A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). Satnav systems operate independently of any telephonic or internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the positioning information generated.
A satellite navigation system with global coverage may be termed a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). As of September 2020, the United States' Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia's Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, and the European Union's Galileo are fully operational GNSSs. Japan's Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) is a (US) GPS satellite-based augmentation system to enhance the accuracy of GPS, with satellite navigation independent of GPS scheduled for 2023. The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) plans to expand to a global version in the long term.
Global coverage for each system is generally achieved by a satellite constellation of 18–30 medium Earth orbit (MEO) satellites spread between several orbital planes. The actual systems vary, but all use orbital inclinations of >50° and orbital periods of roughly twelve hours (at an altitude of about 20,000 kilometres or 12,000 miles).
Classification
GNSS systems that provide enhanced accuracy and integrity monitoring usable for civil navigation are classified as follows:
- GNSS-1 is the first generation system and is the combination of existing satellite navigation systems (GPS and GLONASS), with Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) or Ground Based Augmentation Systems (GBAS). In the United States, the satellite based component is the Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS), in Europe it is the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS), and in Japan it is the Multi-Functional Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS). Ground based augmentation is provided by systems like the Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS).
- GNSS-2 is the second generation of systems that independently provides a full civilian satellite navigation system, exemplified by the European Galileo positioning system. These systems will provide the accuracy and integrity monitoring necessary for civil navigation; including aircraft. Initially, this system consisted of only Upper L Band frequency sets (L1 for GPS, E1 for Galileo, G1 for GLONASS). In recent years, GNSS systems have begun activating Lower L-Band frequency sets (L2 and L5 for GPS, E5a and E5b for Galileo, G3 for GLONASS) for civilian use; they feature higher aggregate accuracy and fewer problems with signal reflection. As of late 2018, a few consumer grade GNSS devices are being sold that leverage both, and are typically called "Dual band GNSS" or "Dual band GPS" devices.
By their roles in the navigation system, systems can be classified as:
- Core Satellite navigation systems, currently GPS (United States), GLONASS (Russian Federation), Beidou (China) and Galileo (European Union).
- Global Satellite Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS) such as OmniSTAR and StarFire.
- Regional SBAS including WAAS (US), EGNOS (EU), MSAS (Japan), GAGAN (India), SDCM (Russia).
- Regional Satellite Navigation Systems such as India's NAVIC, and Japan's QZSS.
- Continental scale Ground Based Augmentation Systems (GBAS) for example the Australian GRAS and the joint US Coast Guard, Canadian Coast Guard, US Army Corps of Engineers and US Department of Transportation National Differential GPS (DGPS) service.
- Regional scale GBAS such as CORS networks.
- Local GBAS typified by a single GPS reference station operating Real Time Kinematic (RTK) corrections.
As many of the global GNSS systems (and augmentation systems) use similar frequencies and signals around L1, many "Multi-GNSS" receivers capable of using multiple systems have been produced. While some systems strive to interoperate with GPS as well as possible by providing the same clock, others do not.
History
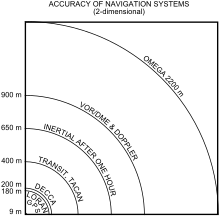
Ground based radio navigation is decades old. The DECCA, LORAN, GEE and Omega systems used terrestrial longwave radio transmitters which broadcast a radio pulse from a known "master" location, followed by a pulse repeated from a number of "slave" stations. The delay between the reception of the master signal and the slave signals allowed the receiver to deduce the distance to each of the slaves, providing a fix.
The first satellite navigation system was Transit, a system deployed by the US military in the 1960s. Transit's operation was based on the Doppler effect: the satellites travelled on well-known paths and broadcast their signals on a well-known radio frequency. The received frequency will differ slightly from the broadcast frequency because of the movement of the satellite with respect to the receiver. By monitoring this frequency shift over a short time interval, the receiver can determine its location to one side or the other of the satellite, and several such measurements combined with a precise knowledge of the satellite's orbit can fix a particular position. Satellite orbital position errors are caused by radio-wave refraction, gravity field changes (as the Earth's gravitational field is not uniform), and other phenomena. A team, led by Harold L Jury of Pan Am Aerospace Division in Florida from 1970-1973, found solutions and/or corrections for many error sources. Using real-time data and recursive estimation, the systematic and residual errors were narrowed down to accuracy sufficient for navigation.
