Ignasius Jonan, Indonesian Minister of Energy and Mineral Resources
Energy in Indonesia describes energy and electricity production, consumption, import and export in Indonesia. In 2009 Indonesia produced oil, coal, natural gas and palm oil, utilised also as energy raw material in 2010. Renewable energy potential in Indonesia is high: solar, wind, hydro and geothermal energy. Tropical rain forests and peat land areas have extensive coal storage. Indonesia is a geologically unstable country.
According to IEA
Indonesia was the 10th top natural gas producer in 2009: 76 billion
cubics (bcm) 2.5% of world production of which 36 bcm was exported. In
2009 Indonesia was the 5th top coal producer: 263 million tonnes hard
coal and 38 million tonnes brown. The majority of this, 230 Mt of hard
coal, was exported.
Indonesia has significant energy resources, starting with oil – it has
22 billion barrels of conventional oil and gas reserves, of which about 4
billion are recoverable. That's the equivalent of about 10 years of oil
production and 50 years of gas. It has about 8 billion barrels of
oil-equivalent of coal-based methane (CBM) resources. It has 28 billion
tonnes of recoverable coal and has 28 gigawatts (GW) of geothermal
potential.
Overview
|
|
Population (million) |
Primary energy (TWh) |
Production (TWh) |
Export (TWh) |
Electricity (TWh) |
CO2-emission (Mt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 217.6 | 2,024 | 3,001 | 973 | 104 | 336 |
| 2007 | 225.6 | 2,217 | 3,851 | 1,623 | 127 | 377 |
| 2008 | 228.3 | 2,311 | 4,035 | 1,714 | 134 | 385 |
| 2009 | 230.0 | 2,349 | 4,092 | 1,787 | 140 | 376 |
| 2010 | 239.9 | 2,417 | 4,436 | 2,007 | 154 | 411 |
| 2012 | 242.3 | 2,431 | 4,589 | 2,149 | 166 | 426 |
| 2012R | 246.9 | 2,484 | 5,120 | 2,631 | 181 | 435 |
| 2013 | 250.0 | 2,485 | 5,350 | 2,858 | 198 | 425 |
| Change 2004-10 | 10.2% | 19.4% | 48% | 106% | 48% | 22% |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh
2012R = CO2 calculation criteria changed, numbers updated
| ||||||
According to IEA energy production increased 34% and export 76% from 2004 to 2008 in Indonesia.
Energy by sources
Fossil Fuel Energy Sources
Coal
Indonesia is well-supplied with medium and low-quality thermal coal.
At current rates of production, Indonesia's coal reserves are expected
to last for over 80 years. In 2009 Indonesia was the world's second top
coal exporter sending coal to, for example, China, India, Japan and
Italy. Kalimantan (Borneo) and South Sumatra
are the centres of Indonesia’s coal mining. In recent years, production
in Indonesia has been rising rapidly, from just over 200 mill tons in
2007 to over 400 mill tons in 2013. Recently (December 2013), the chair
of the Indonesian Coal Mining Association said the production in 2014 may reach 450 mill tons.
The Indonesian coal industry is rather fragmented. Output is
supplied by a few large producers and a large number of small firms.
Large firms in the industry include the following:
- PT Bumi Resources (the controlling shareholder of large coal firms PT Kaltim Prima Coal and PT Arutmin Indonesia)
- PT Adaro Energy
- PT Kideco Jaya Agung
- PT Indo Tambangraya Megah
- PT Berau Coal
- PT Tambang Batubara Bukit Asam (state-owned)
Coal production poses risks for deforestation in Kalimantan.
According to one Greenpeace report, a coal plant in Indonesia has
decreased the fishing catches and increased the respiratory-related
diseases,
Oil
Indonesia used to be a net oil exporter.
Oil is a major sector in the Indonesian economy. During the 1980s,
Indonesia was a significant oil-exporting country. Since 2000, domestic
consumption has continued to rise while production has been falling, so
in recent years Indonesia has begun importing increasing amounts of
oil. Within Indonesia, there are considerable amounts of oil in
Sumatra, Borneo, Java, and West Papua Province. There are said to be around 60 basins across the country, only 22 of which have been explored and exploited. Main oil fields in Indonesia include the following:
- Minas. The Minas field, in Riau in Sumatra, operated by the US-based firm Chevron Pacific Indonesia, is the largest oil block in Indonesia. Output from the field is around 20-25% of current annual oil production in Indonesia.
