In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane.
For curves, the canonical example is that of a circle, which has a curvature equal to the reciprocal of its radius. Smaller circles bend more sharply, and hence have higher curvature. The curvature at a point of a differentiable curve, is the curvature of its osculating circle,
that is the circle that best approximates the curve near this point.
The curvature of a straight line is zero. The curvature of a curve at a
point is normally a scalar quantity, that is, it is expressed by a single real number.
For surfaces (and, more generally for higher-dimensional manifolds), that are embedded in a Euclidean space,
the concept of curvature is more complex, as depending on the choice of
a direction on the surface or manifold. This leads to the concepts of maximal curvature, minimal curvature, and mean curvature.
For Riemannian manifolds (of dimension at least two) that are not necessarily embedded in a Euclidean space, one can define the curvature intrinsically, that is without referring to an external space. See Curvature of Riemannian manifolds for the definition, which is done in terms of lengths of curves traced on the manifold, and expressed, using linear algebra, by the Riemann curvature tensor.
History
The curvature of a differentiable curve was originally defined through osculating circles. In this setting, Augustin-Louis Cauchy showed that the center of curvature is the intersection point of two infinitely close normal lines to the curve.
Plane curves
Intuitively, the curvature is a measure of the instantaneous rate of change
of direction of a point that moves on the curve: the larger the
curvature, the larger this rate of change. In other words, the curvature
measures how fast the unit tangent vector to the curve rotates.
In fact, it can be proved that this instantaneous rate of change is
exactly the curvature. More precisely, suppose that the point is moving
on the curve at a constant speed of one unit, that is, the position of
the point P(s) is a function of the parameter s, which may be thought as the time or as the arc length from a given origin. Let T(s) be a unit tangent vector of the curve at P(s), which is also the derivative of P(s) with respect to s. Then, the derivative of T(s) with respect to s is a vector that is normal to the curve and whose length is the curvature.
For being meaningful, the definition of the curvature and its different characterizations require that the curve is continuously differentiable near P, for having a tangent that varies continuously; it requires also that the curve is twice differentiable at P, for insuring the existence of the involved limits, and of the derivative of T(s).
The characterization of the curvature in terms of the derivative
of the unit tangent vector is probably less intuitive than the
definition in terms of the osculating circle, but formulas for computing
the curvature are easier to deduce. Therefore, and also because of its
use in kinematics, this characterization is often given as a definition of the curvature.
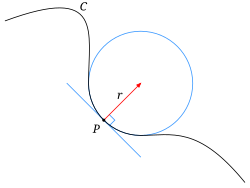
Osculating circle
Historically, the curvature of a differentiable curve was defined
through the osculating circle, which is the circle that best
approximates the curve at a point. More precisely, given a point P on a curve, every other point Q of the curve defines a circle (or sometimes a line) passing through Q and tangent to the curve at P. The osculating circle is the limit, if it exists, of this circle when Q tends to P. Then the center and the radius of curvature of the curve at P are the center and the radius of the osculating circle. The curvature is the reciprocal of radius of curvature. That is, the curvature is
where R is the radius of curvature.
This definition is difficult to manipulate and to express in
formulas. Therefore, other equivalent definitions have been introduced.
In terms of arc-length parametrization
Every differentiable curve can be parametrized with respect to arc length. In the case of a plane curve, this means the existence of a parametrization γ(s) = (x(s), y(s)), where x and y are real-valued differentiable functions whose derivatives verify
This means that the tangent vector
has a norm equal to one and is thus a unit tangent vector.
If the curve is twice differentiable, that is, if the second derivatives of x and y exist, then the derivative of T(s) exists. This vector is normal to the curve, its norm is the curvature κ(s), and it is oriented toward the center of curvature. That is,
Moreover, as the radius of curvature is and the center of curvature is on the normal to the curve, the center of curvature is the point
with k(s) = ± κ(s). The real number k(s) is called the oriented or signed curvature.
It depends on both the orientation of the plane (definition of
counterclockwise), and the orientation of the curve provided by the
parametrization. In fact, the change of variable s → –s provides another arc-length parametrization, and changes the sign of k(s).
