Public opinion on climate change is the aggregate of attitudes or beliefs held by the adult population concerning the science, economics, and politics of climate change. It is affected by media coverage of climate change.
General overview
In January 2021, the United Nations Development Programme reported results of the largest-ever climate survey, which indicated that two-thirds of respondents consider climate change as an emergency, with forest and land conservation being the most popular solutions. Specifically, The Peoples' Climate Vote (1.2 million respondents in over 50 countries) found that 64% said climate change was an emergency – presenting a clear and convincing call for decision-makers to step up on ambition.
Influences on individual opinion
Geographic region
For a list of countries and their opinion see "Climate change opinion by country" below
Between 2007–20010, the Gallup World Poll surveyed individuals in 143 countries. This poll queried whether the respondent knew of global warming. Those who had a basic concept of global warming didn't necessarily connect it to human activities, revealing that knowledge of global warming and the knowledge that it's human-induced are two separate things. Over a third of the world's population were unaware of global warming. Developing countries have less awareness than developed, and Africa the least aware. Of those aware, residents of Latin America and developed countries in Asia led the belief that climate change is a result of human activities while Africa, parts of Asia and the Middle East, and a few countries from the former Soviet Union led in the opposite. Opinion within the United Kingdom was divided.
The first major worldwide poll, conducted by Gallup in 2008–2009 in 127 countries, found that some 62% of people worldwide said they knew about global warming. In the industrialized countries of North America, Europe, and Japan, 67% or more knew about it (97% in the U.S., 99% in Japan); in developing countries, especially in Africa, fewer than a quarter knew about it, although many had noticed local weather changes. The survey results suggest that between 2007 and 2010 only 42% of the world's population were aware of climate change and believed that it is caused by human activity. Among those who knew about global warming, there was a wide variation between nations in belief that the warming was a result of human activities.
Adults in Asia, with the exception of those in developed countries, are the least likely to perceive global warming as a threat. In developed Asian countries like South Korea, perceptions of climate change are associated with strong emotional beliefs about its causes. In the western world, individuals are the most likely to be aware and perceive it as a very or somewhat serious threat to themselves and their families; although Europeans are more concerned about climate change than those in the United States. However, the public in Africa, where individuals are the most vulnerable to global warming while producing the least carbon dioxide, is the least aware – which translates into a low perception that it is a threat.
These variations pose a challenge to policymakers, as different countries travel down different paths, making an agreement over an appropriate response difficult. While Africa may be the most vulnerable and produce the least amount of greenhouse gases, they are the most ambivalent. The top five emitters (China, the United States, India, Russia, and Japan), who together emit half the world's greenhouse gases, vary in both awareness and concern. The United States, Russia, and Japan are the most aware at over 85% of the population. Conversely, only two-thirds of people in China and one-third in India are aware. Japan expresses the greatest concern, which translates into support for environmental policies. People in China, Russia, and the United States, while varying in awareness, have expressed a similar proportion of aware individuals concerned. Similarly, those aware in India are likely to be concerned, but India faces challenges spreading this concern to the remaining population as its energy needs increase over the next decade.
An online survey on environmental questions conducted in 20 countries by Ipsos MORI, "Global Trends 2014", shows broad agreement, especially on climate change and if it is caused by humans, though the U.S. ranked lowest with 54% agreement. It has been suggested that the low U.S. ranking is tied to denial campaigns.
A 2010 survey of 14 industrialized countries found that skepticism about the danger of global warming was highest in Australia, Norway, New Zealand and the United States, in that order, correlating positively with per capita emissions of carbon dioxide.
