Oncogenomics is a sub-field of genomics that characterizes cancer-associated genes. It focuses on genomic, epigenomic and transcript alterations in cancer.
Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.
Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.
Overall goals of oncogenomics
Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiate or drive cancer progression, oncogenomics targets personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations that accumulate randomly. Identifying and targeting the mutations in an individual patient may lead to increased treatment efficacy.
The completion of the Human Genome Project facilitated the field of oncogenomics and increased the abilities of researchers to find oncogenes. Sequencing technologies and global methylation profiling techniques have been applied to the study of oncogenomics.
History
The genomics era began in the 1990s, with the generation of DNA sequences of many organisms. In the 21st century, the completion of the Human Genome Project enabled the study of functional genomics and examining tumor genomes. Cancer is a main focus.The epigenomics era largely began more recently, about 2000. One major source of epigenetic change is altered methylation of CpG islands at the promoter region of genes. A number of recently devised methods can assess the DNA methylation status in cancers versus normal tissues. Some methods assess methylation of CpGs located in different classes of loci, including CpG islands, shores, and shelves as well as promoters, gene bodies, and intergenic regions. Cancer is also a major focus of epigenetic studies.
Access to whole cancer genome sequencing is important to cancer (or cancer genome) research because:
- Mutations are the immediate cause of cancer and define the tumor phenotype.
- Access to cancerous and normal tissue samples from the same patient and the fact that most cancer mutations represent somatic events, allow the identification of cancer-specific mutations.
- Cancer mutations are cumulative and sometimes are related to disease stage. Metastasis and drug resistance are distinguishable.
- Epi-drivers, along with Mut-drivers, can act as immediate causes of cancers
- Cancer epimutations are cumulative and sometimes related to disease stage
Whole genome sequencing
The first cancer genome was sequenced in 2008. This study sequenced a typical acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) genome and its normal counterpart genome obtained from the same patient. The comparison revealed ten mutated genes. Two were already thought to contribute to tumor progression: an internal tandem duplication of the FLT3 receptor tyrosine kinase gene, which activates kinase signaling and is associated with a poor prognosis and a four base insertion in exon 12 of the NPM1 gene (NPMc). These mutations are found in 25-30% of AML tumors and are thought to contribute to disease progression rather than to cause it directly.The remaining 8 were new mutations and all were single base changes: Four were in families that are strongly associated with cancer pathogenesis (PTPRT, CDH24, PCLKC and SLC15A1). The other four had no previous association with cancer pathogenesis. They did have potential functions in metabolic pathways that suggested mechanisms by which they could act to promote cancer (KNDC1, GPR124, EB12, GRINC1B).
These genes are involved in pathways known to contribute to cancer pathogenesis, but before this study most would not have been candidates for targeted gene therapy. This analysis validated the approach of whole cancer genome sequencing in identifying somatic mutations and the importance of parallel sequencing of normal and tumor cell genomes.
In 2011, the genome of an exceptional bladder cancer patient whose tumor had been eliminated by the drug everolimus was sequenced, revealing mutations in two genes, TSC1 and NF2. The mutations disregulated mTOR, the protein inhibited by everolimus, allowing it to reproduce without limit. As a result, in 2015, the Exceptional Responders Initiative was created at the National Cancer Institute. The initiative allows such exceptional patients (who have responded positively for at least six months to a cancer drug that usually fails) to have their genomes sequenced to identify the relevant mutations. Once identified, other patients could be screened for those mutations and then be given the drug. In 2016 To that end, a nationwide cancer drug trial began in 2015, involving up to twenty-four hundred centers. Patients with appropriate mutations are matched with one of more than forty drugs.
In 2014 the Center for Molecular Oncology rolled out the MSK-IMPACT test, a screening tool that looks for mutations in 341 cancer-associated genes. By 2015 more than five thousand patients had been screened. Patients with appropriate mutations are eligible to enroll in clinical trials that provide targeted therapy.
