A superhard material is a material with a hardness value exceeding 40 gigapascals (GPa) when measured by the Vickers hardness test. They are highly incompressible solids with high electron density and high bond covalency. As a result of their unique properties, these materials are of great interest in many industrial areas including, but not limited to, abrasives, polishing and cutting tools and wear-resistant and protective coatings.
Diamond is the hardest known material to date, with a Vickers hardness in the range of 70–150 GPa. Diamond demonstrates both high thermal conductivity and electrically insulating properties and much attention has been put into finding practical applications of this material. However, diamond has several limitations for mass industrial application, including its high cost and oxidation at temperatures above 800 °C. In addition, diamond dissolves in iron and forms iron carbides at high temperatures and therefore is inefficient in cutting ferrous materials including steel. Therefore, recent research of superhard materials has been focusing on compounds which would be thermally and chemically more stable than pure diamond.
Superhard materials can be generally classified into two categories: intrinsic compounds and extrinsic compounds. The intrinsic group includes diamond, cubic boron nitride (c-BN), carbon nitrides and ternary compounds such as B-N-C, which possess an innate hardness. Conversely, extrinsic materials are those that have superhardness and other mechanical properties that are determined by their microstructure rather than composition. An example of extrinsic superhard material is nanocrystalline diamond known as aggregated diamond nanorods.
A nanoindenter, used to measure the hardness and related properties of materials
Definition and mechanics of hardness
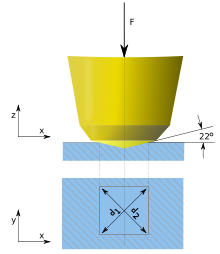
Vickers test scheme
An indentation left in case-hardened steel after a Vickers hardness test.
The hardness of a material is directly related to its
incompressibility, elasticity and resistance to change in shape. A
superhard material has high shear modulus, high bulk modulus and does not deform plastically.
Ideally superhard materials should have a defect-free, isotropic
lattice. This greatly reduces structural deformations that can lower the
strength of the material. However, defects can actually strengthen some
covalent structures. Traditionally, high-pressure and high-temperature
(HPHT) conditions have been used to synthesize superhard materials, but
recent superhard material syntheses aim at using less energy and lower
cost materials.
Historically, hardness was first defined as the ability of one
material to scratch another and quantified by an integer (sometimes
half-integer) from 0 to 10 on the Mohs scale.
This scale was however quickly found too discrete and non-linear.
Measuring the mechanical hardness of materials changed to using a nanoindenter (usually made of diamond) and evaluating bulk moduli, and the Brinell, Rockwell, Knoop and Vickers scales have been developed. Whereas the Vickers scale is widely accepted as a most common test,
there remain controversies on the weight load to be applied during the
test. Bulk moduli, shear moduli, and elasticity are the key factors in
the superhard classification process.
| Material | Vickers hardness (GPa) |
|---|---|
| Diamond | 115 |
| c-BC2N | 76 |
| c-BN | 48 |
| OsB2 | 37 |
| B4C | 30 |
| WB4 | ~30 |
| AlMgB14 | 26.7 |
| ReB2 | ~20 |
The incompressibility of a material is quantified by the bulk modulus
B, which measures the resistance of a solid to volume compression under
hydrostatic stress
as B = −Vdp/dV. Here V is the volume, p is pressure, and dp/dV is the
partial derivative of pressure with respect to the volume. The bulk
modulus test uses an indenter tool to form a permanent deformation in a
material. The size of the deformation depends on the material’s
resistance to the volume compression made by the tool. Elements with
small molar volumes and strong interatomic forces usually have high bulk
moduli. Bulk moduli was the first major test of hardness and originally
shown to be correlated with the molar volume (Vm) and cohesive energy (Ec) as B ~ Ec/Vm
Bulk modulus was believed to be a direct measure of a material’s
hardness but this no longer remains the dominant school of thought. For
example, some alkali and noble metals
(Pd, Ag) have anomalously high ratio of the bulk modulus to the Vickers
of Brinell hardness. In the early 2000s, a direct relationship between
bulk modulus and valence electron density was found as the more
electrons were present the greater the repulsions within the structure
were.
