In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) establishes that, in many situations, when independent random variables are summed up, their properly normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution even if the original variables themselves are not normally distributed.
The theorem is a key concept in probability theory because it implies that probabilistic and statistical methods that work for normal distributions can be applicable to many problems involving other types of distributions.
This theorem has seen many changes during the formal development of probability theory. Previous versions of the theorem date back to 1811, but in its modern general form, this fundamental result in probability theory was precisely stated as late as 1920, thereby serving as a bridge between classical and modern probability theory.
If are random samples drawn from a population with overall mean and finite variance , and if is the sample mean of the first samples, then the limiting form of the distribution, , with , is a standard normal distribution.
For example, suppose that a sample is obtained containing many observations, each observation being randomly generated in a way that does not depend on the values of the other observations, and that the arithmetic mean of the observed values is computed. If this procedure is performed many times, the central limit theorem says that the probability distribution of the average will closely approximate a normal distribution. A simple example of this is that if one flips a coin many times, the probability of getting a given number of heads will approach a normal distribution, with the mean equal to half the total number of flips. At the limit of an infinite number of flips, it will equal a normal distribution.
The central limit theorem has several variants. In its common form, the random variables must be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). In variants, convergence of the mean to the normal distribution also occurs for non-identical distributions or for non-independent observations, if they comply with certain conditions.
The earliest version of this theorem, that the normal distribution may be used as an approximation to the binomial distribution, is the de Moivre–Laplace theorem.
Independent sequences
Classical CLT
Let be a sequence of random samples — that is, a sequence of i.i.d. random variables drawn from a distribution of expected value given by and finite variance given by . Suppose we are interested in the sample average
By the law of large numbers, the sample averages converge almost surely (and therefore also converge in probability) to the expected value as .
The classical central limit theorem describes the size and the distributional form of the stochastic fluctuations around the deterministic number during this convergence. More precisely, it states that as gets larger, the distribution of the difference between the sample average and its limit , when multiplied by the factor (that is ) approximates the normal distribution with mean 0 and variance . For large enough n, the distribution of is close to the normal distribution with mean and variance .
The usefulness of the theorem is that the distribution of approaches normality regardless of the shape of the distribution of the individual . Formally, the theorem can be stated as follows:
Lindeberg–Lévy CLT — Suppose is a sequence of i.i.d. random variables with and . Then as approaches infinity, the random variables converge in distribution to a normal :
In the case , convergence in distribution means that the cumulative distribution functions of converge pointwise to the cdf of the distribution: for every real number ,
Lyapunov CLT
The theorem is named after Russian mathematician Aleksandr Lyapunov. In this variant of the central limit theorem the random variables have to be independent, but not necessarily identically distributed. The theorem also requires that random variables have moments of some order , and that the rate of growth of these moments is limited by the Lyapunov condition given below.
Lyapunov CLT — Suppose is a sequence of independent random variables, each with finite expected value and variance . Define
If for some , Lyapunov’s condition
In practice it is usually easiest to check Lyapunov's condition for .
If a sequence of random variables satisfies Lyapunov's condition, then it also satisfies Lindeberg's condition. The converse implication, however, does not hold.
Lindeberg CLT
In the same setting and with the same notation as above, the Lyapunov condition can be replaced with the following weaker one (from Lindeberg in 1920).
Suppose that for every
Multidimensional CLT
Proofs that use characteristic functions can be extended to cases where each individual is a random vector in , with mean vector and covariance matrix (among the components of the vector), and these random vectors are independent and identically distributed. Summation of these vectors is being done component-wise. The multidimensional central limit theorem states that when scaled, sums converge to a multivariate normal distribution.
Let
The multivariate central limit theorem states that
The rate of convergence is given by the following Berry–Esseen type result:
Theorem — Let be independent -valued random vectors, each having mean zero. Write and assume is invertible. Let be a -dimensional Gaussian with the same mean and same covariance matrix as . Then for all convex sets ,
It is unknown whether the factor is necessary.
Generalized theorem
The central limit theorem states that the sum of a number of independent and identically distributed random variables with finite variances will tend to a normal distribution as the number of variables grows. A generalization due to Gnedenko and Kolmogorov states that the sum of a number of random variables with a power-law tail (Paretian tail) distributions decreasing as where (and therefore having infinite variance) will tend to a stable distribution as the number of summands grows. If then the sum converges to a stable distribution with stability parameter equal to 2, i.e. a Gaussian distribution.
Dependent processes
CLT under weak dependence
