Coal, one of the fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a fuel formed by natural processes, such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms, containing energy originating in ancient photosynthesis.
The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically
millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years.
Fossil fuels contain high percentages of carbon and include petroleum, coal, and natural gas.
Other commonly used derivatives include kerosene and propane.
Fossil fuels range from volatile materials with low carbon to hydrogen ratios like methane, to liquids like petroleum, to nonvolatile materials composed of almost pure carbon, like anthracite coal.
Methane can be found in hydrocarbon fields either alone, associated with oil, or in the form of methane clathrates.
The theory that fossil fuels formed from the fossilized remains of dead plants by exposure to heat and pressure in the Earth's crust over millions of years was first introduced by Andreas Libavius "in his 1597 Alchemia [Alchymia]" and later by Mikhail Lomonosov "as early as 1757 and certainly by 1763". The first use of the term "fossil fuel" was by the German chemist Caspar Neumann, in English translation in 1759.
The United States Energy Information Administration estimates that in 2007 the world's primary energy sources consisted of petroleum (36.0%), coal (27.4%), natural gas (23.0%), amounting to an 86.4% share for fossil fuels in primary energy consumption in the world.
Non-fossil sources in 2006 included nuclear (8.5%), hydroelectric (6.3%), and others (geothermal, solar, tidal, wind, wood, waste) amounting to 0.9%.
World energy consumption was growing at about 2.3% per year.
Although fossil fuels are continually being formed via natural processes, they are generally considered to be non-renewable resources
because they take millions of years to form and the known viable
reserves are being depleted much faster than new ones are being made.
The use of fossil fuels raises serious environmental concerns.
The burning of fossil fuels produces around 21.3 billion tonnes (21.3 gigatonnes) of carbon dioxide (CO2)
per year.
It is estimated that natural processes can only absorb about half of
that amount, so there is a net increase of 10.65 billion tonnes of
atmospheric carbon dioxide per year.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that increases radiative forcing and contributes to global warming.
A global movement towards the generation of low-carbon renewable energy is underway to help reduce global greenhouse gas emissions.
Origin
Since oil fields are located only at certain places on earth, only some countries are oil-independent; the other countries depend on the oil-production capacities of these countries
Aquatic phytoplankton and zooplankton that died and sedimented in large quantities under anoxic conditions millions of years ago began forming petroleum and natural gas as a result of anaerobic decomposition. Over geological time this organic matter, mixed with mud, became buried under further heavy layers of inorganic sediment. The resulting high levels of heat and pressure caused the organic matter to chemically alter, first into a waxy material known as kerogen which is found in oil shales, and then with more heat into liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons in a process known as catagenesis.
Despite these heat driven transformations (which may increase the
energy density compared to typical organic matter), the embedded energy
is still photosynthetic in origin.
Terrestrial plants, on the other hand, tended to form coal and methane. Many of the coal fields date to the Carboniferous period of Earth's history. Terrestrial plants also form type III kerogen, a source of natural gas.
There is a wide range of organic, or hydrocarbon, compounds in
any given fuel mixture. The specific mixture of hydrocarbons gives a
fuel its characteristic properties, such as boiling point, melting
point, density, viscosity, etc. Some fuels like natural gas, for
instance, contain only very low boiling, gaseous components. Others such
as gasoline or diesel contain much higher boiling components.
Importance
A petrochemical refinery in Grangemouth, Scotland, UK
Fossil fuels are of great importance because they can be burned (oxidized to carbon dioxide and water), producing significant amounts of energy per unit mass. The use of coal as a fuel predates recorded history. Coal was used to run furnaces for the melting of metal ore. Semi-solid hydrocarbons from seeps were also burned in ancient times, but these materials were mostly used for waterproofing and embalming.
Commercial exploitation of petroleum began in the 19th century, largely to replace oils from animal sources (notably whale oil) for use in oil lamps.
Natural gas, once flared-off as an unneeded byproduct of petroleum production, is now considered a very valuable resource. Natural gas deposits are also the main source of the element helium.
Heavy crude oil, which is much more viscous than conventional crude oil, and oil sands, where bitumen is found mixed with sand and clay, began to become more important as sources of fossil fuel as of the early 2000s. Oil shale and similar materials are sedimentary rocks containing kerogen, a complex mixture of high-molecular weight organic compounds, which yield synthetic crude oil when heated (pyrolyzed). These materials have yet to be fully exploited commercially.
