From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In physics and other sciences, a nonlinear system, in contrast to a linear system, is a system which does not satisfy the superposition principle – meaning that the output of a nonlinear system is not directly proportional to the input.In mathematics, a nonlinear system of equations is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the unknown variables or functions that appear in it (them). It does not matter if nonlinear known functions appear in the equations. In particular, a differential equation is linear if it is linear in terms of the unknown function and its derivatives, even if nonlinear in terms of the other variables appearing in it.
Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described by a nonlinear system of equations.
Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, physicists and mathematicians and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. As nonlinear equations are difficult to solve, nonlinear systems are commonly approximated by linear equations (linearization). This works well up to some accuracy and some range for the input values, but some interesting phenomena such as chaos[1] and singularities are hidden by linearization. It follows that some aspects of the behavior of a nonlinear system appear commonly to be chaotic, unpredictable or counterintuitive. Although such chaotic behavior may resemble random behavior, it is absolutely not random.
For example, some aspects of the weather are seen to be chaotic, where simple changes in one part of the system produce complex effects throughout. This nonlinearity is one of the reasons why accurate long-term forecasts are impossible with current technology.
 is one which satisfies both of the following properties:
is one which satisfies both of the following properties:
 is a linear map (as defined above) and nonlinear otherwise. The equation is called homogeneous if
is a linear map (as defined above) and nonlinear otherwise. The equation is called homogeneous if  .
.
The definition is very general in that
is very general in that 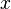 can be any sensible mathematical object (number, vector, function, etc.), and the function
can be any sensible mathematical object (number, vector, function, etc.), and the function  can literally be any mapping, including integration or differentiation with associated constraints (such as boundary values). If
can literally be any mapping, including integration or differentiation with associated constraints (such as boundary values). If  contains differentiation with respect to
contains differentiation with respect to 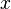 , the result will be a differential equation.
, the result will be a differential equation.
One of the greatest difficulties of nonlinear problems is that it is not generally possible to combine known solutions into new solutions. In linear problems, for example, a family of linearly independent solutions can be used to construct general solutions through the superposition principle. A good example of this is one-dimensional heat transport with Dirichlet boundary conditions, the solution of which can be written as a time-dependent linear combination of sinusoids of differing frequencies; this makes solutions very flexible. It is often possible to find several very specific solutions to nonlinear equations, however the lack of a superposition principle prevents the construction of new solutions.
 as a general solution (and also u = 0 as a particular solution, corresponding to the limit of the general solution when C tends to the infinity). The equation is nonlinear because it may be written as
as a general solution (and also u = 0 as a particular solution, corresponding to the limit of the general solution when C tends to the infinity). The equation is nonlinear because it may be written as
Second and higher order ordinary differential equations (more generally, systems of nonlinear equations) rarely yield closed form solutions, though implicit solutions and solutions involving nonelementary integrals are encountered.
Common methods for the qualitative analysis of nonlinear ordinary differential equations include:
Another common (though less mathematic) tactic, often seen in fluid and heat mechanics, is to use scale analysis to simplify a general, natural equation in a certain specific boundary value problem. For example, the (very) nonlinear Navier-Stokes equations can be simplified into one linear partial differential equation in the case of transient, laminar, one dimensional flow in a circular pipe; the scale analysis provides conditions under which the flow is laminar and one dimensional and also yields the simplified equation.
Other methods include examining the characteristics and using the methods outlined above for ordinary differential equations.
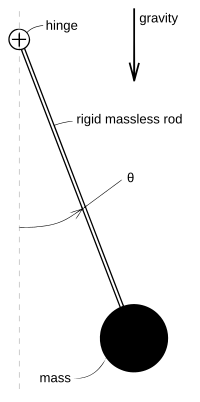
A classic, extensively studied nonlinear problem is the dynamics of a pendulum under influence of gravity. Using Lagrangian mechanics, it may be shown[4] that the motion of a pendulum can be described by the dimensionless nonlinear equation
 is the angle the pendulum forms with its rest position, as shown in the figure at right. One approach to "solving" this equation is to use
is the angle the pendulum forms with its rest position, as shown in the figure at right. One approach to "solving" this equation is to use 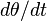 as an integrating factor, which would eventually yield
as an integrating factor, which would eventually yield
 ).
).