Education
In countries varying in awareness, an educational gap translates into a gap in awareness. However an increase in awareness does not always result in an increase in perceived threat. In China, 98% of those who have completed four years or more of college education reported knowing something or a great deal of climate change while only 63% of those who have completed nine years of education reported the same. Despite the differences in awareness in China, all groups perceive a low level of threat from global warming. In India, those who are educated are more likely to be aware, and those who are educated there are far more likely to report perceiving global warming as a threat than those who are not educated. In Europe, individuals who have attained a higher level of education perceive climate change as a serious threat. There is also a strong association between education and Internet use. Europeans who use the Internet more are more likely to perceive climate change as a serious threat. However, a survey of American adults found "little disagreement among culturally diverse citizens on what science knows about climate change. In the US, individuals with greater science literacy and education have more polarized beliefs on climate change.
Demographics
Residential demographics affect perceptions of global warming. In China, 77% of those who live in urban areas are aware of global warming compared to 52% in rural areas. This trend is mirrored in India with 49% to 29% awareness, respectively.
Of the countries where at least half the population is aware of global warming, those with the majority who believe that global warming is due to human activities have a greater national GDP per unit energy—or, a greater energy efficiency.
In Europe, individuals under fifty-five are more likely to perceive both "poverty, lack of food and drinking water" and climate change as a serious threat than individuals over fifty-five. Male individuals are more likely to perceive climate change as a threat than female individuals. Managers, white-collar workers, and students are more likely to perceive climate change as a greater threat than house persons and retired individuals.
In the United States, conservative white men are more likely than other Americans to deny climate change. A very similar trend has been documented in Norway, where 63% of conservative men deny anthropogenic climate change compared to just 36% of the general Norwegian population. In Sweden, political conservatism was similarly found to correlate with climate change denial, while in Brazil, climate change denial has been found to be more correlated with gender, with men being significantly more likely to express denialist viewpoints compared to women.
In Great Britain, a movement of by women known as "birthstrikers" advocates for refraining from procreation until the possibility of "climate breakdown and civilisation collapse" is averted.
In general, there is a substantial variation in the direction in which demographic traits, like age or gender, correlate with climate change concern. While women and younger people tend to be more concerned about climate change in English-speaking constituencies, the opposite is true in most African countries.
Political identification
(Discontinuity resulted from survey changing in 2015 from reciting "global warming" to "climate change".)
In the United States, support for environmental protection was relatively non-partisan in the twentieth century. Republican Theodore Roosevelt established national parks whereas Democrat Franklin Delano Roosevelt established the Soil Conservation Service. Republican Richard Nixon was instrumental in founding the United States Environmental Protection Agency, and tried to install a third pillar of NATO dealing with environmental challenges such as acid rain and the greenhouse effect. Daniel Patrick Moynihan was Nixon's NATO delegate for the topic.
This non-partisanship began to erode during the 1980s, when the Reagan administration described environmental protection as an economic burden. Views over global warming began to seriously diverge between Democrats and Republicans during the negotiations that led up to the creation of the Kyoto Protocol in 1998. In a 2008 Gallup poll of the American public, 76% of Democrats and only 41% of Republicans said that they believed global warming was already happening. The opinions of the political elites, such as members of Congress, tends to be even more polarized.
Public opinion on climate change can be influenced by who people vote for. Although media coverage influences how some view climate change, research shows that voting behavior influences climate change skepticism. This shows that people's views on climate change tend to align with the people they voted for.
In Europe, opinion is not strongly divided among left and right parties. Although European political parties on the left, including Green parties, strongly support measures to address climate change, conservative European political parties maintain similar sentiments, most notably in Western and Northern Europe. For example, Margaret Thatcher, never a friend of the coal mining industry, was a strong supporter of an active climate protection policy and was instrumental in founding the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change and the British Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research. Some speeches, as to the Royal Society on 27 September 1988 and to the UN general assembly in November 1989 helped to put climate change, acid rain, and general pollution in the British mainstream. After her career, however, Thatcher was less of a climate activist, as she called climate action a "marvelous excuse for supranational socialism", and called Al Gore an "apocalyptic hyperbole". France's center-right President Chirac pushed key environmental and climate change policies in France in 2005–2007. Conservative German administrations (under the Christian Democratic Union and Christian Social Union) in the past two decades have supported European Union climate change initiatives; concern about forest dieback and acid rain regulation were initiated under Kohl's archconservative minister of the interior Friedrich Zimmermann. In the period after former President George W. Bush announced that the United States was leaving the Kyoto Treaty, European media and newspapers on both the left and right criticized the move. The conservative Spanish La Razón, the Irish Times, the Irish Independent, the Danish Berlingske Tidende, and the Greek Kathimerini all condemned the Bush administration's decision, as did left-leaning newspapers.
