From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Parsec | |
|---|---|

A parsec is the distance from the Sun to an astronomical object that has a parallax angle of one arcsecond. (the diagram is not to scale).
|
|
| Unit information | |
| Unit system | astronomical units |
| Unit of | length |
| Symbol | pc |
| Unit conversions | |
| 1 pc in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| metric (SI) units | 3.0857×1016 m |
| imperial & US units | 1.9174×1013 mi |
| astronomical units | 2.0626×105 au 3.26156 ly |
A parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the astronomically large distances to objects outside the Solar System. One parsec is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one arcsecond.[1] About 3.26 light-years (31 trillion kilometres or 19 trillion miles) in length, the parsec is shorter than the distance from our solar system to the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, which is 1.3 parsecs from the Sun.[2] Nevertheless, most of the stars visible to the unaided eye in the nighttime sky are within 500 parsecs of the Sun.
The parsec unit was likely first suggested in 1913 by British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner.[3] Named from an abbreviation of the parallax of one arcsecond, it was defined so as to make calculations of astronomical distances quick and easy for astronomers from only their raw observational data. Partly for this reason, it is still the unit preferred in astronomy and astrophysics, though the light year remains prominent in popular science texts and more everyday usage. Although parsecs are used for the shorter distances within the Milky Way, multiples of parsecs are required for the larger scales in the universe, including kiloparsecs for the more distant objects within and around the Milky Way, megaparsecs for the nearer of other galaxies, and gigaparsecs for many quasars and the most distant galaxies.
History and derivation
The parsec is defined as being equal to the length of the longer leg of an extremely elongated imaginary right triangle in space. The two dimensions on which this triangle is based are its shorter leg, of length one astronomical unit (the average Earth-Sun distance), and the subtended angle of the vertex opposite that leg, measuring one arcsecond. Applying the rules of trigonometry to these two values, the unit length of the other leg of the triangle (the parsec) can be derived.One of the oldest methods for astronomers to calculate the distance to a star was to record the difference in angle between two measurements of the position of the star in the sky. The first measurement was taken from the Earth on one side of the Sun, and the second was taken half a year later when the Earth was on the opposite side of the Sun. The distance between the two positions of the Earth when the two measurements were taken was known to be twice the distance between the Earth and the Sun. The difference in angle between the two measurements was known to be twice the parallax angle, which is formed by lines from the Sun and Earth to the star at the distant vertex. Then the distance to the star could be calculated using trigonometry.[4] The first successful published direct measurements of an object at interstellar distances were undertaken by German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel in 1838, who used this approach to calculate the three and a half parsec distance of 61 Cygni.[5]
The parallax of a star is taken to be half of the angular distance that a star appears to move relative to the celestial sphere as Earth orbits the Sun. Equivalently, it is the subtended angle, from that star's perspective, of the semi-major axis of Earth's orbit. The star, the Sun and the Earth form the corners of an imaginary right triangle in space: the right angle is the corner at the Sun, and the corner at the star is the parallax angle. The length of the opposite side to the parallax angle is the distance from the Earth to the Sun (defined as one astronomical unit (au), and the length of the adjacent side gives the distance from the sun to the star. Therefore, given a measurement of the parallax angle, along with the rules of trigonometry, the distance from the Sun to the star can be found. A parsec is defined as the length of the side adjacent to the vertex occupied by a star whose parallax angle is one arcsecond.
The use of the parsec as a unit of distance follows naturally from Bessel's method, because the distance in parsecs can be computed simply as the reciprocal of the parallax angle in arcseconds (i. e., if the parallax angle is 1 arcsecond, the object is 1 pc from the Sun; If the parallax angle is 0.5 arcsecond, the object is 2 pc away; etc.). No trigonometric functions are required in this relationship because the very small angles involved mean that the approximate solution of the skinny triangle can be applied.
Though it may have been used before, the term parsec was first mentioned in an astronomical publication in 1913. Astronomer Royal Frank Watson Dyson expressed his concern for the need of a name for that unit of distance. He proposed the name astron, but mentioned that Carl Charlier had suggested siriometer and Herbert Hall Turner had proposed parsec.[6] It was Turner's proposal that stuck.
Calculating the value of a parsec
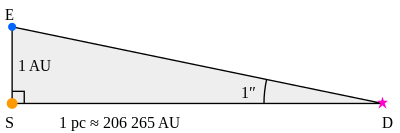
In the diagram above (not to scale), S represents the Sun, and E the Earth at one point in its orbit. Thus the distance ES is one astronomical unit (AU). The angle SDE is one arcsecond (1⁄3600 of a degree) so by definition D is a point in space at a distance of one parsec from the Sun. By trigonometry, the distance SD is
SD=EStan1′′
SD≈ES1′′=1AU(160×60×π180)=648000πAU≈206264.81 AU.
| 1 parsec | ≈ 206264.81 astronomical units |
| ≈ 3.0856776×1016 metres | |
| ≈ 19.173512 trillion miles | |
| ≈ 3.2615638 light years |
A corollary is that 1 parsec is also the distance from which a disc with a diameter of 1 AU must be viewed for it to have an angular diameter of 1 arcsecond (by placing the observer at D and a diameter of the disc on ES).