With additional processing, they can be employed in lieu of other
already established fossil fuel deposits. More recently, there has been disinvestment from exploitation of such resources due to their high carbon cost, relative to more easily processed reserves.
Prior to the latter half of the 18th century, windmills and watermills provided the energy needed for industry such as milling flour, sawing wood or pumping water, and burning wood or peat provided domestic heat. The widescale use of fossil fuels, coal at first and petroleum later, to fire steam engines enabled the Industrial Revolution. At the same time, gas lights using natural gas or coal gas were coming into wide use. The invention of the internal combustion engine and its use in automobiles and trucks greatly increased the demand for gasoline and diesel oil, both made from fossil fuels. Other forms of transportation, railways and aircraft, also required fossil fuels. The other major use for fossil fuels is in generating electricity and as feedstock for the petrochemical industry. Tar, a leftover of petroleum extraction, is used in construction of roads.
Reserves
An oil well in the Gulf of Mexico
Levels of primary energy sources are the reserves in the ground.
Flows are production of fossil fuels from these reserves. The most
important part of primary energy sources are the carbon
based fossil energy sources. Coal, oil, and natural gas provided 79.6%
of primary energy production during 2002 (in million tonnes of oil
equivalent (mtoe)) (34.9+23.5+21.2).
Levels (proved reserves) during 2005–2006
- Coal: 997,748 million short tonnes (905 billion metric tonnes), 4,416 billion barrels (702.1 km3) of oil equivalent
- Oil: 1,119 billion barrels (177.9 km3) to 1,317 billion barrels (209.4 km3)
- Natural gas: 6,183–6,381 trillion cubic feet (175–181 trillion cubic meters), 1,161 billion barrels (184.6×109 m3) of oil equivalent
Flows (daily production) during 2006
- Coal: 18,476,127 short tonnes (16,761,260 metric tonnes), 52,000,000 barrels (8,300,000 m3) of oil equivalent per day
- Oil: 84,000,000 barrels per day (13,400,000 m3/d)
- Natural gas: 104,435 billion cubic feet (2,963 billion cubic meters), 19,000,000 barrels (3,000,000 m3) of oil equivalent per day
Limits and alternatives
P. E. Hodgson, a senior research fellow emeritus in physics at Corpus
Christi College, Oxford, expects the world energy use is doubling every
fourteen years and the need is increasing faster still and he insisted
in 2008 that the world oil production, a main resource of fossil fuel,
was expected to peak in ten years and thereafter fall.
The principle of supply and demand holds that as hydrocarbon supplies diminish, prices will rise. Therefore, higher prices will lead to increased alternative, renewable energy supplies as previously uneconomic sources become sufficiently economical to exploit. Artificial gasolines and other renewable energy sources currently require more expensive production and processing technologies than conventional petroleum reserves, but may become economically viable in the near future.
Different alternative sources of energy include nuclear, hydroelectric, solar, wind, and geothermal.
One of the more promising energy alternatives is the use of
inedible feed stocks and biomass for carbon dioxide capture as well as
biofuel. While these processes are not without problems, they are
currently in practice around the world. Biodiesels are being produced by
several companies and source of great research at several universities.
Some of the most common and promising processes of conversion of
renewable lipids into usable fuels is through hydrotreating and decarboxylation.
Environmental effects
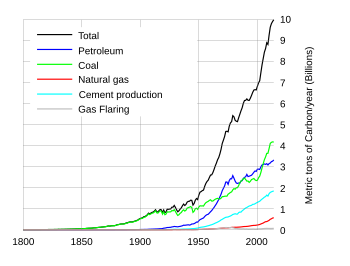
Global fossil carbon emission by fuel type, 1800–2007. Note: Carbon only represents 27% of the mass of CO2
The United States holds less than 5% of the world's population, but
due to large houses and private cars, uses more than 25% of the world's
supply of fossil fuels. As the largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, CO2 from fossil fuel combustion, accounted for 80 percent of [its] weighted emissions in 1998. Combustion of fossil fuels also produces other air pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, volatile organic compounds and heavy metals.