In Norway, a 2013 poll conducted by TNS Gallup found that 92% of those who vote for the Socialist Left Party and 89% of those who vote for the Liberal Party believe that global warming is caused by humans, while the percentage who held this belief is 60% among voters for the Conservative Party and 41% among voters for the Progress Party.
The shared sentiments between the political left and right on climate change further illustrate the divide in perception between the United States and Europe on climate change. As an example, conservative German Prime Ministers Helmut Kohl and Angela Merkel have differed with other parties in Germany only on how to meet emissions reduction targets, not whether or not to establish or fulfill them.
A 2017 study found that those who changed their opinion on climate change between 2010 and 2014 did so "primarily to align better with those who shared their party identification and political ideology. This conforms with the theory of motivated reasoning: Evidence consistent with prior beliefs is viewed as strong and, on politically salient issues, people strive to bring their opinions into conformance with those who share their political identity". Furthermore, a 2019 study examining the growing skepticism of climate change among American Republicans argues that persuasion and rhetoric from party elites play a critical role in public opinion formation, and that these elite cues are propagated through mainstream and social media sources.
For those who care about the environment and want change are not happy about some policies, for example the support of the cap and trade policy but very few people are willing to pay more than 15 dollars per month for a program that is supposed to help the environment. There is evidence that not many people are aware of climate change in the US, only 2% of respondents ranked the environment as the top issue in the US.
Individual risk assessment and assignment
The IPCC attempts to orchestrate global (climate) change research to shape a worldwide consensus. However, the consensus approach has been dubbed more a liability than an asset in comparison to other environmental challenges. The linear model of policy-making, based on a more knowledge we have, the better the political response will be is said to have not been working and is in the meantime rejected by sociology.
Sheldon Ungar, a Canadian sociologist, compares the different public reactions towards ozone depletion and climate change. The public opinion failed to tie climate change to concrete events which could be used as a threshold or beacon to signify immediate danger. Scientific predictions of a temperature rise of two to three degrees Celsius over several decades do not respond with people, e.g. in North America, that experience similar swings during a single day. As scientists define global warming a problem of the future, a liability in "attention economy", pessimistic outlooks in general and assigning extreme weather to climate change have often been discredited or ridiculed (compare Gore effect) in the public arena. While the greenhouse effect per se is essential for life on earth, the case was quite different with the ozone shield and other metaphors about the ozone depletion. The scientific assessment of the ozone problem also had large uncertainties. But the metaphors used in the discussion (ozone shield, ozone hole) reflected better with lay people and their concerns.
The idea of rays penetrating a damaged "shield" meshes nicely with abiding and resonant cultural motifs, including "Hollywood affinities". These range from the shields on the Starship Enterprise to Star Wars, ... It is these pre-scientific bridging metaphors built around the penetration of a deteriorating shield that render the ozone problem relatively simple. That the ozone threat can be linked with Darth Vader means that it is encompassed in common sense understandings that are deeply ingrained and widely shared. (Sheldon Ungar 2000)
The chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) regulation attempts of the end of the 1980s profited from those easy-to-grasp metaphors and the personal risk assumptions taken from them. As well the fate of celebrities like President Ronald Reagan, which had skin cancer removal in 1985 and 1987, was of high importance. In case of the public opinion on climate change, no imminent danger is perceived.