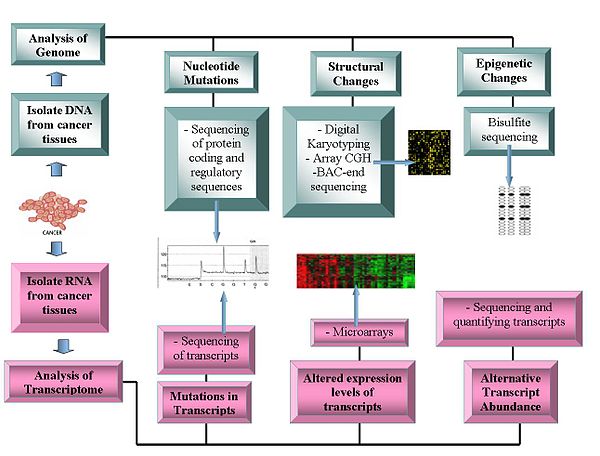
Technologies
Current technologies being used in Oncogenomics.
Genome sequencing
- DNA sequencing: Pyrosequencing-based sequencers offer a relatively low-cost method to generate sequence data.
- Array Comparative Genome Hybridization: This technique measures the DNA copy number differences between normal and cancer genomes. It uses the fluorescence intensity from fluorescent-labeled samples, which are hybridized to known probes on a microarray.
- Representational oligonucleotide microarray analysis: Detects copy number variation using amplified restriction-digested genomic fragments that are hybridized to human oligonucleotides, achieving a resolution between 30 and 35 kbit/s.
- Digital Karyotyping: Detects copy number variation using genomics tags obtained via restriction enzyme digests. These tags are then linked to into ditags, concatenated, cloned, sequenced and mapped back to the reference genome to evaluate tag density.
- Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC)-end sequencing (end-sequence profiling): Identifies chromosomal breakpoints by generating a BAC library from a cancer genome and sequencing their ends. The BAC clones that contain chromosome aberrations have end sequences that do not map to a similar region of the reference genome, thus identifying a chromosomal breakpoint.
Transcriptomes
- Microarrays: Assess transcript abundance. Useful in classification, prognosis, raise the possibility of differential treatment approaches and aid identification of mutations in the proteins' coding regions. The relative abundance of alternative transcripts has become an important feature of cancer research. Particular alternative transcript forms correlate with specific cancer types.
- RNA-Seq
Bioinformatics and functional analysis of oncogenes
Bioinformatics technologies allow the statistical analysis of genomic data. The functional characteristics of oncogenes has yet to be established. Potential functions include their transformational capabilities relating to tumour formation and specific roles at each stage of cancer development.After the detection of somatic cancer mutations across a cohort of cancer samples, bioinformatic computational analyses can be carried out to identify likely functional and likely driver mutations. There are three main approaches routinely used for this identification: mapping mutations, assessing the effect of mutation of the function of a protein or a regulatory element and finding signs of positive selection across a cohort of tumors. The approaches are not necessarily sequential however, there are important relationships of precedence between elements from the different approaches. Different tools are used at each step.
Operomics
Operomics aims to integrate genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics to understand the molecular mechanisms that underlie the cancer development.Comparative oncogenomics
Comparative oncogenomics uses cross-species comparisons to identify oncogenes. This research involves studying cancer genomes, transcriptomes and proteomes in model organisms such as mice, identifying potential oncogenes and referring back to human cancer samples to see whether homologues of these oncogenes are important in causing human cancers. Genetic alterations in mouse models are similar to those found in human cancers. These models are generated by methods including retroviral insertion mutagenesis or graft transplantation of cancerous cells.Source of cancer driver mutations, cancer mutagenesis
Mutations provide the raw material for natural selection in evolution and can be caused by errors of DNA replication, the action of exogenous mutagens or endogenous DNA damage. The machinery of replication and genome maintenance can be damaged by mutations, or altered by physiological conditions and differential levels of expression in cancer (see references in).As pointed out by Gao et al., the stability and integrity of the human genome are maintained by the DNA-damage response (DDR) system. Un-repaired DNA damage is a major cause of mutations that drive carcinogenesis. If DNA repair is deficient, DNA damage tends to accumulate. Such excess DNA damage can increase mutational errors during DNA replication due to error-prone translesion synthesis. Excess DNA damage can also increase epigenetic alterations due to errors during DNA repair. Such mutations and epigenetic alterations can give rise to cancer. DDR genes are often repressed in human cancer by epigenetic mechanisms. Such repression may involve DNA methylation of promoter regions or repression of DDR genes by a microRNA. Epigenetic repression of DDR genes occurs more frequently than gene mutation in many types of cancer. Thus, epigenetic repression often plays a more important role than mutation in reducing expression of DDR genes. This reduced expression of DDR genes is likely an important driver of carcinogenesis.