- Duri. The Duri field, in Bengkalis Regency in Riau in Sumatra, is operated by the US-based firm Chevron Pacific Indonesia.
- Rokan. The Rokan field, in Riau in Sumatra, operated by Chevron Pacific Indonesia, is a recently developed large field in the Rokan Hilir Regency.
- Cepu. The Cepu field, operated by Mobil Cepu Ltd which is a subsidiary of US-based Exxon Mobil, is on the border of Central and East Java near the town of Tuban. The field was discovered in March 2001 and is estimated to have proven reserves of 600 million barrels of oil and 1.7 trillion cu feet of gas. Development of the field has been subject to on-going discussions between the operators and the Indonesian government. Output is forecast to rise from around 20,000 bpd in early 2012 to around 165,000 bpd in late 2014.
Gas
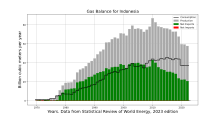
Indonesia's gas balance
There is growing recognition in Indonesia that the gas sector has considerable development potential.
In principle, the Indonesian government is supporting moves to give
increasing priority to investment in natural gas. In practice, private
sector investors, especially foreign investors, have been reluctant to
invest because many of the problems that are holding back investment in
the oil sector also affect investment in gas. At present (mid 2013),
main potential gas fields in Indonesia are believed to include the
following:
- Mahakam. The Mahakam block in East Kalimantan, under the management of Total E&P Indonesie with participation from the Japanese oil and gas firm Inpex, provides around 30% of Indonesia's natural gas output. In mid 2013 the field was reported to be producing around 1.7 billion cu ft (48 million m3) per day of gas as well as 67,000 barrels (10,700 m3) of condensate. At the time discussions were underway about the details of the future management of the block involving a proposal that Pertamina take over all or part of the management of the block. In October 2013 it was reported that Total E&P Indonesie had announced that it would stop exploration for new projects at the field. In 2015 the Energy and Resources Minister issued a regulation stipulating that the management of the block would be transferred from Total E&P Indonesie and Inpex, which had managed the field for over 50 years since 1966, to Pertamina. In late 2017, it was announced that Pertamina Hulu Indonesia, a subsidiary of Pertamina, would take over management of the block on 1 January 2018.
- Tangguh. The Tangguh field in Bintuni Bay in West Papua Province operated by BP (British Petroleum) is estimated to have proven gas reserves of 4.4 trillion cu ft (120 billion m3). It is hoped that annual output of the field in the near future might reach 7.6 million tons of liquefied natural gas.
- Arun. The Arun field in Aceh has been operated by ExxonMobil since the 1970s. The reserves at the field are now largely depleted so production is now slowly being phased out. At the peak, the Arun field produced around 3.4 million cu ft (96 thousand m3) of gas per day (1994) and about 130,000 of condensate per day (1989). ExxonMobil affiliates also operate the nearby South Lhoksukon A and D fields as well as the North Sumatra offshore gas field. In September 2015, ExxonMobil Indonesia sold its assets in Aceh to Pertamina. The sale included the divestment by ExxonMobil of its assets (100%) in the North Sumatra Offshore block, its interests (100%) in B block, and its stake (30%) in the PT Arun Natural Gas Liquefaction (NGL) plant. Following the completion of the deal, Pertamina will have an 85% stake in the Arun NGL plant.
- East Natuna. The East Natuna gas field (formerly known as Natuna D-Alpha) in the Natuna Islands in the South China Sea is believed to be one of the biggest gas reserves in Southeast Asia. It is estimated to have proven reserves of 46 trillion cu ft (1.3 trillion m3) of gas. The aim is to begin expanded production in 2020 with production rising to 4,000 million cu ft/d (110 million m3/d) sustained for perhaps 20 years.
- Banyu Urip. The Banyu Urip field, a major field for Indonesia, is in the Cepu block in Bojonegoro Regency in East Java. Interests in the block are held by Pertamina (45%) through its subsidiary PT Pertamina EP Cepu and ExxonMobil Cepu Limited (45%) which is a subsidiary of ExxonMobil Corporation. ExxonMobil is the operator of the block.
