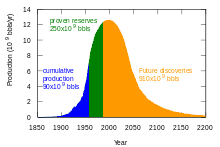
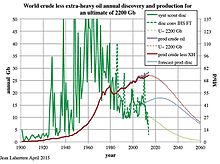
A 1956 world oil production distribution, showing historical data and future production, proposed by M. King Hubbert – it had a peak of 12.5 billion barrels per year in about the year 2000. As of 2016, the world's oil production was 29.4 billion barrels per year (80.6 Mbbl/day),, with an oil glut between 2014 and 2018.
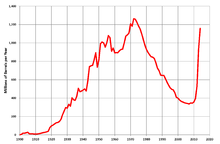
Hubbert's upper-bound prediction for US crude oil production (1956) in red, and actual lower-48 states production through to 2014 in green
Peak oil is the theorized point in time when the maximum rate of extraction of petroleum is reached, after which it is expected to enter terminal decline. Peak oil theory is based on the observed rise, peak, fall, and depletion of aggregate production rate in oil fields over time. It is often confused with oil depletion; however, whereas depletion refers to a period of falling reserves and supply, peak oil refers to the point of maximum production. The concept of peak oil is often credited to geologist M. King Hubbert whose 1956 paper first presented a formal theory.
Some observers, such as petroleum industry experts Kenneth S. Deffeyes and Matthew Simmons, predicted there would be negative global economy effects after a post-peak production decline and subsequent oil price increase because of the continued dependence of most modern industrial transport, agricultural, and industrial systems on the low cost and high availability of oil.
Predictions vary greatly as to what exactly these negative effects
would be. While the notion that petroleum production must peak at some
point is not controversial, the assertion that this must coincide with a
serious economic decline, or even that the decline in production will
necessarily be caused by an exhaustion of available reserves, is not
universally accepted.
Oil production forecasts on which predictions of peak oil are
based are sometimes made within a range which includes optimistic
(higher production) and pessimistic (lower production) scenarios.
According to the International Energy Agency, conventional crude oil production peaked in 2006.
A 2013 study concluded that peak oil "appears probable before 2030",
and that there was a "significant risk" that it would occur before 2020, and assumed that major investments in alternatives
will occur before a crisis, without requiring major changes in the
lifestyle of heavily oil-consuming nations. Pessimistic predictions of
future oil production made after 2007 state either that the peak has
already occurred, that oil production is on the cusp of the peak, or that it will occur soon. These pessimistic predictions have proven false as world oil production has risen and hit a new high in 2018.
Hubbert's original prediction that US peak oil would occur in
about 1970 appeared accurate for a time, as US average annual production
peaked in 1970 at 9.6 million barrels per day and mostly declined for
more than 3 decades after. However, the use of hydraulic fracturing caused US production to rebound during the 2000s, challenging the inevitability of post-peak decline for the US oil production. In addition, Hubbert's original predictions for world peak oil production proved premature.
Nevertheless, the rate of discovery of new petroleum deposits peaked
worldwide during the 1960s and has never approached these levels since.
Modeling global oil production
The idea that the rate of oil production would peak and irreversibly
decline is an old one. In 1919, David White, chief geologist of the United States Geological Survey, wrote of US petroleum: "... the peak of production will soon be passed, possibly within 3 years." In 1953, Eugene Ayers, a researcher for Gulf Oil,
projected that if US ultimate recoverable oil reserves were 100 billion
barrels, then production in the US would peak no later than 1960. If
ultimate recoverable were to be as high as 200 billion barrels, which he
warned was wishful thinking, US peak production would come no later
than 1970. Likewise for the world, he projected a peak somewhere between
1985 (one trillion barrels ultimate recoverable) and 2000 (two trillion
barrels recoverable). Ayers made his projections without a mathematical
model. He wrote: "But if the curve is made to look reasonable, it is
quite possible to adapt mathematical expressions to it and to determine,
in this way, the peak dates corresponding to various ultimate
recoverable reserve numbers"
By observing past discoveries and production levels, and
predicting future discovery trends, the geoscientist M. King Hubbert
used statistical modelling in 1956 to predict that United States oil
production would peak between 1965 and 1971. This prediction appeared accurate for a time
however during 2018 daily production of oil in the United States was
exceeding daily production in 1970, the year that was previously the
peak. Hubbert used a semi-logistical curved model (sometimes incorrectly compared to a normal distribution).
He assumed the production rate of a limited resource would follow a
roughly symmetrical distribution. Depending on the limits of
exploitability and market pressures, the rise or decline of resource
production over time might be sharper or more stable, appear more linear
or curved. That model and its variants are now called Hubbert peak theory;
they have been used to describe and predict the peak and decline of
production from regions, countries, and multinational areas. The same theory has also been applied to other limited-resource production.
More recently, the term "peak oil" was popularized by Colin Campbell and Kjell Aleklett in 2002 when they helped form the Association for the Study of Peak Oil and Gas (ASPO). In his publications, Hubbert used the term "peak production rate" and "peak in the rate of discoveries".
In a 2006 analysis of Hubbert theory, it was noted that
uncertainty in real world oil production amounts and confusion in
definitions increases the uncertainty in general of production
predictions. By comparing the fit of various other models, it was found
that Hubbert's methods yielded the closest fit over all, but that none
of the models were very accurate.
In 1956 Hubbert himself recommended using "a family of possible
production curves" when predicting a production peak and decline curve.
A comprehensive 2009 study of oil depletion by the UK Energy Research Centre noted:
Few analysts now adhere to a symmetrical bell-shaped production curve. This is correct, as there is no natural physical reason why the production of a resource should follow such a curve and little empirical evidence that it does.
— Bentley et al., Comparison of global oil supply forecasts
The report noted that Hubbert had used the logistic curve because it
was mathematically convenient, not because he firmly believed it to be
correct. The study observed that in most cases, the asymmetric
exponential model provided a better fit, and that peaks tended to occur
well before half the oil had been produced, with the result that in
nearly all cases, the post-peak decline was more gradual than the
increase leading up to the peak.
