| Asian elephant | |
|---|---|

| |
| A tusked male Asian elephant in Bandipur National Park, Karnataka, India | |

| |
| A female Asian elephant with calf in Minneriya National Park, Sri Lanka | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae |
| Genus: | Elephas |
| Species: |
E. maximus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Elephas maximus | |
| Subspecies | |
|
E. m. maximus E. m. indicus E. m. sumatranus E. m. borneensis †E. m. sondaicus | |
| |
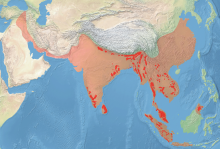
| Asian elephant historical range (pink) and current range (red) | |
The Asian elephant (Elephas maximus), also called Asiatic elephant, is the only living species of the genus Elephas and is distributed throughout the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, from India in the west, Nepal in the north, Sumatra in the south, and to Borneo in the east. Three subspecies are recognised—E. m. maximus from Sri Lanka, E. m. indicus from mainland Asia and E. m. sumatranus from the island of Sumatra.
The Asian elephant is the largest living land animal in Asia. Since 1986, the Asian elephant has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List, as the population has declined by at least 50 percent over the last three generations, estimated to be 60–75 years. It is primarily threatened by loss of habitat, habitat degradation, fragmentation and poaching. In 2003, the wild population was estimated at between 41,410 and 52,345 individuals. Female captive elephants have lived beyond 60 years when kept in semi-natural surroundings, such as forest camps. In zoos, Asian elephants die at a much younger age; captive populations are declining due to a low birth and high death rate.
The genus Elephas originated in Sub-Saharan Africa during the Pliocene and spread throughout Africa before expanding into the southern half of Asia. The earliest indications of captive use of Asian elephants are engravings on seals of the Indus Valley Civilisation dated to the 3rd millennium BC.
Taxonomy
Sri Lankan elephants
Elephas maximus was the scientific name proposed by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 who described the genus and an elephant from Ceylon.
Elephas indicus was proposed by Georges Cuvier in 1798, who described an elephant from India.
Elephas sumatranus was proposed by Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1847 who described an elephant from Sumatra. Frederick Nutter Chasen classified all three as subspecies of the Asian elephant in 1940. These three subspecies are currently recognised as valid taxa.
Elephas maximus borneensis was proposed by Paules Edward Pieris Deraniyagala in 1950 who described an elephant in an illustration published in the National Geographic magazine, but not a living elephant in accordance with the rules of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. The Asian elephants living in northern Borneo are smaller than all the other subspecies, but with larger ears, a longer tail, and straight tusks. Results of genetic analysis indicate that its ancestors separated from the mainland population about 300,000 years ago.
The following Asian elephants were proposed as extinct subspecies, but are considered synonymous with the Indian elephant:
- Syrian elephant (E. m. asurus) proposed by Deraniyagala in 1950 was based on Bronze Age illustrations.
- Chinese elephant (E. m. rubridens) also proposed by Deraniyagala in 1950 was based on a bronze statuette of an elephant.
- Javan elephant (E. m. sondaicus) also by Deraniyagala in 1950 was an illustration of a carving on the Buddhist monument of Borobudur.
Characteristics
Illustration of an elephant skeleton
The nail-like structures on the toes of an Asian elephant
In general, the Asian elephant is smaller than the African bush elephant and has the highest body point on the head. The back is convex or level. The ears are small with dorsal borders folded laterally. It has up to 20 pairs of ribs and 34 caudal vertebrae. The feet have more nail-like structures than those of African elephants—five on each forefoot, and four on each hind foot.
Size
On average, males are about 2.75 m (9.0 ft) tall at the shoulder and
4 t (4.4 short tons) in weight, while females are smaller at about 2.4 m
(7.9 ft) at the shoulder and 2.7 t (3.0 short tons) in weight. Length of body and head including trunk is 5.5–6.5 m (18–21 ft) with the tail being 1.2–1.5 m (3.9–4.9 ft) long. The largest bull elephant ever recorded was shot by the Maharajah of Susang in the Garo Hills of Assam, India
in 1924, it weighed an estimated 7 t (7.7 short tons), stood 3.43 m
(11.3 ft) tall at the shoulder and was 8.06 m (26.4 ft) long from head
to tail. There are reports of larger individuals as tall as 3.7 m (12 ft).
