
Vitamin C was discovered in 1912, isolated in 1928 and synthesized in 1933, making it the first vitamin to be synthesized. Shortly thereafter Tadeus Reichstein succeeded in synthesizing the vitamin in bulk by what is now called the Reichstein process. This made possible the inexpensive mass-production of vitamin C. In 1934 Hoffmann–La Roche trademarked synthetic vitamin C under the brand name Redoxon and began to market it as a dietary supplement.
In 1907 a laboratory animal model which would help to identify
the antiscorbutic factor was discovered by the Norwegian physicians Axel Holst and Theodor Frølich, who when studying shipboard beriberi, fed guinea pigs
their test diet of grains and flour and were surprised when scurvy
resulted instead of beriberi. By luck, this species did not make its own
vitamin C, whereas mice and rats do. In 1912, the Polish biochemist Casimir Funk developed the concept of vitamins.
One of these was thought to be the anti-scorbutic factor. In 1928, this
was referred to as "water-soluble C," although its chemical structure
had not been determined.
Albert Szent-Györgyi, pictured here in 1948, was awarded the 1937 Nobel Prize in Medicine
"for his discoveries in connection with the biological combustion
processes, with special reference to vitamin C and the catalysis of
fumaric acid".
From 1928 to 1932, Albert Szent-Györgyi and Joseph L. Svirbely's Hungarian team, and Charles Glen King's
American team, identified the anti-scorbutic factor. Szent-Györgyi
isolated hexuronic acid from animal adrenal glands, and suspected it to
be the antiscorbutic factor.
In late 1931, Szent-Györgyi gave Svirbely the last of his
adrenal-derived hexuronic acid with the suggestion that it might be the
anti-scorbutic factor. By the spring of 1932, King's laboratory had
proven this, but published the result without giving Szent-Györgyi
credit for it. This led to a bitter dispute over priority. In 1933, Walter Norman Haworth chemically identified the vitamin as L-hexuronic acid, proving this by synthesis in 1933. Haworth and Szent-Györgyi proposed that L-hexuronic acid be named a-scorbic acid, and chemically L-ascorbic acid, in honor of its activity against scurvy. The term's etymology is from Latin, "a-" meaning away, or off from, while -scorbic is from Medieval Latin scorbuticus (pertaining to scurvy), cognate with Old Norse skyrbjugr, French scorbut, Dutch scheurbuik and Low German scharbock. Partly for this discovery, Szent-Györgyi was awarded the 1937 Nobel Prize in Medicine, and Haworth shared that year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
In 1957, J.J. Burns showed that some mammals are susceptible to scurvy as their liver does not produce the enzyme L-gulonolactone oxidase, the last of the chain of four enzymes that synthesize vitamin C. American biochemist Irwin Stone
was the first to exploit vitamin C for its food preservative
properties. He later developed the theory that humans possess a mutated
form of the L-gulonolactone oxidase coding gene.
In 2008, researchers at the University of Montpellier discovered that in humans and other primates the red blood cells have evolved a mechanism to more efficiently utilize the vitamin C present in the body by recycling oxidized L-dehydroascorbic
acid (DHA) back into ascorbic acid for reuse by the body. The mechanism
was not found to be present in mammals that synthesize their own
vitamin C.
Large doses
Vitamin C megadosage is a term describing the consumption or
injection of vitamin C in doses comparable to or higher than the amounts
produced by the livers of mammals which are able to synthesize vitamin
C. The theory behind this, although not the actual term, was described
in 1970 in an article by Linus Pauling. Briefly, his position was that
for optimal health, humans should be consuming at least 2,300 mg/day to
compensate for the inability to synthesize vitamin C. The recommendation
also fell into the consumption range for gorillas - a non-synthesizing
near-relative to humans.
A second argument for high intake is that serum ascorbic acid
concentrations increase as intake increases until it plateaus at about
190 to 200 micromoles per liter (µmol/L) once consumption exceeds 1,250
milligrams.
As noted, government recommendations are a range of 40 to 110 mg/day
and normal plasma is approximately 50 µmol/L, so 'normal' is about 25%
of what can be achieved when oral consumption is in the proposed
megadose range.
Pauling popularized the concept of high dose vitamin C as
prevention and treatment of the common cold in 1970. A few years later
he proposed that vitamin C would prevent cardiovascular disease, and
that 10 grams/day, initially (10 days) administered intravenously and
thereafter orally, would cure late-stage cancer. Mega-dosing with ascorbic acid has other champions, among them chemist Irwin Stone and the controversial Matthias Rath and Patrick Holford, who both have been accused of making unsubstantiated treatment claims for treating cancer and HIV infection.
The mega-dosing theory is to a large degree discredited. Modest
benefits are demonstrated for the common cold. Benefits are not superior
when supplement intakes of more than 1,000 mg/day are compared to
intakes between 200 and 1,000 mg/day, and so not limited to the
mega-dose range.
The theory that large amounts of intravenous ascorbic acid can be used
to treat late-stage cancer is - some forty years after Pauling's seminal
paper - still considered unproven and still in need of high quality
research.
However, a lack of conclusive evidence has not stopped individual
physicians from prescribing intravenous ascorbic acid to thousands of
people with cancer.
Society and culture
In February 2011, the Swiss Post issued a postage stamp bearing a depiction of a model of a molecule of vitamin C to mark the International Year of Chemistry.