Ideology
In the United States, ideology is an effective predictor of party identification, where conservatives are more prevalent among Republicans, and moderates and liberals among independents and Democrats. A shift in ideology is often associated with in a shift in political views. For example, when the number of conservatives rose from 2008 to 2009, the number of individuals who felt that global warming was being exaggerated in the media also rose. The 2006 BBC World Service poll found that when asked about various policy options to reduce greenhouse gas emissions – tax incentives for alternative energy research and development, installment of taxes to encourage energy conservation, and reliance on nuclear energy to reduce fossil fuels. The majority of those asked felt that tax incentives were the path of action that they preferred.
As of May 2016, polls have repeatedly found that a majority of Republican voters, particularly young ones, believe the government should take action to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
The pursuit of green energy is an ideology that defines hydroelectric dams, natural gas power plants, and nuclear power as unacceptable alternative energies for the eight billion tons of coal burnt each year. While there is popular support for wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal energy, all these sources combined only supplied 1.3% of global energy in 2013.
After a country host the annual Conference of the Parties (COP) climate legislation increases which causes policy diffusion. There is strong evidence of policy diffusion which is when a policy is made it is influenced by the policy choices made elsewhere.This can a have positive effect on climate legislation.
Scientific analyses of international survey data show that right-wing orientation and individualism are strongly correlated to climate change denial in the US and other English-speaking countries, but much less in most non-English speaking nations.
Charts
A 2018 study found that individuals were more likely to accept that global temperatures were increasing if they were shown the information in a chart rather than in text.
Issues
Science
A scientific consensus on climate change exists, as recognized by national academies of science and other authoritative bodies. The opinion gap between scientists and the public in 2009 stands at 84% to 49% that global temperatures are increasing because of human-activity. However, more recent research has identified substantial geographical variation in the public's understanding of the scientific consensus.
Economics
Economic debates weigh the benefits of limiting industrial emissions of mitigating global warming against the costs that such changes would entail. While there is a greater amount of agreement over whether global warming exists, there is less agreement over the appropriate response. Electric or petroleum distribution may be government owned or utilities may be regulated by government. The government owned or regulated utilities may, or may not choose to make lower emissions a priority over economics, in unregulated counties industry follows economic priorities. An example of the economic priority is Royal Dutch Shell PLC reporting CO2 emissions of 81 million metric tonnes in 2013.
Media
The popular media in the U.S. gives greater attention to skeptics relative to the scientific community as a whole, and the level of agreement within the scientific community has not been accurately communicated. US popular media coverage differs from that presented in other countries, where reporting is more consistent with the scientific literature. Some journalists attribute the difference to climate change denial being propagated, mainly in the US, by business-centered organizations employing tactics worked out previously by the US tobacco lobby. However, one study suggests that these tactic are less prominent in the media and that the public instead draws their opinions on climate mainly from the cues of political party elites.
The efforts of Al Gore and other environmental campaigns have focused on the effects of global warming and have managed to increase awareness and concern, but despite these efforts as of 2007, the number of Americans believing humans are the cause of global warming was holding steady at 61%, and those believing the popular media was understating the issue remained about 35%. Between 2010 and 2013, the number of Americans who believe the media under-reports the seriousness of global warming has been increasing, and the number who think media over-states it has been falling. According to a 2013 Gallup US opinion poll, 57% believe global warming is at least as bad as portrayed in the media (with 33% thinking media has downplayed global warming and 24% saying coverage is accurate). Less than half of Americans (41%) think the problem is not as bad as media portrays it.
September 2011 Angus Reid Public Opinion poll found that Britons (43%) are less likely than Americans (49%) or Canadians (52%) to say that "global warming is a fact and is mostly caused by emissions from vehicles and industrial facilities". The same poll found that 20% of Americans, 20% of Britons and 14% of Canadians think "global warming is a theory that has not yet been proven".
A March 2013 Public Policy Polling poll about widespread and infamous conspiracy theories found that 37% of American voters believe that global warming is a hoax, while 51% do not.
A 2013 poll in Norway conducted by TNS Gallup found that 66% of the population believe that climate change is caused by humans, while 17% do not believe this.