According to Environment Canada:
The electricity sector is unique among industrial sectors in its very large contribution to emissions associated with nearly all air issues. Electricity generation produces a large share of Canadian nitrogen oxides and sulphur dioxide emissions, which contribute to smog and acid rain and the formation of fine particulate matter. It is the largest uncontrolled industrial source of mercury emissions in Canada. Fossil fuel-fired electric power plants also emit carbon dioxide, which may contribute to climate change. In addition, the sector has significant impacts on water and habitat and species. In particular, hydropower dams and transmission lines have significant effects on water and biodiversity.
Carbon dioxide variations over the last 400,000 years, showing a rise since the industrial revolution
According to U.S. Scientist Jerry Mahlman and USA Today: Mahlman, who
crafted the IPCC language used to define levels of scientific
certainty, says the new report will lay the blame at the feet of fossil
fuels with "virtual certainty," meaning 99% sure. That's a significant
jump from "likely," or 66% sure, in the group's last report in 2001,
Mahlman says. His role in this year's effort involved spending two
months reviewing the more than 1,600 pages of research that went into
the new assessment.
Combustion of fossil fuels generates sulfuric, carbonic, and nitric acids, which fall to Earth as acid rain, impacting both natural areas and the built environment. Monuments and sculptures made from marble and limestone are particularly vulnerable, as the acids dissolve calcium carbonate.
Fossil fuels also contain radioactive materials, mainly uranium and thorium, which are released into the atmosphere. In 2000, about 12,000 tonnes of thorium and 5,000 tonnes of uranium were released worldwide from burning coal. It is estimated that during 1982, US coal burning released 155 times as much radioactivity into the atmosphere as the Three Mile Island accident.
Burning coal also generates large amounts of bottom ash and fly ash. These materials are used in a wide variety of applications, utilizing, for example, about 40% of the US production.
Harvesting, processing, and distributing fossil fuels can also create environmental concerns. Coal mining methods, particularly mountaintop removal and strip mining, have negative environmental impacts, and offshore oil drilling poses a hazard to aquatic organisms. Oil refineries
also have negative environmental impacts, including air and water
pollution. Transportation of coal requires the use of diesel-powered
locomotives, while crude oil is typically transported by tanker ships,
each of which requires the combustion of additional fossil fuels.
Environmental regulation
uses a variety of approaches to limit these emissions, such as
command-and-control (which mandates the amount of pollution or the
technology used), economic incentives, or voluntary programs.
An example of such regulation in the USA is the "EPA is
implementing policies to reduce airborne mercury emissions. Under
regulations issued in 2005, coal-fired power plants will need to reduce
their emissions by 70 percent by 2018."
In economic terms, pollution from fossil fuels is regarded as a negative externality.
Taxation is considered one way to make societal costs explicit, in
order to 'internalize' the cost of pollution. This aims to make fossil
fuels more expensive, thereby reducing their use and the amount of
pollution associated with them, along with raising the funds necessary
to counteract these factors.
According to Rodman D. Griffin, "The burning of coal and oil have
saved inestimable amounts of time and labor while substantially raising
living standards around the world".
Although the use of fossil fuels may seem beneficial to our lives, this
act is playing a role on global warming and it is said to be dangerous
for the future.
Moreover, these environmental pollutions impacts on the human
beings because its particles of the fossil fuel on the air cause
negative health effects when inhaled by people. These health effects
include premature death, acute respiratory illness, aggravated asthma,
chronic bronchitis and decreased lung function. So, the poor,
undernourished, very young and very old, and people with preexisting
respiratory disease and other ill health, are more at risk.
Industry
Economic effects
Europe spent €406 billion on importing fossil fuels in 2011 and €545
billion in 2012. This is around three times more than the cost of the Greek bailout up to 2013. In 2012 wind energy in Europe avoided €9.6 billion of fossil fuel costs. A 2014 report by the International Energy Agency said that the fossil fuels industry collects $550 billion a year in global government fossil fuel subsidies. This amount was $490 billion in 2014, but would have been $610 billion without agreements made in 2009.
A 2015 report studied 20 fossil fuel companies and found that,
while highly profitable, the hidden economic cost to society was also
large.
The report spans the period 2008–2012 and notes that: "For all
companies and all years, the economic cost to society of their CO2 emissions was greater than their after‐tax profit, with the single exception of ExxonMobil in 2008."
Pure coal companies fare even worse: "the economic cost to society
exceeds total revenue in all years, with this cost varying between
nearly $2 and nearly $9 per $1 of revenue." In this case, total revenue includes "employment, taxes, supply purchases, and indirect employment."