Trunk
Asian elephant drinking water
The distinctive trunk is an elongation of the nose and upper lip
combined; the nostrils are at its tip, which has a one finger-like
process. The trunk contains as many as 60,000 muscles, which consist of
longitudinal and radiating sets. The longitudinals are mostly
superficial and subdivided into anterior, lateral, and posterior. The
deeper muscles are best seen as numerous distinct fasciculi in a cross-section of the trunk. The trunk is a multipurpose prehensile organ and highly sensitive, innervated by the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve and by the facial nerve. The acute sense of smell uses both the trunk and Jacobson's organ.
Elephants use their trunks for breathing, watering, feeding, touching,
dusting, sound production and communication, washing, pinching,
grasping, defence and offence.
The "proboscis" or trunk consists wholly of muscular and membranous tissue,
and is a tapering muscular structure of nearly circular cross-section
extending proximally from attachment at the anterior nasal orifice, and
ending distally in a tip or finger. The length may vary from 1.5 to 2 m
(59 to 79 in) or longer depending on the species and age. Four basic
muscle masses—the radial, the longitudinal and two oblique layers—and
the size and attachments points of the tendon
masses allow the shortening, extension, bending, and twisting movements
accounting for the ability to hold, and manipulate loads of up to
300 kg (660 lb). Muscular and tendinous ability combined with nervous
control allows extraordinary strength and agility movements of the
trunk, such as sucking and spraying of water or dust and directed air
flow blowing.
The trunk can hold about four litres of water. Elephants will
playfully wrestle with each other using their trunks, but generally use
their trunks only for gesturing when fighting.
Tusks
Tusker debarking a tree
Tusks
serve to dig for water, salt, and rocks, to debark and uproot trees, as
levers for maneuvering fallen trees and branches, for work, for
display, for marking trees,
as weapon for offence and defence, as trunk-rests, and as protection
for the trunk. Elephants are known to be right or left tusked.
Female Asian elephants usually lack tusks; if tusks—in that case called "tushes"—are present, they are barely visible, and only seen when the mouth is open.[citation needed] The enamel plates of the molars
are greater in number and closer together in Asian elephants. Some
males may also lack tusks; these individuals are called "filsy makhnas",
and are especially common among the Sri Lankan elephant population.
Furthermore, the forehead has two hemispherical bulges, unlike the flat
front of the African elephant. Unlike African elephants which rarely use
their forefeet for anything other than digging or scraping soil, Asian
elephants are more agile at using their feet in conjunction with the
trunk for manipulating objects. They can sometimes be known for their
violent behaviour.
A record tusk described by George P. Sanderson measured 5 ft (1.5 m) along the curve, with a girth of 16 in (41 cm) at the point of emergence from the jaw, the weight being 104 1⁄2 lb
(47.4 kg). This was from an elephant killed by Sir Brooke and measured
8 ft (2.4 m) in length, and nearly 17 in (43 cm) in circumference, and
weighed 90 lb (41 kg). The tusk's weight was, however, exceeded by the
weight of a shorter tusk of about 6 ft (1.8 m) in length which weighed
100 lb (45 kg).
Skin
Depigmented skin on the forehead and ears of an Asian elephant
Skin colour is usually grey, and may be masked by soil because of dusting and wallowing. Their wrinkled skin is movable and contains many nerve centres. It is smoother than that of African elephants, and may be depigmented on the trunk, ears, or neck. The epidermis and dermis of the body average 18 mm (0.71 in) thick; skin on the dorsum
is 30 mm (1.2 in) thick providing protection against bites, bumps, and
adverse weather. Its folds increase surface area for heat dissipation.
They can tolerate cold better than excessive heat. Skin temperature
varies from 24 to 32.9 °C (75.2 to 91.2 °F). Body temperature averages
35.9 °C (96.6 °F).
Intelligence
Asian elephants have a very large and highly developed neocortex, a trait also shared by humans, apes and certain dolphin species. They have a greater volume of cerebral cortex available for cognitive processing than all other existing land animals. Results of studies indicate that Asian elephants have cognitive abilities for tool use and tool-making similar to great apes. They exhibit a wide variety of behaviours, including those associated with grief, learning, allomothering, mimicry, play, altruism, use of tools, compassion, cooperation, self-awareness, memory, and language.
Elephants are reported to head to safer ground during natural disasters
like tsunamis and earthquakes, although there have been no scientific
records of this since it is hard to recreate or predict natural
disasters.
Several students of elephant cognition and neuroanatomy are convinced that Asian elephants are highly intelligent and self-aware. Others contest this view.
