
The climate of Antarctica is the coldest on Earth. The continent is also extremely dry (it is a desert), averaging 166 mm (6.5 in) of precipitation per year. Snow rarely melts on most parts of the continent, and, after being compressed, becomes the glacier ice that makes up the ice sheet. Weather fronts rarely penetrate far into the continent, because of the katabatic winds. Most of Antarctica has an ice-cap climate (Köppen classification EF) with extremely cold and dry weather.
Temperature
The highest temperature ever recorded on Antarctica was 19.8 °C (67.6 °F) recorded at Signy Research Station, Signy Island on 30 January 1982.
The highest temperature on the Antarctic mainland was 18.3 °C (64.9 °F) at the Esperanza Base (Argentina) on 6 February 2020.

The lowest air temperature record, the lowest reliably measured temperature on Antarctica was set on 21 July 1983, when a temperature of −89.2 °C (−128.6 °F) was observed at Vostok Station. For comparison, this is 10.7 °C (19.3 °F) colder than subliming dry ice (at sea level pressure). The elevation of the location is 3,488 meters (11,444 feet).
Satellite measurements have identified even lower ground temperatures, with −93.2 °C (−135.8 °F) having been observed at the cloud-free East Antarctic Plateau on 10 August 2010.
The lowest recorded temperature of any location on Earth's surface at 81.8°S 63.5°E was revised with new data in 2018 in nearly 100 locations, ranging from −93.2 °C (−135.8 °F)[7] to −98 °C (−144.4 °F). This unnamed part of the Antarctic plateau, between Dome A and Dome F, was measured on 10 August 2010, and the temperature was deduced from radiance measured by the Landsat 8 and other satellites. It was discovered during a National Snow and Ice Data Center review of stored data in December 2013 but revised by researchers on 25 June 2018. This temperature is not directly comparable to the –89.2 °C reading quoted above, since it is a skin temperature deduced from satellite-measured upwelling radiance, rather than a thermometer-measured temperature of the air 1.5 m (5 ft) above the ground surface.
The mean annual temperature of the interior is −43.5 °C (−46.3 °F). The coast is warmer; on the coast Antarctic average temperatures are around −10 °C (14.0 °F) (in the warmest parts of Antarctica) and in the elevated inland they average about −55 °C (−67.0 °F) in Vostok. Monthly means at McMurdo Station range from −26 °C (−14.8 °F) in August to −3 °C (26.6 °F) in January. At the South Pole, the highest temperature ever recorded was −12.3 °C (9.9 °F) on 25 December 2011. Along the Antarctic Peninsula, temperatures as high as 18.3 °C (64.9 °F) have been recorded, though the summer temperature is below 0 °C (32 °F) most of the time. Severe low temperatures vary with latitude, elevation, and distance from the ocean. East Antarctica is colder than West Antarctica because of its higher elevation. The Antarctic Peninsula has the most moderate climate. Higher temperatures occur in January along the coast and average slightly below freezing.
Precipitation
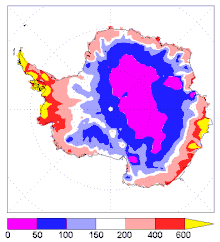
The total precipitation on Antarctica, averaged over the entire continent, is about 166 millimetres (6.5 inches) per year (Vaughan et al., J. Clim., 1999). The actual rates vary widely, from high values over the Peninsula (380 to 640 millimetres (15 to 25 inches) a year) to very low values (as little as 50 millimetres (2.0 inches) in the high interior (Bromwich, Reviews of Geophysics, 1988). Areas that receive less than 250 millimetres (9.8 inches) of precipitation per year are classified as deserts. Almost all Antarctic precipitation falls as snow. Rainfall is rare and mainly occurs during the summer in coastal areas and surrounding islands. Note that the quoted precipitation is a measure of its equivalence to water, rather than being the actual depth of snow. The air in Antarctica is also very dry. The low temperatures result in a very low absolute humidity, which means that dry skin and cracked lips are a continual problem for scientists and expeditioners working on the continent.
Weather condition classification
The weather in Antarctica can be highly variable, and the weather conditions can often change dramatically in short periods of time. There are various classifications for describing weather conditions in Antarctica; restrictions given to workers during the different conditions vary by station and nation.
