Example
of a family tree. Reading left to right Lucas Grey is the father of
three children, the grandfather of five grandchildren and the
great-grandfather of three siblings Joseph, John and Laura Wetter.
An ahnenblatt family tree
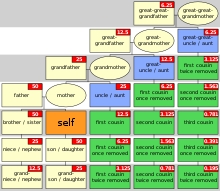
Family tree showing the relationship of each person to the orange person, including cousins and gene share.
A family tree, or pedigree chart, is a chart representing family relationships in a conventional tree structure. The more detailed family trees used in medicine and social work are known as genograms.
Family history representations
Genealogical data can be represented in several formats, for example as a pedigree or ancestry chart.
Family trees are often presented with the oldest generations at the top
and the newer generations at the bottom. An ancestry chart, which is a
tree showing the ancestors of an individual, will more closely resemble a
tree in shape, being wider at the top than the bottom. In some ancestry
charts, an individual appears on the left and his or her ancestors
appear to the right. A descendancy chart, which depicts all the
descendants of an individual will be narrowest at the top.
Family trees can have many themes. One might encompass all direct
descendants of a single figure, or all known ancestors of a living
person. Another might include all members of a particular surname (e.g.
male-line descendants). Yet another approach is to construct a tree
including all holders of a certain office, such as kings of Germany. This relies on dynastic marriage to hold together the links between dynasties.
The image of the tree probably originated with one in medieval art of the Tree of Jesse, used to illustrate the Genealogy of Christ in terms of a prophecy of Isaiah
(Isaiah 11:1). Possibly the first non-Biblical use, and the first to
show full family relationships rather than a purely patrilineal scheme,
was that involving family trees of the classical gods in Boccaccio's Genealogia deorum gentilium ("On the Genealogy of the Gods of the Gentiles"), whose first version dates to 1360.
Ahnentafel
An ahnentafel family tree displaying an ancestor chart of Sigmund Christoph, Graf von Zeil und Trauchburg
An ahnentafel (German for "ancestor table") is a genealogical numbering system for listing a person's direct ancestors in a fixed sequence of ascent:
- Subject (or proband)
- Father
- Mother
- Paternal grandfather
- Paternal grandmother
- Maternal grandfather
- Maternal grandmother
and so on, back through the generations. Apart from No. 1, who can be
male or female, all even-numbered persons are male, and all
odd-numbered persons are female. In this scheme,
the number of any person's father is double the person's number, and a
person's mother is double the person's number plus one. This system can
be displayed as a tree:
An ahnentafel family tree, showing three generations of the Kennedy Family
Fan chart
Screenshot of Gramps (v. 5.0.1) displaying a fan chart and the Given name cloud gramplet on the bottom.
A "fan chart" features a half circle chart with concentric rings: the
person of interest is the inner circle, the second circle is divided in
two (each side is one parent), the third circle is divided in four, and
so forth. Fan charts depict paternal and maternal ancestors.
Graph theory
While family trees are depicted as trees, family relations do not in general form a tree in the sense of graph theory,
since distant relatives can mate, so a person can have a common
ancestor on their mother's and father's side. However, because a parent
must be born before their child is born, a person cannot be their own
ancestor, and thus there are no loops, so ancestry forms a directed acyclic graph.
The graphs of matrilineal descent ("mother" relationships between women) and patrilineal descent ("father" relationships between men) are trees however.
Assuming no common ancestor, an ancestry chart is a perfect binary tree,
as each person has exactly one mother and one father, for two parents;
these thus have a regular structure. A descendancy chart, on the other
hand, does not in general have a regular structure, as a person can have
any number of children, or none at all.
Notable examples
The longest family tree in the world is that of the Chinese philosopher and educator Confucius (551–479 BC), and he is the descendant of King Tang
(1675–1646 BC). The tree spans more than 80 generations from him, and
includes more than 2 million members. An international effort involving
more than 450 branches around the world was started in 1998 to retrace
and revise this family tree. A new edition of the Confucius genealogy
was printed in September 2009 by the Confucius Genealogy Compilation Committee,
to coincide with the 2560th anniversary of the birth of the Chinese
thinker. This latest edition is expected to include some 1.3 million
living members who are scattered around the world today.