A useful generalization of a sequence of independent, identically distributed random variables is a mixing random process in discrete time; "mixing" means, roughly, that random variables temporally far apart from one another are nearly independent. Several kinds of mixing are used in ergodic theory and probability theory. See especially strong mixing (also called α-mixing) defined by where is so-called strong mixing coefficient.
A simplified formulation of the central limit theorem under strong mixing is:
Theorem — Suppose that is stationary and -mixing with and that and . Denote , then the limit
In fact,
The assumption cannot be omitted, since the asymptotic normality fails for where are another stationary sequence.
There is a stronger version of the theorem: the assumption is replaced with , and the assumption is replaced with
Existence of such ensures the conclusion. For encyclopedic treatment of limit theorems under mixing conditions see (Bradley 2007).
Martingale difference CLT
Theorem — Let a martingale satisfy
- in probability as n → ∞,
- for every ε > 0, as n → ∞,
then converges in distribution to as .
Remarks
Proof of classical CLT
The central limit theorem has a proof using characteristic functions. It is similar to the proof of the (weak) law of large numbers.
Assume are independent and identically distributed random variables, each with mean and finite variance . The sum has mean and variance . Consider the random variable
All of the higher order terms vanish in the limit . The right hand side equals the characteristic function of a standard normal distribution , which implies through Lévy's continuity theorem that the distribution of will approach as . Therefore, the sample average
Convergence to the limit
The central limit theorem gives only an asymptotic distribution. As an approximation for a finite number of observations, it provides a reasonable approximation only when close to the peak of the normal distribution; it requires a very large number of observations to stretch into the tails.
The convergence in the central limit theorem is uniform because the limiting cumulative distribution function is continuous. If the third central moment exists and is finite, then the speed of convergence is at least on the order of (see Berry–Esseen theorem). Stein's method can be used not only to prove the central limit theorem, but also to provide bounds on the rates of convergence for selected metrics.
The convergence to the normal distribution is monotonic, in the sense that the entropy of increases monotonically to that of the normal distribution.
The central limit theorem applies in particular to sums of independent and identically distributed discrete random variables. A sum of discrete random variables is still a discrete random variable, so that we are confronted with a sequence of discrete random variables whose cumulative probability distribution function converges towards a cumulative probability distribution function corresponding to a continuous variable (namely that of the normal distribution). This means that if we build a histogram of the realizations of the sum of n independent identical discrete variables, the curve that joins the centers of the upper faces of the rectangles forming the histogram converges toward a Gaussian curve as n approaches infinity, this relation is known as de Moivre–Laplace theorem. The binomial distribution article details such an application of the central limit theorem in the simple case of a discrete variable taking only two possible values.
Relation to the law of large numbers
The law of large numbers as well as the central limit theorem are partial solutions to a general problem: "What is the limiting behavior of Sn as n approaches infinity?" In mathematical analysis, asymptotic series are one of the most popular tools employed to approach such questions.
Suppose we have an asymptotic expansion of :
Dividing both parts by φ1(n) and taking the limit will produce a1, the coefficient of the highest-order term in the expansion, which represents the rate at which f(n) changes in its leading term.
Informally, one can say: "f(n) grows approximately as a1φ1(n)". Taking the difference between f(n) and its approximation and then dividing by the next term in the expansion, we arrive at a more refined statement about f(n):
Here one can say that the difference between the function and its approximation grows approximately as a2φ2(n). The idea is that dividing the function by appropriate normalizing functions, and looking at the limiting behavior of the result, can tell us much about the limiting behavior of the original function itself.
Informally, something along these lines happens when the sum, Sn, of independent identically distributed random variables, X1, ..., Xn, is studied in classical probability theory. If each Xi has finite mean μ, then by the law of large numbers, Sn/n → μ. If in addition each Xi has finite variance σ2, then by the central limit theorem,
In the case where the Xi do not have finite mean or variance, convergence of the shifted and rescaled sum can also occur with different centering and scaling factors:
Distributions Ξ which can arise in this way are called stable. Clearly, the normal distribution is stable, but there are also other stable distributions, such as the Cauchy distribution, for which the mean or variance are not defined. The scaling factor bn may be proportional to nc, for any c ≥ 1/2; it may also be multiplied by a slowly varying function of n.
The law of the iterated logarithm specifies what is happening "in between" the law of large numbers and the central limit theorem. Specifically it says that the normalizing function √n log log n, intermediate in size between n of the law of large numbers and √n of the central limit theorem, provides a non-trivial limiting behavior.
Alternative statements of the theorem
Density functions
The density of the sum of two or more independent variables is the convolution of their densities (if these densities exist). Thus the central limit theorem can be interpreted as a statement about the properties of density functions under convolution: the convolution of a number of density functions tends to the normal density as the number of density functions increases without bound. These theorems require stronger hypotheses than the forms of the central limit theorem given above. Theorems of this type are often called local limit theorems. See Petrov for a particular local limit theorem for sums of independent and identically distributed random variables.