Nucleotide sequence context influences mutation probability and analysis of mutational (mutable) DNA motifs can be essential for understanding the mechanisms of mutagenesis in cancer. Such motifs represent the fingerprints of interactions between DNA and mutagens, between DNA and repair/replication/modification enzymes. Examples of motifs are the AID motif WRCY/RGYW (W = A or T, R = purine and Y = pyrimidine) with C to T/G/A mutations, and error-prone DNA pol η attributed AID-related mutations (A to G/C/G) in WA/TW motifs.
Another (agnostic) way to analyze the observed mutational spectra and DNA sequence context of mutations in tumors involves pooling all mutations of different types and contexts from cancer samples into a discrete distribution. If multiple cancer samples are available, their context-dependent mutations can be represented in the form of a nonnegative matrix. This matrix can be further decomposed into components (mutational signatures) which ideally should describe individual mutagenic factors. Several computational methods have been proposed for solving this decomposition problem. The first implementation of Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) method is available in Sanger Institute Mutational Signature Framework in the form of a MATLAB package. On the other hand, if mutations from a single tumor sample are only available, the DeconstructSigs R package and MutaGene server may provide the identification of contributions of different mutational signatures for a single tumor sample. In addition, MutaGene server provides mutagen or cancer-specific mutational background models and signatures that can be applied to calculate expected DNA and protein site mutability to decouple relative contributions of mutagenesis and selection in carcinogenesis.
Synthetic lethality
Synthetic lethality arises when a combination of deficiencies in the expression of two or more genes leads to cell death, whereas a deficiency in only one of these genes does not. The deficiencies can arise through mutations, epigenetic alterations or inhibitors of one of the genes.The therapeutic potential of synthetic lethality as an efficacious anti-cancer strategy is continually improving. Recently, the applicability of synthetic lethality to targeted cancer therapy has heightened due to the recent work of scientists including Ronald A. DePinho and colleagues, in what is termed 'collateral lethality'. Muller et al. found that passenger genes, with chromosomal proximity to tumor suppressor genes, are collaterally deleted in some cancers. Thus, the identification of collaterally deleted redundant genes carrying out an essential cellular function may be the untapped reservoir for then pursuing a synthetic lethality approach. Collateral lethality therefore holds great potential in identification of novel and selective therapeutic targets in oncology. In 2012, Muller et al. identified that homozygous deletion of redundant-essential glycolytic ENO1 gene in human glioblastoma (GBM) is the consequence of proximity to 1p36 tumor suppressor locus deletions and may hold potential for a synthetic lethality approach to GBM inhibition. ENO1 is one of three homologous genes (ENO2, ENO3) that encodes the mammalian alpha-enolase enzyme. ENO2, which encodes enolase 2, is mostly expressed in neural tissues, leading to the postulation that in ENO1-deleted GBM, ENO2 may be the ideal target as the redundant homologue of ENO1. Muller found that both genetic and pharmacological ENO2 inhibition in GBM cells with homozygous ENO1 deletion elicits a synthetic lethality outcome by selective killing of GBM cells). In 2016, Muller and colleagues discovered antibiotic SF2312 as a highly potent nanomolar-range enolase inhibitor which preferentially inhibits glioma cell proliferation and glycolytic flux in ENO1-deleted cells. SF2312 was shown to be more efficacious than pan-enolase inhibitor PhAH and have more specificity for ENO2 inhibition over ENO1. Subsequent work by the same team showed that the same approach could be applied to pancreatic cancer, whereby homozygously deleted SMAD4 results in the collateral deletion of mitochondrial malic enzyme 2 (ME2), an oxidative decarboxylase essential for redox homeostasis. Dey et al. show that ME2 genomic deletion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells results in high endogenous reactive oxygen species, consistent with KRAS-driven pancreatic cancer, and essentially primes ME2-null cells for synthetic lethality by depletion of redundant NAD(P)+-dependent isoform ME3. The effects of ME3 depletion were found to be mediated by inhibition of de novo nucleotide synthesis resulting from AMPK activation and mitochondrial ROS-mediated apoptosis. Meanwhile, Oike et al. demonstrated the generalizability of the concept by targeting redundant essential-genes in process other than metabolism, namely the SMARCA4 and SMARCA2 subunits in the chromatin-remodeling SWI/SNF complex.
