 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | EpiPen, Adrenaclick, others |
| Synonyms | Epinephrine, adrenaline, adrenalin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a603002 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Addiction liability | None |
| Routes of administration | IV, IM, endotracheal, IC, nasal, eye drop |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | adrenergic synapse (MAO and COMT) |
| Onset of action | Rapid |
| Elimination half-life | 2 minutes |
| Duration of action | Few minutes |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.090 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
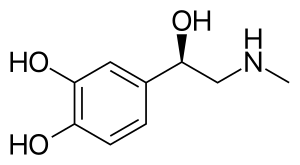
| Formula | C9H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 183.204 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.283±0.06 g/cm3 @ 20 °C, 760 Torr |
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication. Adrenaline is normally produced by both the adrenal glands and a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata where it acts as a neurotransmitter involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It plays an important role in the fight-or-flight response by increasing blood flow to muscles, output of the heart, pupil dilation response, and blood sugar level. It does this by binding to alpha and beta receptors. It is found in many animals and some single cell organisms. Napoleon Cybulski first isolated epinephrine in 1895.
Medical uses
As a medication, it is used to treat a number of conditions including anaphylaxis, cardiac arrest, and superficial bleeding. Inhaled adrenaline may be used to improve the symptoms of croup. It may also be used for asthma when other treatments are not effective. It is given intravenously, by injection into a muscle, by inhalation, or by injection just under the skin. Common side effects include shakiness, anxiety, and sweating. A fast heart rate and high blood pressure may occur. Occasionally it may result in an abnormal heart rhythm. While the safety of its use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is unclear, the benefits to the mother must be taken into account.
A case has been made for the use of adrenaline infusion in place
of the widely accepted treatment of inotopes for preterm infants with
clinical cardiovascular compromise. Although there is sufficient data
which strongly recommends Adrenaline infusions as a viable treatment,
more trials are needed in order to conclusively determine that these
infusions will successfully reduce morbidity and mortality rates among
preterm, cardiovascularly compromised infants.
Physiological effects
The adrenal medulla is a minor contributor to total circulating catecholamines (L-DOPA is at a higher concentration in the plasma), though it contributes over 90% of circulating adrenaline. Little adrenaline is found in other tissues, mostly in scattered chromaffin cells. Following adrenalectomy, adrenaline disappears below the detection limit in the blood stream.
The adrenal glands contribute about 7% of circulating noradrenaline, most of which is a spill over from neurotransmission with little activity as a hormone.
Pharmacological doses of adrenaline stimulate α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3 adrenoceptors of the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathetic nerve receptors are classified as adrenergic, based on their responsiveness to adrenaline.
The term "adrenergic" is often misinterpreted in that the main
sympathetic neurotransmitter is noradrenaline, rather than adrenaline,
as discovered by Ulf von Euler in 1946.
Adrenaline does have a β2 adrenoceptor-mediated effect on metabolism and the airway, there being no direct neural connection from the sympathetic ganglia to the airway.
The concept of the adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system being involved in the flight, fight and fright response was originally proposed by Cannon.
But the adrenal medulla, in contrast to the adrenal cortex, is not
required for survival. In adrenalectomized patients hemodynamic and
metabolic responses to stimuli such as hypoglycemia and exercise remain
normal.
Exercise
One
physiological stimulus to adrenaline secretion is exercise. This was
first demonstrated using the denervated pupil of a cat as an assay, later confirmed using a biological assay on urine samples. Biochemical methods for measuring catecholamines in plasma were published from 1950 onwards.
Although much valuable work has been published using fluorimetric
assays to measure total catecholamine concentrations, the method is too
non-specific and insensitive to accurately determine the very small
quantities of adrenaline in plasma. The development of extraction
methods and enzyme-isotope derivate radio-enzymatic assays (REA)
transformed the analysis down to a sensitivity of 1 pg for adrenaline.
Early REA plasma assays indicated that adrenaline and total
catecholamines rise late in exercise, mostly when anaerobic metabolism
commences.
During exercise the adrenaline blood concentration rises
partially from increased secretion from the adrenal medulla and partly
from decreased metabolism because of reduced hepatic blood flow.
Infusion of adrenaline to reproduce exercise circulating concentrations
of adrenaline in subjects at rest has little haemodynamic effect, other
than a small β2-mediated fall in diastolic blood pressure.
Infusion of adrenaline well within the physiological range suppresses
human airway hyper-reactivity sufficiently to antagonize the constrictor
effects of inhaled histamine.