In terms of a general parametrization
Let γ(t) = (x(t), y(t)) be a proper parametric representation of a twice differentiable plane curve. Here proper means that on the domain of definition of the parametrization, the derivative
is defined, differentiable and nowhere equal to the zero vector.
With such a parametrization, the signed curvature is
where primes refer to derivatives with respect to t. The curvature κ is thus
These can be expressed in a coordinate-free way as
These formulas can be derived from the special case of arc-length
parametrization in the following way. The above condition on the
parametrisation imply that the arc length s is a differentiable monotonic function of the parameter t, and conversely that t is a monotonic function of s. Moreover, by changing, if needed, s to –s,
one may suppose that these functions are increasing and have a positive
derivative. Using notation of the preceding section and the chain rule, one has
and thus, by taking the norm of both sides
where the prime denotes the derivation with respect to t.
The curvature is the norm of the derivative of T with respect to s.
By using the above formula and the chain rule this derivative and its norm can be expressed in terms of and only, with the arc-length parameter s completely eliminated, giving the above formulas for the curvature.
Graph of a function
The graph of a function y = f(x), is a special case of a parametrized curve, of the form
As the first and second derivatives of x are 1 and 0, previous formulas simplify to
for the curvature, and to
for the signed curvature.
In the general case of a curve, the sign of the signed curvature
is somehow arbitrary, as depending on an orientation of the curve. In
the case of the graph of a function, there is a natural orientation by
increasing values of x. This makes significant the sign of the signed curvature.
The sign of the signed curvature is the same as the sign of the second derivative of f.
If it is positive then the graph has an upward concavity, and, if it is
negative the graph has a downward concavity. It is zero, then one has
an inflection point or an undulation point.
When the slope
of the graph (that is the derivative of the function) is small, the
signed curvature is well approximated by the second derivative. More
precisely, using big O notation, one has
It is common in physics and engineering to approximate the curvature with the second derivative, for example, in beam theory or for deriving wave equation of a tense string, and other applications where small slopes are involved. This allows often considering as linear systems that are nonlinear otherwise.
Polar coordinates
If a curve is defined in polar coordinates by the radius expressed as a function of the polar angle, that is r is a function of θ, then its curvature is
where the prime refers to differentiation with respect to θ.
This results from the formula for general parametrizations, by considering the parametrization
Implicit curve
For a curve defined by an implicit equation F(x, y) = 0 with partial derivatives denoted Fx, Fy, Fxx, Fxy, Fyy,
the curvature is given by
The signed curvature is not defined, as it depends on an orientation
of the curve that is not provided by the implicit equation. Also,
changing F into –F does not change the curve, but changes the sign of the numerator if the absolute value is omitted in the preceding formula.
A point of the curve where Fx = Fy = 0 is a singular point,
which means that the curve in not differentiable at this point, and
thus that the curvature is not defined (most often, the point is either a
crossing point or a cusp).
Above formula for the curvature can be derived from the expression of the curvature of the graph of a function by using the implicit function theorem and the fact that, on such a curve, one has
Examples
It can be useful to verify on simple examples that the different formulas given in the preceding sections give the same result.
Circle
A common parametrization of a circle of radius r is γ(t) = (r cos t, r sin t). The formula for the curvature gives
It follows, as expected, that the radius of curvature is the radius
of the circle, and that the center of curvature is the center of the
circle.
The circle is a rare case where the arc-length parametrization is easy to compute, as it is It is an arc-length parametrization, since the norm of is equal to one. This parametrization gives the same value for the curvature, as it amounts to divides by both the numerator and the denominator in the preceding formula.
The same circle can also be defined by the implicit equation F(x, y) = 0 with F(x, y) = x2 + y2 – r2. Then, the formula for the curvature in this case gives
Parabola
Consider the parabola y = ax2 + bx + c.
It is the graph of a function, with derivative 2ax + b, and second derivative 2a. So, the signed curvature is
It has the sign of a for all values of x. This means that, if a > 0, the concavity is upward directed everywhere; if a < 0, the concavity is downward directed; for a = 0, the curvature is zero everywhere, confirming that the parabola degenerates into a line in this case.
The (unsigned) curvature is maximal for x = –b / 2a, that is at the stationary point (zero derivative) of the function, which is the vertex of the parabola.