Some oncogenes are essential for survival of all cells (not only cancer cells). Thus, drugs that knock out these oncogenes (and thereby kill cancer cells) may also damage normal cells, inducing significant illness. However, other genes may be essential to cancer cells but not to healthy cells.
Treatments based on the principle of synthetic lethality have prolonged the survival of cancer patients, and show promise for future advances in reversal of carcinogenesis. A major type of synthetic lethality operates on the DNA repair defect that often initiates a cancer, and is still present in the tumor cells. Some examples are given here.
BRCA1 or BRCA2 expression is deficient in a majority of high-grade breast and ovarian cancers, usually due to epigenetic methylation of its promoter or epigenetic repression by an over-expressed microRNA (see articles BRCA1 and BRCA2). BRCA1 and BRCA2 are important components of the major pathway for homologous recombinational repair of double-strand breaks. If one or the other is deficient, it increases the risk of cancer, especially breast or ovarian cancer. A back-up DNA repair pathway, for some of the damages usually repaired by BRCA1 and BRCA2, depends on PARP1. Thus, many ovarian cancers respond to an FDA-approved treatment with a PARP inhibitor, causing synthetic lethality to cancer cells deficient in BRCA1 or BRCA2. This treatment is also being evaluated for breast cancer and numerous other cancers in Phase III clinical trials in 2016.
There are two pathways for homologous recombinational repair of double-strand breaks. The major pathway depends on BRCA1, PALB2 and BRCA2 while an alternative pathway depends on RAD52. Pre-clinical studies, involving epigenetically reduced or mutated BRCA-deficient cells (in culture or injected into mice), show that inhibition of RAD52 is synthetically lethal with BRCA-deficiency.
Mutations in genes employed in DNA mismatch repair (MMR) cause a high mutation rate. In tumors, such frequent subsequent mutations often generate “non-self” immunogenic antigens. A human Phase II clinical trial, with 41 patients, evaluated one synthetic lethal approach for tumors with or without MMR defects. The product of gene PD-1 ordinarily represses cytotoxic immune responses. Inhibition of this gene allows a greater immune response. When cancer patients with a defect in MMR in their tumors were exposed to an inhibitor of PD-1, 67% - 78% of patients experienced immune-related progression-free survival. In contrast, for patients without defective MMR, addition of PD-1 inhibitor generated only 11% of patients with immune-related progression-free survival. Thus inhibition of PD-1 is primarily synthetically lethal with MMR defects.
ARID1A, a chromatin modifier, is required for non-homologous end joining, a major pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA, and also has transcription regulatory roles. ARID1A mutations are one of the 12 most common carcinogenic mutations. Mutation or epigenetically decreased expression of ARID1A has been found in 17 types of cancer. Pre-clinical studies in cells and in mice show that synthetic lethality for ARID1A deficiency occurs by either inhibition of the methyltransferase activity of EZH2, or with addition of the kinase inhibitor dasatinib.
Another approach is to individually knock out each gene in a genome and observe the effect on normal and cancerous cells. If the knockout of an otherwise nonessential gene has little or no effect on healthy cells, but is lethal to cancerous cells containing a mutated oncogene, then the system-wide suppression of the suppressed gene can destroy cancerous cells while leaving healthy ones relatively undamaged. The technique was used to identify PARP-1 inhibitors to treat BRCA1/BRCA2-associated cancers. In this case, the combined presence of PARP-1 inhibition and of the cancer-associated mutations in BRCA genes is lethal only to the cancerous cells.
Databases for cancer research
The Cancer Genome Project is an initiative to map out all somatic mutations in cancer. The project systematically sequences the exons and flanking splice junctions of the genomes of primary tumors and cancerous cell lines. COSMIC software displays the data generated from these experiments. As of February 2008, the CGP had identified 4,746 genes and 2,985 mutations in 1,848 tumours. The Cancer Genome Anatomy Project includes information of research on cancer genomes, transcriptomes and proteomes.Progenetix is an oncogenomic reference database, presenting cytogenetic and molecular-cytogenetic tumor data.
Oncomine has compiled data from cancer transcriptome profiles.
