| Scarlet fever | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Scarlatina, scarletina |
 | |
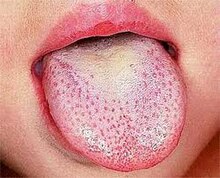
| Strawberry tongue seen in scarlet fever | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Sore throat, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, characteristic rash |
| Complications | Glomerulonephritis, rheumatic heart disease, arthritis |
| Usual onset | 5–15 years old |
| Causes | Strep throat, streptococcal skin infections |
| Diagnostic method | Throat culture |
| Prevention | Handwashing, not sharing personal items, staying away from sick people |
| Treatment | Antibiotics |
| Prognosis | Typically good |
Scarlet fever is a disease resulting from a group A streptococcus (group A strep) infection, also known as Streptococcus pyogenes. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The rash is red and feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age.
Scarlet fever affects a small number of people who have strep throat or streptococcal skin infections. The bacteria are usually spread by people coughing or sneezing. It can also be spread when a person touches an object that has the bacteria on it and then touches their mouth or nose. The characteristic rash is due to the erythrogenic toxin, a substance produced by some types of the bacterium. The diagnosis is typically confirmed by culturing the throat.
There is no vaccine. Prevention is by frequent handwashing, not sharing personal items, and staying away from other people when sick. The disease is treatable with antibiotics, which prevent most complications. Outcomes with scarlet fever are typically good if treated. Long-term complications as a result of scarlet fever include kidney disease, rheumatic heart disease, and arthritis. In the early 20th century, before antibiotics were available, it was a leading cause of death in children.
Signs and symptoms
Characteristic strawberry tongue of scarlet fever
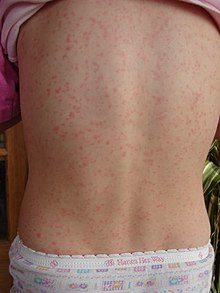
The rash of scarlet fever
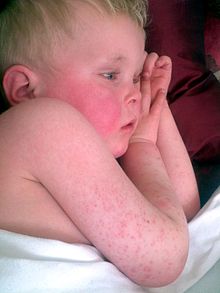
Red cheeks and pale area around the mouth in scarlet fever
Characteristic red cheeks and rash of scarlet fever
Rash which has a characteristic appearance, spreading pattern, and desquamating process
"Strawberry tongue"
- The tongue initially has a white coating on it, while the papillae of the tongue are swollen and reddened. The protrusion of the red papillae through the white coating gives the tongue a "white strawberry" appearance.
- A few days later (following the desquamating process, or the shedding of the tissue which created the white coating), the whiteness disappears, and the red and enlarged papillae give the tongue the "red strawberry" appearance. The symptomatic appearance of the tongue is part of the rash that is characteristic of scarlet fever.
- Pastia's lines
- Lines of petechiae, which appear as pink/red areas located in arm pits and elbow pits
- Vomiting and abdominal pain
Strep throat
Typical symptoms of streptococcal pharyngitis (also known as strep throat):
- Sore throat, painful swallowing
- Fever - typically over 39 °C (102.2 °F)
- Fatigue
- Enlarged and reddened tonsils with yellow or white exudates present (this is typically an exudative pharyngitis)
- Enlarged and tender lymph nodes usually located on the front of the neck
The following symptoms will usually be absent: cough, hoarseness, runny nose, diarrhea, and conjunctivitis. Such symptoms indicate what is more likely a viral infection.
Rash
The rash begins 1–2 days following the onset of symptoms caused by the strep pharyngitis (sore throat, fever, fatigue).
This characteristic rash has been denoted as "scarlatiniform," and it
appears as a diffuse redness of the skin with small papules, or bumps,
which resemble goose bumps. These bumps are what give the characteristic sandpaper
texture to the rash. The reddened skin will blanch when pressure is
applied to it. The skin may feel itchy, but it will not be painful. The rash generally starts at the flexion of the elbow and other surfaces. It appears next on the trunk and gradually spreads out to the arms and legs.
The palms, soles and face are usually left uninvolved by the rash. The
face, however, is usually flushed, most prominently in the cheeks, with a
ring of paleness around the mouth.
After the rash spreads, it becomes more pronounced in creases in the
skin, such as the skin folds in the inguinal and axillary regions of the
body. Also in those areas, Pastia's Lines may appear: petechiae arranged in a linear pattern.
Within 1 week of onset, the rash begins to fade followed by a longer
process of desquamation, or shedding of the outer layer of skin. This
lasts several weeks. The desquamation process usually begins on the face and progresses downward on the body. After the desquamation, the skin will be left with a sunburned appearance.