Bulk modulus is still used as a preliminary measure of a material as
superhard but it is now known that other properties must be taken into
account.
In contrast to bulk modulus, shear modulus measures the
resistance to shape change at a constant volume, taking into account the
crystalline plane and direction of shear. The shear modulus G is
defined as ratio of shear stress to shear strain: G = stress/strain =
F·L/(A·dx), where F is the applied force, A is the area upon which the
force acts, dx is the resulting displacement and L is the initial
length. The larger the shear modulus, the greater the ability for a
material to resist shearing forces. Therefore, the shear modulus is a
measure of rigidity. Shear modulus is related to bulk modulus as 3/G = 2B(1 − 2v)(1 + v),
where v is the Poisson’s ratio, which is typically ~0.1 in covalent
materials. If a material contains highly directional bonds, the shear
modulus will increase and give a low Poisson ratio.
A material is also considered hard if it resists plastic
deformation. If a material has short covalent bonds, atomic dislocations
that lead to plastic deformation are less likely to occur than in
materials with longer, delocalized bonds. If a material contains many
delocalized bonds it is likely to be soft. Somewhat related to hardness is another mechanical property fracture toughness, which is a material's ability to resist breakage from forceful impact (note that this concept is distinct from the notion of toughness). A superhard material is not necessarily "supertough". For example, the fracture toughness of diamond is about 7–10 MPa·m1/2,
which is high compared to other gemstones and ceramic materials, but
poor compared to many metals and alloys – common steels and aluminium
alloys have the toughness values at least 5 times higher.
Several properties must be taken into account when evaluating a
material as (super)hard. While hard materials have high bulk moduli, a
high bulk modulus does not mean a material is hard. Inelastic
characteristics must be considered as well, and shear modulus might even
provide a better correlation with hardness than bulk modulus. Covalent
materials generally have high bond-bending force constants and high
shear moduli and are more likely to give superhard structures than, for
example, ionic solids.
Diamond
Diamond and graphite materials and structure
Diamond is an allotrope of carbon where the atoms are arranged in a modified version of face-centered cubic (fcc) structure known as "diamond cubic".
It is known for its hardness (see table above) and incompressibility
and is targeted for some potential optical and electrical applications.
The properties of individual natural diamonds or carbonado vary too widely for industrial purposes, and therefore synthetic diamond became a major research focus.
Synthetic diamond
The high-pressure synthesis of diamond in 1953 in Sweden and in 1954 in the US,
made possible by the development of new apparatus and techniques,
became a milestone in synthesis of artificial superhard materials. The
synthesis clearly showed the potential of high-pressure applications for
industrial purposes and stimulated growing interest in the field. Four
years after the first synthesis of artificial diamond, cubic boron nitride c-BN was obtained and found to be the second hardest solid.
Synthetic diamond
can exist as a single, continuous crystal or as small polycrystals
interconnected through the grain boundaries. The inherent spatial
separation of these subunits causes the formation of grains, which are
visible by the unaided eye due to the light absorption and scattering
properties of the material.
The hardness of synthetic diamond (70–150 GPa) is very dependent
on the relative purity of the crystal itself. The more perfect the
crystal structure, the harder the diamond becomes. It has recently been
reported that HPHT single crystals and nanocrystalline diamond
aggregates (aggregated diamond nanorods) can be harder than natural diamond.
Historically, it was thought that synthetic diamond should be
structurally perfect to be useful. This is because diamond was mainly
preferred for its aesthetic qualities, and small flaws in structure and
composition were visible by naked eye. Although this is true, the
properties associated with these small changes has led to interesting
new potential applications of synthetic diamond. For example, nitrogen
doping can enhance mechanical strength of diamond, and heavy doping with boron (several atomic percent) makes it a superconductor.