Demand
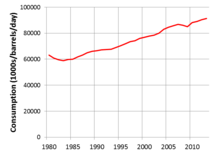
Global consumption of oil 1980–2013 (Energy Information Administration)
The demand
side of peak oil over time is concerned with the total quantity of oil
that the global market would choose to consume at various possible
market prices and how this entire listing of quantities at various
prices would evolve over time. Global demand for crude oil grew an
average of 1.76% per year from 1994 to 2006, with a high growth of 3.4%
in 2003–2004. After reaching a high of 85.6 million barrels
(13,610,000 m3) per day in 2007, world consumption decreased in both 2008 and 2009 by a total of 1.8%, despite fuel costs plummeting in 2008.
In spite of this lull, world's demanded for oil is projected to
increase 21% over 2007 levels by 2030 (104 million barrels per day (16.5×106 m3/d) from 86 million barrels (13.7×106 m3)), or about 0.8% average annual growth, largely due to increases in demand from the transportation sector. According to projections by the International Energy Agency
(IEA) in 2013, growth in global oil demand will be significantly
outpaced by growth in production capacity over the next 5 years. Developments in late 2014–2015 have seen an oversupply of global markets leading to a significant drop in the price of oil.
Energy demand is distributed amongst four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial.
In terms of oil use, transportation is the largest sector and the one
that has seen the largest growth in demand in recent decades. This
growth has largely come from new demand for personal-use vehicles
powered by internal combustion engines. This sector also has the highest consumption rates, accounting for approximately 71% of the oil used in the United States in 2013. and 55% of oil use worldwide as documented in the Hirsch report. Transportation is therefore of particular interest to those seeking to mitigate the effects of peak oil.
Oil consumption in bbl per day per capita (darker colors represent more consumption, gray represents no data) (source: NationMaster statistics, 2007-01-13)
| > 0.07 0.07 - 0.05 0.05 - 0.035 0.035 - 0.025 0.025 - 0.02 | 0.02 - 0.015 0.015 - 0.01 0.01 - 0.005 0.005 - 0.0015 < 0.0015 |
Although demand growth is highest in the developing world,
the United States is the world's largest consumer of petroleum. Between
1995 and 2005, US consumption grew from 17,700,000 barrels per day
(2,810,000 m3/d) to 20,700,000 barrels per day (3,290,000 m3/d), a 3,000,000 barrels per day (480,000 m3/d) increase. China, by comparison, increased consumption from 3,400,000 barrels per day (540,000 m3/d) to 7,000,000 barrels per day (1,100,000 m3/d), an increase of 3,600,000 barrels per day (570,000 m3/d), in the same time frame. The Energy Information Administration
(EIA) stated that gasoline usage in the United States may have peaked
in 2007, in part because of increasing interest in and mandates for use
of biofuels and energy efficiency.
As countries develop, industry and higher living standards drive up energy use, oil usage being a major component. Thriving economies, such as China and India, are quickly becoming large oil consumers. For example, China surpassed the United States as the world's largest crude oil importer in 2015.
Oil consumption growth is expected to continue; however, not at
previous rates, as China's economic growth is predicted to decrease from
the high rates of the early part of the 21st century. India's oil imports are expected to more than triple from 2005 levels by 2020, rising to 5 million barrels per day (790×103 m3/d).
Population
World population
Another significant factor affecting petroleum demand has been human population growth. The United States Census Bureau predicts that world population in 2030 will be almost double that of 1980. Oil production per capita peaked in 1979 at 5.5 barrels/year but then declined to fluctuate around 4.5 barrels/year since. In this regard, the decreasing population growth rate since the 1970s has somewhat ameliorated the per capita decline.
Economic growth
Some
analysts argue that the cost of oil has a profound effect on economic
growth due to its pivotal role in the extraction of resources and the
processing, manufacturing, and transportation of goods.
As the industrial effort to extract new unconventional oil sources
increases, this has a compounding negative effect on all sectors of the
economy, leading to economic stagnation or even eventual contraction.
Such a scenario would result in an inability for national economies to
pay high oil prices, leading to declining demand and a price collapse.
Supply
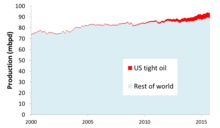
Global liquids production 2000-2015, indicating the component of US tight oil (Energy Information Administration)
Our analysis suggests there are ample physical oil and liquid fuel resources for the foreseeable future. However, the rate at which new supplies can be developed and the break-even prices for those new supplies are changing.
Defining sources of oil
Oil
may come from conventional or unconventional sources. The terms are not
strictly defined, and vary within the literature as definitions based
on new technologies tend to change over time.
As a result, different oil forecasting studies have included different
classes of liquid fuels. Some use the terms "conventional" oil for what
is included in the model, and "unconventional" oil for classes excluded.
In 1956, Hubbert confined his peak oil prediction to that crude oil "producible by methods now in use." By 1962, however, his analyses included future improvements in exploration and production.
All of Hubbert's analyses of peak oil specifically excluded oil
manufactured from oil shale or mined from oil sands. A 2013 study
predicting an early peak excluded deepwater oil, tight oil, oil with API
gravity less than 17.5, and oil close to the poles, such as that on the
North Slope of Alaska, all of which it defined as non-conventional. Some commonly used definitions for conventional and unconventional oil are detailed below.
Conventional sources
Conventional oil is extracted on land and offshore using standard techniques,
and can be categorized as light, medium, heavy, or extra heavy in
grade. The exact definitions of these grades vary depending on the
region from which the oil came.
Light oil flows naturally to the surface or can be extracted by simply
pumping it out of the ground. Heavy refers to oil that has higher
density and therefore lower API gravity.
It does not flow easily, and its consistency is similar to that of
molasses. While some of it can be produced using conventional
techniques, recovery rates are better using unconventional methods.
According to the International Energy Agency, conventional crude oil production peaked in 2006, with al all-time maximum of 70 millions of barrels per day.
Unconventional sources
Oil currently considered unconventional is derived from multiple sources.