Another way to approach the problem is to linearize any nonlinearities (the sine function term in this case) at the various points of interest through Taylor expansions. For example, the linearization at , called the small angle approximation, is
, called the small angle approximation, is
 for
for 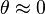 . This is a simple harmonic oscillator corresponding to oscillations of the pendulum near the bottom of its path. Another linearization would be at
. This is a simple harmonic oscillator corresponding to oscillations of the pendulum near the bottom of its path. Another linearization would be at  , corresponding to the pendulum being straight up:
, corresponding to the pendulum being straight up:
 for
for  . The solution to this problem involves hyperbolic sinusoids, and note that unlike the small angle approximation, this approximation is unstable, meaning that
. The solution to this problem involves hyperbolic sinusoids, and note that unlike the small angle approximation, this approximation is unstable, meaning that  will usually grow without limit, though bounded solutions are possible. This corresponds to the difficulty of balancing a pendulum upright, it is literally an unstable state.
will usually grow without limit, though bounded solutions are possible. This corresponds to the difficulty of balancing a pendulum upright, it is literally an unstable state.
One more interesting linearization is possible around , around which
, around which  :
:
See also the list of nonlinear partial differential equations
Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described by a nonlinear system of equations.
Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, physicists and mathematicians and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. As nonlinear equations are difficult to solve, nonlinear systems are commonly approximated by linear equations (linearization). This works well up to some accuracy and some range for the input values, but some interesting phenomena such as chaos[1] and singularities are hidden by linearization. It follows that some aspects of the behavior of a nonlinear system appear commonly to be chaotic, unpredictable or counterintuitive. Although such chaotic behavior may resemble random behavior, it is absolutely not random.
For example, some aspects of the weather are seen to be chaotic, where simple changes in one part of the system produce complex effects throughout. This nonlinearity is one of the reasons why accurate long-term forecasts are impossible with current technology.
Definition
In mathematics, a linear function (or map) is one which satisfies both of the following properties:
is one which satisfies both of the following properties:- additivity (Superposition),

- homogeneity,

 is a linear map (as defined above) and nonlinear otherwise. The equation is called homogeneous if
is a linear map (as defined above) and nonlinear otherwise. The equation is called homogeneous if  .
.The definition
 is very general in that
is very general in that 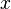 can be any sensible mathematical object (number, vector, function, etc.), and the function
can be any sensible mathematical object (number, vector, function, etc.), and the function  can literally be any mapping, including integration or differentiation with associated constraints (such as boundary values). If
can literally be any mapping, including integration or differentiation with associated constraints (such as boundary values). If  contains differentiation with respect to
contains differentiation with respect to 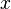 , the result will be a differential equation.
, the result will be a differential equation.Nonlinear algebraic equations
Nonlinear algebraic equations, which are also called polynomial equations, are defined by equating polynomials to zero. For example,Nonlinear recurrence relations
A nonlinear recurrence relation defines successive terms of a sequence as a nonlinear function of preceding terms. Examples of nonlinear recurrence relations are the logistic map and the relations that define the various Hofstadter sequences. Nonlinear discrete models that represent a wide class of nonlinear recurrence relationships include the NARMAX (Nonlinear Autoregressive Moving Average with eXogenous inputs) model and the related nonlinear system identification and analysis procedures.[3] These approaches can be used to study a wide class of complex nonlinear behaviors in the time, frequency, and spatio-temporal domains.Nonlinear differential equations
A system of differential equations is said to be nonlinear if it is not a linear system. Problems involving nonlinear differential equations are extremely diverse, and methods of solution or analysis are problem dependent. Examples of nonlinear differential equations are the Navier–Stokes equations in fluid dynamics and the Lotka–Volterra equations in biology.One of the greatest difficulties of nonlinear problems is that it is not generally possible to combine known solutions into new solutions. In linear problems, for example, a family of linearly independent solutions can be used to construct general solutions through the superposition principle. A good example of this is one-dimensional heat transport with Dirichlet boundary conditions, the solution of which can be written as a time-dependent linear combination of sinusoids of differing frequencies; this makes solutions very flexible. It is often possible to find several very specific solutions to nonlinear equations, however the lack of a superposition principle prevents the construction of new solutions.
Ordinary differential equations
First order ordinary differential equations are often exactly solvable by separation of variables, especially for autonomous equations. For example, the nonlinear equation as a general solution (and also u = 0 as a particular solution, corresponding to the limit of the general solution when C tends to the infinity). The equation is nonlinear because it may be written as
as a general solution (and also u = 0 as a particular solution, corresponding to the limit of the general solution when C tends to the infinity). The equation is nonlinear because it may be written asSecond and higher order ordinary differential equations (more generally, systems of nonlinear equations) rarely yield closed form solutions, though implicit solutions and solutions involving nonelementary integrals are encountered.