Characteristic functions
Since the characteristic function of a convolution is the product of the characteristic functions of the densities involved, the central limit theorem has yet another restatement: the product of the characteristic functions of a number of density functions becomes close to the characteristic function of the normal density as the number of density functions increases without bound, under the conditions stated above. Specifically, an appropriate scaling factor needs to be applied to the argument of the characteristic function.
An equivalent statement can be made about Fourier transforms, since the characteristic function is essentially a Fourier transform.
Calculating the variance
Let Sn be the sum of n random variables. Many central limit theorems provide conditions such that Sn/√Var(Sn) converges in distribution to N(0,1) (the normal distribution with mean 0, variance 1) as n → ∞. In some cases, it is possible to find a constant σ2 and function f(n) such that Sn/(σ√n⋅f(n)) converges in distribution to N(0,1) as n→ ∞.
Lemma — Suppose is a sequence of real-valued and strictly stationary random variables with for all , , and . Construct
- If is absolutely convergent, , and then as where .
- If in addition and converges in distribution to as then also converges in distribution to as .
Extensions
Products of positive random variables
The logarithm of a product is simply the sum of the logarithms of the factors. Therefore, when the logarithm of a product of random variables that take only positive values approaches a normal distribution, the product itself approaches a log-normal distribution. Many physical quantities (especially mass or length, which are a matter of scale and cannot be negative) are the products of different random factors, so they follow a log-normal distribution. This multiplicative version of the central limit theorem is sometimes called Gibrat's law.
Whereas the central limit theorem for sums of random variables requires the condition of finite variance, the corresponding theorem for products requires the corresponding condition that the density function be square-integrable.
Beyond the classical framework
Asymptotic normality, that is, convergence to the normal distribution after appropriate shift and rescaling, is a phenomenon much more general than the classical framework treated above, namely, sums of independent random variables (or vectors). New frameworks are revealed from time to time; no single unifying framework is available for now.
Convex body
Theorem — There exists a sequence εn ↓ 0 for which the following holds. Let n ≥ 1, and let random variables X1, ..., Xn have a log-concave joint density f such that f(x1, ..., xn) = f(|x1|, ..., |xn|) for all x1, ..., xn, and E(X2
k) = 1 for all k = 1, ..., n. Then the distribution of
These two εn-close distributions have densities (in fact, log-concave densities), thus, the total variance distance between them is the integral of the absolute value of the difference between the densities. Convergence in total variation is stronger than weak convergence.
An important example of a log-concave density is a function constant inside a given convex body and vanishing outside; it corresponds to the uniform distribution on the convex body, which explains the term "central limit theorem for convex bodies".
Another example: f(x1, ..., xn) = const · exp(−(|x1|α + ⋯ + |xn|α)β) where α > 1 and αβ > 1. If β = 1 then f(x1, ..., xn) factorizes into const · exp (−|x1|α) … exp(−|xn|α), which means X1, ..., Xn are independent. In general, however, they are dependent.
The condition f(x1, ..., xn) = f(|x1|, ..., |xn|) ensures that X1, ..., Xn are of zero mean and uncorrelated; still, they need not be independent, nor even pairwise independent. By the way, pairwise independence cannot replace independence in the classical central limit theorem.
Here is a Berry–Esseen type result.
Theorem — Let X1, ..., Xn satisfy the assumptions of the previous theorem, then
1 + ⋯ + c2
n = 1,
The distribution of X1 + ⋯ + Xn/√n need not be approximately normal (in fact, it can be uniform). However, the distribution of c1X1 + ⋯ + cnXn is close to N(0,1) (in the total variation distance) for most vectors (c1, ..., cn) according to the uniform distribution on the sphere c2
1 + ⋯ + c2
n = 1.
Lacunary trigonometric series
Theorem (Salem–Zygmund) — Let U be a random variable distributed uniformly on (0,2π), and Xk = rk cos(nkU + ak), where
- nk satisfy the lacunarity condition: there exists q > 1 such that nk + 1 ≥ qnk for all k,
- rk are such that
- 0 ≤ ak < 2π.
Then
Gaussian polytopes
Theorem — Let A1, ..., An be independent random points on the plane R2 each having the two-dimensional standard normal distribution. Let Kn be the convex hull of these points, and Xn the area of Kn Then
The same also holds in all dimensions greater than 2.
The polytope Kn is called a Gaussian random polytope.
A similar result holds for the number of vertices (of the Gaussian polytope), the number of edges, and in fact, faces of all dimensions.
Linear functions of orthogonal matrices
A linear function of a matrix M is a linear combination of its elements (with given coefficients), M ↦ tr(AM) where A is the matrix of the coefficients; see Trace (linear algebra)#Inner product.
A random orthogonal matrix is said to be distributed uniformly, if its distribution is the normalized Haar measure on the orthogonal group O(n,R); see Rotation matrix#Uniform random rotation matrices.
Theorem — Let M be a random orthogonal n × n matrix distributed uniformly, and A a fixed n × n matrix such that tr(AA*) = n, and let X = tr(AM). Then the distribution of X is close to N(0,1) in the total variation metric up to 2√3/n − 1.
Subsequences
Theorem — Let random variables X1, X2, ... ∈ L2(Ω) be such that Xn → 0 weakly in L2(Ω) and X
n → 1 weakly in L1(Ω). Then there exist integers n1 < n2 < ⋯ such that
Random walk on a crystal lattice
The central limit theorem may be established for the simple random walk on a crystal lattice (an infinite-fold abelian covering graph over a finite graph), and is used for design of crystal structures.
Applications and examples
Simple example