Distribution and habitat
Asian elephants inhabit grasslands, tropical evergreen forests, semi-evergreen forests, moist deciduous forests,
dry deciduous forests and dry thorn forests, in addition to cultivated
and secondary forests and scrublands. Over this range of habitat types
elephants occur from sea level to over 3,000 m (9,800 ft). In the
eastern Himalaya in northeast India, they regularly move up above 3,000 m (9,800 ft) in summer at a few sites.
In China, the Asian elephant survives only in the prefectures of Xishuangbanna, Simao, and Lincang of southern Yunnan.
In Bangladesh, some isolated populations survive in the south-east Chittagong Hills. A herd of 20–25 wild elephants was reported as being present in the Garo Hills of Mymensingh
in the late-1990s, being detached from a big herd in the Peack hills of
India and prevented from returning by fences put up in the meantime by
the Indian border security force. The herd was estimated at about 60
individuals in 2014.
Three subspecies are recognised:
- the Sri Lankan elephant occurs in Sri Lanka;
- the Indian elephant occurs in mainland Asia: Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China, India, Laos, Malay Peninsula, Myanmar, Nepal, Thailand, Vietnam;
- the Sumatran elephant occurs in Sumatra.
The Borneo elephant occurs in Borneo's northern and northeastern parts. In 2003, mitochondrial DNA analysis and microsatellite data indicated that the Borneo elephant population is derived from stock that originated in the region of the Sunda Islands. The genetic divergence of Borneo elephants warrants their recognition as a separate Evolutionarily Significant Unit.
Ecology and behaviour
A 5-month-old calf and its 17-month-old cousin in a sanctuary in Laos
Elephants are crepuscular. They are classified as megaherbivores and consume up to 150 kg (330 lb) of plant matter per day. They are generalist feeders, and are both grazers and browsers. They are known to feed on at least 112 different plant species, most commonly of the order Malvales, as well as the legume, palm, sedge and true grass families. They browse more in the dry season with bark constituting a major part of their diet in the cool part of that season. They drink at least once a day and are never far from a permanent source of fresh water. They need 80–200 litres of water a day and use even more for bathing. At times, they scrape the soil for clay or minerals.
Adult females and calves move about together as groups, while
adult males disperse from their mothers upon reaching adolescence. Bull
elephants are solitary or form temporary 'bachelor groups'.
Cow-calf units generally tend to be small, typically consisting of three
adults (most likely related females) and their offspring. Larger groups of as many as 15 adult females have also been recorded.
Seasonal aggregations of 17 individuals including calves and young adults have been observed in Sri Lanka's Uda Walawe National Park. Until recently, Asian elephants, like African elephants, were thought to be under the leadership of older adult females, or matriarchs.
It is now recognized that females form extensive and very fluid social
networks, with varying degrees of associations between individuals. Social ties generally tend to be weaker than in African elephants.
Elephants are able to distinguish low-amplitude sounds. They can use infrasound to communicate.
Rarely, tigers
have been recorded attacking and killing calves, especially if the
calves become separated from their mothers, stranded from their herd, or
orphaned. Adults are largely invulnerable to natural predation. There
is a singular anecdotal case of a mother Asian elephant allegedly being
killed alongside her calf; however, this account is contestable. In 2011 and 2014, two instances were recorded of tigers successfully killing adult elephants; one by a single tiger in Jim Corbett National Park on a 20-year-old elephant, and another on a 28-year-old elephant in Kaziranga National Park further east, which was taken down and eaten by several tigers hunting cooperatively.
Reproduction
Indian elephants in the Coimbatore Forests, Tamil Nadu
A cow elephant with suckling young at the Chester Zoo
Bulls will fight one another to get access to oestrous
females. Strong fights over access to females are extremely rare. Bulls
reach sexual maturity around the age of 12–15. Between the age of 10
and 20 years, bulls undergo an annual phenomenon known as "musth". This is a period where the testosterone level is up to 100 times greater than non-musth periods, and they become aggressive. Secretions containing pheromones
occur during this period, from the paired temporal glands located on
the head between the lateral edge of the eye and the base of the ear.
The gestation period is 18–22 months, and the female gives birth to one calf, only occasionally twins. The calf is fully developed by the 19th month, but stays in the womb to grow so that it can reach its mother to feed. At birth, the calf weighs about 100 kg (220 lb), and is suckled
for up to three years. Once a female gives birth, she usually does not
breed again until the first calf is weaned, resulting in a four to
five-year birth interval. Females stay on with the herd, but mature
males are chased away.