There are extensive genealogies for the ruling dynasties of
China, but these do not form a single, unified family tree; and it is
unclear at which point(s) the most ancient historical figures named
become mythological.
In Japan, the ancestry of the Imperial Family
is traced back to the mythological origins of Japan. The connection to
persons from the established historical record begins in the mid-first
millennium AD.
Another very old and extensive tree is that of the Lurie lineage—which includes Sigmund Freud and Martin Buber—and traces back to Jehiel Lurie, a 13th-century rabbi in Brest-Litovsk, and from there to Rashi and purportedly back to the legendary King David, as documented by Neil Rosenstein in his book The Lurie Legacy. The 1999 edition of the Guinness Book of Records recorded the Lurie family in the "longest lineage" category as oldest-known living family in the world today.
The Biblical genealogies of Jesus also claim descent from the House of David; covering a period of approximately 1000 years.
In the Torah and Old Testament, genealogies are provided for many
biblical persons, including a record of the descendants of Adam.
According to the Torah, the Kohanim are descended from Aaron. Genetic testing performed at the Technion has shown that most modern Kohanim share common Y-chromosome origins, although there is no complete family tree of the Kohanim.
In the Islamic world, claimed descent from the prophet Mohammed
greatly enhanced the status of political and religious leaders. New
dynasties often used claims of such descent to help establish their
legitimacy.
In Europe, the pedigree of Niall Noígíallach would be a contender for the longest, through Conn of the Hundred Battles (fl. 123 AD); in the legendary history of Ireland he is further descended from Breogán,
and ultimately from Adam, through the sons of Noah. Many noble and
aristocratic families of European and West-Asian origin can reliably
trace their ancestry back as far as the mid to late first millennium AD;
some claiming undocumented descent from Classical Antiquity or
mythological ancestors.
Before the Dark Ages, in the Greco-Roman
world, some reliable pedigrees dated back perhaps at least as far as
the first half of the first millennium BC; with claimed or mythological
origins reaching back further. Roman
clan and family lineages played an important part in the structure of
their society, and were the basis of their intricate system of personal
names. However, there was a break in the continuity of records-keeping
at the end of Classical Antiquity. Records of the lines of succession of the Popes
and the Eastern Roman Emperors through this transitional period have
survived, but these are not continuous genealogical histories of single
families. See: descent from antiquity.
In Africa, the ruling dynasty of Ethiopia claimed descent from King Solomon via the Queen of Sheba. Through this claim, the family traced their descent back to the aforementioned House of David.
The genealogy of Ancient Egyptian ruling dynasties was recorded from the beginnings of the Pharaonic era circa 3000 BC, to the end of the Ptolomaic Kingdom; although this is not a record of one continuously-linked family lineage, and surviving records are incomplete.
Elsewhere in Africa, oral traditions of genealogical recording predominate. Members of the Keita dynasty of Mali, for example, have had their pedigrees sung by griots during annual ceremonies since the 14th century. Meanwhile, in Nigeria, many ruling clans - most notably those descended from Oduduwa - claim descent from the legendary King Kisra. Here too, pedigrees are recited by griots attached to the royal courts.
In some pre-contact Native American civilizations, genealogical records of ruling and priestly families were kept, some of which extended over at least several centuries.
In many human cultures, clan and tribal associations are based on claims of common ancestry; although detailed documentation of those origins is often very limited.
Other uses
The author Pete Frame is notable for having produced "family trees" of rock bands.
In this instance, the entries represent membership of certain groups,
and personnel changes within them, rather than family relationships.
Several books have been produced with his family trees, which in turn have led to a BBC television series about them, including interviews from the bands depicted in the trees.