A simple example of the central limit theorem is rolling many identical, unbiased dice. The distribution of the sum (or average) of the rolled numbers will be well approximated by a normal distribution. Since real-world quantities are often the balanced sum of many unobserved random events, the central limit theorem also provides a partial explanation for the prevalence of the normal probability distribution. It also justifies the approximation of large-sample statistics to the normal distribution in controlled experiments.
Real applications
Published literature contains a number of useful and interesting examples and applications relating to the central limit theorem. One source states the following examples:
- The probability distribution for total distance covered in a random walk (biased or unbiased) will tend toward a normal distribution.
- Flipping many coins will result in a normal distribution for the total number of heads (or equivalently total number of tails).
From another viewpoint, the central limit theorem explains the common appearance of the "bell curve" in density estimates applied to real world data. In cases like electronic noise, examination grades, and so on, we can often regard a single measured value as the weighted average of many small effects. Using generalisations of the central limit theorem, we can then see that this would often (though not always) produce a final distribution that is approximately normal.
In general, the more a measurement is like the sum of independent variables with equal influence on the result, the more normality it exhibits. This justifies the common use of this distribution to stand in for the effects of unobserved variables in models like the linear model.
Regression
Regression analysis and in particular ordinary least squares specifies that a dependent variable depends according to some function upon one or more independent variables, with an additive error term. Various types of statistical inference on the regression assume that the error term is normally distributed. This assumption can be justified by assuming that the error term is actually the sum of many independent error terms; even if the individual error terms are not normally distributed, by the central limit theorem their sum can be well approximated by a normal distribution.
Other illustrations
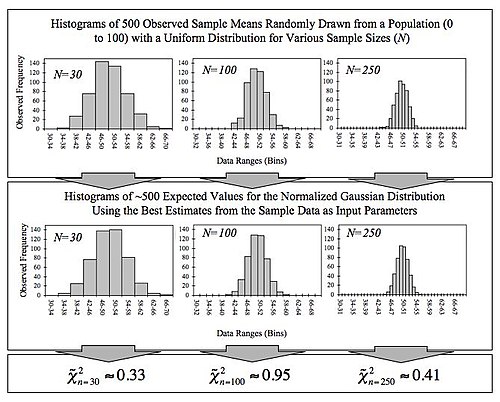
Given its importance to statistics, a number of papers and computer packages are available that demonstrate the convergence involved in the central limit theorem.
History
Dutch mathematician Henk Tijms writes:
The central limit theorem has an interesting history. The first version of this theorem was postulated by the French-born mathematician Abraham de Moivre who, in a remarkable article published in 1733, used the normal distribution to approximate the distribution of the number of heads resulting from many tosses of a fair coin. This finding was far ahead of its time, and was nearly forgotten until the famous French mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace rescued it from obscurity in his monumental work Théorie analytique des probabilités, which was published in 1812. Laplace expanded De Moivre's finding by approximating the binomial distribution with the normal distribution. But as with De Moivre, Laplace's finding received little attention in his own time. It was not until the nineteenth century was at an end that the importance of the central limit theorem was discerned, when, in 1901, Russian mathematician Aleksandr Lyapunov defined it in general terms and proved precisely how it worked mathematically. Nowadays, the central limit theorem is considered to be the unofficial sovereign of probability theory.
Sir Francis Galton described the Central Limit Theorem in this way:
I know of scarcely anything so apt to impress the imagination as the wonderful form of cosmic order expressed by the "Law of Frequency of Error". The law would have been personified by the Greeks and deified, if they had known of it. It reigns with serenity and in complete self-effacement, amidst the wildest confusion. The huger the mob, and the greater the apparent anarchy, the more perfect is its sway. It is the supreme law of Unreason. Whenever a large sample of chaotic elements are taken in hand and marshalled in the order of their magnitude, an unsuspected and most beautiful form of regularity proves to have been latent all along.
The actual term "central limit theorem" (in German: "zentraler Grenzwertsatz") was first used by George Pólya in 1920 in the title of a paper. Pólya referred to the theorem as "central" due to its importance in probability theory. According to Le Cam, the French school of probability interprets the word central in the sense that "it describes the behaviour of the centre of the distribution as opposed to its tails". The abstract of the paper On the central limit theorem of calculus of probability and the problem of moments by Pólya in 1920 translates as follows.
The occurrence of the Gaussian probability density 1 = e−x2 in repeated experiments, in errors of measurements, which result in the combination of very many and very small elementary errors, in diffusion processes etc., can be explained, as is well-known, by the very same limit theorem, which plays a central role in the calculus of probability. The actual discoverer of this limit theorem is to be named Laplace; it is likely that its rigorous proof was first given by Tschebyscheff and its sharpest formulation can be found, as far as I am aware of, in an article by Liapounoff. ...
A thorough account of the theorem's history, detailing Laplace's foundational work, as well as Cauchy's, Bessel's and Poisson's contributions, is provided by Hald. Two historical accounts, one covering the development from Laplace to Cauchy, the second the contributions by von Mises, Pólya, Lindeberg, Lévy, and Cramér during the 1920s, are given by Hans Fischer. Le Cam describes a period around 1935. Bernstein presents a historical discussion focusing on the work of Pafnuty Chebyshev and his students Andrey Markov and Aleksandr Lyapunov that led to the first proofs of the CLT in a general setting.
A curious footnote to the history of the Central Limit Theorem is that a proof of a result similar to the 1922 Lindeberg CLT was the subject of Alan Turing's 1934 Fellowship Dissertation for King's College at the University of Cambridge. Only after submitting the work did Turing learn it had already been proved. Consequently, Turing's dissertation was not published.
