Consider the parametrization γ(t) = (t, at2 + bt + c) = (x, y). The first derivative of x is 1,
and the second derivative is zero. Substituting into the formula for
general parametrizations gives exactly the same result as above, with x replaced by tIf we use primes for derivatives with respect to the parameter t.
The same parabola can also be defined by the implicit equation F(x, y) = 0 with F(x, y) = ax2 + bx + c – y. As Fy = –1, and Fyy = Fxy = 0, one obtains exactly the same value for the (unsigned) curvature. However, the signed curvature is meaningless here, as –F(x, y) = 0 is a valid implicit equation for the same parabola, which gives the opposite sign for the curvature.
Frenet–Serret formulas for plane curves
The vectors T and N at two points on a plane curve, a translated version of the second frame (dotted), and the change in T: δT. δs is the distance between the points. In the limit dTds will be in the direction N and the curvature describes the speed of rotation of the frame.
The expression of the curvature In terms of arc-length parametrization is essentially the first Frenet–Serret formula
where the primes refer to the derivatives with respect to the arc length s, and N(s) is the normal unit vector in the direction of T'(s).
As planar curves have zero torsion, the second Frenet–Serret formula provides the relation
For a general parametrization by a parameter t, one needs expressions involving derivatives with respect to t. As these are obtained by multiplying by dsdt the derivatives with respect to s, one has, for any proper parametrization
Space curves
Animation of the curvature and the acceleration vector T′(s)
As in the case of curves in two dimensions, the curvature of a regular space curve C
in three dimensions (and higher) is the magnitude of the acceleration
of a particle moving with unit speed along a curve. Thus if γ(s) is the arc-length parametrization of C then the unit tangent vector T(s) is given by
and the curvature is the magnitude of the acceleration:
The direction of the acceleration is the unit normal vector N(s), which is defined by
The plane containing the two vectors T(s) and N(s) is the osculating plane to the curve at γ(s). The curvature has the following geometrical interpretation. There exists a circle in the osculating plane tangent to γ(s) whose Taylor series to second order at the point of contact agrees with that of γ(s). This is the osculating circle to the curve. The radius of the circle R(s) is called the radius of curvature, and the curvature is the reciprocal of the radius of curvature:
The tangent, curvature, and normal vector together describe the
second-order behavior of a curve near a point. In three-dimensions, the
third order behavior of a curve is described by a related notion of torsion,
which measures the extent to which a curve tends to move in a helical
path in space. The torsion and curvature are related by the Frenet–Serret formulas (in three dimensions) and their generalization (in higher dimensions).
General expressions
For a parametrically-defined space curve in three dimensions given in Cartesian coordinates by γ(t) = (x(t), y(t), z(t)), the curvature is
where the prime denotes differentiation with respect to the parameter t. This can be expressed independently of the coordinate system by means of the formula
where × denotes the vector cross product. Equivalently,
Here the T denotes the matrix transpose. This last formula (without cross product) is also valid for the curvature of curves in a Euclidean space of any dimension.
Curvature from arc and chord length
Given two points P and Q on C, let s(P,Q) be the arc length of the portion of the curve between P and Q and let d(P,Q) denote the length of the line segment from P to Q. The curvature of C at P is given by the limit
where the limit is taken as the point Q approaches P on C. The denominator can equally well be taken to be d(P,Q)3. The formula is valid in any dimension. Furthermore, by considering the limit independently on either side of P, this definition of the curvature can sometimes accommodate a singularity at P. The formula follows by verifying it for the osculating circle.
Surfaces
The curvature of curves drawn on a surface is the main tool for the defining and studying the curvature of the surface.
Curves on surfaces
For a curve drawn on a surface (embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space), several curvatures are defined, which relates the direction of curvature to the surface's unit normal vector. These are the normal curvature, geodesic curvature and geodesic torsion. Any non-singular curve on a smooth surface has its tangent vector T contained in the tangent plane of the surface. The normal curvature, kn, is the curvature of the curve projected onto the plane containing the curve's tangent T and the surface normal u; the geodesic curvature, kg, is the curvature of the curve projected onto the surface's tangent plane; and the geodesic torsion (or relative torsion), τr, measures the rate of change of the surface normal around the curve's tangent.