Principles
Part of an orbiting satellite's broadcast includes its precise orbital data. Originally, the US Naval Observatory (USNO) continuously observed the precise orbits of these satellites. As a satellite's orbit deviated, the USNO sent the updated information to the satellite. Subsequent broadcasts from an updated satellite would contain its most recent ephemeris.
Modern systems are more direct. The satellite broadcasts a signal that contains orbital data (from which the position of the satellite can be calculated) and the precise time the signal was transmitted. Orbital data include a rough almanac for all satellites to aid in finding them, and a precise ephemeris for this satellite. The orbital ephemeris is transmitted in a data message that is superimposed on a code that serves as a timing reference. The satellite uses an atomic clock to maintain synchronization of all the satellites in the constellation. The receiver compares the time of broadcast encoded in the transmission of three (at sea level) or four (which allows an altitude calculation also) different satellites, measuring the time-of-flight to each satellite. Several such measurements can be made at the same time to different satellites, allowing a continual fix to be generated in real time using an adapted version of trilateration: see GNSS positioning calculation for details.
Each distance measurement, regardless of the system being used, places the receiver on a spherical shell at the measured distance from the broadcaster. By taking several such measurements and then looking for a point where they meet, a fix is generated. However, in the case of fast-moving receivers, the position of the signal moves as signals are received from several satellites. In addition, the radio signals slow slightly as they pass through the ionosphere, and this slowing varies with the receiver's angle to the satellite, because that changes the distance through the ionosphere. The basic computation thus attempts to find the shortest directed line tangent to four oblate spherical shells centred on four satellites. Satellite navigation receivers reduce errors by using combinations of signals from multiple satellites and multiple correlators, and then using techniques such as Kalman filtering to combine the noisy, partial, and constantly changing data into a single estimate for position, time, and velocity.
Einstein's theory of general relativity is applied to GPS time correction, the net result is that time on a GPS satellite clock advances faster than a clock on the ground by about 38 microseconds per day.
Applications
The original motivation for satellite navigation was for military applications. Satellite navigation allows precision in the delivery of weapons to targets, greatly increasing their lethality whilst reducing inadvertent casualties from mis-directed weapons. (See Guided bomb). Satellite navigation also allows forces to be directed and to locate themselves more easily, reducing the fog of war.
Now a global navigation satellite system, such as Galileo, is used to determine users location and the location of other people or objects at any given moment. The range of application of satellite navigation in the future is enormous, including both the public and private sectors across numerous market segments such as science, transport, agriculture etc.
The ability to supply satellite navigation signals is also the ability to deny their availability. The operator of a satellite navigation system potentially has the ability to degrade or eliminate satellite navigation services over any territory it desires.
In order of first launch year:
GPS
First launch year: 1978
The United States' Global Positioning System (GPS) consists of up to 32 medium Earth orbit satellites in six different orbital planes. The exact number of satellites varies as older satellites are retired and replaced. Operational since 1978 and globally available since 1994, GPS is the world's most utilized satellite navigation system.
GLONASS
First launch year: 1982
The formerly Soviet, and now Russian, Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, (GLObal NAvigation Satellite System or GLONASS), is a space-based satellite navigation system that provides a civilian radionavigation-satellite service and is also used by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. GLONASS has full global coverage since 1995 and with 24 active satellites.
BeiDou
First launch year: 2000
BeiDou started as the now-decommissioned Beidou-1, an Asia-Pacific local network on the geostationary orbits. The second generation of the system BeiDou-2 became operational in China in December 2011. The BeiDou-3 system is proposed to consist of 30 MEO satellites and five geostationary satellites (IGSO). A 16-satellite regional version (covering Asia and Pacific area) was completed by December 2012. Global service was completed by December 2018. On 23 June 2020, the BDS-3 constellation deployment is fully completed after the last satellite was successfully launched at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center.