Politics
Public opinion impacts on the issue of climate change because governments need willing electorates and citizens in order to implement policies that address climate change. Further, when climate change perceptions differ between the populace and governments, the communication of risk to the public becomes problematic. Finally, a public that is not aware of the issues surrounding climate change may resist or oppose climate change policies, which is of considerable importance to politicians and state leaders.
Public support for action to forestall global warming is as strong as public support has been historically for many other government actions; however, it is not "intense" in the sense that it overrides other priorities.
A 2009 Eurobarometer survey found that, on the average, Europeans rate climate change as the second most serious problem facing the world today, between "poverty, the lack of food and drinking water" and "a major global economic downturn." 87% of Europeans consider climate change to be a "serious" or "very serious" problem, while 10% "do not consider it a serious problem." However, the proportion who believe it to be a problem has dropped in the period 2008/9 when the surveys were conducted. While the small majority believe climate change is a serious threat, 55% percent believe the EU is doing too little and 30% believe the EU is going the right amount. As a result of European Union climate change perceptions, "climate change is an issue that has reached such a level of social and political acceptability across the EU that it enables (indeed, forces) the EU Commission and national leaders to produce all sorts of measures, including taxes." Despite the persistent high level of personal involvement of European citizens, found in another Eurobarometer survey in 2011, EU leaders have begun to downscale climate policy issues on the political agenda since the beginning of the Eurozone crisis.
Although public opinion may not be the only factor influencing renewable energy policies, it is a key catalyst. Research has found that the shifts in public opinion in the direction of pro-environmentalism strongly increased the adoption of renewable energy policies in Europe, which can thus be applied in the U.S. and how important climate solutions are to Americans. Moreover, other research shows that countries in which more people believe in human-made climate change tend to have higher carbon prices.
The proportion of Americans who believe that the effects of global warming have begun or will begin in a few years rose to a peak in 2008 where it then declined, and a similar trend was found regarding the belief that global warming is a threat to their lifestyle within their lifetime. Concern over global warming often corresponds with economic downturns and national crisis such as 9/11 as Americans prioritize the economy and national security over environmental concerns. However the drop in concern in 2008 is unique compared to other environmental issues. Considered in the context of environmental issues, Americans consider global warming as a less critical concern than the pollution of rivers, lakes, and drinking water; toxic waste; fresh water needs; air pollution; damage to the ozone layer; and the loss of tropical rain forests. However, Americans prioritize global warming over species extinction and acid rain issues. Since 2000 the partisan gap has grown as Republican and Democratic views diverge.
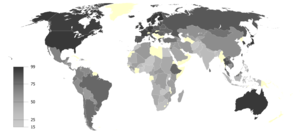
Climate change opinion by country
Climate change opinion is the aggregate of public opinion held by the adult population. Cost constraints often restrict surveys to sample only one or two countries from each continent or focus on only one region. Because of differences among questions, wording, and methods—it is difficult to reliably compare results or to generalize them to opinions held worldwide.
In 2007–2008, the Gallup Poll surveyed individuals from 128 countries in the first comprehensive study of global opinions. The Gallup Organization aggregated opinion from the adult population fifteen years of age and older, either through the telephone or personal interviews, and in both rural and urban areas except in areas where the safety of interviewer was threatened and in scarcely populated islands. Personal interviews were stratified by population size or geography and cluster sampling was achieved through one or more stages. Although error bounds vary, they were all below ±6% with 95% confidence.
Weighting countries to a 2008 World Bank population estimate, 61% of individuals worldwide were aware of global warming, developed countries more aware than developing, with Africa the least aware. The median of people perceiving it as a threat was 47%. Latin America and developed countries in Asia led the belief that climate change was a result of human activities, while Africa, parts of Asia and the Middle East, and countries from the Former Soviet Union led in the opposite. Awareness often translates to concern, although of those aware, individuals in Europe and developed countries in Asia perceived global warming as a greater threat than others.