Mouth
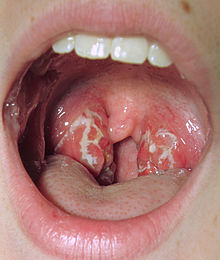
Throat of a child with a positive throat culture for streptococcal pharyngitis
The streptococcal pharyngitis, which is the usual presentation of
scarlet fever in combination with the characteristic rash, commonly
involves the tonsils. The tonsils will appear swollen and reddened. The
palate and uvula are also commonly affected by the infection. The
involvement of the soft palate can be seen as tiny red and round spots
known as Forchheimer spots.
Variable presentations
The
features of scarlet fever can differ depending on the age and race of
the person. Children less than 5 years old can have atypical
presentations. Children less than 3 years old can present with nasal
congestion and a lower grade fever. Infants may present with symptoms of increased irritability and decreased appetite.
Children who have darker skin can have a different presentation,
as the redness of the skin involved in the rash and the ring of paleness
around the mouth can be less obvious. Suspicion based on accompanying symptoms and diagnostic studies are important in these cases.
Course
Following
exposure to streptococcus, onset of symptoms occur 12 hours to 7 days
later. These may include fever, fatigue, and sore throat. The
characteristic scarlatiniform rash appears 12–48 hours later. During the
first few days of the rash development and rapid generalization, the
Pastia's Lines and strawberry tongue are also present. The rash starts fading within 3–4 days, followed by the desquamation of the rash, which lasts several weeks to a month.
If the case of scarlet fever is uncomplicated, recovery from the fever
and clinical symptoms, other than the process of desquamation, occurs in
5–10 days.
Complications
The
complications, which can arise from scarlet fever when left untreated
or inadequately treated, can be divided into two categories: suppurative
and nonsuppurative.
Suppurative
complications: These are rare complications that arise either from
direct spread to structures that are close to the primary site of
infection, or spread through the lymphatic system
or blood. In the first case, scarlet fever may spread to the pharynx.
Possible problems from this method of spread include peritonsillar or
retropharyngeal abscesses, cellulitis, mastoiditis or sinusitis.
In the second case, the streptococcal infection may spread through the lymphatic system
or the blood to areas of the body further away from the pharynx. A few
examples of the many complications that can arise from those methods of
spread include endocarditis, pneumonia, or meningitis.
Nonsuppurative complications: These complications arise from
certain subtypes of group A streptococci that cause an autoimmune
response in the body through what has been termed molecular mimicry.
In these cases, the antibodies which the person's immune system
developed to attack the group A streptococci are also able to attack the
person's own tissues. The following complications result, depending on
which tissues in the person's body are targeted by those antibodies.
- Acute rheumatic fever: This is a complication that results 2–6 weeks after a group A streptococcal infection of the upper respiratory tract. It presents in developing countries, where antibiotic treatment of streptococcal infections is less common, as a febrile illness with several clinical manifestations, which are organized into what is called the Jones criteria. These criteria include arthritis, carditis, neurological issues, and skin findings. Diagnosis also depends on evidence of a prior group A streptococcal infection in the upper respiratory tract (as seen in streptococcal pharyngitis and scarlet fever). The carditis is the result of the immunologic response targeting the person's heart tissue, and it is the most serious sequelae that develops from acute rheumatic fever. When this involvement of the heart tissue occurs, it is called rheumatic heart disease. In most cases of rheumatic heart disease, the mitral valve is affected, ultimately leading to mitral stenosis.
- Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: This is inflammation of the kidney, which presents 1–2 weeks after a group A streptococcal pharyngitis. It can also develop after an episode of Impetigo or any group A streptococcal infection in the skin (this differs from acute rheumatic fever which only follows group A streptococcal pharyngitis). It is the result of the autoimmune response to the streptococcal infection affecting part of the kidney. Persons present with what is called acute nephritic syndrome, in which they have high blood pressure, swelling, and urinary abnormalities. Urinary abnormalities include blood and protein found in the urine, as well as less urine production overall.
- Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis: The presentation of arthritis after a recent episode of group A streptococcal pharyngitis raises suspicion for acute rheumatic fever, since it is one of the Jones criteria for that separate complication. But, when the arthritis is an isolated symptom, it is referred to as poststreptococcal reactive arthritis. This arthritis can involve a variety of joints throughout the body, unlike the arthritis of acute rheumatic fever, which primarily affects larger joints such as the knee joints. It can present less than 10 days after the group A streptococcal pharyngitis.
Cause
Strep throat spreads by close contact among people, via respiratory droplets (for example, saliva or nasal discharge).