- Masela. The Masela field, currently (early 2016) under consideration for development by the Indonesian Government, is situated to the east of Timor Island, roughly halfway between Timor and Darwin in Australia. The main investors in the field are currently (early 2016) Inpex and Shell who hold stakes of 65% and 35% respectively. The field, if developed, is likely to become the biggest deepwater gas project in Indonesia, involving an estimated investment of between $14–19 billion. Over 10 trillion cu ft (280 billion m3) of gas are said to exist in the block. However, development of the field is being delayed over uncertainty as to whether the field might be operated through an offshore or onshore processing facility. In March 2016, after a row between his ministers, President Jokowi decreed that the processing facility should be onshore. This change of plans will involve the investors in greatly increased costs and will delay the start of the project. It was proposed that they submit revised Plans of Development (POD) to the Indonesian Government.
Shale
There is potential for tight oil and shale gas in northern Sumatra and eastern Kalimantan. There are estimated to be 46 trillion cu ft (1.3 trillion m3) of shale gas and 7.9 billion barrels (1.26×109 m3) of shale oil which could be recovered with existing technologies. Pertamina has taken the lead in using hydraulic fracturing
to explore for shale gas in northern Sumatra. Chevron Pacific Indonesia
and NuEnergy Gas are also pioneers in using fracking in existing oil
fields and in new exploration. Environmental concerns and a
government-imposed cap on oil prices present barriers to full
development of the substantial shale deposits in the country.
Sulawesi, Seram, Buru, Irian Jaya in eastern Indonesia have shales that
were deposited in marine environments which may be more brittle and
thus more suitable for fracking than the source rocks in western
Indonesia which have higher clay content.
Coal Bed Methane
With 453 trillion cu ft (12.8 trillion m3) of Coal Bed Methane (CBM) reserve mainly in Kalimantan and Sumatra,
Indonesia has potential to redraft its energy charts as United States
with its Shale Gas. With low enthusiasm to develop CBM project, partly
in relation to environmental concern regarding emissions of greenhouse gases and contamination of water in the extraction process, the government targeted 8.9 million cu ft (250 thousand m3) per day at standard pressure for 2015.[27]
Renewable energy sources
The contribution of renewable sources of energy to energy supply as a percentage of total primary energy (potential) supply in 2010 was 34.5%. Renewable generation sources supplied 5% to 6% of Indonesia's electricity in 2015. Indonesia has set a target of 23% of electricity generation from renewable sources by 2025. By November 2018, Indonesia had announced it was unlikely to meet the 23% renewable energy by 2025 target set in the Paris Accords.
In February 2020, it was announced that the People's Consultative Assembly is preparing its first renewable energy bill.
Biomass
An estimated 55% of Indonesia's population, i.e. 128 million people primarily rely upon traditional biomass (mainly wood) for cooking.
Reliance on this source of energy has the disadvantage that poor
people in rural areas have little alternative but to collect timber from
forests, and often cut down trees, to collect wood for cooking.
A pilot project of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) Power Generator
with capacity of 1 Megawatt has been inaugurated in September 2014. Indonesia has many Palm Oil Mills.
Hydroelectricity
Indonesia has set a target of 2 GW installed capacity in hydroelectricity, including 0.43 GW micro hydro, by 2025.
Geothermal energy
Indonesia uses some geothermal energy. According to the Renewable Energy Policy Network's Renewables 2013 Global Status Report,
Indonesia has the third largest installed generating capacity in the
world. With 1.3 GW installed capacity, Indonesia trails only the United
States (3.4 GW) and the Philippines (1.9 GW). However it leads Mexico
(1.0 GW), Italy (0.9 GW), New Zealand (0.8 GW), Iceland (0.7 GW), and
Japan (0.5 GW).
Current official policy is to encourage the increasing use of
geothermal energy for electricity production. Geothermal sites in
Indonesia include the Wayang Windu Geothermal Power Station and the Kamojang plant, both in West Java.
The development of the sector has been proceeding rather more
slowly than hoped. Expansion appears to be held up by a range of
technical, economic, and policy issues which have attracted considerable
comment in Indonesia. However, it has proved difficult to formulate
policies to respond to the problems.