Let the curve be arc-length parametrized, and let t = u × T so that T, t, u form an orthonormal basis, called the Darboux frame. The above quantities are related by:
Principal curvature
Saddle surface with normal planes in directions of principal curvatures
All curves with the same tangent vector will have the same normal
curvature, which is the same as the curvature of the curve obtained by
intersecting the surface with the plane containing T and u. Taking all possible tangent vectors, the maximum and minimum values of the normal curvature at a point are called the principal curvatures, k1 and k2, and the directions of the corresponding tangent vectors are called principal normal directions.
Normal sections
Curvature can be evaluated along surface normal sections, similar to § Curves on surfaces above (see for example the Earth radius of curvature).
Gaussian curvature
In contrast to curves, which do not have intrinsic curvature, but do
have extrinsic curvature (they only have a curvature given an
embedding), surfaces can have intrinsic curvature, independent of an
embedding. The Gaussian curvature, named after Carl Friedrich Gauss, is equal to the product of the principal curvatures, k1k2. It has a dimension of length−2 and is positive for spheres, negative for one-sheet hyperboloids and zero for planes. It determines whether a surface is locally convex (when it is positive) or locally saddle-shaped (when it is negative).
Gaussian curvature is an intrinsic property of the surface, meaning it does not depend on the particular embedding
of the surface; intuitively, this means that ants living on the surface
could determine the Gaussian curvature. For example, an ant living on a
sphere could measure the sum of the interior angles of a triangle and
determine that it was greater than 180 degrees, implying that the space
it inhabited had positive curvature. On the other hand, an ant living on
a cylinder would not detect any such departure from Euclidean geometry;
in particular the ant could not detect that the two surfaces have
different mean curvatures (see below), which is a purely extrinsic type
of curvature.
Formally, Gaussian curvature only depends on the Riemannian metric of the surface. This is Gauss's celebrated Theorema Egregium, which he found while concerned with geographic surveys and mapmaking.
An intrinsic definition of the Gaussian curvature at a point P is the following: imagine an ant which is tied to P with a short thread of length r. It runs around P while the thread is completely stretched and measures the length C(r) of one complete trip around P. If the surface were flat, the ant would find C(r) = 2πr. On curved surfaces, the formula for C(r) will be different, and the Gaussian curvature K at the point P can be computed by the Bertrand–Diguet–Puiseux theorem as
The integral of the Gaussian curvature over the whole surface is closely related to the surface's Euler characteristic; see the Gauss–Bonnet theorem.
The discrete analog of curvature, corresponding to curvature being concentrated at a point and particularly useful for polyhedra, is the (angular) defect; the analog for the Gauss–Bonnet theorem is Descartes' theorem on total angular defect.
Because (Gaussian) curvature can be defined without reference to
an embedding space, it is not necessary that a surface be embedded in a
higher-dimensional space in order to be curved. Such an intrinsically
curved two-dimensional surface is a simple example of a Riemannian manifold.
Mean curvature
The mean curvature is an extrinsic measure of curvature equal to half the sum of the principal curvatures, k1 + k22. It has a dimension of length−1. Mean curvature is closely related to the first variation of surface area. In particular, a minimal surface such as a soap film has mean curvature zero and a soap bubble
has constant mean curvature. Unlike Gauss curvature, the mean curvature
is extrinsic and depends on the embedding, for instance, a cylinder and a plane are locally isometric but the mean curvature of a plane is zero while that of a cylinder is nonzero.
Second fundamental form
The intrinsic and extrinsic curvature of a surface can be combined in the second fundamental form. This is a quadratic form in the tangent plane to the surface at a point whose value at a particular tangent vector X to the surface is the normal component of the acceleration of a curve along the surface tangent to X; that is, it is the normal curvature to a curve tangent to X (see above). Symbolically,
where N is the unit normal to the surface. For unit tangent vectors X, the second fundamental form assumes the maximum value k1 and minimum value k2, which occur in the principal directions u1 and u2, respectively. Thus, by the principal axis theorem, the second fundamental form is
Thus the second fundamental form encodes both the intrinsic and extrinsic curvatures.
Shape operator
An encapsulation of surface curvature can be found in the shape operator, S, which is a self-adjoint linear operator from the tangent plane to itself (specifically, the differential of the Gauss map).
