Potential graphene applications include lightweight, thin, flexible, yet incredibly lightweight to, electric/photonics circuits, solar cells, and various medical, chemical and industrial processes enhanced or enabled by the use of new graphene materials.
In 2008, graphene produced by exfoliation was one of the most expensive materials on Earth, with a sample the area of a cross section of a human hair costing more than $1,000 as of April 2008 (about $100,000,000/cm2).[2] Since then, exfoliation procedures have been scaled up, and now companies sell graphene in large quantities.[3] The price of epitaxial graphene on silicon carbide is dominated by the substrate price, which was approximately $100/cm2 as of 2009. Hong and his team in South Korea pioneered the synthesis of large-scale graphene films using chemical vapour deposition (CVD) on thin nickel layers, which triggered research on practical applications,[4] with wafer sizes up to 30 inches (760 mm) reported.[5] By 2017, graphene electronics were being manufactured in a commercial fab on a 200 mm line.[6]
In 2013, the European Union made a €1 billion grant to be used for research into potential graphene applications.[7] In 2013 the Graphene Flagship consortium formed, including Chalmers University of Technology and seven other European universities and research centers, along with Nokia.[8]
Medicine
Researchers in 2011 discovered the ability of graphene to accelerate the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells without the use of biochemical inducers.[9]In 2015 researchers used graphene to create biosensors with epitaxial graphene on silicon carbide. The sensors bind to 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) and is capable of selective binding with antibodies. The presence of 8-OHdG in blood, urine and saliva is commonly associated with DNA damage. Elevated levels of 8-OHdG have been linked to increased risk of several cancers.[10] By the next year, a commercial version of a graphene biosensor was being used by biology researchers as a protein binding sensor platform.[11]
In 2016 researchers revealed that uncoated graphene can be used as neuro-interface electrode without altering or damaging properties such as signal strength or formation of scar tissue. Graphene electrodes in the body stay significantly more stable than electrodes of tungsten or silicon because of properties such as flexibility, bio-compatibility and conductivity.[12]
Tissue engineering
Graphene has been investigated for tissue engineering. It has been used as a reinforcing agent to improve the mechanical properties of biodegradable polymeric nanocomposites for engineering bone tissue applications.[13] Dispersion of low weight % of graphene (≈0.02 wt.%) increased in compressive and flexural mechanical properties of polymeric nanocomposites [14]. The addition of graphene nanoparticles in the polymer matrix lead to improvements in the crosslinking density of the nanocomposite and better load transfer from the polymer matrix to the underlying nanomaterial thereby increasing the mechanical properties.Contrast agents, bioimaging
Functionalized and surfactant dispersed graphene solutions have been designed as blood pool MRI contrast agents.[15] Further, iodine and manganese incorporating graphene nanoparticles have served as multimodal MRI-computerized tomograph (CT) contrast agents.[16] Graphene micro- and nano-particles have served as contrast agents for photoacoustic and thermoacoustic tomography.[17] Graphene has also been reported to be efficiently taking up cancerous cells thereby enabling the design of drug delivery agents for cancer therapy.[18] Graphene nanoparticles of various morphologies such as graphene nanoribbons, graphene nanoplatelets and graphene nanoonions are non-toxic at low concentrations and do not alter stem cell differentiation suggesting that they may be safe to use for biomedical applications.[19]Polymerase chain reaction
Graphene is reported to have enhanced PCR by increasing the yield of DNA product.[20] Experiments revealed that graphene's thermal conductivity could be the main factor behind this result. Graphene yields DNA product equivalent to positive control with up to 65% reduction in PCR cycles.Devices
Graphene's modifiable chemistry, large surface area, atomic thickness and molecularly gatable structure make antibody-functionalized graphene sheets excellent candidates for mammalian and microbial detection and diagnosis devices.[21] Graphene is so thin water has near-perfect wetting transparency which is an important property particularly in developing bio-sensor applications.[22] This means that a sensors coated in graphene have as much contact with an aqueous system as an uncoated sensor, while it remains protected mechanically from its environment.
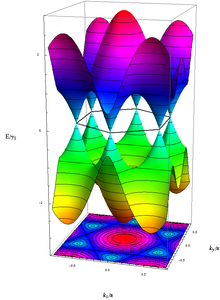
Energy of the electrons with wavenumber k in graphene, calculated in the Tight Binding-approximation. The unoccupied (occupied) states, colored in blue–red (yellow–green), touch each other without energy gap exactly at the above-mentioned six k-vectors.
Integration of graphene (thickness of 0.34 nm) layers as nanoelectrodes into a nanopore[23] can potentially solve a bottleneck for nanopore-based single-molecule DNA sequencing.