![{\textstyle \mathbb {E} [X_{i}]=\mu }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/72ca6904a07544cb510973b19c644024f7e15a4a)
![{\textstyle \operatorname {Var} [X_{i}]=\sigma ^{2}<\infty }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/448bb57a7caae2db8c4c5bf94d9672bfe71fb9b2)




![{\displaystyle \lim _{n\to \infty }\mathbb {P} \left[{\sqrt {n}}({\bar {X}}_{n}-\mu )\leq z\right]=\lim _{n\to \infty }\mathbb {P} \left[{\frac {{\sqrt {n}}({\bar {X}}_{n}-\mu )}{\sigma }}\leq {\frac {z}{\sigma }}\right]=\Phi \left({\frac {z}{\sigma }}\right),}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/defd4cf70972fa6a76a8570fee6551f4cb7d70b8)

![{\displaystyle \lim _{n\to \infty }\;\sup _{z\in \mathbb {R} }\;\left|\mathbb {P} \left[{\sqrt {n}}({\bar {X}}_{n}-\mu )\leq z\right]-\Phi \left({\frac {z}{\sigma }}\right)\right|=0~,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/835addcb3ec37594d1e9a6a78c0373a5e7b2eddc)







![{\displaystyle \lim _{n\to \infty }\;{\frac {1}{s_{n}^{2+\delta }}}\,\sum _{i=1}^{n}\mathbb {E} \left[\left|X_{i}-\mu _{i}\right|^{2+\delta }\right]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/94a9702c705f509d1e7c582a0e9fcf5415d667aa)