A link between what we now know as the sympathetic system and the
lung was shown in 1887 when Grossman showed that stimulation of cardiac
accelerator nerves reversed muscarine-induced airway constriction.
In experiments in the dog, where the sympathetic chain was cut at the
level of the diaphragm, Jackson showed that there was no direct
sympathetic innervation to the lung, but that bronchoconstriction was
reversed by release of adrenaline from the adrenal medulla.
An increased incidence of asthma has not been reported for
adrenalectomized patients; those with a predisposition to asthma will
have some protection from airway hyper-reactivity from their
corticosteroid replacement therapy. Exercise induces progressive airway
dilation in normal subjects that correlates with work load and is not
prevented by beta blockade.
The progressive dilation of the airway with increasing exercise is
mediated by a progressive reduction in resting vagal tone. Beta blockade
with propranolol causes a rebound in airway resistance after exercise
in normal subjects over the same time course as the bronchoconstriction
seen with exercise induced asthma. The reduction in airway resistance during exercise reduces the work of breathing.
Emotional response
Every
emotional response has a behavioral component, an autonomic component,
and a hormonal component. The hormonal component includes the release of
adrenaline, an adrenomedullary response that occurs in response to
stress and that is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system.
The major emotion studied in relation to adrenaline is fear. In an
experiment, subjects who were injected with adrenaline expressed more
negative and fewer positive facial expressions to fear films compared to
a control group. These subjects also reported a more intense fear from
the films and greater mean intensity of negative memories than control
subjects.
The findings from this study demonstrate that there are learned
associations between negative feelings and levels of adrenaline.
Overall, the greater amount of adrenaline is positively correlated with
an arousal state of negative feelings. These findings can be an effect
in part that adrenaline elicits physiological sympathetic responses
including an increased heart rate and knee shaking, which can be
attributed to the feeling of fear regardless of the actual level of fear
elicited from the video. Although studies have found a definite
relation between adrenaline and fear, other emotions have not had such
results. In the same study, subjects did not express a greater amusement
to an amusement film nor greater anger to an anger film.
Similar findings were also supported in a study that involved rodent
subjects that either were able or unable to produce adrenaline. Findings
support the idea that adrenaline does have a role in facilitating the
encoding of emotionally arousing events, contributing to higher levels
of arousal due to fear.
Memory
It has been found that adrenergic hormones, such as adrenaline, can produce retrograde enhancement of long-term memory
in humans. The release of adrenaline due to emotionally stressful
events, which is endogenous adrenaline, can modulate memory
consolidation of the events, ensuring memory strength that is
proportional to memory importance. Post-learning adrenaline activity
also interacts with the degree of arousal associated with the initial
coding.
There is evidence that suggests adrenaline does have a role in
long-term stress adaptation and emotional memory encoding specifically.
Adrenaline may also play a role in elevating arousal and fear memory
under particular pathological conditions including post-traumatic stress
disorder.
Overall, "Extensive evidence indicates that epinephrine (EPI) modulates
memory consolidation for emotionally arousing tasks in animals and
human subjects.”
Studies have also found that recognition memory involving adrenaline depends on a mechanism that depends on β adrenoceptors.
Adrenaline does not readily cross the blood–brain barrier, so its
effects on memory consolidation are at least partly initiated by β
adrenoceptors in the periphery. Studies have found that sotalol, a β adrenoceptor antagonist that also does not readily enter the brain, blocks the enhancing effects of peripherally administered adrenaline on memory. These findings suggest that β adrenoceptors are necessary for adrenaline to have an effect on memory consolidation.
For noradrenaline to be acted upon by PNMT in the cytosol, it must first be shipped out of granules of the chromaffin cells. This may occur via the catecholamine-H+ exchanger VMAT1.
VMAT1 is also responsible for transporting newly synthesized adrenaline
from the cytosol back into chromaffin granules in preparation for
release.
In liver cells, adrenaline binds to the β adrenergic receptor, which changes conformation and helps Gs, a G protein, exchange GDP to GTP. This trimeric G protein dissociates to Gs alpha and Gs
beta/gamma subunits. Gs alpha binds to adenyl cyclase, thus converting
ATP into cyclic AMP. Cyclic AMP binds to the regulatory subunit of
protein kinase A: Protein kinase A phosphorylates phosphorylase kinase.