- Tight oil is extracted from deposits of low-permeability rock, sometimes shale deposits but often other rock types, using hydraulic fracturing, or "fracking." It is often confused with shale oil, which is oil manufactured from the kerogen contained in an oil shale (see below), Production of tight oil has led to a resurgence of US production in recent years. U.S. tight oil production peaked in March 2015, and fell a total of 12 percent over the next 18 months. But then U.S. tight oil production rose again, and by September 2017 had exceeded the old peak, and as of October 2017, U.S. tight oil production was still rising.
US
Lower 48 oil production from 2012 and anticipated decline in production
to the end of 2017, with rig count (Energy Information Administration)
- Oil shale is a common term for sedimentary rock such as shale or marl, containing kerogen, a waxy oil precursor that has not yet been transformed into crude oil by the high pressures and temperatures caused by deep burial. The term "oil shale" is somewhat confusing, because what is referred to in the U.S. as "oil shale" is not really oil and the rock it is found in is generally not shale. Since it is close to the surface rather than buried deep in the earth, the shale or marl is typically mined, crushed, and retorted, producing synthetic oil from the kerogen. Its net energy yield is much lower than conventional oil, so much so that estimates of the net energy yield of shale discoveries are considered extremely unreliable.
- Oil sands are unconsolidated sandstone deposits containing large amounts of very viscous crude bitumen or extra-heavy crude oil that can be recovered by surface mining or by in-situ oil wells using steam injection or other techniques. It can be liquefied by upgrading, blending with diluent, or by heating; and then processed by a conventional oil refinery. The recovery process requires advanced technology but is more efficient than that of oil shale. The reason is that, unlike U.S. "oil shale", Canadian oil sands actually contain oil, and the sandstones they are found in are much easier to produce oil from than shale or marl. In the U.S. dialect of English, these formations are often called "tar sands", but the material found in them is not tar but an extra-heavy and viscous form of oil technically known as bitumen. Venezuela has oil sands deposits similar in size to those of Canada, and approximately equal to the world's reserves of conventional oil. Venezuela's Orinoco Belt tar sands are less viscous than Canada's Athabasca oil sands – meaning they can be produced by more conventional means – but they are buried too deep to be extracted by surface mining. Estimates of the recoverable reserves of the Orinoco Belt range from 100 billion barrels (16×109 m3) to 270 billion barrels (43×109 m3). In 2009, USGS updated this value to 513 billion barrels (8.16×1010 m3).
United States crude oil production exceeds imports for the first time since the early 1990s
- Coal liquefaction or gas to liquids product are liquid hydrocarbons that are synthesised from the conversion of coal or natural gas by the Fischer-Tropsch process, Bergius process, or Karrick process. Currently, two companies SASOL and Shell, have synthetic oil technology proven to work on a commercial scale. Sasol's primary business is based on CTL (coal-to-liquid) and GTL (natural gas-to-liquid) technology, producing US$4.40 billion in revenues (FY2009). Shell has used these processes to recycle waste flare gas (usually burnt off at oil wells and refineries) into usable synthetic oil. However, for CTL there may be insufficient coal reserves to supply global needs for both liquid fuels and electric power generation.
- Minor sources include thermal depolymerization, as discussed in a 2003 article in Discover magazine, that could be used to manufacture oil indefinitely, out of garbage, sewage, and agricultural waste. The article claimed that the cost of the process was $15 per barrel. A follow-up article in 2006 stated that the cost was actually $80 per barrel, because the feedstock that had previously been considered as hazardous waste now had market value. A 2008 news bulletin published by Los Alamos Laboratory proposed that hydrogen (possibly produced using hot fluid from nuclear reactors to split water into hydrogen and oxygen) in combination with sequestered CO2 could be used to produce methanol (CH3OH), which could then be converted into gasoline.
Discoveries
All the easy oil and gas in the world has pretty much been found. Now comes the harder work in finding and producing oil from more challenging environments and work areas.
— William J. Cummings, Exxon-Mobil company spokesman, December 2005
It is pretty clear that there is not much chance of finding any significant quantity of new cheap oil. Any new or unconventional oil is going to be expensive.
— Lord Ron Oxburgh, a former chairman of Shell, October 2008
World oil discoveries peaked in the 1960s
The peak of world oilfield discoveries occurred in the 1960s at around 55 billion barrels (8.7×109 m3)(Gb)/year.
According to the Association for the Study of Peak Oil and Gas (ASPO),
the rate of discovery has been falling steadily since. Less than 10
Gb/yr of oil were discovered each year between 2002 and 2007.
According to a 2010 Reuters article, the annual rate of discovery of
new fields has remained remarkably constant at 15–20 Gb/yr.
Although
US proved oil reserves grew by 3.8 billion barrels in 2011, even after
deducting 2.07 billion barrels of production, only 8 percent of the 5.84
billion barrels of the newly booked oil was because of new field
discoveries (U.S. EIA)
But despite the fall-off in new field discoveries, and record-high
production rates, the reported proved reserves of crude oil remaining in
the ground in 2014, which totaled 1,490 billion barrels, not counting
Canadian heavy oil sands, were more than quadruple the 1965 proved
reserves of 354 billion barrels. A researcher for the U.S. Energy Information Administration
has pointed out that after the first wave of discoveries in an area,
most oil and natural gas reserve growth comes not from discoveries of
new fields, but from extensions and additional gas found within existing
fields.
A report by the UK Energy Research Centre noted that "discovery"
is often used ambiguously, and explained the seeming contradiction
between falling discovery rates since the 1960s and increasing reserves
by the phenomenon of reserve growth. The report noted that increased
reserves within a field may be discovered or developed by new technology
years or decades after the original discovery. But because of the
practice of "backdating," any new reserves within a field, even those to
be discovered decades after the field discovery, are attributed to the
year of initial field discovery, creating an illusion that discovery is
not keeping pace with production.
Reserves
Proven oil reserves, 2013
Total possible conventional crude oil reserves
include crude oil with 90% certainty of being technically able to be
produced from reservoirs (through a wellbore using primary, secondary,
improved, enhanced, or tertiary methods); all crude with a 50%
probability of being produced in the future (probable); and discovered
reserves that have a 10% possibility of being produced in the future
(possible). Reserve estimates based on these are referred to as 1P,
proven (at least 90% probability); 2P, proven and probable (at least 50%
probability); and 3P, proven, probable and possible (at least 10%
probability), respectively. This does not include liquids extracted from mined solids or gasses (oil sands, oil shale, gas-to-liquid processes, or coal-to-liquid processes).