Cubic boron nitride
History
Cubic boron nitride or c-BN was first synthesized in 1957 by Robert H. Wentorf at General Electric, shortly after the synthesis of diamond.
The general process for c-BN synthesis is the dissolution of hexagonal
boron nitride (h-BN) in a solvent-catalyst, usually alkali or alkaline earth metals or their nitrides, followed by spontaneous nucleation of c-BN under high pressure, high temperature (HPHT) conditions.
The yield of c-BN is lower and substantially slower compared to
diamond's synthetic route due to the complicated intermediate steps. Its
insolubility in iron and other metal alloys makes it more useful for
some industrial applications than diamond.
Sphalerite BN structure
Pure cubic boron nitride is transparent or slightly amber. Different
colors can be produced depending on defects or an excess of boron (less
than 1%).
Defects can be produced by doping solvent-catalysts (i.e. Li, Ca, or Mg
nitrides) with Al, B, Ti, or Si. This induces a change in the
morphology and color of c-BN crystals.
The result is darker and larger (500 μm) crystals with better shapes and a higher yield.
Structure and properties
Cubic boron nitride adopts a sphalerite crystal structure,
which can be constructed by replacing every two carbon atoms in diamond
with one boron atom and one nitrogen atom. The short B-N (1.57 Å) bond
is close to the diamond C-C bond length (1.54 Å), that results in strong
covalent bonding between atoms in the same fashion as in diamond. The
slight decrease in covalency for B-N bonds compared to C-C bonds reduces
the hardness from ~100 GPa for diamond down to 48 GPa in c-BN. As
diamond is less stable than graphite, c-BN is less stable than h-BN, but
the conversion rate between those forms is negligible at room
temperature.
Cubic boron nitride is insoluble in iron, nickel, and related
alloys at high temperatures, but it binds well with metals due to
formation of interlayers of metal borides and nitrides. It is also
insoluble in most acids, but is soluble in alkaline molten salts and
nitrides, such as LiOH, KOH, NaOH/Na2CO3, NaNO3 which are used to etch c-BN.
Because of its stability with heat and metals, c-BN surpasses diamond
in mechanical applications. The thermal conductivity of BN is among the
highest of all electric insulators. In addition, c-BN consists of only
light elements and has low X-ray absorptivity, capable of reducing the
X-ray absorption background.
Research and development
Due
to its great chemical and mechanical robustness, c-BN has widespread
application as an abrasive, such as on cutting tools and scratch
resistant surfaces. Cubic boron nitride is also highly transparent to
X-rays. This, along with its high strength, makes it possible to have
very thin coatings of c-BN on structures that can be inspected using
X-rays. Several hundred tonnes of c-BN are produced worldwide each year.
By modification, Borazon, a US brand name of c-BN, is used in
industrial applications to shape tools, as it can withstand temperatures
greater than 2,000 °C. Cubic boron nitride-coated grinding wheels,
referred to as Borazon wheels, are routinely used in the machining of
hard ferrous metals, cast irons, and nickel-base and cobalt-base superalloys. Other brand names, such as Elbor and Cubonite, are marketed by Russian vendors.
New approaches in research focus on improving c-BN pressure capabilities of the devices used for c-BN synthesis.
At present, the capabilities for the production of c-BN are restricted
to pressures of about 6 GPa. Increasing the pressure limit will permit
synthesis of larger single crystals than from the present catalytic
synthesis. However, the use of solvents under supercritical conditions
for c-BN synthesis has been shown to reduce pressure requirements. The high cost of c-BN still limits its application, which motivates the search for other superhard materials.
Carbon nitride
The structure of beta carbon nitride (β-C3N4) was first proposed by Marvin Cohen and Amy Liu in 1989. It is isostructural with Si3N4 and was predicted to be harder than diamond.