A person in close contact with another person infected with group A
streptococcal pharyngitis has a 35% chance of becoming infected. One in ten children who are infected with group A streptococcal pharyngitis will develop scarlet fever.
Pathophysiology
Streptococcus pyogenes (pictured)
The rash of scarlet fever, which is what differentiates this disease
from an isolated group A strep pharyngitis (or strep throat), is caused
by specific strains of group A streptococcus which produce a pyrogenic exotoxin. These toxin-producing strains cause scarlet fever in people who do not already have antitoxin antibodies.
Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins A, B, and C (speA, speB, and speC)
have been identified. The pyrogenic exotoxins are also called
erythrogenic toxins and cause the erythematous rash of scarlet fever.
The strains of group A streptococcus that cause scarlet fever need
specific bacteriophages in order for there to be pyrogenic exotoxin
production. Specifically, bacteriophage T12 is responsible for the production of speA.
Streptococcal Pyrogenic Exotoxin A, speA, is the one which is most
commonly associated with cases of scarlet fever which are complicated by
the immune-mediated sequelae acute rheumatic fever and
post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
These toxins are also known as “superantigens”
because they are able to cause an extensive immune response within the
body through activation of some of the main cells responsible for the
person's immune system.
The body responds to these toxins by making antibodies to those
specific toxins. However, those antibodies do not completely protect the
person from future group A streptococcal infections, because there are
12 different pyrogenic exotoxins possible.
Microbiology
The disease is caused by secretion of pyrogenic exotoxins by the infecting Streptococcus bacteria. Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A (speA)
is probably the best studied of these toxins. It is carried by the
bacteriophage T12 which integrates into the streptococcal genome from
where the toxin is transcribed. The phage itself integrates into a
serine tRNA gene on the chromosome.
The T12 virus itself has not been placed into a taxon by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. It has a double-stranded DNA genome and on morphological grounds appears to be a member of the Siphoviridae.
The speA gene was cloned and sequenced in 1986. It is 753 base pairs in length and encodes a 29.244 kiloDalton (kDa) protein. The protein contains a putative 30-
amino-acid signal peptide;
removal of the signal sequence gives a predicted molecular weight of
25.787 kDa for the secreted protein. Both a promoter and a ribosome
binding site (Shine-Dalgarno sequence)
are present upstream of the gene. A transcriptional terminator is
located 69 bases downstream from the translational termination codon. The carboxy terminal portion of the protein exhibits extensive homology with the carboxy terminus of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins B and C1.
Streptococcal phages other than T12 may also carry the speA gene.
Diagnosis
Although
the presentation of scarlet fever can be clinically diagnosed, further
testing may be required to distinguish it from other illnesses. Also, history of a recent exposure to someone with strep throat can be useful in diagnosis. There are two methods used to confirm suspicion of scarlet fever; rapid antigen detection test and throat culture.
The rapid antigen detection test is a very specific test
but not very sensitive. This means that if the result is positive
(indicating that the group A strep antigen was detected and therefore
confirming that the person has a group A strep pharyngitis), then it is
appropriate to treat the patient with antibiotics. But, if the rapid
antigen detection test is negative (indicating that they do not have
group A strep pharyngitis), then a throat culture is required to
confirm, as the first test could have yielded a false negative result. In the early 21st century, the throat culture is the current "gold standard" for diagnosis.
Serologic testing
seeks evidence of the antibodies that the body produces against the
streptococcal infection, including antistreptolysin-O and
antideoxyribonuclease B. It takes the body 2–3 weeks to make these
antibodies, so this type of testing is not useful for diagnosing a
current infection. But, it is useful when assessing a person who may
have one of the complications from a previous streptococcal infection.
Throat cultures done after antibiotic therapy can show if the
infection has been removed. These throat swabs, however, are not
indicated, because up to 25% of properly treated individuals can
continue to carry the streptococcal infection while being asymptomatic.
Differential diagnosis
- Viral exanthem: Viral infections are often accompanied by a rash which can be described as morbilliform or maculopapular. This type of rash is accompanied by a prodromal period of cough and runny nose in addition to a fever, indicative of a viral process.
- Allergic or contact dermatitis: The erythematous appearance of the skin will be in a more localized distribution rather than the diffuse and generalized rash seen in scarlet fever.
- Drug eruption: These are potential side effects of taking certain drugs such as penicillin. The reddened maculopapular rash which results can be itchy and be accompanied by a fever.
- Kawasaki disease: Children with this disease also present a strawberry tongue and undergo a desquamative process on their palms and soles. However, these children tend to be younger than 5 years old, their fever lasts longer (at least five days), and they have additional clinical criteria (including signs such as conjunctival redness and cracked lips), which can help distinguish this from scarlet fever.