Galileo
First launch year: 2011
The European Union and European Space Agency agreed in March 2002 to introduce their own alternative to GPS, called the Galileo positioning system. Galileo became operational on 15 December 2016 (global Early Operational Capability, EOC). At an estimated cost of €10 billion, the system of 30 MEO satellites was originally scheduled to be operational in 2010. The original year to become operational was 2014. The first experimental satellite was launched on 28 December 2005. Galileo is expected to be compatible with the modernized GPS system. The receivers will be able to combine the signals from both Galileo and GPS satellites to greatly increase the accuracy. The full Galileo constellation consists of 24 active satellites, the last of which was launched in December 2021. The main modulation used in Galileo Open Service signal is the Composite Binary Offset Carrier (CBOC) modulation.
The NavIC or NAVigation with Indian Constellation is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system developed by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The government approved the project in May 2006, and consists of a constellation of 7 navigational satellites. Three of the satellites are placed in the Geostationary orbit (GEO) and the remaining four in the Geosynchronous orbit (GSO) to have a larger signal footprint and lower number of satellites to map the region. It is intended to provide an all-weather absolute position accuracy of better than 7.6 metres (25 ft) throughout India and within a region extending approximately 1,500 km (930 mi) around it. An Extended Service Area lies between the primary service area and a rectangle area enclosed by the 30th parallel south to the 50th parallel north and the 30th meridian east to the 130th meridian east, 1,500–6,000 km beyond borders. A goal of complete Indian control has been stated, with the space segment, ground segment and user receivers all being built in India.
The constellation was in orbit as of 2018, and the system was available for public use in early 2018. NavIC provides two levels of service, the "standard positioning service", which will be open for civilian use, and a "restricted service" (an encrypted one) for authorized users (including military). There are plans to expand NavIC system by increasing constellation size from 7 to 11.
QZSS
The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) is a four-satellite regional time transfer system and enhancement for GPS covering Japan and the Asia-Oceania regions. QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of January 12, 2018, and were started in November 2018. The first satellite was launched in September 2010. An independent satellite navigation system (from GPS) with 7 satellites is planned for 2023.
Comparison of systems
| System | BeiDou | Galileo | GLONASS | GPS | NavIC | QZSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | China | European Union | Russia | United States | India | Japan |
| Coverage | Global | Global | Global | Global | Regional | Regional |
| Coding | CDMA | CDMA | FDMA & CDMA | CDMA | CDMA | CDMA |
| Altitude | 21,150 km (13,140 mi) | 23,222 km (14,429 mi) | 19,130 km (11,890 mi) | 20,180 km (12,540 mi) | 36,000 km (22,000 mi) | 32,600 km (20,300 mi) – 39,000 km (24,000 mi) |
| Period | 12.63 h (12 h 38 min) | 14.08 h (14 h 5 min) | 11.26 h (11 h 16 min) | 11.97 h (11 h 58 min) | 23.93 h (23 h 56 min) | 23.93 h (23 h 56 min) |
| Rev./S. day | 17/9 (1.888...) | 17/10 (1.7) | 17/8 (2.125) | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Satellites | BeiDou-3: 28 operational (24 MEO, 3 IGSO, 1 GSO) 5 in orbit validation 2 GSO planned 20H1 BeiDou-2: 15 operational 1 in commissioning |
By design:
27 operational + 3 spares Currently: 26 in orbit 2 inactive |
24 by design 24 operational 1 commissioning 1 in flight tests |
24 by design 30 operational |
8 operational (3 GEO, 5 GSO MEO) |
4 operational (3 GSO, 1 GEO) 7 in the future |
| Frequency | 1.561098 GHz (B1) 1.589742 GHz (B1-2) 1.20714 GHz (B2) 1.26852 GHz (B3) |
1.559–1.592 GHz (E1)
1.164–1.215 GHz (E5a/b) |
1.593–1.610 GHz (G1) 1.237–1.254 GHz (G2) 1.189–1.214 GHz (G3) |
1.563–1.587 GHz (L1) 1.215–1.2396 GHz (L2) 1.164–1.189 GHz (L5) |
1.17645 GHz(L5) 2.492028 GHz (S) |
1.57542 GHz (L1C/A,L1C,L1S) 1.22760 GHz (L2C) 1.17645 GHz (L5,L5S) 1.27875 GHz (L6) |
| Status | Operational | Operating since 2016 2020 completion |