The calculated bond length was 1.47 Å, 5% shorter than the C-C bond
length in diamond. Later calculations indicated that the shear modulus
is 60% of that of diamond, and carbon nitride is less hard than c-BN.
Despite two decades of pursuit of this compound, no synthetic sample of C3N4 has validated the hardness predictions; this has been attributed to the difficulty in synthesis and the instability of C3N4.
Carbon nitride is only stable at a pressure that is higher than that of
the graphite-to-diamond transformation. The synthesis conditions would
require extremely high pressures because carbon is four- and sixfold
coordinated. In addition, C3N4
would pose problems of carbide formation if they were to be used to
machine ferrous metals. Although publications have reported preparation
of C3N4 at lower pressures than stated, synthetic C3N4 was not proved superhard.
Boron carbon nitride
The
similar atomic sizes of boron, carbon and nitrogen, as well as the
similar structures of carbon and boron nitride polymorphs, suggest that
it might be possible to synthesize diamond-like phase containing all
three elements. It is also possible to make compounds containing B-C-O,
B-O-N, or B-C-O-N under high pressure, but their synthesis would expect
to require a complex chemistry and in addition, their elastic properties
would be inferior to that of diamond.
Beginning in 1990, a great interest has been put in studying the
possibility to synthesize dense B-C-N phases. They are expected to be
thermally and chemically more stable than diamond, and harder than c-BN,
and would therefore be excellent materials for high speed cutting and
polishing of ferrous alloys. These characteristic properties are
attributed to the diamond-like structure combined with the sp3 σ-bonds
among carbon and the heteroatoms. BCxNy thin films were synthesized by chemical vapor deposition in 1972.
However, data on the attempted synthesis of B-C-N dense phases reported
by different authors have been contradictory. It is unclear whether the
synthesis products are diamond-like solid solutions between carbon and
boron nitride or just mechanical mixtures of highly dispersed diamond
and c-BN. In 2001, a diamond-like-structured c-BC2N was
synthesized at pressures >18 GPa and temperatures >2,200 K by a
direct solid-state phase transition of graphite-like (BN)0.48C0.52.
The reported Vickers and Knoop hardnesses were intermediate between
diamond and c-BN, making the new phase the second hardest known
material.
Ternary B–C–N phases can also be made using shock-compression
synthesis. It was further suggested to extend the B–C–N system to
quaternary compounds with silicon included.
Metal borides
Unlike
carbon-based systems, metal borides can be easily synthesized in large
quantities under ambient conditions, an important technological
advantage. Most metal borides are hard; however, a few stand out among them for their particularly high hardnesses (for example, WB4, RuB2, OsB2 and ReB2).
These metal borides are still metals and not semiconductors or insulators (as indicated by their high electronic density of states at the Fermi Level); however, the additional covalent B-B and M-B bonding (M = metal) lead to high hardness. Dense heavy metals, such as osmium, rhenium, tungsten
etc., are particularly apt at forming hard borides because of their
high electron densities, small atomic radii, high bulk moduli, and
ability to bond strongly with boron.
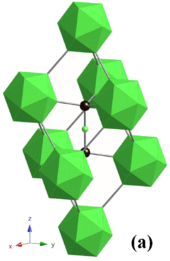
Osmium diboride
Crystal structure of OsB2
Osmium diboride (OsB2)
has a high bulk modulus of 395 GPa and therefore is considered as a
candidate superhard material, but the maximum achieved Vickers hardness
is 37 GPa, slightly below the 40 GPa limit of superhardness. A common
way to synthesize OsB2 is by a solid-state metathesis reaction containing a 2:3 mixture of OsCl3:MgB2. After the MgCl2 product is washed away, X-ray diffraction indicates products of OsB2, OsB and Os. Heating this product at 1,000 °C for three days produces pure OsB2 crystalline product. OsB2 has an orthorhombic structure (space group Pmmn)
with two planes of osmium atoms separated by a non-planar layer of
hexagonally coordinated boron atoms; the lattice parameters are a = 4.684 Å, b = 2.872 Å and c = 4.096 Å. The b direction of the crystal is the most compressible and the c direction is the least compressible. This can be explained by the orthorhombic structure. When looking at the boron and osmium atoms in the a and b
directions, they are arranged in a way that is offset from one another.