- Toxic shock syndrome: Both streptococcal and staphylococcal bacteria can cause this syndrome. Clinical manifestations include diffuse rash and desquamation of the palms and soles. It can be distinguished from scarlet fever by low blood pressure, lack of sandpaper texture for the rash, and multi-organ system involvement.
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: This is a disease that occurs primarily in young children due to a toxin-producing strain of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. The abrupt start of the fever and diffused sunburned appearance of the rash can resemble scarlet fever. However, this rash is associated with tenderness and large blister formation. These blisters easily pop, followed by causing the skin to peel.
- Staphylococcal scarlet fever: The rash is identical to the streptococcal scarlet fever in distribution and texture, but the skin affected by the rash will be tender.
Prevention
One
method is long-term use of antibiotics to prevent future group A
streptococcal infections. This method is only indicated for people who
have had complications like recurrent attacks of acute rheumatic fever
or rheumatic heart disease. Antibiotics are limited in their ability to
prevent these infections since there are a variety of subtypes of group A
streptococci that can cause the infection.
The vaccine approach has a greater likelihood of effectively
preventing group A streptococcal infections because vaccine formulations
can target multiple subtypes of the bacteria.
A vaccine developed by George and Gladys Dick in 1924 was discontinued
due to poor efficacy and the introduction of antibiotics. Difficulties
in vaccine development include the considerable strain variety of group A
streptococci present in the environment and the amount of time and
number of people needed for appropriate trials for safety and efficacy
of any potential vaccine.
There have been several attempts to create a vaccine in the past few
decades. These vaccines, which are still in the development phase,
expose the person to proteins present on the surface of the group A
streptococci to activate an immune response that will prepare the person
to fight and prevent future infections.
There used to be a diphtheria scarlet fever vaccine. It was, however, found not to be effective. This product was discontinued by the end of World War II.
Treatment
Antibiotics
to combat the streptococcal infection are the mainstay of treatment for
scarlet fever. Prompt administration of appropriate antibiotics
decreases the length of illness. Peeling of the outer layer of skin,
however, will happen despite treatment.
One of the main goals of treatment is to prevent the child from
developing one of the suppurative or nonsuppurative complications,
especially acute rheumatic fever. As long as antibiotics are started within nine days, it is very unlikely for the child to develop acute rheumatic fever. Antibiotic therapy has not been shown to prevent the development of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Another important reason for prompt treatment with antibiotics is the
ability to prevent transmission of the infection between children. An
infected individual is most likely to pass on the infection to another
person during the first 2 weeks. A child is no longer contagious (able to pass the infection to another child) after 24 hours of antibiotics.
The antibiotic of choice is penicillin V which is taken by mouth in pill form. Children who are not able to take pills can be given amoxicillin which comes in a liquid form and is equally effective. Duration of treatment is 10 days. Benzathine Penicillin G can be given as a one time intramuscular injection as another alternative if swallowing pills is not possible. If the person is allergic to the family of antibiotics which both penicillin and amoxicillin are a part of (beta-lactam antibiotics), a first generation cephalosporin is used. Cephalosporin antibiotics, however, can still cause adverse reactions in people whose allergic reaction to penicillin is a Type 1 Hypersensitivity reaction. In those cases it is appropriate to choose clindamycin or erythromycin instead. Tonsillectomy,
although once a reasonable treatment for recurrent streptococcal
pharyngitis, is not indicate, as a person can still be infected with
group A streptococcus without their tonsils.
Antibiotic resistance
A drug-resistant strain of scarlet fever, resistant to macrolide antibiotics such as erythromycin, but retaining drug-sensitivity to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillin, emerged in Hong Kong in 2011, accounting for at least two deaths in that city—the first such in over a decade. About 60% of circulating strains of the group A streptococcus that cause scarlet fever in Hong Kong are resistant to macrolide antibiotics, says Professor Kwok-yung Yuen, head of Hong Kong University's microbiology department. Previously, observed resistance rates had been 10–30%; the increase is likely the result of overuse of macrolide antibiotics in recent years.
Epidemiology
Scarlet fever occurs equally in both males and females.
Children are most commonly infected, typically between 5–15 years old.
Although streptococcal infections can happen at any time of year,
infection rates peak in the winter and spring months, typically in
colder climates.
The morbidity and mortality of scarlet fever has declined since
the 18th and 19th century when there were epidemics caused by this
disease. Around 1900 the mortality rate in multiple places reached 25%. The improvement in prognosis can be attributed to the use of penicillin in the treatment of this disease.
