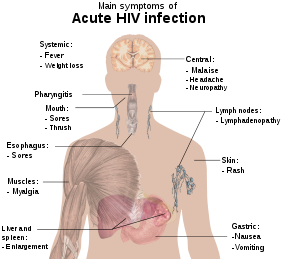
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body.
Signs and symptoms
Signs
A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernails or toenails, an abnormal gait, and a limbal ring a darkened ring around the iris of the eye.
Indications
A sign is different from an "indication" – the activity of a condition 'pointing to' (thus "indicating") a remedy, not the reverse (viz., it is not a remedy 'pointing to' a condition) – which is a specific reason for using a particular treatment.
Symptoms
A symptom is something felt or experienced, such as pain or dizziness. Signs and symptoms are not mutually exclusive, for example a subjective feeling of fever can be noted as sign by using a thermometer that registers a high reading. The CDC lists various diseases by their signs and symptoms such as for measles which includes a high fever, conjunctivitis, and cough, followed a few days later by the measles rash.
Cardinal signs and symptoms
Cardinal signs and symptoms are specific even to the point of being pathognomonic. A cardinal sign or cardinal symptom can also refer to the major sign or symptom of a disease. Abnormal reflexes can indicate problems with the nervous system. Signs and symptoms are also applied to physiological states outside the context of disease, as for example when referring to the signs and symptoms of pregnancy, or the symptoms of dehydration. Sometimes a disease may be present without showing any signs or symptoms when it is known as being asymptomatic. The disorder may be discovered through tests including scans. An infection may be asymptomatic which may still be transmissible.
Syndrome
Signs and symptoms are often non-specific, but some combinations can be suggestive of certain diagnoses, helping to narrow down what may be wrong. A particular set of characteristic signs and symptoms that may be associated with a disorder is known as a syndrome. In cases where the underlying cause is known the syndrome is named as for example Down syndrome and Noonan syndrome. Other syndromes such as acute coronary syndrome may have a number of possible causes.
Terms
When a disease is evidenced by symptoms it is known as symptomatic. There are many conditions including subclinical infections that display no symptoms, and these are termed asymptomatic. Signs and symptoms may be mild or severe, brief or longer-lasting when they may become reduced (remission), or then recur (relapse or recrudescence) known as a flare-up. A flare-up may show more severe symptoms.
The term chief complaint, also "presenting problem", is used to describe the initial concern of an individual when seeking medical help, and once this is clearly noted a history of the present illness may be taken. The symptom that ultimately leads to a diagnosis is called a cardinal symptom. Some symptoms can be misleading as a result of referred pain, where for example a pain in the right shoulder may be due to an inflamed gallbladder and not to presumed muscle strain.
Prodrome
Many diseases have an early prodromal stage where a few signs and symptoms may suggest the presence of a disorder before further specific symptoms may emerge. Measles for example has a prodromal presentation that includes a hacking cough, fever, and Koplik's spots in the mouth. Over half of migraine episodes have a prodromal phase. Schizophrenia has a notable prodromal stage, as has dementia.
Nonspecific symptoms
Some symptoms are specific, that is, they are associated with a single, specific medical condition.
Nonspecific symptoms, sometimes also called equivocal symptoms, are not specific to a particular condition. They include unexplained weight loss, headache, pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, night sweats, and malaise. A group of three particular nonspecific symptoms – fever, night sweats, and weight loss – over a period of six months are termed B symptoms associated with lymphoma and indicate a poor prognosis.
Other sub-types of symptoms include:
- constitutional or general symptoms, which affect general well-being or the whole body, such as a fever;
- concomitant symptoms, which are symptoms that occur at the same time as the primary symptom;
- prodromal symptoms, which are the first symptoms of an bigger set of problems;
- delayed symptoms, which happen some time after the trigger; and
- objective symptoms, which are symptoms whose existence can be observed and confirmed by a healthcare provider.
Vital signs
Vital signs are the four signs that can give an immediate measurement of the body's overall functioning and health status. They are temperature, heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure. The ranges of these measurements vary with age, weight, gender and with general health.
A digital application has been developed for use in clinical settings that measures three of the vital signs (not temperature) using just a smartphone, and has been approved by NHS England. The application is registered as Lifelight First, and Lifelight Home is under development (2020) for monitoring-use by people at home using just the camera on their smartphone or tablet. This will additionally measure oxygen saturation and atrial fibrillation. Other devices are then not needed.