Asiatic elephants reach adulthood at 17 years of age in both sexes. Elephants' life expectancy has been exaggerated in the past. They live on average for 60 years in the wild and 80 in captivity.
Generation length of the Asian elephant is 22 years.
Females produce sex pheromones.
A principal component thereof, (Z)-7-dodecen-1-yl acetate, has also
been found to be a sex pheromone in numerous species of insects.
Threats
The pre-eminent threats to the Asian elephant today are the loss,
degradation and fragmentation of its habitat, which leads to increasing
conflicts between humans and elephants. Asian elephants are poached for ivory and a variety of other products including meat and leather. The demand for elephant skin has risen due to it being an increasingly-common ingredient in traditional Chinese medicine.
Human–elephant conflict
Prime elephant habitat cleared for jhum—a type of shifting cultivation practiced in Arunachal Pradesh
Elephants on the road in Khao Yai National Park, Thailand
One of the major instigators of human–wildlife conflict in general is
competition for space. This is especially true for wild Asian
elephants, which require relatively large territories to live in. Destruction of forests through logging, encroachment, slash-and-burn, shifting cultivation, and monoculture
tree plantations are major threats to the survival of elephants.
Human–elephant conflicts occur when elephants raid crops of shifting
cultivators in fields, which are scattered over a large area
interspersed with forests. Depredation
in human settlements is another major area of human–elephant conflict
occurring in small forest pockets, encroachments into elephant habitat,
and on elephant migration routes.
However, studies in Sri Lanka indicate that traditional slash-and-burn
agriculture may create optimal habitat for elephants by creating a
mosaic of successional-stage vegetation. Populations inhabiting small
habitat fragments are much more liable to come into conflict with
humans.
Human-elephant conflict can be categorised into:
- ultimate causes including growing human population, large-scale development projects and poor top-down governance;
- proximate causes including habitat loss due to deforestation, disruption of elephant migratory routes, expansion of agriculture and illegal encroachment into protected areas.
Development such as border fencing along the India-Bangladesh border
has become a major impediment to the free movement of elephants. In Assam, more than 1,150 humans and 370 elephants died as a result of human-elephant conflict between 1980 and 2003.
In India alone, over 400 people are killed by elephants every year, and
0.8 to 1 million hectares are damaged, affecting at least 500,000
families across the country. Moreover, elephants are known to destroy crops worth up to US$2–3 million annually. This has major impacts on the welfare and livelihoods of local communities, as well as the future conservation of this species. In countries like Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, the Asian elephant is one of the most feared wild animals, even though they are less deadly than other local animals such as venomous snakes (which were estimated to claim more than 30 times more lives in Sri Lanka than elephants).
As a whole, Asian elephants display highly sophisticated and sometimes
unpredictable behaviour. Most untamed elephants try to avoid humans, but
if they are caught off guard by any perceived physical threat,
including humans, they will likely charge. This is especially true of
males in musth and of females with young. Gunfire and other similar
methods of deterring, which are known to be effective against many kinds
of wild animals including tigers, may or may not work with elephants,
and can even worsen the situation. Elephants that have been abused by
humans in the past often become "rogue elephants", which regularly
attack people with no provocation.
Poaching
For ivory
18th century ivory powder flask
The demand for ivory during the 1970s and 1980s, particularly in East Asia, led to rampant poaching and the serious decline of elephants in both Africa and Asia. In Thailand, the illegal trade
in live elephants and ivory still flourishes. Although the amount of
ivory being openly sold has decreased substantially since 2001, Thailand
still has one of the largest and most active black markets for ivory
seen anywhere in the world. Tusks from Thai poached elephants also enter
the market; between 1992 and 1997 at least 24 male elephants were
killed for their tusks.
Up to the early 1990s, Vietnamese ivory craftsmen used
exclusively Asian elephant ivory from Vietnam and neighbouring Lao and
Cambodia. Before 1990, there were few tourists and the low demand for
worked ivory could be supplied by domestic elephants. Economic
liberalisation and an increase in tourism raised both local and
visitors' demands for worked ivory, which resulted in heavy poaching.