Wind power
On
average, low wind speeds mean that for many locations there is limited
scope for large-scale energy generation from wind in Indonesia. Only
small (<10 6.5="" 8.2="" a="" according="" amount="" an="" and="" annual="" are="" assessments="" average="" basis.="" be="" could="" east="" economically="" electricity="" enough="" estimated="" feasible.="" for="" found="" from="" generated="" generators="" have="" highest="" href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wind_power" in="" is="" island="" kw="" m="" medium="" nbsp="" nrel="" nusa="" of="" off-grid="" on="" ranging="" resources="" s="" separate="" small="" speeds="" strong="" sumba="" technical="" tengarra="" that="" the="" three="" title="Wind power" to="" umba="" using="" very="" viable="" wind="" with="">wind power
. For example, a small plant was established at Pandanmino, a small village on the south coast of Java in Bantul Regency, Yogyakarta Province, in 2011. However it was established as experimental plant and it is not clear whether funding for long-term maintenance will be available.
Indonesia’s first wind farm opened in 2018, the 75MW Sidrap Wind Farm in Sindereng Rappang regency, South Sulawesi.
Solar power
The
Indonesian solar PV sector is relatively underdeveloped but has
significant potential. However, for a range of reasons, it is unlikely
that it will be practical to expand electricity output from solar
sources in Indonesia quickly. A range of technical, financial, economic
and social constraints are likely to be constraints on the rapid
installation of solar power in Indonesia, including in rural areas.
Output from the solar photovoltaic sector is almost exclusively
set aside for decentralised rural electrification. In 2011 the sector
produced a relatively small amount of electricity—only 22 MWh.
Use of energy
Transport sector
Much
energy in Indonesia is used for domestic transportation. The dominance
of private vehicles - mostly cars and motorbikes - in Indonesia has led
to an enormous demand for fuel. Energy consumption in the transport
sector is growing by about 4.5% every year. There is therefore an urgent
need for policy reform and infrastructure investment to enhance the
energy efficiency of transport, particularly in urban areas.
There are large opportunities to reduce both the energy
consumption from the transport sector, for example through the adoption
of higher energy efficiency standards for private cars/motorbikes and
expanding mass transit networks. Many of these measures would be more
cost-effective than the current transport systems.
There is also scope to reduce the carbon intensity of transport energy,
particularly through replacing diesel with biodiesel or through
electrification. Both would require comprehensive supply chain analysis
to ensure that the biofuels and power plants are not having wider
environmental impacts such as deforestation or air pollution.
Electricity sector
Access to electricity
Over 50% of households in 2011 had an electricity connection. An
estimated 63 million people in 2011 did not have direct access to
electricity.
Organisations
The electricity sector, dominated by the state-owned electricity utility Perusahaan Listrik Negara, is another major consumer of primary energy.
Major energy companies in Indonesia
The logo of Pertamina
Indonesian firms
- Pertamina, the state-owned oil company
- Perusahaan Listrik Negara, the state-owned electricity company.
- Perusahaan Gas Negara, the state-owned gas company
- PT Bumi Resources owned by the Bakrie Group
- PT Medco Energi International, the largest publicly listed oil and gas company in Indonesia
- Adaro Energy, one of the largest coal mining companies in Indonesia
Foreign firms
- US-based firm PT Chevron Pacific Indonesia is the largest producer of crude oil in Indonesia; Chevron produces (2014) around 40% of the crude oil in Indonesia
- Total E&P Indonesie which operates the East Mahakam field in Kalimantan and other fields
- ExxonMobil is one of the main foreign operators in Indonesia
- Statoil, a Norwegian multinational firm, which has been operating in Indonesia since 2007, especially in Eastern Indonesia
- BP which is a major LNG operator in the Tangguh gas field in West Papua.
- ConocoPhilips which currently operates four production-sharing contracts including at Natuna and in Sumatra.
- Inpex, a Japanese firm established in 1966 as North Sumatra Offshore Petroleum Exploration Co. Ltd.
Global warming
The CO2 emissions of Indonesia in total were over Italy in 2009. However, in all greenhouse gas emissions including construction and deforestation in 2005 Indonesia was top-4 after China, US and
Brazil.