Usage and measurement
The parallax method is the fundamental calibration step for distance determination in astrophysics; however, the accuracy of ground-based telescope measurements of parallax angle is limited to about 0.01 arcsecond, and thus to stars no more than 100 pc distant.[8] This is because the Earth’s atmosphere limits the sharpness of a star's image.[9] Space-based telescopes are not limited by this effect and can accurately measure distances to objects beyond the limit of ground-based observations. Between 1989 and 1993, the Hipparcos satellite, launched by the European Space Agency (ESA), measured parallaxes for about 100000 stars with an astrometric precision of about 0.97 milliarcsecond, and obtained accurate measurements for stellar distances of stars up to 1000 pc away.[10][11]ESA's Gaia satellite, which launched on 19 December 2013, is intended to measure one billion stellar distances to within 20 microarcseconds, producing errors of 10% in measurements as far as the Galactic Centre, about 8000 pc away in the constellation of Sagittarius.[12]
Distances in parsecs
Distances less than a parsec
Distances expressed in fractions of a parsec usually involve objects within a single star system. So, for example:- One astronomical unit (au), the distance from the Sun to the Earth, is just under 5×10−6 parsecs.
- The most distant space probe, Voyager 1, was 0.0006 parsecs from Earth as of May 2013[update]. It took Voyager 35 years to cover that distance.
- The Oort cloud is estimated to be approximately 0.6 parsecs in diameter

The jet erupting from the active galactic nucleus of M87 is thought to be 1.5 kiloparsecs (4890 ly) long. (image from Hubble Space Telescope)
Parsecs and kiloparsecs
Distances expressed in parsecs (pc) include distances between nearby stars, such as those in the same spiral arm or globular cluster. A distance of 1000 parsecs (3262 light-years) is commonly denoted by the kiloparsec (kpc). Astronomers typically use kiloparsecs to express distances between parts of a galaxy, or within groups of galaxies. So, for example:- One parsec is approximately 3.26 light-years.
- The nearest known star to the Earth, other than the Sun, Proxima Centauri, is about 1.30 parsecs (4.24 light-years) away, by direct parallax measurement.
- The distance to the open cluster Pleiades is 130 ± 10 pc (420 ± 32.6 light-years) from us, per Hipparcos parallax measurement.
- The centre of the Milky Way is more than 8 kiloparsecs (26000 ly) from the Earth, and the Milky Way is roughly 34 kpc (110000 ly) across.
- The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) is ~780 kpc (~2.5 million light-years) away from the Earth.
Megaparsecs and gigaparsecs
A distance of one million parsecs is commonly denoted by the megaparsec (Mpc). Astronomers typically express the distances between neighbouring galaxies and galaxy clusters in megaparsecs.Galactic distances are sometimes given in units of Mpc/h (as in "50/h Mpc"). h is a parameter in the range [0.5,0.75] reflecting the uncertainty in the value of the Hubble constant H for the rate of expansion of the universe: h = H / (100 km/s/Mpc). The Hubble constant becomes relevant when converting an observed redshift z into a distance d using the formula d ≈ (c / H) × z.[13]
One gigaparsec (Gpc) is one billion parsecs — one of the largest units of length commonly used. One gigaparsec is about 3.26 billion light-years (3.26 "Gly"), or roughly one fourteenth of the distance to the horizon of the observable universe (dictated by the cosmic background radiation). Astronomers typically use gigaparsecs to express the sizes of large-scale structures such as the size of, and distance to, the CfA2 Great Wall; the distances between galaxy clusters; and the distance to quasars.
For example:
- The Andromeda Galaxy is about 0.78 Mpc (2.5 million light-years) from the Earth.
- The nearest large galaxy cluster, the Virgo Cluster, is about 16.5 Mpc (54 million light-years) from the Earth.[14]
- The galaxy RXJ1242-11, observed to have a supermassive black hole core similar to the Milky Way's, is about 200 Mpc (650 million light-years) from the Earth.
- The galaxy filament Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, currently the largest known structure in the universe, is about 3 Gpc (10 billion light-years) across.
- The particle horizon (the boundary of the observable universe) has a radius of about 14.0 Gpc (46 billion light-years).[15]
Volume units
To determine the number of stars in the Milky Way, volumes in cubic kiloparsecs[a] (kpc3) are selected in various directions. All the stars in these volumes are counted and the total number of stars statistically determined. The number of globular clusters, dust clouds, and interstellar gas is determined in a similar fashion. To determine the number of galaxies in superclusters, volumes in cubic megaparsecs[a] (Mpc3) are selected. All the galaxies in these volumes are classified and tallied.The total number of galaxies can then be determined statistically. The huge void in Boötes[16] is measured in cubic megaparsecs.
In cosmology, volumes of cubic gigaparsecs[a] (Gpc3) are selected to determine the distribution of matter in the visible universe and to determine the number of galaxies and quasars. The Sun is alone in its cubic parsec,[a] (pc3) but in globular clusters the stellar density per cubic parsec could be from 100 to 1000.