Hubbert's 1956 peak projection for the United States depended on
geological estimates of ultimate recoverable oil resources, but starting
in his 1962 publication, he concluded that ultimate oil recovery was an
output of his mathematical analysis, rather than an assumption. He
regarded his peak oil calculation as independent of reserve estimates.
Many current 2P calculations predict reserves to be between 1150
and 1350 Gb, but some authors have written that because of
misinformation, withheld information, and misleading reserve
calculations, 2P reserves are likely nearer to 850–900 Gb.
The Energy Watch Group wrote that actual reserves peaked in 1980, when
production first surpassed new discoveries, that apparent increases in
reserves since then are illusory, and concluded (in 2007): "Probably the
world oil production has peaked already, but we cannot be sure yet."
Concerns over stated reserves
[World] reserves are confused and in fact inflated. Many of the so-called reserves are in fact resources. They're not delineated, they're not accessible, they're not available for production.
— Sadad Al Husseini, former VP of Aramco, presentation to the Oil and Money conference, October 2007.
Sadad Al Husseini estimated that 300 billion barrels (48×109 m3) of the world's 1,200 billion barrels (190×109 m3) of proven reserves should be recategorized as speculative resources.
Graph
of OPEC reported reserves showing jumps in stated reserves without
associated discoveries, as well as the lack of depletion despite yearly
production
One difficulty in forecasting the date of peak oil is the opacity
surrounding the oil reserves classified as "proven". In many major
producing countries, the majority of reserves claims have not been
subject to outside audit or examination. Many worrying signs concerning the depletion of proven reserves have emerged in recent years. This was best exemplified by the 2004 scandal surrounding the "evaporation" of 20% of Shell's reserves.
For the most part, proven reserves are stated by the oil
companies, the producer states and the consumer states. All three have
reasons to overstate their proven reserves: oil companies may look to
increase their potential worth; producer countries gain a stronger international stature; and governments of consumer countries may seek a means to foster sentiments of security and stability within their economies and among consumers.
Major discrepancies arise from accuracy issues with the self-reported numbers from the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries
(OPEC). Besides the possibility that these nations have overstated
their reserves for political reasons (during periods of no substantial
discoveries), over 70 nations also follow a practice of not reducing
their reserves to account for yearly production. Analysts have suggested
that OPEC member nations have economic incentives to exaggerate their
reserves, as the OPEC quota system allows greater output for countries
with greater reserves.
Kuwait, for example, was reported in the January 2006 issue of Petroleum Intelligence Weekly to have only 48 billion barrels (7.6×109 m3)
in reserve, of which only 24 were fully proven. This report was based
on the leak of a confidential document from Kuwait and has not been
formally denied by the Kuwaiti authorities. This leaked document is from
2001, but excludes revisions or discoveries made since then. Additionally, the reported 1.5 billion barrels (240×106 m3) of oil burned off by Iraqi soldiers in the First Persian Gulf War are conspicuously missing from Kuwait's figures.
On the other hand, investigative journalist Greg Palast argues that oil companies have an interest in making oil look more rare than it is, to justify higher prices. This view is contested by ecological journalist Richard Heinberg. Other analysts argue that oil producing countries understate the extent of their reserves to drive up the price.
The EUR reported by the 2000 USGS survey of 2,300 billion barrels (370×109 m3)
has been criticized for assuming a discovery trend over the next twenty
years that would reverse the observed trend of the past 40 years. Their
95% confidence EUR of 2,300 billion barrels (370×109 m3)
assumed that discovery levels would stay steady, despite the fact that
new-field discovery rates have declined since the 1960s. That trend of
falling discoveries has continued in the ten years since the USGS made
their assumption. The 2000 USGS is also criticized for other
assumptions, as well as assuming 2030 production rates inconsistent with
projected reserves.
Reserves of unconventional oil
Syncrude's Mildred Lake mine site and plant near Fort McMurray, Alberta
As conventional oil becomes less available, it can be replaced with production of liquids from unconventional sources such as tight oil, oil sands, ultra-heavy oils, gas-to-liquid technologies, coal-to-liquid technologies, biofuel technologies, and shale oil. In the 2007 and subsequent International Energy Outlook editions, the word "Oil" was replaced with "Liquids" in the chart of world energy consumption. In 2009 biofuels was included in "Liquids" instead of in "Renewables".
The inclusion of natural gas liquids, a bi-product of natural gas
extraction, in "Liquids" has been criticized as it is mostly a chemical
feedstock which is generally not used as transport fuel.
Texas oil production declined since peaking in 1972 but has recently had a resurgence due to tight oil production
Reserve estimates are based on the oil price. Hence, unconventional
sources such as heavy crude oil, oil sands, and oil shale may be
included as new techniques reduce the cost of extraction. With rule changes by the SEC, oil companies can now book them as proven reserves after opening a strip mine or thermal facility for extraction.
These unconventional sources are more labor and resource intensive to
produce, however, requiring extra energy to refine, resulting in higher
production costs and up to three times more greenhouse gas
emissions per barrel (or barrel equivalent) on a "well to tank" basis
or 10 to 45% more on a "well to wheels" basis, which includes the carbon
emitted from combustion of the final product.
While the energy used, resources needed, and environmental
effects of extracting unconventional sources have traditionally been
prohibitively high, major unconventional oil sources being considered for large-scale production are the extra heavy oil in the Orinoco Belt of Venezuela, the Athabasca Oil Sands in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin, and the oil shale of the Green River Formation in Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming in the United States. Energy companies such as Syncrude and Suncor have been extracting bitumen for decades but production has increased greatly in recent years with the development of Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage and other extraction technologies.
Chuck Masters of the USGS estimates that, "Taken together, these resource occurrences, in the Western Hemisphere, are approximately equal to the Identified Reserves of conventional crude oil accredited to the Middle East."