Views on climate change by region
Africa
People in Africa are relatively concerned about climate change compared to the Middle East and parts of Asia. However, they are less concerned than most of Latin America and Europe. Currently, 61% of people in Africa consider climate change to be a very serious problem, and 52% believe that climate change is harming people now. While 59% of Africans are worried about droughts or water shortages, only 16% are concerned about severe weather, and 3% are concerned about rising sea levels. Countries in Sub-Saharan Africa are especially troubled about increasing desertification even as they account for .04% of global carbon dioxide emissions. In Sub-Saharan Africa, the concern over climate change drops to only 34% of the population considering climate change to be a "very" or "somewhat serious issue". Even so, according to the Pew Research Center 2015 Global Attitudes Survey, some particular countries are more concerned than others. In Uganda 79% of people, 68% in Ghana, 45% in South Africa and 40% in Ethiopia consider climate change to be a very serious problem.
Latin America
Latin America has a larger percentage of people concerned with climate change than other regions of the world. 74% consider climate change to be a serious problem and 77% say that it is harming people now which is 20 points higher than the global median according to the Pew Research Center. 63% of people in Latin America are very concerned that climate change will harm them personally. When looked at more specifically, Mexico and Central America are the most worried at 81.5% believing that climate change is a very serious issue. South America is slightly less anxious at 75% and the Caribbean, at the relatively high rate of 66.7%, is the least concerned. Brazil is an important country in global climate change politics because it is the eleventh largest emitter and unlike other large emitter countries, 86% consider global warming to be a very serious problem. Compared to the rest of the world, Latin America is more consistently concerned with high percentages of the population worried about climate change. Further, in Latin America, 67% believe in personal responsibility for climate change and say that people will have to make major lifestyle modifications.
Europe
Europeans have a tendency to be more concerned about climate change than much of the world, with the exception of Latin America. However there is a divide between Eastern Europe, where people are less worried about climate change, and Western Europe. A global climate survey by the European Investment Bank showed that climate is the number one concern for Europeans. Most respondents said they were already feeling the effects of climate change. Many people believed climate change can still be reversed with 68% of Spanish respondents believing it can be reversed and 80% seeing themselves as part of the solution.
In Europe, there is a range from 88% to 97% of people feeling that climate change is happening and similar ranges are present for agreeing that climate change is caused by human activity and that the impacts of it will be bad. Generally Eastern European countries are slightly less likely to believe in climate change, or the dangers of it, with 63% saying it is very serious, 24% considering it to be fairly serious and only 10% saying it is not a serious problem. When asked if they feel a personal responsibility to help reduce climate change, on a scale of 0, not at all, to 10, a great deal, Europeans respond with the average score of 5.6. When looked at more specifically, Western Europeans are closer to the response of 7 while Eastern European countries respond with an average of less than 4. When asked if Europeans are willing to pay more for climate change, 49% are willing, however only 9% of Europeans have already switched to a greener energy supply. While a large majority of Europeans believe in the dangers of climate change, their feelings of personal responsibility to deal with the issue are much more limited. Especially in terms of actions that could already have been taken - such as having already switched to greener energies discussed above - one can see Europeans' feelings of personal responsibility are limited. 90% of Europeans interviewed for the European Investment Bank Climate Survey 2019 believe their children will be impacted by climate change in their everyday lives and 70% are willing to pay an extra tax to fight climate change.
Asia/Pacific
Asia and the Pacific have a tendency to be less concerned about climate change, except small island states, with developing countries in Asia being less concerned than developed countries. In Asia and the Pacific, around 45% of people believe that climate change is a very serious problem and similarly 48% believe that it is harming people now. Only 37% of people in Asia and the Pacific are very concerned that climate change will harm them personally. There is a large gap between developing Asia and developed Asia. Only 31% of developing Asia considers global warming to be a "very" or "somewhat" serious threat and 74% of developed Asia considers global warming to be a serious threat. It could be argued that one reason for this is that people in more developed countries in Asia are more educated on the issues, especially given that developing countries in Asia do face significant threats from climate change. The most relevant views on climate change are those of the citizens in the countries that are emitting the most. For example, in China, the world's largest emitter, 68% of Chinese people are satisfied with their government's efforts to preserve the environment. And in India, the world's third largest emitter, 77% of Indian people are satisfied with their country's efforts to preserve the environment. 80% of Chinese citizens interviewed in the European Investment Bank Climate Survey 2019 believe climate change is still reversible, 72% believe their individual behaviour can make a difference in addressing climate change.