![{\displaystyle \lim _{n\to \infty }{\frac {1}{s_{n}^{2}}}\sum _{i=1}^{n}\mathbb {E} \left[(X_{i}-\mu _{i})^{2}\cdot \mathbf {1} _{\left\{X_{i}:\left|X_{i}-\mu _{i}\right|>\varepsilon s_{n}\right\}}\right]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/919a24fda71d1e6997e391b8445e633e0a756beb)





![{\textstyle {\boldsymbol {\mu }}=\mathbb {E} [\mathbf {X} _{i}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6244dc64b15d110166d68121979554959b73c907)


![{\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}X_{1(1)}\\\vdots \\X_{1(k)}\end{bmatrix}}+{\begin{bmatrix}X_{2(1)}\\\vdots \\X_{2(k)}\end{bmatrix}}+\cdots +{\begin{bmatrix}X_{n(1)}\\\vdots \\X_{n(k)}\end{bmatrix}}={\begin{bmatrix}\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[X_{i(1)}\right]\\\vdots \\\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[X_{i(k)}\right]\end{bmatrix}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\mathbf {X} _{i}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e0aec2e3895f5d517973d01b48f22a9ae94296cc)

![{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[\mathbf {X} _{i}-\mathbb {E} \left(X_{i}\right)\right]={\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}\sum _{i=1}^{n}(\mathbf {X} _{i}-{\boldsymbol {\mu }})={\sqrt {n}}\left({\overline {\mathbf {X} }}_{n}-{\boldsymbol {\mu }}\right)~.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/04cd4a073edaf3e3a0ddb8fdabe603e016be039f)






![{\displaystyle \Sigma =\operatorname {Cov} [S]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6bbdd46ff8928b02fc4e37a7fc14c51ceaf58b40)




![{\displaystyle \left|\mathbb {P} [S\in U]-\mathbb {P} [Z\in U]\right|\leq C\,d^{1/4}\gamma ~,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6c26c26cb1dedbb0db401fd2ebfb479ec45fb4cc)

![{\displaystyle \gamma =\sum _{i=1}^{n}\mathbb {E} \left[\left\|\Sigma ^{-1/2}X_{i}\right\|_{2}^{3}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/84812af63e8f6578d530dae6334daab92c838f1e)










![{\textstyle \mathbb {E} [X_{n}]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9fcb1c7905f404857da94b55b6d27ffdbe4403ee)
![{\textstyle \mathbb {E} [{X_{n}}^{12}]<\infty }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3ea8d68104e3816de7e359cbe19e43710e219dba)







![{\textstyle \mathbb {E} \left[{X_{n}}^{12}\right]<\infty }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/18140252ec815b42ffbbb84d0044c7b27303a7db)
![{\textstyle \mathbb {E} \left[{\left|X_{n}\right|}^{2+\delta }\right]<\infty }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b0965a2a802164542e33ad8198ac0a65006fe419)


![{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{n}}\sum _{k=1}^{n}\mathbb {E} \left[\left(M_{k}-M_{k-1}\right)^{2}|M_{1},\dots ,M_{k-1}\right]\to 1}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7a14df227d6a9d49d219a7468a62dadb55efb136)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{n}}\sum _{k=1}^{n}{\mathbb {E} \left[\left(M_{k}-M_{k-1}\right)^{2}\mathbf {1} \left[|M_{k}-M_{k-1}|>\varepsilon {\sqrt {n}}\right]\right]}\to 0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1d1472d6d4a4f31b01758cdb2bf14d6c34c72110)









![{\displaystyle \varphi _{Z_{n}}\!(t)=\varphi _{\sum _{i=1}^{n}{{\frac {1}{\sqrt {n}}}Y_{i}}}\!(t)\ =\ \varphi _{Y_{1}}\!\!\left({\frac {t}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)\varphi _{Y_{2}}\!\!\left({\frac {t}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)\cdots \varphi _{Y_{n}}\!\!\left({\frac {t}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)\ =\ \left[\varphi _{Y_{1}}\!\!\left({\frac {t}{\sqrt {n}}}\right)\right]^{n},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/412edc029b680d1254078fd2c5727db6cf30ea76)











![{\textstyle \operatorname {E} \left[(X_{1}-\mu )^{3}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/389b355cd56db15cdf7e88c8b0aff830a381726f)












![{\displaystyle g:[0,1]\to \mathbb {R} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/26aef45c20ce13e8d53e79e068df9b5804c5c170)