Ice cover
Nearly all of Antarctica is covered by a sheet of ice that is, on average, at least 1,500 m (5,000 ft) thick. Antarctica contains 90% of the world's ice and more than 70% of its fresh water. If all the land-ice covering Antarctica were to melt — around 30×106 km3 (7.2×106 cu mi) of ice — the seas would rise by over 60 m (200 ft). The Antarctic is so cold that even with increases of a few degrees, temperatures would generally remain below the melting point of ice. Higher temperatures are expected to lead to more precipitation, which takes the form of snow. This would increase the amount of ice in Antarctica, offsetting approximately one third of the expected sea level rise from thermal expansion of the oceans. During a recent decade, East Antarctica thickened at an average rate of about 1.8 cm (11⁄16 in) per year while West Antarctica showed an overall thinning of 0.9 cm (3⁄8 in) per year. For the contribution of Antarctica to present and future sea level change, see sea level rise. Because ice flows, albeit slowly, the ice within the ice sheet is younger than the age of the sheet itself.
| Surface | Area | Mean ice thickness (m) |
Volume | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (km2) | Percent | (km3) | Percent | ||
| Inland ice sheet | 11,965,700 | 85.97 | 2,450 | 29,324,700 | 97.00 |
| Ice shelves | 1,541,710 | 11.08 | 475 | 731,900 | 2.43 |
| Ice rises | 78,970 | 0.57 | 670 | 53,100 | 0.18 |
| Glacier ice (total) | 13,586,380 | 2,160 | 30,109,800 |
| |
| Rock outcrop | 331,690 | 2.38 |
|
|
|
| Antarctica (total) | 13,918,070 | 100.00 | 2,160 | 30,109,800 | 100.00 |
| Region | Area (km2) |
Mean ice thickness (m) |
Volume (km3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| East Antarctica | |||
| Inland ice | 9,855,570 | 2,630 | 25,920,100 |
| Ice shelves | 293,510 | 400 | 117,400 |
| Ice rises | 4,090 | 400 | 1,600 |
| West Antarctica (excluding Antarctic Peninsula) | |||
| Inland ice sheet | 1,809,760 | 1,780 | 3,221,400 |
| Ice shelves | 104,860 | 375 | 39,300 |
| Ice rises | 3,550 | 375 | 1,300 |
| Antarctic Peninsula | |||
| Inland ice sheet | 300,380 | 610 | 183,200 |
| Ice shelves | 144,750 | 300 | 43,400 |
| Ice rises | 1,570 | 300 | 500 |
| Ross Ice Shelf | |||
| Ice shelf | 525,840 | 427 | 224,500 |
| Ice rises | 10,320 | 500 | 5,100 |
| Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf | |||
| Ice shelf | 472,760 | 650 | 307,300 |
| Ice rises | 59,440 | 750 | 44,600 |
Ice shelves

About 75% of the coastline of Antarctica is ice shelf. The majority of ice shelf consists of floating ice, and a lesser amount consists of glaciers that move slowly from the land mass into the sea. Ice shelves lose mass through breakup of glacial ice (calving), or basal melting due to warm ocean water under the ice.
Melting or breakup of floating shelf ice does not directly affect global sea levels; however, ice shelves have a buttressing effect on the ice flow behind them. If ice shelves break up, the ice flow behind them may accelerate, resulting in increasing melt of the Antarctic ice sheet and an increasing contribution to sea level rise.
Known changes in coastline ice around the Antarctic Peninsula:
- 1936–1989: Wordie Ice Shelf significantly reduced in size.
- 1995: Ice in the Prince Gustav Channel disintegrated.
- Parts of the Larsen Ice Shelf broke up in recent decades.
- 1995: The Larsen A ice shelf disintegrated in January 1995.
- 2001: 3,250 km2 (1,250 sq mi) of the Larsen B ice shelf disintegrated in February 2001. It had been gradually retreating before the breakup event.
- 2015: A study concluded that the remaining Larsen B ice-shelf will disintegrate by the end of the decade, based on observations of faster flow and rapid thinning of glaciers in the area.
The George VI Ice Shelf, which may be on the brink of instability, has probably existed for approximately 8,000 years, after melting 1,500 years earlier. Warm ocean currents may have been the cause of the melting. Not only are the ice sheets losing mass, they are losing mass at an accelerating rate.
Climate change
Climate change caused by greenhouse gas emissions from human activities occurs everywhere on Earth, and while Antarctica is less vulnerable to it than any other continent, climate change in Antarctica has been observed. Since 1959, there has been an average temperature increase of >0.05 °C/decade since 1957 across the continent, although it had been uneven. West Antarctica warmed by over 0.1 °C/decade from the 1950s to the 2000s, and the exposed Antarctic Peninsula has warmed by 3 °C (5.4 °F) since the mid-20th century. The colder, stabler East Antarctica had been experiencing cooling until the 2000s. Around Antarctica, the Southern Ocean has absorbed more oceanic heat than any other ocean, and has seen strong warming at depths below 2,000 m (6,600 ft). Around the West Antarctic, the ocean has warmed by 1 °C (1.8 °F) since 1955.
The warming of the Southern Ocean around Antarctica has caused the weakening or collapse of ice shelves, which float just offshore of glaciers and stabilize them. Many coastal glaciers have been losing mass and retreating, causing net-annual ice loss across Antarctica, although the East Antarctic ice sheet continues to gain ice inland. By 2100, net ice loss from Antarctica is expected to add about 11 cm (5 in) to global sea level rise. Marine ice sheet instability may cause West Antarctica to contribute tens of centimeters more if it is triggered before 2100. With higher warming, instability would be much more likely, and could double global, 21st-century sea-level rise.