Authorities familiar with the resources believe that the world's
ultimate reserves of unconventional oil are several times as large as
those of conventional oil and will be highly profitable for companies as
a result of higher prices in the 21st century. In October 2009, the USGS updated the Orinoco tar sands (Venezuela) recoverable "mean value" to 513 billion barrels (8.16×1010 m3), with a 90% chance of being within the range of 380-652 billion barrels (103.7×109 m3), making this area "one of the world's largest recoverable oil accumulations".
Unconventional resources are much larger than conventional ones.
Despite the large quantities of oil available in non-conventional
sources, Matthew Simmons argued in 2005 that limitations on production
prevent them from becoming an effective substitute for conventional
crude oil. Simmons stated "these are high energy intensity projects that
can never reach high volumes" to offset significant losses from other
sources.
Another study claims that even under highly optimistic assumptions,
"Canada's oil sands will not prevent peak oil," although production
could reach 5,000,000 bbl/d (790,000 m3/d) by 2030 in a "crash program" development effort.
Moreover, oil extracted from these sources typically contains contaminants such as sulfur and heavy metals that are energy-intensive to extract and can leave tailings, ponds containing hydrocarbon sludge, in some cases. The same applies to much of the Middle East's
undeveloped conventional oil reserves, much of which is heavy, viscous,
and contaminated with sulfur and metals to the point of being unusable. However, high oil prices make these sources more financially appealing.
A study by Wood Mackenzie suggests that by the early 2020s all the
world's extra oil supply is likely to come from unconventional sources.
Production
The point in time when peak global oil production occurs defines peak
oil. Some adherents of 'peak oil' believe that production capacity will
remain the main limitation of supply, and that when production
decreases, it will be the main bottleneck to the petroleum supply/demand equation.
Others believe that the increasing industrial effort to extract oil
will have a negative effect on global economic growth, leading to demand
contraction and a price collapse,
thereby causing production decline as some unconventional sources
become uneconomical. Yet others believe that the peak may be to some
extent led by declining demand as new technologies and improving
efficiency shift energy usage away from oil.
Worldwide oil discoveries have been less than annual production since 1980. World population has grown faster than oil production. Because of this, oil production per capita peaked in 1979 (preceded by a plateau during the period of 1973–1979).
Countries producing oil 2013, bbl/day (CIA World Factbook)
Oil producing countries (information from 2006–2012)
The increasing investment in harder-to-reach oil as of 2005 was said to signal oil companies' belief in the end of easy oil.
While it is widely believed that increased oil prices spur an increase
in production, an increasing number of oil industry insiders were
reportedly coming to believe in 2009 that even with higher prices, oil
production was unlikely to increase significantly. Among the reasons
cited were both geological factors as well as "above ground" factors
that are likely to see oil production plateau.
A 2008 Journal of Energy Security analysis of the energy return on drilling effort (energy returned on energy invested,
also referred to as EROEI) in the United States concluded that there
was extremely limited potential to increase production of both gas and
(especially) oil. By looking at the historical response of production to
variation in drilling effort, the analysis showed very little increase
of production attributable to increased drilling. This was because of
diminishing returns with increasing drilling effort: as drilling effort
increased, the energy obtained per active drill rig was reduced according to a severely diminishing power law.
The study concluded that even an enormous increase of drilling effort
was unlikely to significantly increase oil and gas production in a
mature petroleum region such as the United States.
However, contrary to the study's conclusion, since the analysis was
published in 2008, US production of crude oil has increased 86%, and
production of dry natural gas has increased 34% (2015 compared to 2008).
The assumption of inevitable declining volumes of oil and gas
produced per unit of effort is contrary to recent experience in the US.
In the United States, as of 2017, there has been an ongoing decade-long
increase in the productivity of oil and gas drilling in all the major
tight oil and gas plays. The US Energy Information Administration
reports, for instance, that in the Bakken Shale production area of North
Dakota, the volume of oil produced per day of drilling rig time in
January 2017 was 4 times the oil volume per day of drilling five years
previous, in January 2012, and nearly 10 times the oil volume per day of
ten years previous, in January 2007. In the Marcellus gas region of the
northeast, The volume of gas produced per day of drilling time in
January 2017 was 3 times the gas volume per day of drilling five years
previous, in January 2012, and 28 times the gas volume per day of
drilling ten years previous, in January 2007.
Anticipated production by major agencies
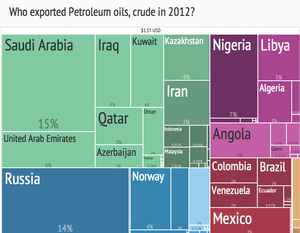
Crude oil export treemap (2012) from Harvard Atlas of Economic Complexity
Average yearly gains in global supply from 1987 to 2005 were 1.2 million barrels per day (190×103 m3/d) (1.7%). In 2005, the IEA predicted that 2030 production rates would reach 120,000,000 barrels per day (19,000,000 m3/d), but this number was gradually reduced to 105,000,000 barrels per day (16,700,000 m3/d).
A 2008 analysis of IEA predictions questioned several underlying
assumptions and claimed that a 2030 production level of 75,000,000
barrels per day (11,900,000 m3/d) (comprising 55,000,000 barrels (8,700,000 m3) of crude oil and 20,000,000 barrels (3,200,000 m3) of both non-conventional oil and natural gas liquids) was more realistic than the IEA numbers.
More recently, the EIA's Annual Energy Outlook 2015 indicated no
production peak out to 2040. However, this required a future Brent crude
oil price of $US144/bbl (2013 dollars) "as growing demand leads to the
development of more costly resources". Whether the world economy can grow and maintain demand for such a high oil price remains to be seen.
Oil field decline
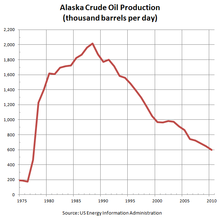
Alaska's oil production has declined 70% since peaking in 1988
In a 2013 study of 733 giant oil fields, only 32% of the ultimately recoverable oil, condensate and gas remained. Ghawar,
which is the largest oil field in the world and responsible for
approximately half of Saudi Arabia's oil production over the last
50 years, was in decline before 2009. The world's second largest oil field, the Burgan Field in Kuwait, entered decline in November 2005.