On November 20, 2013 the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation awarded $100,000 'to develop new elastic composite materials for condoms containing nanomaterials like graphene'.[24]
In 2014, graphene-based, transparent (across infrared to ultraviolet frequencies), flexible, implantable medical sensor microarrays were announced that allow the viewing of brain tissue hidden by implants. Optical transparency was >90%. Applications demonstrated include optogenetic activation of focal cortical areas, in vivo imaging of cortical vasculature via fluorescence microscopy and 3D optical coherence tomography.[25][26]
Drug delivery
- Researchers in Monash University discovered that the sheet of graphene oxide can be transformed into liquid crystal droplets spontaneously – like a polymer - simply by placing the material in a solution and manipulating the pH. The graphene droplets change their structure at the presence of an external magnetic field. This finding opens the door for potential use of carrying drug in the graphene droplets and drug release upon reaching the targeted tissue when the droplets change shape under the magnetic field. Another possible application is in disease detection if graphene is found to change shape at the presence of certain disease markers such as toxins.[27][28]
- A graphene ‘flying carpet’ was demonstrated to deliver two anti-cancer drugs sequentially to the lung tumor cells (A549 cell) in a mouse model. Doxorubicin (DOX) is embedded onto the graphene sheet, while the molecules of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) are linked to the nanostructure via short peptide chains. Injected intravenously, the graphene strips with the drug playload preferentially concentrate to the cancer cells due to common blood vessel leakage around the tumor. Receptors on the cancer cell membrane bind TRAIL and cell surface enzymes clip the peptide thus release the drug onto the cell surface. Without the bulky TRAIL, the graphene strips with the embedded DOX are swallowed into the cells. The intracellular acidic environment promotes DOX’s release from graphene. TRAIL on the cell surface triggers the apoptosis while DOX attacks the nucleus. These two drugs work synergistically and were found to be more effective than either drug alone.[29][30]
Biomicrorobotics
Researchers demonstrated a nanoscale biomicrorobot (or cytobot) made by cladding a living endospore cell with graphene quantum dots. The device acted as a humidity sensor.[31]Testing
In 2014 a graphene based blood glucose testing product was announced.[32][33]Toxicity
The toxicity of graphene has been extensively debated in the literature. The most comprehensive review on graphene toxicity published by Lalwani et al., exclusively summarizes the in vitro, in vivo, antimicrobial, environmental and highlights the various mechanisms of graphene toxicity.[34] Results show that the toxicity of graphene is dependent on several factors such as shape, size, purity, post-production processing steps, oxidative state, functional groups, dispersion state, synthesis methods, route and dose of administration, and exposure times.Electronics
Graphene has a high carrier mobility, and low noise, allowing it to be used as the channel in a field-effect transistor.[35] Unmodified graphene does not have an energy band gap, making it unsuitable for digital electronics. However, modifications have created potential uses in various areas of electronics.Transistors
Graphene exhibits a pronounced response to perpendicular external electric fields, potentially forming field-effect transistors (FET). A 2004 paper documented FETs with an on-off ratio of ≈30 at room temperature.[citation needed] A 2006 paper announced an all-graphene planar FET with side gates.[36] Their devices showed changes of 2% at cryogenic temperatures. The first top-gated FET (on–off ratio of <2 2007.="" class="reference" demonstrated="" id="cite_ref-37" in="" sup="" was="">[37]Graphene nanoribbons may prove generally capable of replacing silicon as a semiconductor.[38]
US patent 7015142 for graphene-based electronics was issued in 2006. In 2008, researchers at MIT Lincoln Lab produced hundreds of transistors on a single chip[39] and in 2009, very high frequency transistors were produced at Hughes Research Laboratories.[40]
A 2008 paper demonstrated a switching effect based on a reversible chemical modification of the graphene layer that gives an on–off ratio of greater than six orders of magnitude. These reversible switches could potentially be employed in nonvolatile memories.[41] In 2008, the smallest transistor so far, one atom thick, 10 atoms wide was made of graphene.[42] IBM announced in December 2008 that they had fabricated and characterized graphene transistors operating at GHz frequencies.[43]
In 2009, researchers demonstrated four different types of logic gates, each composed of a single graphene transistor.[44] In May 2009, an n-type transistor was announced meaning that both n and p-type graphene transistors had been created.[45][46] A functional graphene integrated circuit was demonstrated – a complementary inverter consisting of one p- and one n-type graphene transistor.[47] However, this inverter suffered from a very low voltage gain.Typically, the amplitude of the output signal is about 40 times less than that of the input signal. Moreover, none of these circuits operated at frequencies higher than 25 kHz.