For a surface with tangent vectors X and normal N, the shape operator can be expressed compactly in index summation notation as
(Compare the alternative expression of curvature for a plane curve.)
The Weingarten equations give the value of S in terms of the coefficients of the first and second fundamental forms as
The principal curvatures are the eigenvalues of the shape operator, the principal curvature directions are its eigenvectors, the Gauss curvature is its determinant, and the mean curvature is half its trace.
Curvature of space
By extension of the former argument, a space of three or more dimensions can be intrinsically curved. The curvature is intrinsic
in the sense that it is a property defined at every point in the space,
rather than a property defined with respect to a larger space that
contains it. In general, a curved space may or may not be conceived as
being embedded in a higher-dimensional ambient space; if not then its curvature can only be defined intrinsically.
After the discovery of the intrinsic definition of curvature, which is closely connected with non-Euclidean geometry,
many mathematicians and scientists questioned whether ordinary physical
space might be curved, although the success of Euclidean geometry up to
that time meant that the radius of curvature must be astronomically
large. In the theory of general relativity, which describes gravity and cosmology, the idea is slightly generalised to the "curvature of spacetime"; in relativity theory spacetime is a pseudo-Riemannian manifold.
Once a time coordinate is defined, the three-dimensional space
corresponding to a particular time is generally a curved Riemannian
manifold; but since the time coordinate choice is largely arbitrary, it
is the underlying spacetime curvature that is physically significant.
Although an arbitrarily curved space is very complex to describe, the curvature of a space which is locally isotropic and homogeneous
is described by a single Gaussian curvature, as for a surface;
mathematically these are strong conditions, but they correspond to
reasonable physical assumptions (all points and all directions are
indistinguishable). A positive curvature corresponds to the inverse
square radius of curvature; an example is a sphere or hypersphere. An example of negatively curved space is hyperbolic geometry. A space or space-time with zero curvature is called flat. For example, Euclidean space is an example of a flat space, and Minkowski space is an example of a flat spacetime. There are other examples of flat geometries in both settings, though. A torus or a cylinder can both be given flat metrics, but differ in their topology. Other topologies are also possible for curved space. See also shape of the universe.
Generalizations
Parallel transporting a vector from A → N → B → A yields a different vector. This failure to return to the initial vector is measured by the holonomy of the surface.
The mathematical notion of curvature is also defined in much more general contexts. Many of these generalizations emphasize different aspects of the curvature as it is understood in lower dimensions.
One such generalization is kinematic. The curvature of a curve
can naturally be considered as a kinematic quantity, representing the
force felt by a certain observer moving along the curve; analogously,
curvature in higher dimensions can be regarded as a kind of tidal force (this is one way of thinking of the sectional curvature).
This generalization of curvature depends on how nearby test particles
diverge or converge when they are allowed to move freely in the space;
see Jacobi field.
Another broad generalization of curvature comes from the study of parallel transport
on a surface. For instance, if a vector is moved around a loop on the
surface of a sphere keeping parallel throughout the motion, then the
final position of the vector may not be the same as the initial position
of the vector. This phenomenon is known as holonomy.[7] Various generalizations capture in an abstract form this idea of curvature as a measure of holonomy; see curvature form. A closely related notion of curvature comes from gauge theory in physics, where the curvature represents a field and a vector potential for the field is a quantity that is in general path-dependent: it may change if an observer moves around a loop.
Two more generalizations of curvature are the scalar curvature and Ricci curvature.
In a curved surface such as the sphere, the area of a disc on the
surface differs from the area of a disc of the same radius in flat
space. This difference (in a suitable limit) is measured by the scalar
curvature. The difference in area of a sector of the disc is measured by
the Ricci curvature. Each of the scalar curvature and Ricci curvature
are defined in analogous ways in three and higher dimensions. They are
particularly important in relativity theory, where they both appear on
the side of Einstein's field equations
that represents the geometry of spacetime (the other side of which
represents the presence of matter and energy). These generalizations of
curvature underlie, for instance, the notion that curvature can be a
property of a measure; see curvature of a measure.
Another generalization of curvature relies on the ability to compare a curved space with another space that has constant curvature. Often this is done with triangles in the spaces. The notion of a triangle makes senses in metric spaces, and this gives rise to CAT(k) spaces.