Mexico announced that production from its giant Cantarell Field began to decline in March 2006, reportedly at a rate of 13% per year. Also in 2006, Saudi Aramco Senior Vice President Abdullah Saif estimated that its existing fields were declining at a rate of 5% to 12% per year. According to a study of the largest 811 oilfields conducted in early 2008 by Cambridge Energy Research Associates,
the average rate of field decline is 4.5% per year. The Association for
the Study of Peak Oil and Gas agreed with their decline rates, but
considered the rate of new fields coming online overly optimistic. The IEA
stated in November 2008 that an analysis of 800 oilfields showed the
decline in oil production to be 6.7% a year for fields past their peak,
and that this would grow to 8.6% in 2030.
A more rapid annual rate of decline of 5.1% in 800 of the world's
largest oil fields weighted for production over their whole lives was
reported by the International Energy Agency in their World Energy Outlook 2008.
The 2013 study of 733 giant fields mentioned previously had an average
decline rate 3.83% which was described as "conservative."
Control over supply
Entities
such as governments or cartels can reduce supply to the world market by
limiting access to the supply through nationalizing oil, cutting back
on production, limiting drilling rights, imposing taxes, etc.
International sanctions, corruption, and military conflicts can also
reduce supply.
Nationalization of oil supplies
Another factor affecting global oil supply is the nationalization of oil reserves by producing nations. The nationalization of oil occurs as countries begin to deprivatize
oil production and withhold exports. Kate Dourian, Platts' Middle East
editor, points out that while estimates of oil reserves may vary,
politics have now entered the equation of oil supply. "Some countries
are becoming off limits. Major oil companies operating in Venezuela find
themselves in a difficult position because of the growing
nationalization of that resource. These countries are now reluctant to
share their reserves."
According to consulting firm PFC Energy,
only 7% of the world's estimated oil and gas reserves are in countries
that allow companies like ExxonMobil free rein. Fully 65% are in the
hands of state-owned companies such as Saudi Aramco, with the rest in
countries such as Russia and Venezuela, where access by Western European
and North American companies is difficult. The PFC study implies
political factors are limiting capacity increases in Mexico, Venezuela, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Russia. Saudi Arabia is also limiting capacity expansion, but because of a self-imposed cap, unlike the other countries.
As a result of not having access to countries amenable to oil
exploration, ExxonMobil is not making nearly the investment in finding
new oil that it did in 1981.
OPEC influence on supply
OPEC surplus crude oil production capacity, 2002–2012 (US EIA)
OPEC is an alliance among 14 diverse oil-producing countries (as of
May 2017: Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran,
Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates,
Venezuela) to manage the supply of oil. OPEC's power was consolidated
in the 1960s and 1970s as various countries nationalized their oil
holdings, and wrested decision-making away from the "Seven Sisters"
(Anglo-Iranian, Socony, Royal Dutch Shell, Gulf, Esso, Texaco, Socal),
and created their own oil companies to control the oil. OPEC often tries
to influence prices by restricting production. It does this by
allocating each member country a quota for production. Members agree to
keep prices high by producing at lower levels than they otherwise would.
There is no way to enforce adherence to the quota, so each member has
an individual incentive to "cheat" the cartel.
Commodities trader Raymond Learsy, author of Over a Barrel: Breaking the Middle East Oil Cartel,
contends that OPEC has trained consumers to believe that oil is a much
more finite resource than it is. To back his argument, he points to past
false alarms and apparent collaboration.
He also believes that peak oil analysts have conspired with OPEC and
the oil companies to create a "fabricated drama of peak oil" to drive up
oil prices and profits;
oil had risen to a little over $30/barrel at that time. A
counter-argument was given in the Huffington Post after he and Steve
Andrews, co-founder of ASPO, debated on CNBC in June 2007.
Predictions
| Pub. | Made by | Peak year/range | Pub. | Made by | Peak year/range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1972 | Esso | About 2000 | 1999 | Parker | 2040 |
| 1972 | United Nations | By 2000 | 2000 | Bartlett | 2004 or 2019 |
| 1974 | Hubbert | 1991–2000 | 2000 | Duncan | 2006 |
| 1976 | UK Dep. of Energy | About 2000 | 2000 | EIA | 2021–2067 |
| 1977 | Hubbert | 1996 | 2000 | EIA (WEO) | Beyond 2020 |
| 1977 | Ehrlich, et al. | 2000 | 2001 | Deffeyes | 2003–2008 |
| 1979 | Shell | Plateau by 2004 | 2001 | Goodstein | 2007 |
| 1981 | World Bank | Plateau around 2000 | 2002 | Smith | 2010–2016 |
| 1985 | J. Bookout | 2020 | 2002 | Campbell | 2010 |
| 1989 | Campbell | 1989 | 2002 | Cavallo | 2025–2028 |
| 1994 | L. F. Ivanhoe | OPEC plateau 2000–50 | 2003 | Greene | 2020–2050 |
| 1995 | Petroconsultants | 2005 | 2003 | Laherrère | 2010–2020 |
| 1997 | Ivanhoe | 2010 | 2003 | Lynch | No visible peak |
| 1997 | J. D. Edwards | 2020 | 2003 | Shell | After 2025 |
| 1998 | IEA | 2014 | 2003 | Simmons | 2007–2009 |
| 1998 | Campbell & Laherrère | 2004 | 2004 | Bakhitari | 2006–2007 |
| 1999 | Campbell | 2010 | 2004 | CERA | After 2020 |
| 1999 | Peter Odell | 2060 | 2004 | PFC Energy | 2015–2020 |
In 1962, Hubbert predicted that world oil production would peak at a
rate of 12.5 billion barrels per year, around the year 2000. In 1974, Hubbert predicted that peak oil would occur in 1995 "if current trends continue".
Those predictions proved incorrect. However, a number of industry
leaders and analysts believe that world oil production will peak between
2015 and 2030, with a significant chance that the peak will occur
before 2020. They consider dates after 2030 implausible. By comparison, a 2014 analysis of production and reserve data predicted a peak in oil production about 2035. Determining a more specific range is difficult due to the lack of certainty over the actual size of world oil reserves. Unconventional oil is not currently predicted to meet the expected shortfall even in a best-case scenario.