For skin
The skin of the Asian elephant is used as an ingredient in Chinese medicine
as well as in the manufacture of ornamental beads. The practice has
been aided by China's State Forestry Administration (SFA), which has
issued licences for the manufacture and sale of pharmaceutical products
containing elephant skin, thereby making trading legal. In 2010, four
skinned elephants were found in a forest in Myanmar; 26 elephants were
killed by poachers in 2013 and 61 in 2016. According to the NGO Elephant Family, Myanmar is the main source of elephant skin, where a poaching crisis has developed rapidly since 2010.
Handling methods
Young elephants are captured and illegally imported to Thailand from Myanmar
for use in the tourism industry; calves are used mainly in amusement
parks and are trained to perform various stunts for tourists.
The calves are often subjected to a 'breaking in' process, which
may involve being tied up, confined, starved, beaten and tortured; as a
result, two-thirds may perish. Handlers use a technique known as the training crush,
in which "handlers use sleep-deprivation, hunger, and thirst to "break"
the elephants' spirit and make them submissive to their owners";
moreover, handlers drive nails into the elephants' ears and feet.
Conservation
The Asian elephant is listed on CITES Appendix I.
It is a quintessential flagship species, deployed to catalyze a range of conservation goals, including:
- habitat conservation at landscape scales
- generating public awareness of conservation issues
- mobilisation as a popular cultural icon both in India and the West.
In captivity
Rhythmic swaying behaviour is not reported in free ranging wild elephants and may be symptomatic of psychological disorders.
About half of the global zoo elephant population is kept in European zoos, where they have about half the median life span of conspecifics
in protected populations in range countries. This discrepancy is
clearest in Asian elephants: infant mortality is twice that seen in
Burmese timber camps, and adult survivorship in zoos has not improved
significantly in recent years. One risk factor for Asian zoo elephants
is being moved between institutions, with early removal from the mother
tending to have additional adverse effects. Another risk factor is being
born into a zoo rather than being imported from the wild, with poor
adult survivorship in zoo-born Asians apparently being conferred
prenatally or in early infancy. Likely causes for compromised
survivorship is stress and/or obesity.
Demographic analysis of captive Asian elephants in North America indicates that the population is not self-sustaining. First year mortality is nearly 30 per cent, and fecundity is extremely low throughout the prime reproductive years. Data from North American and European regional studbooks
from 1962 to 2006 were analysed for deviation of the birth and juvenile
death sex ratio. Of 349 captive calves born, 142 died prematurely. They
died within one month of birth, major causes being stillbirth and infanticide
by either the calf's mother or by one of the exhibition mates. The sex
ratio of stillbirths in Europe was found to have a tendency for excess
of males.
In culture
A folio from the Hastividyarnava manuscript
Elephants are used for safari tourism throughout Asia
Sri Lankan elephants at Esala Perahera
At this elephant training camp, captive elephants are taught to handle logs.
Bones of Asian elephants excavated at Mohenjo-daro in the Indus Valley indicate that they were tamed in the Indus Valley Civilization and used for work. Decorated elephants are also depicted on seals and were modelled in clay.
The elephant became a siege engine, a mount in war, a status symbol, a beast of burden, and an elevated platform for hunting during historical times in South Asia.
Elephants have been captured from the wild and tamed for use by
humans. Their ability to work under instruction makes them particularly
useful for carrying heavy objects. They have been used particularly for timber-carrying
in jungle areas. Other than their work use, they have been used in war,
in ceremonies, and for carriage. It is reported that war elephants are
still in use by the Kachin Independence Army (KIA) to take control of Kachin State in northern Myanmar from Myanmar's military. The KIA use about four dozen elephants to carry supplies.
The elephant plays an important part in the culture of the subcontinent and beyond, being featured prominently in the Panchatantra fables and the Buddhist Jataka tales. They play a major role in Hinduism: the god Ganesha's head is that of an elephant, and the "blessings" of a temple elephant are highly valued. Elephants are frequently used in processions where the animals are adorned with festive outfits.
The elephant is depicted in several Indian manuscripts and treatises. Notable amongst these is the Matanga Lila (elephant sport) of Nilakantha. The manuscript Hastividyarnava is from Assam in northeast India.
In the Burmese, Thai and Sinhalese animal and planetary zodiac, the elephant, both tusked and tuskless, are the fourth and fifth animal zodiacs of the Burmese, the fourth animal zodiac of the Thai, and the second animal zodiac of the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka. Similarly, the elephant is the twelfth animal zodiac in the Dai animal zodiac of the Dai people in southern China.






