The integrative oncogenomics database IntOGen and the Gitools datasets integrate multidimensional human oncogenomic data classified by tumor type. The first version of IntOGen focused on the role of deregulated gene expression and CNV in cancer. A later version emphasized mutational cancer driver genes across 28 tumor types. All releases of IntOGen data are made available at the IntOGen database.
The International Cancer Genome Consortium is the biggest project to collect human cancer genome data. The data is accessible through the ICGC website. The BioExpress® Oncology Suite contains gene expression data from primary, metastatic and benign tumor samples and normal samples, including matched adjacent controls. The suite includes hematological malignancy samples for many well-known cancers.
Specific databases for model animals include the Retrovirus Tagged Cancer Gene Database (RTCGD) that compiled research on retroviral and transposon insertional mutagenesis in mouse tumors.
Gene families
Mutational analysis of entire gene families revealed that genes of the same family have similar functions, as predicted by similar coding sequences and protein domains. Two such classes are the kinase family, involved in adding phosphate groups to proteins and the phosphatase family, involved with removing phosphate groups from proteins. These families were first examined because of their apparent role in transducing cellular signals of cell growth or death. In particular, more than 50% of colorectal cancers carry a mutation in a kinase or phosphatase gene. Phosphatidylinositold 3-kinases (PIK3CA) gene encodes for lipid kinases that commonly contain mutations in colorectal, breast, gastric, lung and various other cancers. Drug therapies can inhibit PIK3CA. Another example is the BRAF gene, one of the first to be implicated in melanomas. BRAF encodes a serine/threonine kinase that is involved in the RAS-RAF-MAPK growth signaling pathway. Mutations in BRAF cause constitutive phosphorylation and activity in 59% of melanomas. Before BRAF, the genetic mechanism of melanoma development was unknown and therefore prognosis for patients was poor.Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations are linked the formation of tumors. Four types of mtDNA mutations have been identified:Point mutations
Point mutations have been observed in the coding and non-coding region of the mtDNA contained in cancer cells. In individuals with bladder, head/neck and lung cancers, the point mutations within the coding region show signs of resembling each other. This suggests that when a healthy cell transforms into a tumor cell (a neoplastic transformation) the mitochondria seem to become homogenous. Abundant point mutations located within the non-coding region, D-loop, of the cancerous mitochondria suggest that mutations within this region might be an important characteristic in some cancers.Deletions
This type of mutation is sporadically detected due to its small size ( < 1kb). The appearance of certain specific mtDNA mutations (264-bp deletion and 66-bp deletion in the complex 1 subunit gene ND1) in multiple types of cancer provide some evidence that small mtDNA deletions might appear at the beginning of tumorigenesis. It also suggests that the amount of mitochondria containing these deletions increases as the tumor progresses. An exception is a relatively large deletion that appears in many cancers (known as the "common deletion"), but more mtDNA large scale deletions have been found in normal cells compared to tumor cells. This may be due to a seemingly adaptive process of tumor cells to eliminate any mitochondria that contain these large scale deletions (the "common deletion" is > 4kb).Insertions
Two small mtDNA insertions of ~260 and ~520 bp can be present in breast cancer, gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and colon cancer and in normal cells. No correlation between these insertions and cancer are established.Copy number mutations
The characterization of mtDNA via real-time polymerase chain reaction assays shows the presence of quantitative alteration of mtDNA copy number in many cancers. Increase in copy number is expected to occur because of oxidative stress. On the other hand, decrease is thought to be caused by somatic point mutations in the replication origin site of the H-strand and/or the D310 homopolymeric c-stretch in the D-loop region, mutations in the p53 (tumor suppressor gene) mediated pathway and/or inefficient enzyme activity due to POLG mutations. Any increase/decrease in copy number then remains constant within tumor cells. The fact that the amount of mtDNA is constant in tumor cells suggests that the amount of mtDNA is controlled by a much more complicated system in tumor cells, rather than simply altered as a consequence of abnormal cell proliferation. The role of mtDNA content in human cancers apparently varies for particular tumor types or sites.57.7% (500/867) contained somatic point putations and of the 1172 mutations surveyed 37.8% (443/1127) were located in the D-loop control region, 13.1% (154/1172) were located in the tRNA or rRNA genes and 49.1% (575/1127) were found in the mRNA genes needed for producing complexes required for mitochondrial respiration.