In the same year, tight-binding numerical simulations[48] demonstrated that the band-gap induced in graphene bilayer field effect transistors is not sufficiently large for high-performance transistors for digital applications, but can be sufficient for ultra-low voltage applications, when exploiting a tunnel-FET architecture.[49]
In February 2010, researchers announced transistors with an on-off rate of 100 gigahertz, far exceeding the rates of prior attempts, and exceeding the speed of silicon transistors with an equal gate length. The 240 nm devices were made with conventional silicon-manufacturing equipment.[50][51][52] According to a January 2010 report,[53] graphene was epitaxially grown on SiC in a quantity and with quality suitable for mass production of integrated circuits. At high temperatures, the quantum Hall effect could be measured in these samples. IBM built 'processors' using 100 GHz transistors on 2-inch (51 mm) graphene sheets.[54]
In June 2011, IBM researchers announced that they had succeeded in creating the first graphene-based integrated circuit, a broadband radio mixer.[55] The circuit handled frequencies up to 10 GHz. Its performance was unaffected by temperatures up to 127 °C. In November researchers used 3d printing (additive manufacturing) as a method for fabricating graphene devices.[56]
In 2013, researchers demonstrated graphene's high mobility in a detector that allows broad band frequency selectivity ranging from the THz to IR region (0.76–33 THz)[57] A separate group created a terahertz-speed transistor with bistable characteristics, which means that the device can spontaneously switch between two electronic states. The device consists of two layers of graphene separated by an insulating layer of boron nitride a few atomic layers thick. Electrons move through this barrier by quantum tunneling. These new transistors exhibit negative differential conductance, whereby the same electric current flows at two different applied voltages.[58] In June, an 8 transistor 1.28 GHz ring oscillator circuit was described.[59]
The negative differential resistance experimentally observed in graphene field-effect transistors of conventional design allows for construction of viable non-Boolean computational architectures with graphene. The negative differential resistance — observed under certain biasing schemes — is an intrinsic property of graphene resulting from its symmetric band structure. The results present a conceptual change in graphene research and indicate an alternative route for graphene's applications in information processing.[60]
In 2013 researchers created transistors printed on flexible plastic that operate at 25 gigahertz, sufficient for communications circuits and that can be fabricated at scale. The researchers first fabricated non-graphene-containing structures—the electrodes and gates—on plastic sheets. Separately, they grew large graphene sheets on metal, then peeled it and edtransfer it to the plastic. Finally, they topped the sheet with a waterproof layer. The devices work after being soaked in water, and are flexible enough to be folded.[61]
In 2015 researchers devised a digital switch by perforating a graphene sheet with boron-nitride nanotubes that exhibited a switching ratio of 105 at a turn-on voltage of 0.5 V. Density functional theory suggested that the behavior came from the mismatch of the density of states.[62]
Trilayer
An electric field can change trilayer graphene's crystal structure, transforming its behavior from metal-like into semiconductor-like. A sharp metal scanning tunneling microscopy tip was able to move the domain border between the upper and lower graphene configurations. One side of the material behaves as a metal, while the other side behaves as a semiconductor. Trilayer graphene can be stacked in either Bernal or rhombohedral configurations, which can exist in a single flake. The two domains are separated by a precise boundary at which the middle layer is strained to accommodate the transition from one stacking pattern to the other.[63]Silicon transistors function as either p-type or n-type semiconductors, whereas graphene could operate as both. This lowers costs and is more versatile. The technique provides the basis for a field-effect transistor. Scalable manufacturing techniques have yet to be developed.[63]
In trilayer graphene, the two stacking configurations exhibit very different electronic properties. The region between them consists of a localized strain soliton where the carbon atoms of one graphene layer shift by the carbon–carbon bond distance. The free-energy difference between the two stacking configurations scales quadratically with electric field, favoring rhombohedral stacking as the electric field increases.[63]
This ability to control the stacking order opens the way to new devices that combine structural and electrical properties.[63][64]
Graphene-based transistors could be much thinner than modern silicon devices, allowing faster and smaller configurations.[65]
Transparent conducting electrodes
Graphene's high electrical conductivity and high optical transparency make it a candidate for transparent conducting electrodes, required for such applications as touchscreens, liquid crystal displays, inorganic photovoltaics cells,[66][67] organic photovoltaic cells, and organic light-emitting diodes. In particular, graphene's mechanical strength and flexibility are advantageous compared to indium tin oxide, which is brittle. Graphene films may be deposited from solution over large areas.Large-area, continuous, transparent and highly conducting few-layered graphene films were produced by chemical vapor deposition and used as anodes for application in photovoltaic devices. A power conversion efficiency (PCE) up to 1.71% was demonstrated, which is 55.2% of the PCE of a control device based on indium tin oxide.[70]
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) with graphene anodes have been demonstrated. The device was formed by solution-processed graphene on a quartz substrate. The electronic and optical performance of graphene-based devices are similar to devices made with indium tin oxide.[71] In 2017 OLED electrodes were produced by CVD on a copper substrate.[72]
A carbon-based device called a light-emitting electrochemical cell (LEC) was demonstrated with chemically-derived graphene as the cathode and the conductive polymer Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) as the anode.[73] Unlike its predecessors, this device contains only carbon-based electrodes, with no metal.