For unconventional oil to fill the gap without "potentially serious
impacts on the global economy", oil production would have to remain
stable after its peak, until 2035 at the earliest.
Papers published since 2010 have been relatively pessimistic. A 2010 Kuwait University study predicted production would peak in 2014. A 2010 Oxford University study predicted that production will peak before 2015,
but its projection of a change soon "... from a demand-led market to a
supply constrained market ..." was incorrect. A 2014 validation of a
significant 2004 study in the journal Energy proposed that it is
likely that conventional oil production peaked, according to various
definitions, between 2005 and 2011. A set of models published in a 2014
Ph.D. thesis predicted that a 2012 peak would be followed by a drop in
oil prices, which in some scenarios could turn into a rapid rise in
prices thereafter. According to energy blogger Ron Patterson, the peak of world oil production was probably around 2010.
Major oil companies hit peak production in 2005. Several sources in 2006 and 2007 predicted that worldwide production was at or past its maximum. However, in 2013 OPEC's figures showed that world crude oil production and remaining proven reserves were at record highs. According to Matthew Simmons, former Chairman of Simmons & Company International and author of Twilight in the Desert: The Coming Saudi Oil Shock and the World Economy,
"peaking is one of these fuzzy events that you only know clearly when
you see it through a rear view mirror, and by then an alternate
resolution is generally too late."
Possible consequences
The wide use of fossil fuels has been one of the most important stimuli of economic growth and prosperity since the industrial revolution,
allowing humans to participate in takedown, or the consumption of
energy at a greater rate than it is being replaced. Some believe that
when oil production decreases, human culture and modern technological
society will be forced to change drastically. The impact of peak oil
will depend heavily on the rate of decline and the development and
adoption of effective alternatives.
In 2005, the United States Department of Energy published a report titled Peaking of World Oil Production: Impacts, Mitigation, & Risk Management. Known as the Hirsch report,
it stated, "The peaking of world oil production presents the U.S. and
the world with an unprecedented risk management problem. As peaking is
approached, liquid fuel prices and price volatility will increase
dramatically, and, without timely mitigation, the economic, social, and
political costs will be unprecedented. Viable mitigation options exist
on both the supply and demand sides, but to have substantial impact,
they must be initiated more than a decade in advance of peaking." Some
of the information was updated in 2007.
Oil prices
Historical oil prices
Long-term oil prices, 1861–2015 (top line adjusted for inflation)
The oil price historically was comparatively low until the 1973 oil crisis and the 1979 energy crisis
when it increased more than tenfold during that six-year timeframe.
Even though the oil price dropped significantly in the following years,
it has never come back to the previous levels. Oil price began to
increase again during the 2000s until it hit historical heights of $143
per barrel (2007 inflation adjusted dollars) on 30 June 2008. As these prices were well above those that caused the 1973 and 1979 energy crises, they contributed to fears of an economic recession similar to that of the early 1980s.
It is generally agreed that the main reason for the price spike in 2005–2008 was strong demand pressure. For example, global consumption of oil rose from 30 billion barrels (4.8×109 m3)
in 2004 to 31 billion in 2005. The consumption rates were far above new
discoveries in the period, which had fallen to only eight billion
barrels of new oil reserves in new accumulations in 2004.
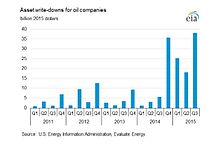
Asset write downs for oil companies 2015
Oil price increases were partially fueled by reports that petroleum production is at or near full capacity.
In June 2005, OPEC stated that they would 'struggle' to pump enough oil
to meet pricing pressures for the fourth quarter of that year.
From 2007 to 2008, the decline in the U.S. dollar against other
significant currencies was also considered as a significant reason for
the oil price increases, as the dollar lost approximately 14% of its value against the Euro from May 2007 to May 2008.
Besides supply and demand pressures, at times security related factors may have contributed to increases in prices, including the War on Terror, missile launches in North Korea, the Crisis between Israel and Lebanon, nuclear brinkmanship between the U.S. and Iran, and reports from the U.S. Department of Energy and others showing a decline in petroleum reserves.
Depicts EIA projections for West Texas Intermediate crude oil price for 2016-2017
More recently, between 2011 and 2014 the price of crude oil was
relatively stable, fluctuating around $US100 per barrel. It dropped
sharply in late 2014 to below $US70 where it remained for most of 2015.
In early 2016 it traded at a low of $US27. The price drop has been attributed to both oversupply and reduced demand as a result of the slowing global economy, OPEC reluctance to concede market share, and a stronger US dollar.
These factors may be exacerbated by a combination of monetary policy
and the increased debt of oil producers, who may increase production to
maintain liquidity.
This price drop has placed many US tight oil producers under considerable financial pressure. As a result, there has been a reduction by oil companies in capital expenditure of over $US400 billion.
It is anticipated that this will have effects on global production in
the longer term, leading to statements of concern by the International
Energy Agency that governments should not be complacent about energy
security. Energy Information Agency projections anticipate market oversupply and prices below $US50 until late 2017.
Effects of historical oil price rises
World consumption of primary energy by energy type
In the past, sudden increases in the price of oil have led to economic recessions, such as the 1973 and 1979 energy crises. The effect the increased price of oil has on an economy is known as a price shock. In many European countries, which have high taxes on fuels,
such price shocks could potentially be mitigated somewhat by
temporarily or permanently suspending the taxes as fuel costs rise.
This method of softening price shocks is less useful in countries with
much lower gas taxes, such as the United States. A baseline scenario for
a recent IMF
paper found oil production growing at 0.8% (as opposed to a historical
average of 1.8%) would result in a small reduction in economic growth of
0.2–0.4%.
Researchers at the Stanford Energy Modeling Forum found that the economy can adjust to steady, gradual increases in the price of crude better than wild lurches.
Some economists predict that a substitution effect will spur demand for alternate energy sources, such as coal or liquefied natural gas. This substitution can be only temporary, as coal and natural gas are finite resources as well.