Therefore, when they are compressed they are not pushed right up
against one another. Electrostatic repulsion is the force that maximizes
the materials incompressibility and so in this case the electrostatic
repulsion is not taken full advantage of. When compressed in the c
direction, the osmium and boron atoms are almost directly in line with
one another and the electrostatic repulsion is therefore high, causing
direction c to be the least compressible. This model implies that
if boron is more evenly distributed throughout the lattice then
incompressibility could be higher. Electron backscatter diffraction coupled with hardness measurements reveals that in the (010) plane, the crystal is 54% harder in the <100>
than <001> direction. This is seen by looking at how long the
indentation is along a certain direction (related to the indentations
made with a Vickers hardness test). Along with the alignment of the
atoms, this is also due to the short covalent B-B (1.80 Å) bonds in the
<100> direction, which are absent in the <001> direction
(B-B = 4.10 Å).
Rhenium borides
Rhenium
was targeted as a candidate for superhard metal borides because of its
desirable physical and chemical characteristics. It has a high electron
density, a small atomic radius and a high bulk modulus. When combined
with boron, it makes a crystal with highly covalent bonding allowing it
to be incompressible and potentially very hard. A wide array of rhenium borides have been investigated including Re3B, Re7B3, Re2B, ReB, Re2B3, Re3B7, Re2B5, ReB3 and ReB2.
Each of these materials has their own set of properties and
characteristics. Some show promise as superconductors and some have
unique elastic and electronic properties, but the most relevant to
superhard materials is ReB2.
Rhenium diboride (ReB2) is a refractory compound which was first synthesized in the 1960s, using arc melting, zone melting,
or optical floating zone furnaces. An example synthesis of this
material is the flux method, which is conducted by placing rhenium metal
and amorphous boron in an alumina
crucible with excess aluminium. This can be run with a ratio of 1:2:50
for Re:B:Al, with the excess aluminum as a growth medium. The crucible
is placed in an alumina tube, inserted into a resistively heated furnace
with flowing argon gas and sintered at 1,400 °C for several hours. After cooling, the aluminium is dissolved in NaOH. Each ReB2 synthesis route has its own drawbacks, and this one gives small inclusions of aluminum incorporated into the crystal lattice.
Rhenium diboride has a very high melting point approaching 2,400 °C and a highly anisotropic, layered crystal structure. Its symmetry is either hexagonal (space group P63mc) or orthorhombic (Cmcm)
depending on the phase. There, close-packed Re layers alternate with
puckered triangular boron layers along the (001) plane. This can be seen
above on the example of osmium diboride. The density of states for ReB2 has one of the lowest values among the metal borides, indicating strong covalent bonding and high hardness.
Owing to the anisotropic nature of this material, the hardness
depends on the crystal orientation. The (002) plane contains the most
covalent character and exhibits a maximum Vickers hardness value of 40.5
GPa, while the perpendicular planes were 6% lower at 38.1 GPa. These
values decrease with increased load, settling at around 28 GPa each. The
nanoindentation
values were found to be 36.4 GPa and 34.0 GPa for the (002) and
perpendicular planes respectively. The hardness values depend on the
material purity and composition – the more boron the harder the boride –
and the above values are for a Re:B ratio of approximately 1.00:1.85.
Rhenium diboride also has a reported bulk modulus of 383 GPa and a shear
modulus of 273 GPa.