In 2014 a prototype graphene-based flexible display was demonstrated.[74]
In 2016 researchers demonstrated a display that used interferometry modulation to control colors, dubbed a "graphene balloon device" made of silicon containing 10 μm circular cavities covered by two graphene sheets. The degree of curvature of the sheets above each cavity defines the color emitted. The device exploits the phenomena known as Newton's rings created by interference between light waves bouncing off the bottom of the cavity and the (transparent) material. Increasing the distance between the silicon and the membrane increased the wavelength of the light. The approach is used in colored e-reader displays and smartwatches, such as the Qualcomm Toq. They use silicon materials instead of graphene. Graphene reduces power requirements.[75]
Frequency multiplier
In 2009, researchers built experimental graphene frequency multipliers that take an incoming signal of a certain frequency and output a signal at a multiple of that frequency.[76]Optoelectronics
Graphene strongly interacts with photons, with the potential for direct band-gap creation. This is promising for optoelectronic and nanophotonic devices. Light interaction arises due to the Van Hove singularity. Graphene displays different time scales in response to photon interaction, ranging from femtoseconds (ultra-fast) to picoseconds. Potential uses include transparent films, touch screens and light emitters or as a plasmonic device that confines light and alters wavelengths.[77]Hall effect sensors
Due to extremely high electron mobility, graphene may be used for production of highly sensitive Hall effect sensors.[78] Potential application of such sensors is connected with DC current transformers for special applications.[citation needed] New record high sensitive Hall sensors are reported in April 2015. These sensors are two times better than existing Si based sensors.[79]Quantum dots
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) keep all dimensions less than 10 nm. Their size and edge crystallography govern their electrical, magnetic, optical, and chemical properties. GQDs can be produced via graphite nanotomy[80] or via bottom-up, solution-based routes (Diels-Alder, cyclotrimerization and/or cyclodehydrogenation reactions).[81] GQDs with controlled structure can be incorporated into applications in electronics, optoelectronics and electromagnetics. Quantum confinement can be created by changing the width of graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) at selected points along the ribbon.[42][82] It is studied as a catalyst for fuel cells.[83]Organic electronics
A semiconducting polymer (poly(3-hexylthiophene)[84] placed on top of single-layer graphene vertically conducts electric charge better than on a thin layer of silicon. A 50 nm thick polymer film conducted charge about 50 times better than a 10 nm thick film, potentially because the former consists of a mosaic of variably-oriented crystallites forms a continuous pathway of interconnected crystals. In a thin film or on silicon,[84] plate-like crystallites are oriented parallel to the graphene layer. Uses include solar cells.[85]Spintronics
Large-area graphene created by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and layered on a SiO2 substrate, can preserve electron spin over an extended period and communicate it. Spintronics varies electron spin rather than current flow. The spin signal is preserved in graphene channels that are up to 16 micrometers long over a nanosecond. Pure spin transport and precession extended over 16 μm channel lengths with a spin lifetime of 1.2 ns and a spin diffusion length of ≈6 μm at room temperature.[86]Spintronics is used in disk drives for data storage and in magnetic random-access memory. Electronic spin is generally short-lived and fragile, but the spin-based information in current devices needs to travel only a few nanometers. However, in processors, the information must cross several tens of micrometers with aligned spins. Graphene is the only known candidate for such behavior.[86]
Conductive ink
Researchers used a printing process to deposit graphene on paper. The ink was able to conduct electricity. Applying pressure to the ink increased conductivity 50-fold.[87]Light processing
Optical modulator
When the Fermi level of graphene is tuned, its optical absorption can be changed. In 2011, researchers reported the first graphene-based optical modulator. Operating at 1.2 GHz without a temperature controller, this modulator has a broad bandwidth (from 1.3 to 1.6 μm) and small footprint (~25 μm2).[88]A Mach-Zehnder modulator based on a hybrid graphene-silicon waveguide has been demonstrated recently, which can process signals nearly chirp-free.[89] An extinction up to 34.7 dB and a minimum chirp parameter of -0.006 are obtained. Its insertion loss is roughly -1.37 dB.
Ultraviolet lens
A hyperlens is a real-time super-resolution lens that can transform evanescent waves into propagating waves and thus break the diffraction limit. In 2016 a hyperlens based on dielectric layered graphene and h-boron nitride (h-BN) can surpass metal designs. Based on its anisotropic properties, flat and cylindrical hyperlenses were numerically verified with layered graphene at 1200 THz and layered h-BN at 1400 THz, respectively.[90] In 2016 a 1-nm thick graphene microlens that can image objects the size of a single bacterium. The lens was created by spraying a sheet of graphene oxide solution, then molding the lens using a laser beam. It can resolve objects as small as 200 nanometers, and see into the near infrared. It breaks the diffraction limit and achieve a focal length less than half the wavelength of light. Possible applications include thermal imaging for mobile phones, endoscopes, nanosatellites and photonic chips in supercomputers and superfast broadband distribution.[91]Infrared light detection
Graphene reacts to the infrared spectrum at room temperature, albeit with sensitivity 100 to 1000 times too low for practical applications. However, two graphene layers separated by an insulator allowed an electric field produced by holes left by photo-freed electrons in one layer to affect a current running through the other layer. The process produces little heat, making it suitable for use in night-vision optics. The sandwich is thin enough to be integrated in handheld devices, eyeglass-mounted computers and even contact lenses.[92]Photodetector