Syndromes
Many conditions are indicated by a group of known signs, or signs and symptoms. These can be a group of three known as a triad: a group of four known as a tetrad, and a group of five known as a petrad. An example of a triad is Meltzer's triad presenting purpura a rash, arthralgia painful joints, and myalgia painful and weak muscles. Meltzer's triad indicates the condition cryoglobulinemia. Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by a triad of motor, cognitive, and psychiatric signs and symptoms. A large number of these groups that can be characteristic of a particular disease are known as a syndrome. Noonan syndrome for example, has a diagnostic set of unique facial and musculoskeletal features. Some syndromes such as nephrotic syndrome may have a number of underlying causes that are all related to diseases that affect the kidneys.
Sometimes a child or young adult may have symptoms suggestive of a genetic disorder that cannot be identified even after genetic testing. In such cases the term SWAN (syndrome without a name) may be used. Often a diagnosis may be made at some future point when other more specific symptoms emerge but many cases may remain undiagnosed. The inability to diagnose may be due to a unique combination of symptoms or an overlap of conditions, or to the symptoms being atypical of a known disorder, or to the disorder being extremely rare.
Positive and negative
Sensory symptoms can also be described as positive symptoms, or as negative symptoms depending on whether the symptom is abnormally present such as tingling or itchiness, or abnormally absent such as loss of smell. The following terms are used for negative symptoms – hypoesthesia is a partial loss of sensitivity to moderate stimuli, such as pressure, touch, warmth, cold. Anesthesia is the complete loss of sensitivity to stronger stimuli, such as pinprick. Hypoalgesia (analgesia) is loss of sensation to painful stimuli.
Symptoms are also grouped in to negative and positive for some mental disorders such as schizophrenia.
Positive symptoms are those that are present in the disorder and are not normally experienced by most individuals and reflects an excess or distortion of normal functions. Examples are hallucinations, delusions, and bizarre behavior.
Negative symptoms are functions that are normally found but that are diminished or absent; for example, the negative symptoms of schizophrenia include apathy and anhedonia.
Dynamic and static
Dynamic symptoms are capable of change depending on circumstance, whereas static symptoms are fixed or unchanging regardless of circumstance. For example, the symptoms of exercise intolerance are dynamic as they are brought on by exercise, but alleviate during rest. Fixed muscle weakness is a static symptom as the muscle will be weak regardless of exercise or rest.
A majority of patients with metabolic myopathies have dynamic rather than static findings, typically experiencing exercise intolerance, muscle pain, and cramps with exercise rather than fixed weakness. Those with the metabolic myopathy of McArdle's disease (GSD-V) and some individuals with phosphoglucomutase deficiency (CDG1T/GSD-XIV), initially experience exercise intolerance during mild-moderate aerobic exercise, but the symptoms alleviate after 6–10 minutes in what is known as "second wind".
Neuropsychiatric
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are present in many degenerative disorders including dementia, and Parkinson's disease. Symptoms commonly include apathy, anxiety, and depression. Neurological and psychiatric symptoms are also present in some genetic disorders such as Wilson's disease. Symptoms of executive dysfunction are often found in many disorders including schizophrenia, and ADHD.
Radiologic
Radiologic signs are abnormal medical findings on imaging scanning. These include the Mickey Mouse sign and the Golden S sign. When using imaging to find the cause of a complaint, another unrelated finding may be found known as an incidental finding.
Cardinal
Cardinal signs and symptoms are those that may be diagnostic, and pathognomonic – of a certainty of diagnosis. Inflammation for example has a recognised group of cardinal signs and symptoms, as does exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, and Parkinson's disease.
In contrast to a pathognomonic cardinal sign, the absence of a sign or symptom can often rule out a condition. This is known by the Latin term sine qua non. For example, the absence of known genetic mutations specific for a hereditary disease would rule out that disease. Another example is where the vaginal pH is less than 4.5, a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis would be excluded.
Reflexes
A reflex is an automatic response in the body to a stimulus. Its absence, reduced (hypoactive), or exaggerated (hyperactive) response can be a sign of damage to the central nervous system or peripheral nervous system. In the patellar reflex (knee-jerk) for example, its reduction or absence is known as Westphal's sign and may indicate damage to lower motor neurons. When the response is exaggerated damage to the upper motor neurons may be indicated.