Meanwhile, Gs beta/gamma binds to the calcium channel and allows calcium
ions to enter the cytoplasm. Calcium ions bind to calmodulin proteins, a
protein present in all eukaryotic cells, which then binds to
phosphorylase kinase and finishes its activation. Phosphorylase kinase
phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase, which then phosphorylates glycogen and converts it to glucose-6-phosphate.
Pathology
Increased adrenaline secretion is observed in pheochromocytoma,
hypoglycemia, myocardial infarction and to a lesser degree in benign
essential familial tremor. A general increase in sympathetic neural
activity is usually accompanied by increased adrenaline secretion, but
there is selectivity during hypoxia and hypoglycaemia, when the ratio of
adrenaline to noradrenaline is considerably increased. Therefore, there must be some autonomy of the adrenal medulla from the rest of the sympathetic system.
Myocardial infarction is associated with high levels of
circulating adrenaline and noradrenaline, particularly in cardiogenic
shock.
Benign familial tremor (BFT) is responsive to peripheral β adrenergic blockers and β2-stimulation is known to cause tremor. Patients with BFT were found to have increased plasma adrenaline, but not noradrenaline.
Low, or absent, concentrations of adrenaline can be seen in
autonomic neuropathy or following adrenalectomy. Failure of the adrenal
cortex, as with Addisons disease, can suppress adrenaline secretion as
the activity of the synthesing enzyme, phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase, depends on the high concentration of cortisol that drains from the cortex to the medulla.
Terminology
In 1901, Jōkichi Takamine patented a purified extract from the adrenal glands, and called it "adrenalin" (from the Latin ad and renal, "near the kidneys"), which was trademarked by Parke, Davis & Co in the US. The British Approved Name and European Pharmacopoeia term for this drug is hence adrenaline.
However, the pharmacologist John Abel had already prepared an extract from adrenal glands as early as 1897, and coined the name epinephrine to describe it (from the Greek epi and nephros, "on top of the kidneys"). In the belief that Abel's extract was the same as Takamine's (a belief since disputed), epinephrine became the generic name in the US, and remains the pharmaceutical's United States Adopted Name and International Nonproprietary Name (though the name adrenaline is frequently used).
The terminology is now one of the few differences between the INN and BAN systems of names. Although European health professionals and scientists preferentially use the term adrenaline,
the converse is true among American health professionals and
scientists. Nevertheless, even among the latter, receptors for this
substance are called adrenergic receptors or adrenoceptors, and pharmaceuticals that mimic its effects are often called adrenergics. The history of adrenaline and epinephrine is reviewed by Rao [Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism, 30(6): 331-334, 2019].
Mechanism of action
| Organ | Effects |
|---|---|
| Heart | Increases heart rate; contractility; conduction across AV node |
| Lungs | Increases respiratory rate; bronchodilation |
| Liver | Stimulates glycogenolysis |
| Brain |
|
| Systemic | Vasoconstriction and vasodilation |
| Triggers lipolysis | |
| Muscle contraction |
As a hormone, adrenaline acts on nearly all body tissues. Its actions vary by tissue type and tissue expression of adrenergic receptors. For example, high levels of adrenaline causes smooth muscle relaxation in the airways but causes contraction of the smooth muscle that lines most arterioles.
Adrenaline acts by binding to a variety of adrenergic receptors. Adrenaline is a nonselective agonist of all adrenergic receptors, including the major subtypes α1, α2, β1, β2, and β3. Adrenaline's binding to these receptors triggers a number of metabolic changes. Binding to α-adrenergic receptors inhibits insulin secretion by the pancreas, stimulates glycogenolysis in the liver and muscle, and stimulates glycolysis and inhibits insulin-mediated glycogenesis in muscle. β adrenergic receptor binding triggers glucagon secretion in the pancreas, increased adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion by the pituitary gland, and increased lipolysis by adipose tissue. Together, these effects lead to increased blood glucose and fatty acids, providing substrates for energy production within cells throughout the body.
Its actions are to increase peripheral resistance via α1 receptor-dependent vasoconstriction and to increase cardiac output via its binding to β1
receptors. The goal of reducing peripheral circulation is to increase
coronary and cerebral perfusion pressures and therefore increase oxygen
exchange at the cellular level. While adrenaline does increase aortic, cerebral, and carotid circulation pressure, it lowers carotid blood flow and end-tidal CO2 or ETCO2
levels. It appears that adrenaline may be improving macrocirculation at
the expense of the capillary beds where actual perfusion is taking
place.