A graphene/n-type silicon heterojunction has been demonstrated to exhibit strong rectifying behavior and high photoresponsivity. By introducing a thin interfacial oxide layer, the dark current of graphene/n-Si heterojunction has been reduced by two orders of magnitude at zero bias. At room temperature, the graphene/n-Si photodetector with interfacial oxide exhibits a specific detectivity up to 5.77 × 1013 cm Hz1/2 W² at the peak wavelength of 890 nm in vacuum. In addition, the improved graphene/n-Si heterojunction photodetectors possess high responsivity of 0.73 A W−1 and high photo-to-dark current ratio of ≈107. These results demonstrate that graphene/Si heterojunction with interfacial oxide is promising for the development of high detectivity photodetectors.[93] Recently, a graphene/si Schottky photodetector with record-fast response speed (< 25 ns) from wavelength 350 nm to 1100 nm are presented.[94] The photodetectors exhibit excellent long-term stability even stored in air for more than 2 years. These results not only advance the development of high-performance photodetectors based on the graphene/Si Schottky junction, but also have important implications for mass-production of graphene-based photodetector array devices for cost-effective environmental monitoring, medical images, free-space communications, photoelectric smart-tracking, and integration with CMOS circuits for emerging interest-of-things applications, etc.Energy
Generation
Ethanol distillation
Graphene oxide membranes allow water vapor to pass through, but are impermeable to other liquids and gases.[95] This phenomenon has been used for further distilling of vodka to higher alcohol concentrations, in a room-temperature laboratory, without the application of heat or vacuum as used in traditional distillation methods.[96] Further development and commercialization of such membranes could revolutionize the economics of biofuel production and the alcoholic beverage industry.[citation needed]Solar cells
Charge conductor
Graphene solar cells use graphene's unique combination of high electrical conductivity and optical transparency.[97] This material absorbs only 2.6% of green light and 2.3% of red light.[98] Graphene can be assembled into a film electrode with low roughness. These films must be made thicker than one atomic layer to obtain useful sheet resistances. This added resistance can be offset by incorporating conductive filler materials, such as a silica matrix. Reduced conductivity can be offset by attaching large aromatic molecules such as pyrene-1-sulfonic acid sodium salt (PyS) and the disodium salt of 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic diimide bisbenzenesulfonic acid (PDI). These molecules, under high temperatures, facilitate better π-conjugation of the graphene basal plane.[99]Light collector
Using graphene as a photoactive material requires its bandgap to be 1.4–1.9 eV. In 2010, single cell efficiencies of nanostructured graphene-based PVs of over 12% were achieved. According to P. Mukhopadhyay and R. K. Gupta organic photovoltaics could be "devices in which semiconducting graphene is used as the photoactive material and metallic graphene is used as the conductive electrodes".[99]In 2008, chemical vapor deposition produced graphene sheets by depositing a graphene film made from methane gas on a nickel plate. A protective layer of thermoplastic is laid over the graphene layer and the nickel underneath is then dissolved in an acid bath. The final step is to attach the plastic-coated graphene to a flexible polymer sheet, which can then be incorporated into a PV cell. Graphene/polymer sheets range in size up to 150 square centimeters and can be used to create dense arrays.[100]
Silicon generates only one current-driving electron for each photon it absorbs, while graphene can produce multiple electrons. Solar cells made with graphene could offer 60% conversion efficiency.[101]
Electrode
In 2010, researchers first reported creating a graphene-silicon heterojunction solar cell, where graphene served as a transparent electrode and introduced a built-in electric field near the interface between the graphene and n-type silicon to help collect charge carriers.[102] In 2012 researchers reported efficiency of 8.6% for a prototype consisting of a silicon wafer coated with trifluoromethanesulfonyl-amide (TFSA) doped graphene. Doping increased efficiency to 9.6% in 2013.[103] In 2015 researchers reported efficiency of 15.6% by choosing the optimal oxide thickness on the silicon.[104] This combination of carbon materials with traditional silicon semiconductors to fabricate solar cells has been a promising field of carbon science.[105]In 2013, another team reported 15.6% percent by combining titanium oxide and graphene as a charge collector and perovskite as a sunlight absorber. The device is manufacturable at temperatures under 150 °C (302 °F) using solution-based deposition. This lowers production costs and offers the potential using flexible plastics.[106]
In 2015, researchers developed a prototype cell that used semitransparent perovskite with graphene electrodes. The design allowed light to be absorbed from both sides. It offered efficiency of around 12 percent with estimated production costs of less than $0.06/watt. The graphene was coated with PEDOT:PSS conductive polymer (poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate). Multilayering graphene via CVD created transparent electrodes reducing sheet resistance. Performance was further improved by increasing contact between the top electrodes and the hole transport layer.[107]
Fuel cells
Appropriately perforated graphene (and hexagonal boron nitride hBN) can allow protons to pass through it, offering the potential for using graphene monolayers as a barrier that blocks hydrogen atoms but not protons/ionized hydrogen (hydrogen atoms with their electrons stripped off). They could even be used to extract hydrogen gas out of the atmosphere that could power electric generators with ambient air.[108]The membranes are more effective at elevated temperatures and when covered with catalytic nanoparticles such as platinum.[108]
Graphene could solve a major problem for fuel cells: fuel crossover that reduces efficiency and durability.[108]