Facies
A number of medical conditions are associated with a distinctive facial expression or appearance known as a facies An example is elfin facies which has facial features like those of the elf, and this may be associated with Williams syndrome, or Donohue syndrome. The most well-known facies is probably the Hippocratic facies that is seen on a person as they near death.
Anamnestic signs
Anamnestic signs (from anamnēstikós, ἀναμνηστικός, "able to recall to mind") are signs that indicate a past condition, for example paralysis in an arm may indicate a past stroke.
Asymptomatic
Some diseases including cancers, and infections may be present but show no signs or symptoms and these are known as asymptomatic. A gallstone may be asymptomatic and only discovered as an incidental finding. Easily spreadable viral infections such as COVID-19 may be asymptomatic but may still be transmissible.
History
Symptomatology
A symptom (from Greek σύμπτωμα, "accident, misfortune, that which befalls", from συμπίπτω, "I befall", from συν- "together, with" and πίπτω, "I fall") is a departure from normal function or feeling. Symptomatology (also called semiology) is a branch of medicine dealing with the signs and symptoms of a disease. This study also includes the indications of a disease. It was first described as semiotics by Henry Stubbe in 1670 a term now used for the study of sign communication.
Prior to the nineteenth century there was little difference in the powers of observation between physician and patient. Most medical practice was conducted as a co-operative interaction between the physician and patient; this was gradually replaced by a "monolithic consensus of opinion imposed from within the community of medical investigators". Whilst each noticed much the same things, the physician had a more informed interpretation of those things: "the physicians knew what the findings meant and the layman did not".
Development of medical testing

A number of advances introduced mostly in the 19th century, allowed for more objective assessment by the physician in search of a diagnosis, and less need of input from the patient. During the 20th century the introduction of a wide range of imaging techniques and other testing methods such as genetic testing, clinical chemistry tests, molecular diagnostics and pathogenomics have made a huge impact on diagnostic capability.
- In 1761 the percussion technique for diagnosing respiratory conditions was discovered by Leopold Auenbrugger. This method of tapping body cavities to note any abnormal sounds had already been in practice for a long time in cardiology. Percussion of the thorax became more widely known after 1808 with the translation of Auenbrugger's work from Latin into French by Jean-Nicolas Corvisart.
- In 1819 the introduction of the stethoscope by René Laennec began to replace the centuries-old technique of immediate auscultation – listening to the heart by placing the ear directly on the chest, with mediate auscultation using the stethoscope to listen to the sounds of the heart and respiratory tract. Laennec's publication was translated into English, 1824, by John Forbes.
- The 1846 introduction by surgeon John Hutchinson (1811–1861) of the spirometer, an apparatus for assessing the mechanical properties of the lungs via measurements of forced exhalation and forced inhalation. (The recorded lung volumes and air flow rates are used to distinguish between restrictive disease (in which the lung volumes are decreased: e.g., cystic fibrosis) and obstructive diseases (in which the lung volume is normal but the air flow rate is impeded; e.g., emphysema).)
- The 1851 invention by Hermann von Helmholtz (1821–1894) of the ophthalmoscope, which allowed physicians to examine the inside of the human eye.
- The (c. 1870) immediate widespread clinical use of Sir Thomas Clifford Allbutt's (1836–1925) six-inch (rather than twelve-inch) pocket clinical thermometer, which he had devised in 1867.
- The 1882 introduction of bacterial cultures by Robert Koch, initially for tuberculosis, being the first laboratory test to confirm bacterial infections.
- The 1895 clinical use of X-rays which began almost immediately after they had been discovered that year by Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (1845–1923).
- The 1896 introduction of the sphygmomanometer, designed by Scipione Riva-Rocci (1863–1937), to measure blood pressure.
Diagnosis
The recognition of signs, and noting of symptoms may lead to a diagnosis. Otherwise a physical examination may be carried out, and a medical history taken. Further diagnostic medical tests such as blood tests, scans, and biopsies, may be needed. An X-ray for example would soon be diagnostic of a suspected bone fracture. A noted significance detected during an examination or from a medical test may be known as a medical finding.
Examples
- Ascites
- Nail clubbing (deformed nails)
- Cough
- Death rattle (last moments of life)
- Hemoptysis (blood-stained sputum)
- Jaundice
- Organomegaly an enlarged organ such as the liver (hepatomegaly)
- Palmar erythema (reddening of hands)
- Hypersalivation excessive (saliva)
- Unintentional weight loss