Common methods for the qualitative analysis of nonlinear ordinary differential equations include:
- Examination of any conserved quantities, especially in Hamiltonian systems.
- Examination of dissipative quantities (see Lyapunov function) analogous to conserved quantities.
- Linearization via Taylor expansion.
- Change of variables into something easier to study.
- Bifurcation theory.
- Perturbation methods (can be applied to algebraic equations too).
Partial differential equations
The most common basic approach to studying nonlinear partial differential equations is to change the variables (or otherwise transform the problem) so that the resulting problem is simpler (possibly even linear). Sometimes, the equation may be transformed into one or more ordinary differential equations, as seen in separation of variables, which is always useful whether or not the resulting ordinary differential equation(s) is solvable.Another common (though less mathematic) tactic, often seen in fluid and heat mechanics, is to use scale analysis to simplify a general, natural equation in a certain specific boundary value problem. For example, the (very) nonlinear Navier-Stokes equations can be simplified into one linear partial differential equation in the case of transient, laminar, one dimensional flow in a circular pipe; the scale analysis provides conditions under which the flow is laminar and one dimensional and also yields the simplified equation.
Other methods include examining the characteristics and using the methods outlined above for ordinary differential equations.
Pendula
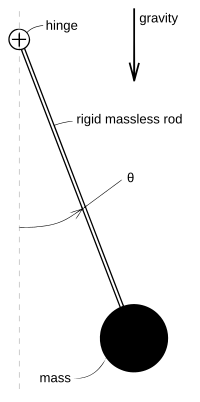
A classic, extensively studied nonlinear problem is the dynamics of a pendulum under influence of gravity. Using Lagrangian mechanics, it may be shown[4] that the motion of a pendulum can be described by the dimensionless nonlinear equation
 is the angle the pendulum forms with its rest position, as shown in the figure at right. One approach to "solving" this equation is to use
is the angle the pendulum forms with its rest position, as shown in the figure at right. One approach to "solving" this equation is to use 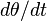 as an integrating factor, which would eventually yield
as an integrating factor, which would eventually yield ).
).Another way to approach the problem is to linearize any nonlinearities (the sine function term in this case) at the various points of interest through Taylor expansions. For example, the linearization at
 , called the small angle approximation, is
, called the small angle approximation, is for
for 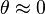 . This is a simple harmonic oscillator corresponding to oscillations of the pendulum near the bottom of its path. Another linearization would be at
. This is a simple harmonic oscillator corresponding to oscillations of the pendulum near the bottom of its path. Another linearization would be at  , corresponding to the pendulum being straight up:
, corresponding to the pendulum being straight up: for
for  . The solution to this problem involves hyperbolic sinusoids, and note that unlike the small angle approximation, this approximation is unstable, meaning that
. The solution to this problem involves hyperbolic sinusoids, and note that unlike the small angle approximation, this approximation is unstable, meaning that  will usually grow without limit, though bounded solutions are possible. This corresponds to the difficulty of balancing a pendulum upright, it is literally an unstable state.
will usually grow without limit, though bounded solutions are possible. This corresponds to the difficulty of balancing a pendulum upright, it is literally an unstable state.One more interesting linearization is possible around
 , around which
, around which  :
:Types of nonlinear behaviors
- Classical chaos – the behavior of a system cannot be predicted.
- Multistability – alternating between two or more exclusive states.
- Aperiodic oscillations – functions that do not repeat values after some period (otherwise known as chaotic oscillations or chaos).
- Amplitude death – any oscillations present in the system cease due to some kind of interaction with other system or feedback by the same system.
- Solitons – self-reinforcing solitary waves
Examples of nonlinear equations
- AC power flow model
- Algebraic Riccati equation
- Ball and beam system
- Bellman equation for optimal policy
- Boltzmann transport equation
- Colebrook equation
- General relativity
- Ginzburg–Landau equation
- Navier–Stokes equations of fluid dynamics
- Korteweg–de Vries equation
- Nonlinear optics
- Nonlinear Schrödinger equation
- Richards equation for unsaturated water flow
- Robot unicycle balancing
- Sine–Gordon equation
- Landau–Lifshitz equation
- Ishimori equation
- Van der Pol equation
- Liénard equation
- Vlasov equation
Software for solving nonlinear systems
- interalg – A solver from OpenOpt / FuncDesigner frameworks for searching either any or all solutions of nonlinear algebraic equations system
- A collection of non-linear models and demo applets (in Monash University's Virtual Lab)
- FyDiK – Software for simulations of nonlinear dynamical systems