In methanol fuel cells, graphene used as a barrier layer in the membrane area, has reduced fuel cross over with negligible proton resistance, improving the performance.[109]
At room temperature, proton conductivity with monolayer hBN, outperforms graphene, with resistivity to proton flow of about 10 Ω cm2 and a low activation energy of about 0.3 electronvolts. At higher temperatures, graphene outperforms with resistivity estimated to fall below 10−3 Ω cm2 above 250 degrees Celsius.[110]
In another project, protons easily pass through slightly imperfect graphene membranes on fused silica in water.[111] The membrane was exposed to cycles of high and low pH. Protons transferred reversibly from the aqueous phase through the graphene to the other side where they undergo acid–base chemistry with silica hydroxyl groups. Computer simulations indicated energy barriers of 0.61–0.75 eV for hydroxyl-terminated atomic defects that participate in a Grotthuss-type relay, while pyrylium-like ether terminations did not.[112] Recently, Paul and co-workers at IISER Bhopal demonstrated solid state proton conduction for oxygen functionalized few-layer graphene(8.7x10−3 S/cm) with a low activation barrier (0.25 eV).[113]
Thermoelectrics
Adding .6% graphene to a mixture of lanthanum and partly reduced strontium titanium oxide produces a strong Seebeck at temperatures ranging from room temperature to 750 °C (compared to 500-750 without graphene). The material converts 5% of the heat into electricity (compared to 1% for strontium titanium oxide.)[114]Condenser coating
In 2015 a graphene coating on steam condensers quadrupled condensation efficiency, increasing overall plant efficiency by 2-3 percent.[115]Storage
Supercapacitor
Due to graphene's high surface-area-to-mass ratio, one potential application is in the conductive plates of supercapacitors.[116]In February 2013 researchers announced a novel technique to produce graphene supercapacitors based on the DVD burner reduction approach.[117]
In 2014 a supercapacitor was announced that was claimed to achieve energy density comparable to current lithium-ion batteries.[32][33]
In 2015 the technique was adapted to produce stacked, 3-D supercapacitors. Laser-induced graphene was produced on both sides of a polymer sheet. The sections were then stacked, separated by solid electrolytes, making multiple microsupercapacitors. The stacked configuration substantially increased the energy density of the result. In testing, the researchers charged and discharged the devices for thousands of cycles with almost no loss of capacitance.[118] The resulting devices were mechanically flexible, surviving 8,000 bending cycles. This makes them potentially suitable for rolling in a cylindrical configuration. Solid-state polymeric electrolyte-based devices exhibit areal capacitance of >9 mF/cm2 at a current density of 0.02 mA/cm2, over twice that of conventional aqueous electrolytes.[119]
Also in 2015 another project announced a microsupercapacitor that is small enough to fit in wearable or implantable devices. Just one-fifth the thickness of a sheet of paper, it is capable of holding more than twice as much charge as a comparable thin-film lithium battery. The design employed laser-scribed graphene, or LSG with manganese dioxide. They can be fabricated without extreme temperatures or expensive “dry rooms”. Their capacity is six times that of commercially available supercapacitors.[120] The device reached volumetric capacitance of over 1,100 F/cm3. This corresponds to a specific capacitance of the constituent MnO2 of 1,145 F/g, close to the theoretical maximum of 1,380 F/g. Energy density varies between 22 and 42 Wh/l depending on device configuration.[121]
In May 2015 a boric acid-infused, laser-induced graphene supercapacitor tripled its areal energy density and increased its volumetric energy density 5-10 fold. The new devices proved stable over 12,000 charge-discharge cycles, retaining 90 percent of their capacitance. In stress tests, they survived 8,000 bending cycles.[122][123]
Batteries
Silicon-graphene anode lithium ion batteries were demonstrated in 2012.[124]Stable Lithium ion cycling was demonstrated in bi- and few layer graphene films grown on nickel substrates,[125] while single layer graphene films have been demonstrated as a protective layer against corrosion in battery components such as the battery case.[126] This creates possibilities for flexible electrodes for microscale Li-ion batteries, where the anode acts as the active material and the current collector.[127]
Researchers built a lithium-ion battery made of graphene and silicon, which was claimed to last over a week on one charge and took only 15 minutes to charge.[128]
In 2015 argon-ion based plasma processing was used to bombard graphene samples with argon ions. That knocked out some carbon atoms and increased the capacitance of the materials three-fold. These “armchair” and “zigzag” defects are named based on the configurations of the carbon atoms that surround the holes.[129][130]
Sensors
Biosensors
Graphene does not oxidize in air or in biological fluids, making it an attractive material for use as a biosensor.[131] A graphene circuit can be configured as a field effect biosensor by applying biological capture molecules and blocking layers to the graphene, then controlling the voltage difference between the graphene and the liquid that includes the biological test sample. Of the various types of graphene sensors that can be made, biosensors were the first to be available for sale.[6]Pressure sensors
The electronic properties of graphene/h-BN heterostructures can be modulated by changing the interlayer distances via applying external pressure, leading to potential realization of atomic thin pressure sensors. In 2011 researchers proposed an in-plane pressure sensor consisting of graphene sandwiched between hexagonal boron nitride and a tunneling pressure sensor consisting of h-BN sandwiched by graphene.[132] The current varies by 3 orders of magnitude as pressure increases from 0 to 5 nN/nm². This structure is insensitive to the number of wrapping h-BN layers, simplifying process control. Because h-BN and graphene are inert to high temperature, the device could support ultra-thin pressure sensors for application under extreme conditions.In 2016 researchers demonstrated a biocompatible pressure sensor made from mixing graphene flakes with cross-linked polysilicone (found in silly putty).[133]