The hardness of rhenium diboride, and most other materials also depends
on the load during the test. The above values of about 40 GPa were all
measured with an effective load of 0.5–1 N. At such low load, the
hardness values are also overestimated for other materials, for example
it exceeds 100 GPa for c-BN. Other researchers, while having reproduced the high ReB2 hardness at low load, reported much lower values of 19–17 GPa at a more conventional load of 3–49 N, that makes ReB2 a hard, but not a superhard material.
Rhenium diboride exhibits metallic conductivity which increases
as temperature decreases and can be explained by a nonzero density of
states due to the d and p overlap of rhenium and boron respectively. At
this point, it is the only superhard material with metallic behavior.
The material also exhibits relatively high thermal stability. Depending
on the heating method, it will maintain its mass up to temperatures of
600–800 °C, with any drop being due to loss of absorbed water. A small
loss of mass can then be seen at temperatures approaching 1,000 °C. It
performs better when a slower heat ramp is utilized. Part of this small
drop at around 1,000 °C was explained by the formation of a dull B2O3
coating on the surface as boron is leached out of the solid, which
serves as a protective coating, thereby reducing additional boron loss.
This can be easily dissolved by methanol to restore the material to it
native shiny state.
Aluminum Magnesium Boride
Aluminum magnesium boride or BAM is a chemical compound of aluminium, magnesium and boron. Whereas its nominal formula is AlMgB14, the chemical composition is closer to Al0.75Mg0.75B14. It is a ceramic alloy that is highly resistive to wear and has a low coefficient of sliding friction.
Other boron-rich superhard materials
Boron carbide
Crystal structure of B6O
Other hard boron-rich compounds include B4C and B6O. Amorphous a-B4C has a hardness of about 50 GPa, which is in the range of superhardness.
It can be looked at as consisting of boron icosahedra-like crystals
embedded in an amorphous medium. However, when studying the crystalline
form of B4C, the hardness is only about 30 GPa. This crystalline form has the same stoichiometry as B13C3, which consists of boron icosahedra connected by boron and carbon atoms. Boron suboxide (B6O) has a hardness of about 35 GPa. Its structure contains eight B12
icosahedra units, which are sitting at the vertices of a rhombohedral
unit cell. There are two oxygen atoms located along the (111)
rhombohedral direction.
Nanostructured superhard materials
Nanosuperhard
materials fall into the extrinsic category of superhard materials.
Because molecular defects affect the superhard properties of bulk
materials it is obvious that the microstructure of superhard materials
give the materials their unique properties. Focus on synthesizing nano
superhard materials is around minimizing microcracks occurring within
the structure through grain boundary hardening. The elimination of
microcracks can strengthen the material by 3 to 7 times its original
strength. Grain boundary strengthening is described by the Hall-Petch equation
Here σc is the critical fracture stress, d the crystallite size and σ0 and kgb are constants.
If a material is brittle its strength depends mainly on the
resistance to forming microcracks. The critical stress which causes the
growth of a microcrack of size a0 is given by a general formula
Here E is the Young's modulus, kcrack is a constant dependent on the nature and shape of the microcrack and the stress applied and γs the surface cohesive energy.
The average hardness of a material decreases with d (crystallite
size) decreasing below 10 nm. There have been many mechanisms proposed
for grain boundary sliding
and hence material softening, but the details are still not understood.
Besides grain boundary strengthening, much attention has been put into
building microheterostructures,
or nanostructures of two materials with very large differences in
elastic moduli. Heterostructures were first proposed in 1970 and
contained such highly ordered thin layers that they could not
theoretically be separated by mechanical means. These highly ordered
heterostructures were believed to be stronger than simple mixtures. This
theory was confirmed with Al/Cu and Al/Ag structures. After the
formation of Al/Cu and Al/Ag, the research was extended to multilayer
systems including Cu/Ni, TiN/VN, W/WN, Hf/HfN and more. In all cases,
decreasing the lattice period increased the hardness. One common form of a nanostructured material is aggregated diamond nanorods, which is harder than bulk diamond and is currently the hardest (~150 GPa) material known.