The frequency of scarlet fever cases has also been declining over the
past century. There have been several reported outbreaks of the disease
in various countries in the past decade.
The reason for these recent increases remains unclear in the medical
community. Between 2013 and 2016 population rates of scarlet fever in
England increased from 8.2 to 33.2 per 100,000 and hospital admissions
for scarlet fever increased by 97%.
History
It is unclear when a description of this disease was first recorded. Hippocrates, writing around 400 BC, described the condition of a person with a reddened skin and fever.
The first description of the disease in the medical literature appeared in the 1553 book De Tumoribus praeter Naturam by the Sicilian anatomist and physician Giovanni Filippo Ingrassia, where he referred to it as rossalia. He also made a point to distinguish that this presentation had different characteristics to measles. It was redescribed by Johann Weyer during an epidemic in lower Germany between 1564 and 1565; he referred to it as scalatina anginosa. The first unequivocal description of scarlet fever appeared in a book by Joannes Coyttarus of Poitiers, De febre purpura epidemiale et contagiosa libri duo, which was published in 1578 in Paris. Daniel Sennert of Wittenberg described the classical 'scarlatinal desquamation' in 1572 and was also the first to describe the early arthritis, scarlatinal dropsy, and ascites associated with the disease.
In 1675 the term that has been commonly used to refer to scarlet fever, "scarlatina", was written by Thomas Sydenham, an English physician.
In 1827, Richard Bright was the first to recognize the involvement of the renal system in scarlet fever.
The association between streptococci and disease was first described in 1874 by Theodor Billroth, discussing people with skin infections. Billroth also coined the genus name Streptococcus. In 1884 Friedrich Julius Rosenbach edited the name to its current one, Streptococcus pyogenes, after further looking at the bacteria in the skin lesions. The organism was first cultured in 1883 by the German surgeon Friedrich Fehleisen from erysipelas lesions.
Also in 1884, the German physician Friedrich Loeffler
was the first to show the presence of streptococci in the throats of
people with scarlet fever. Because not all people with pharyngeal
streptococci developed scarlet fever, these findings remained
controversial for some time. The association between streptococci and
scarlet fever was confirmed by Alphonse Dochez and George and Gladys Dick in the early 1900s.
Nil Filatov (in 1895) and Clement Dukes (in 1894) described an exanthematous disease which they thought was a form of rubella, but in 1900, Dukes described it as a separate illness which came to be known as Dukes' disease,
Filatov's disease, or fourth disease. However, in 1979, Keith Powell
identified it as in fact the same illness as the form of scarlet fever
which is caused by staphylococcal exotoxin and is known as staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome.
Scarlet fever serum from horses' blood was used in the treatment of children beginning in 1900 and reduced mortality rates significantly.
In 1906, the Austrian pediatrician Clemens von Pirquet postulated that disease-causing immune complexes were responsible for the nephritis that followed scarlet fever.
Bacteriophages were discovered in 1915 by Frederick Twort. His work was overlooked and bacteriophages were later rediscovered by Felix d'Herelle in 1917. The specific association of scarlet fever with the group A streptococci had to await the development of Lancefield's
streptococcal grouping scheme in the 1920s. George and Gladys Dick
showed that cell-free filtrates could induce the erythematous reaction
characteristic of scarlet fever, proving that this reaction was due to a
toxin. Karelitz and Stempien discovered that extracts from human serum
globulin and placental globulin can be used as lightening agents for
scarlet fever and this was used later as the basis for the Dick test.
The association of scarlet fever and bacteriophages was described in
1926 by Cantucuzene and Boncieu.
An antitoxin for scarlet fever was developed in 1924.
The first toxin which causes this disease was cloned and sequenced in 1986 by Weeks and Ferretti.
The discovery of penicillin and its subsequent widespread use has
significantly reduced the mortality of this once feared disease. Reports
of cases of scarlet fever have been on the rise in countries including England, Wales, South Korea, Vietnam, China, and Hong Kong in recent years. Researchers are unsure as to what has caused the spike in cases of the disease.
The Dick test
The Dick test, invented in 1924 by George F. Dick and Gladys Dick, was used to identify those susceptible to scarlet fever.
The Dick test consisted of injecting a diluted strain of the
streptococci known to cause scarlet fever into a person's skin. A local
reaction in the skin at the site of injection appeared in people who
were susceptible to developing scarlet fever. This reaction was most
notable around 24 hours after the injection but could be seen as early
as 4–6 hours. If there is no reaction seen in the skin, then that person
was assumed to have already developed immunity to the disease and was
not at risk of developing it.