NEMS
Nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) can be designed and characterized by understanding the interaction and coupling between the mechanical, electrical, and the van der Waals energy domains. Quantum mechanical limit governed by Heisenberg uncertainty relation decides the ultimate precision of nanomechanical systems. Quantum squeezing can improve the precision by reducing quantum fluctuations in one desired amplitude of the two quadrature amplitudes. Traditional NEMS hardly achieve quantum squeezing due to their thickness limits. A scheme to obtain squeezed quantum states through typical experimental graphene NEMS structures taking advantages of its atomic scale thickness has been proposed.[134]Molecular adsorbtion
Theoretically graphene makes an excellent sensor due to its 2D structure. The fact that its entire volume is exposed to its surrounding environment makes it very efficient to detect adsorbed molecules. However, similar to carbon nanotubes, graphene has no dangling bonds on its surface. Gaseous molecules cannot be readily adsorbed onto graphene surfaces, so intrinsically graphene is insensitive.[135] The sensitivity of graphene chemical gas sensors can be dramatically enhanced by functionalization, for example, coating the film with a thin layer of certain polymers. The thin polymer layer acts like a concentrator that absorbs gaseous molecules. The molecule absorption introduces a local change in electrical resistance of graphene sensors. While this effect occurs in other materials, graphene is superior due to its high electrical conductivity (even when few carriers are present) and low noise, which makes this change in resistance detectable.[136]Piezoelectric effect
Density functional theory simulations predict that depositing certain adatoms on graphene can render it piezoelectrically responsive to an electric field applied in the out-of-plane direction. This type of locally engineered piezoelectricity is similar in magnitude to that of bulk piezoelectric materials and makes graphene a candidate for control and sensing in nanoscale devices.[137]Body motion
Promoted by the demand for wearable devices, graphene has been proved to be a promising material for potential applications in flexible and highly sensitive strain sensors. An environment-friendly and cost-effective method to fabricate large-area ultrathin graphene films is proposed for highly sensitive flexible strain sensor. The assembled graphene films are derived rapidly at the liquid/air interface by Marangoni effect and the area can be scaled up. These graphene-based strain sensors exhibit extremely high sensitivity with gauge factor of 1037 at 2% strain, which represents the highest value for graphene platelets at this small deformation so far.[138]Rubber bands infused with graphene("G-bands") can be used as inexpensive body sensors. The bands remain pliable and can be used as a sensor to measure breathing, heart rate, or movement. Lightweight sensor suits for vulnerable patients could make it possible to remotely monitor subtle movement. These sensors display 10×104-fold increases in resistance and work at strains exceeding 800%. Gauge factors of up to 35 were observed. Such sensors can function at vibration frequencies of at least 160 Hz. At 60 Hz, strains of at least 6% at strain rates exceeding 6000%/s can be monitored.[139]
Magnetic
In 2015 researchers announced a graphene-based magnetic sensor 100 times more sensitive than an equivalent device based on silicon (7,000 volts per amp-tesla). The sensor substrate was hexagonal boron nitride. The sensors were based on the Hall effect, in which a magnetic field induces a Lorentz force on moving electric charge carriers, leading to deflection and a measurable Hall voltage. In the worst case graphene roughly matched a best case silicon design. In the best case graphene required lower source current and power requirements.[140]Environmental
Contaminant removal
Graphene oxide is non-toxic and biodegradable. Its surface is covered with epoxy, hydroxyl, and carboxyl groups that interact with cations and anions. It is soluble in water and forms stable colloid suspensions in other liquids because it is amphiphilic (able to mix with water or oil). Dispersed in liquids it shows excellent sorption capacities. It can remove copper, cobalt, cadmium, arsenate, and organic solvents.In 2013 it was shown to be able to remove radioactive nuclides from water, including radioactive isotopes of actinides (elements with atomic numbers 89 to 103, including thorium, uranium, neptunium, plutonium, and americium) and lanthanides (the ‘rare earths’ with atomic numbers 57 to 71, including europium).[141]
Even at concentrations < 0.1 g/L, radionuclide sorption proceeds rapidly. At pH between 4 and 8, graphene oxide removes over 90% of nuclides, including uranium and europium. At pH >7, more than 70% of strontium and technetium are removed with up to 20% of neptunium.[141]
Water filtration
Research suggests that graphene filters could outperform other techniques of desalination by a significant margin.[142]Permeation barrier
Instead of allowing the permeation, blocking is also necessary. Gas permeation barriers are important for almost all applications ranging from food, pharmaceutical, medical, inorganic and organic electronic devices, etc. packaging. It enhances life of the product and allow keeping the total thickess of devices small. Being atomically thin, defectless graphene is immpermeable to all gases. In particular, ultra-thin moisture permeation barrier layers based on graphene are shown to be important for organic-FETs and OLEDs.[143][144] Graphene barrier applications in biological sciences are under study.Other
Plasmonics and metamaterials
Graphene accommodates a plasmonic surface mode,[145] observed recently via near field infrared optical microscopy techniques[146][147] and infrared spectroscopy [148] Potential applications are in the terahertz to mid-infrared frequencies,[149] such as terahertz and midinfrared light modulators, passive terahertz filters, mid-infrared photodetectors and biosensors.[150]Lubricant
Scientists discovered using graphene as a lubricant works better than traditionally used graphite. A one atom thick layer of graphene in between a steel ball and steel disc lasted for 6,500 cycles. Conventional lubricants lasted 1,000 cycles.[151]Radio wave absorption