Middle East
While the increasing severity of droughts and other dangerous realities are and will continue to be a problem in the Middle East, the region has one of the smallest rates of concern in the world. 38% believe that climate change is a very serious problem and 26% believe that climate change is harming people now. Of the four Middle Eastern countries polled in a Pew Global Study, on what is their primary concern, Israel, Jordan, and Lebanon named ISIS, and Turkey stated United States encroachment. 38% of Israel considers climate change to be a major threat to their country, 40% of Jordan, 58% of Lebanon and 53% of Turkey. This is compared to relatively high numbers of residents who believe that ISIS is a major threat to their country ranging from 63% to 97%. In the poll, 38% of the Middle East are concerned about drought and 19% are concerned about long periods of unusually hot weather. 42% are satisfied with their own country's current efforts to preserve the environment.
North America
(Discontinuity resulted from survey changing in 2015 from reciting "global warming" to "climate change".)
North America has mixed perceptions on climate change ranging from Mexico and Canada that are both more concerned, and the United States, the world's second largest emitter, that is less concerned. Mexico is the most concerned about climate change of the three countries in North America. 90% consider climate change to be a very serious problem and 83% believe that climate change is harming people substantially right now. Canadians are also seriously concerned, 20% are extremely concerned, 30% are definitely concerned, 31% are somewhat concerned and only 19% are not very/not at all concerned about climate change. While the United States which is the largest emitter of CO2 in North America and the second largest emitter of CO2 in the world has the lowest degrees of concern about climate change in North America. While 61% of Americans say they are concerned about climate change, that is 30% lower than Mexico and 20% lower than Canada. 41% believe that climate change could impact them personally. Nonetheless, 70% of Americans believe that environmental protections are more important than economic growth according to a Yale climate opinion study. 76% of US citizens interviewed for the European Investment Bank Climate Survey 2019 believe developed countries have a responsibility to help developing countries address climate change.
United States
In 2009 Yale University conducted a study identifying global warming's "Six Americas". The report identifies six audiences with different opinions about global warming: The alarmed (18%), the concerned (33%), the cautious (19%), the disengaged (12%), the doubtful (11%) and the dismissive (7%). The alarmed and concerned make out the largest percentage and think something should be done about global warming. The cautious, disengaged and doubtful are less likely to take action. The dismissive are convinced global warming is not happening. These audiences can be used to define the best approaches for environmental action. The theory of the 'Six Americas' is also used for marketing purposes.
Opinions in the United States vary intensely enough to be considered a culture war.
In a January 2013 survey, Pew found that 69% of Americans say there is solid evidence that the Earth's average temperature has gotten warmer over the past few decades, up six points since November 2011 and 12 points since 2009.
A Gallup poll in 2014 concluded that 51 percent of Americans were a little or not at all worried about climate change, 24 percent a great deal and 25 percent a fair amount.
In 2015, 32 percent or Americans were worried about global warming as a great deal, 37 percent in 2016, and 45 percent in 2017. A poll taken in 2016 shows that 52% of Americans believe climate change to be caused by human activity, while 34% state it is caused by natural changes. Data is increasingly showing that 62 percent of Americans believe that the effects of global warming are happening now in 2017.
In 2016 GALLUP found that 64% of Americans are worried about global warming, 59% believed that global warming is already happening and 65% is convinced that global warming is caused by human activities. These numbers show that awareness of global warming is increasing in the United States
In 2019 GALLUP found that one-third of Americans blame unusual winter temperatures on climate change.