Operational | Operational | Operational | Operational |
| Accuracy | 3.6 m or 12 ft (public) 0.1 m or 3.9 in (encrypted) |
1 m or 3 ft 3 in (public) 0.01 m or 0.39 in (encrypted) |
2–4 m or 6 ft 7 in – 13 ft 1 in | 0.3–5 m or 1 ft 0 in – 16 ft 5 in (no DGPS or WAAS) | 1 m or 3 ft 3 in (public) 0.1 m or 3.9 in (encrypted) |
1 m or 3 ft 3 in (public) 0.1 m or 3.9 in (encrypted) |
| System | BeiDou | Galileo | GLONASS | GPS | NavIC | QZSS |
Using multiple GNSS systems for user positioning increases the number of visible satellites, improves precise point positioning (PPP) and shortens the average convergence time. The signal-in-space ranging error (SISRE) in November 2019 were 1.6 cm for Galileo, 2.3 cm for GPS, 5.2 cm for GLONASS and 5.5 cm for BeiDou when using real-time corrections for satellite orbits and clocks.
Augmentation
GNSS augmentation is a method of improving a navigation system's attributes, such as accuracy, reliability, and availability, through the integration of external information into the calculation process, for example, the Wide Area Augmentation System, the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service, the Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System, Differential GPS, GPS-aided GEO augmented navigation (GAGAN) and inertial navigation systems.
Related techniques
DORIS
Doppler Orbitography and Radio-positioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) is a French precision navigation system. Unlike other GNSS systems, it is based on static emitting stations around the world, the receivers being on satellites, in order to precisely determine their orbital position. The system may be used also for mobile receivers on land with more limited usage and coverage. Used with traditional GNSS systems, it pushes the accuracy of positions to centimetric precision (and to millimetric precision for altimetric application and also allows monitoring very tiny seasonal changes of Earth rotation and deformations), in order to build a much more precise geodesic reference system.
LEO satellites
The two current operational low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite phone networks are able to track transceiver units with accuracy of a few kilometres using doppler shift calculations from the satellite. The coordinates are sent back to the transceiver unit where they can be read using AT commands or a graphical user interface. This can also be used by the gateway to enforce restrictions on geographically bound calling plans.
International regulation
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) defines a radionavigation-satellite service (RNSS) as "a radiodetermination-satellite service used for the purpose of radionavigation. This service may also include feeder links necessary for its operation".
RNSS is regarded as a safety-of-life service and an essential part of navigation which must be protected from interferences.
Classification
ITU Radio Regulations (article 1) classifies radiocommunication services as:
- Radiodetermination service (article 1.40)
- Radiodetermination-satellite service (article 1.41)
- Radionavigation service (article 1.42)
- Radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.43)
- Maritime radionavigation service (article 1.44)
- Maritime radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.45)
- Aeronautical radionavigation service (article 1.46)
- Aeronautical radionavigation-satellite service (article 1.47)
- Examples of RNSS use
- Augmentation system GNSS augmentation
- Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast
- BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)
- GALILEO, European GNSS
- Global Positioning System (GPS), with Differential GPS (DGPS)
- GLONASS
- NAVIC
- Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
Frequency allocation
The allocation of radio frequencies is provided according to Article 5 of the ITU Radio Regulations (edition 2012).
To improve harmonisation in spectrum utilisation, most service allocations are incorporated in national Tables of Frequency Allocations and Utilisations within the responsibility of the appropriate national administration. Allocations are:
- primary: indicated by writing in capital letters
- secondary: indicated by small letters
- exclusive or shared utilization: within the responsibility of administrations.
| Allocation to services | ||
| Region 1 | Region 2 | Region 3 |
5 000–5 010 MHz
| ||