Stacked graphene layers on a quartz substrate increased the absorption of millimeter (radio) waves by 90 per cent over 125 – 165 GHz bandwidth, extensible to microwave and low-terahertz frequencies, while remaining transparent to visible light. For example, graphene could be used as a coating for buildings or windows to block radio waves. Absorption is a result of mutually coupled Fabry–Perot resonators represented by each graphene-quartz substrate. A repeated transfer-and-etch process was used to control surface resistivity.[152][153]Redox
Graphene oxide can be reversibly reduced and oxidized via electrical stimulus. Controlled reduction and oxidation in two-terminal devices containing multilayer graphene oxide films are shown to result in switching between partly reduced graphene oxide and graphene, a process that modifies electronic and optical properties. Oxidation and reduction are related to resistive switching.[154]Nanoantennas
A graphene-based plasmonic nano-antenna (GPN) can operate efficiently at millimeter radio wavelengths. The wavelength of surface plasmon polaritons for a given frequency is several hundred times smaller than the wavelength of freely propagating electromagnetic waves of the same frequency. These speed and size differences enable efficient graphene-based antennas to be far smaller than conventional alternatives. The latter operate at frequencies 100-1000 times larger than GPNs, producing .01-.001 as many photons.[155]An electromagnetic (EM) wave directed vertically onto a graphene surface excites the graphene into oscillations that interact with those in the dielectric on which the graphene is mounted, thereby forming surface plasmon polaritons (SPP). When the antenna becomes resonant (an integral number of SPP wavelengths fit into the physical dimensions of the graphene), the SPP/EM coupling increases greatly, efficiently transferring energy between the two.[155]
A phased array antenna 100 µm in diameter could produce 300 GHz beams only a few degrees in diameter, instead of the 180 degree radiation from tsa conventional metal antenna of that size. Potential uses include smart dust, low-power terabit wireless networks[155] and photonics.[156]
A nanoscale gold rod antenna captured and transformed EM energy into graphene plasmons, analogous to a radio antenna converting radio waves into electromagnetic waves in a metal cable. The plasmon wavefronts can be directly controlled by adjusting antenna geometry. The waves were focused (by curving the antenna) and refracted (by a prism-shaped graphene bilayer because the conductivity in the two-atom-thick prism is larger than in the surrounding one-atom-thick layer.)[156]
The plasmonic metal-graphene nanoantenna was composed by inserting a few nanometers of oxide between a dipole gold nanorod and the monolayer graphene.[157] The used oxide layer here can reduce the quantum tunelling effect between graphene and metal antenna. With tuning the chemical potential of the graphene layer through field effect transistor architecture, the in-phase and out-phase mode coupling between graphene palsmonics and metal plasmonics is realized.[157] The tunable propeties of the plasmonic metal-graphene nanoantenna can be switched on and off via modifying the electrostatic gate-voltage on graphene.
Sound transducers
Graphene's light weight provides relatively good frequency response, suggesting uses in electrostatic audio speakers and microphones.[158] In 2015 an ultrasonic microphone and speaker were demonstrated that could operate at frequencies from 20 Hz-500 kHz.[159] The speaker operated at a claimed 99% efficiency with a flat frequency response across the audible range. One application was as a radio replacement for long-distance communications, given sound's ability to penetrate steel and water, unlike radio waves.[159]Waterproof coating
Graphene could potentially usher in a new generation of waterproof devices whose chassis may not need to be sealed like today's devices.Coolant additive
Graphene's high thermal conductivity suggests that it could be used as an additive in coolants. Preliminary research work showed that 5% graphene by volume can enhance the thermal conductivity of a base fluid by 86%.[160] Another application due to graphene's enhanced thermal conductivity was found in PCR.[20]Reference material
Graphene's properties suggest it as a reference material for characterizing electroconductive and transparent materials. One layer of graphene absorbs 2.3% of red light.[161]This property was used to define the conductivity of transparency that combines sheet resistance and transparency. This parameter was used to compare materials without the use of two independent parameters.[162]
Thermal management
In 2011, researchers reported that a three-dimensional, vertically aligned, functionalized multilayer graphene architecture can be an approach for graphene-based thermal interfacial materials (TIMs) with superior thermal conductivity and ultra-low interfacial thermal resistance between graphene and metal.[163]Graphene-metal composites can be used in thermal interface materials.[164]
Adding a layer of graphene to each side of a copper film increased the metal's heat-conducting properties up to 24%. This suggests the possibility of using them for semiconductor interconnects in computer chips. The improvement is the result of changes in copper’s nano- and microstructure, not from graphene’s independent action as an added heat conducting channel. High temperature chemical vapor deposition stimulates grain size growth in copper films. The larger grain sizes improve heat conduction. The heat conduction improvement was more pronounced in thinner copper films, which is useful as copper interconnects shrink.[165]
Attaching graphene functionalized with silane molecules increases its thermal conductivity (κ) by 15%–56% with respect to the number density of molecules. This is because of enhanced in-plane heat conduction resulting from the simultaneous increase of thermal resistance between the graphene and the substrate, which limited cross-plane phonon scattering. Heat spreading ability doubled.[166]
However, mismatches at the boundary between horizontally adjacent crystals reduces heat transfer by a factor of 10.[167]