Measurement in biological fluids
Adrenaline
may be quantified in blood, plasma or serum as a diagnostic aid, to
monitor therapeutic administration, or to identify the causative agent
in a potential poisoning victim. Endogenous plasma adrenaline
concentrations in resting adults are normally less than 10 ng/L, but may
increase by 10-fold during exercise and by 50-fold or more during times
of stress. Pheochromocytoma
patients often have plasma adrenaline levels of 1000–10,000 ng/L.
Parenteral administration of adrenaline to acute-care cardiac patients
can produce plasma concentrations of 10,000 to 100,000 ng/L.
Biosynthesis and regulation
The biosynthesis of adrenaline involves a series of enzymatic reactions.
In chemical terms, adrenaline is one of a group of monoamines called the catecholamines. Adrenaline is synthesized in the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla of the adrenal gland and a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata in the brain through a metabolic pathway that converts the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine into a series of metabolic intermediates and, ultimately, adrenaline. Tyrosine is first oxidized to L-DOPA by Tyrosine hydroxylase, this is the rate-limiting step. Then it is subsequently decarboxylated to give dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase). Dopamine is then converted to noradrenaline by dopamine beta-hydroxylase which utilizes ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) and copper. The final step in adrenaline biosynthesis is the methylation of the primary amine of noradrenaline. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) which utilizes S-adenosyl methionine (SAMe) as the methyl donor. While PNMT is found primarily in the cytosol of the endocrine cells of the adrenal medulla (also known as chromaffin cells), it has been detected at low levels in both the heart and brain.
Regulation
The major physiologic triggers of adrenaline release center upon stresses,
such as physical threat, excitement, noise, bright lights, and high or
low ambient temperature. All of these stimuli are processed in the central nervous system.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and the sympathetic nervous system stimulate the synthesis of adrenaline precursors by enhancing the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine β-hydroxylase, two key enzymes involved in catecholamine synthesis. ACTH also stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol,
which increases the expression of PNMT in chromaffin cells, enhancing
adrenaline synthesis. This is most often done in response to stress. The sympathetic nervous system, acting via splanchnic nerves to the adrenal medulla, stimulates the release of adrenaline. Acetylcholine released by preganglionic sympathetic fibers of these nerves acts on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, causing cell depolarization and an influx of calcium through voltage-gated calcium channels.
Calcium triggers the exocytosis of chromaffin granules and, thus, the
release of adrenaline (and noradrenaline) into the bloodstream.
Unlike many other hormones adrenaline (as with other catecholamines) does not exert negative feedback to down-regulate its own synthesis.
Abnormally elevated levels of adrenaline can occur in a variety of
conditions, such as surreptitious adrenaline administration, pheochromocytoma, and other tumors of the sympathetic ganglia.
Its action is terminated with reuptake into nerve terminal endings, some minute dilution, and metabolism by monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyl transferase.
History
Extracts of the adrenal gland were first obtained by Polish physiologist Napoleon Cybulski in 1895. These extracts, which he called nadnerczyna ("adrenalin"), contained adrenaline and other catecholamines. American ophthalmologist William H. Bates discovered adrenaline's usage for eye surgeries prior to 20 April 1896. Japanese chemist Jōkichi Takamine and his assistant Keizo Uenaka independently discovered adrenaline in 1900. In 1901, Takamine successfully isolated and purified the hormone from the adrenal glands of sheep and oxen. Adrenaline was first synthesized in the laboratory by Friedrich Stolz and Henry Drysdale Dakin, independently, in 1904.
Society and culture
Adrenaline junkie
An adrenaline junkie is somebody who engages in
sensation-seeking behavior through "the pursuit of novel and intense
experiences without regard for physical, social, legal or financial
risk".
Such activities include extreme and risky sports, substance abuse,
unsafe sex, and crime. The term relates to the increase in circulating
levels of adrenaline during physiological stress.
Such an increase in the circulating concentration of adrenaline is
secondary to activation of the sympathetic nerves innervating the
adrenal medulla, as it is rapid and not present in animals where the
adrenal gland has been removed. Although such stress triggers adrenaline release, it also activates many other responses within the central nervous system reward system
which drives behavioral responses, so while the circulating adrenaline
concentration is present, it may not drive behavior. Nevertheless,
adrenaline infusion alone does increase alertness and has roles in the brain including the augmentation of memory consolidation.
Strength
Adrenaline has been implicated in feats of great strength, often
occurring in times of crisis. For example, there are stories of a parent
lifting part of a car when their child is trapped underneath.