In 2019 the Yale Program on Climate Change Communication found that 69% of Americans believe that climate change is happening. Additionally, their research also found that Americans think that only 54% of the country believes that climate change is happening. These figures show that there is a disconnect between perceived public perception of the issue and reality.
Differences between regions
While climate change will affect the entire world, opinion differences between regions of the world about these affects vary significantly. The Middle East has one of the smallest rates of concern in the world, especially compared to Latin America. Europe and Africa have mixed views on climate change but lean towards action by a significant degree. Europeans focus substantially on climate change when compared to United States residents, which are less concerned than the global median, even as the United States is the second biggest emitter in the world. Droughts/water shortages are one of the biggest fears about the impacts of climate change, especially in Latin America and Africa. Developed countries in Asia have levels of concern about climate change similar to Latin America which has one of the highest rates of concern. This is surprising as developing countries in Asia have levels of worry similar to the Middle East, one of the areas with the lowest levels of concern. Large emitters such as China usually ignore issues surrounding climate change as people in China have very low levels of concern about it. The only significant exception to this tendency by large emitters, is Brazil and India . India I'd the third and Brazil is eleventh biggest emitter in the world and are countries that have high levels of concern about climate change, levels similar to much of Latin America.
| Region | Climate change is a very serious problem | Climate change is harming people now | Very concerned that climate change will harm me personally |
|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | 61% | 52% | 61% |
| Latin America | 74% | 77% | 63% |
| Europe | 54% | 60% | 27% |
| Asia/Pacific | 45% | 48% | 37% |
| Middle East | 38% | 26% | 27% |
| United States | 45% | 41% | 30% |
| China | 18% | 49% | 15% |
| Global Median | 54% | 51% | 40% |
Source: Pew Research Center's Spring 2015 Global Attitudes Survey - Q32, Q41 & Q42
| Country | Climate change is a very serious problem |
|---|---|
| Canada | 51% |
| U.S. | 45% |
| France | 56% |
| Italy | 55% |
| Germany | 55% |
| Spain | 53% |
| UK | 41% |
| Poland | 19% |
| Russia | 33% |
| Ukraine | 80% |
| Lebanon | 67% |
| Jordan | 44% |
| Palestine | 38% |
| Turkey | 37% |
| Israel | 24% |
| India | 76% |
| Philippines | 72% |
| Vietnam | 69% |
| South Korea | 48% |
| Japan | 45% |
| Malaysia | 44% |
| Australia | 43% |
| Indonesia | 41% |
| Pakistan | 29% |
| China | 18% |
| Brazil | 86% |
| Chile | 77% |
| Peru | 75% |
| Venezuela | 72% |
| Mexico | 66% |
| Argentina | 59% |
| Burkina Faso | 79% |
| Uganda | 76% |
| Ghana | 68% |
| Kenya | 62% |
| Nigeria | 61% |
| Senegal | 58% |
| Tanzania | 57% |
| South Africa | 45% |
| Ethiopia | 40% |
Source: Pew Research Center's Spring 2015 Global Attitudes Survey - Q32
Developing countries vs developed countries
Awareness about climate change is higher in developed countries than in developing countries. A large majority of people in Indonesia, Pakistan and Nigeria do not know about climate change, particularly in Muslim majority countries. There is often awareness about environmental changes in developing countries, but the framework for understanding it is limited. In developing and developed countries, people similarly believe that poor countries have a responsibility to act on climate change. Since the 2009 Copenhagen summit, concern over climate change in wealthy countries has gone down. In 2009, 63% of people in OECD member states considered climate change to be "very serious" but by 2015, it had gone down to 48%. Support for national leadership creating further action addressing climate change has also gone down. Of the 21 countries surveyed in GlobeScan's 2015 survey, Canada, France, Spain and the UK are the only ones that have the majority of the population desiring their leadership to take further action to meet the emission targets set by the Paris climate accord. While concern and desire for action has gone down in developed countries, awareness over it is higher. Since 2000, twice as many people will connect extreme weather events with human caused climate change.