Prior to the run-up in fuel prices, many motorists opted for larger, less fuel-efficient sport utility vehicles
and full-sized pickups in the United States, Canada, and other
countries. This trend has been reversing because of sustained high
prices of fuel. The September 2005 sales data for all vehicle vendors
indicated SUV sales dropped while small cars sales increased. Hybrid and diesel vehicles are also gaining in popularity.
EIA published Household Vehicles Energy Use: Latest Data and Trends
in Nov 2005 illustrating the steady increase in disposable income and
$20–30 per barrel price of oil in 2004. The report notes "The average
household spent $1,520 on fuel purchases for transport." According to
CNBC that expense climbed to $4,155 in 2011.
In 2008, a report by Cambridge Energy Research Associates
stated that 2007 had been the year of peak gasoline usage in the United
States, and that record energy prices would cause an "enduring shift"
in energy consumption practices. The total miles driven in the U.S. peaked in 2006.
The Export Land Model
states that after peak oil petroleum exporting countries will be forced
to reduce their exports more quickly than their production decreases
because of internal demand growth. Countries that rely on imported
petroleum will therefore be affected earlier and more dramatically than
exporting countries.
Mexico is already in this situation. Internal consumption grew by 5.9%
in 2006 in the five biggest exporting countries, and their exports
declined by over 3%. It was estimated that by 2010 internal demand would
decrease worldwide exports by 2,500,000 barrels per day (400,000 m3/d).
Canadian economist Jeff Rubin has stated that high oil prices are
likely to result in increased consumption in developed countries
through partial manufacturing de-globalisation of trade. Manufacturing
production would move closer to the end consumer to minimise
transportation network costs, and therefore a demand decoupling from
gross domestic product would occur. Higher oil prices would lead to
increased freighting costs and consequently, the manufacturing industry
would move back to the developed countries since freight costs would
outweigh the current economic wage advantage of developing countries. Economic research carried out by the International Monetary Fund puts overall price elasticity of demand for oil at −0.025 short-term and −0.093 long term.
Agricultural effects and population limits
Since supplies of oil and gas are essential to modern agriculture techniques, a fall in global oil supplies could cause spiking food prices and unprecedented famine in the coming decades. Geologist Dale Allen Pfeiffer contends that current population levels are unsustainable, and that to achieve a sustainable economy and avert disaster the United States population would have to be reduced by at least one-third, and world population by two-thirds.
The largest consumer of fossil fuels in modern agriculture is ammonia production (for fertilizer) via the Haber process, which is essential to high-yielding intensive agriculture. The specific fossil fuel input to fertilizer production is primarily natural gas, to provide hydrogen via steam reforming. Given sufficient supplies of renewable electricity, hydrogen can be generated without fossil fuels using methods such as electrolysis. For example, the Vemork hydroelectric plant in Norway used its surplus electricity output to generate renewable ammonia from 1911 to 1971.
Iceland currently generates ammonia using the electrical output from its hydroelectric and geothermal power plants,
because Iceland has those resources in abundance while having no
domestic hydrocarbon resources, and a high cost for importing natural
gas.
Long-term effects on lifestyle
World transport energy use by fuel type 2012
A majority of Americans live in suburbs, a type of low-density settlement designed around universal personal automobile use. Commentators such as James Howard Kunstler
argue that because over 90% of transportation in the U.S. relies on
oil, the suburbs' reliance on the automobile is an unsustainable living
arrangement. Peak oil would leave many Americans unable to afford
petroleum based fuel for their cars, and force them to use bicycles or electric vehicles. Additional options include telecommuting, moving to rural areas, or moving to higher density areas, where walking and public transportation are more viable options. In the latter two cases, suburbs may become the "slums of the future."
The issue of petroleum supply and demand is also a concern for growing
cities in developing countries (where urban areas are expected to absorb
most of the world's projected 2.3 billion population increase by 2050).
Stressing the energy component of future development plans is seen as
an important goal.
Rising oil prices, if they occur, would also affect the cost of
food, heating, and electricity. A high amount of stress would then be
put on current middle to low income families as economies contract from
the decline in excess funds, decreasing employment rates. The Hirsch/US
DoE Report concludes that "without timely mitigation, world
supply/demand balance will be achieved through massive demand
destruction (shortages), accompanied by huge oil price increases, both
of which would create a long period of significant economic hardship
worldwide."
Methods that have been suggested for mitigating these urban and
suburban issues include the use of non-petroleum vehicles such as electric cars, battery electric vehicles, transit-oriented development, carfree cities, bicycles, new trains, new pedestrianism, smart growth, shared space, urban consolidation, urban villages, and New Urbanism.
An extensive 2009 report on the effects of compact development by the United States National Research Council of the Academy of Sciences, commissioned by the United States Congress, stated six main findings.
First, that compact development is likely to reduce "Vehicle Miles
Traveled" (VMT) throughout the country. Second, that doubling
residential density in a given area could reduce VMT by as much as 25%
if coupled with measures such as increased employment density and
improved public transportation. Third, that higher density, mixed-use
developments would produce both direct reductions in CO2
emissions (from less driving), and indirect reductions (such as from
lower amounts of materials used per housing unit, higher efficiency
climate control, longer vehicle lifespans, and higher efficiency
delivery of goods and services). Fourth, that although short term
reductions in energy use and CO2 emissions would be modest,
that these reductions would become more significant over time. Fifth,
that a major obstacle to more compact development in the United States
is political resistance from local zoning regulators, which would hamper
efforts by state and regional governments to participate in land-use
planning. Sixth, the committee agreed that changes in development that
would alter driving patterns and building efficiency would have various
secondary costs and benefits that are difficult to quantify. The report
recommends that policies supporting compact development (and especially
its ability to reduce driving, energy use, and CO2 emissions) should be encouraged.
An economic theory that has been proposed as a remedy is the introduction of a steady state economy.
Such a system could include a tax shifting from income to depleting
natural resources (and pollution), as well as the limitation of
advertising that stimulates demand and population growth. It could also
include the institution of policies that move away from globalization
and toward localization to conserve energy resources, provide local
jobs, and maintain local decision-making authority. Zoning policies
could be adjusted to promote resource conservation and eliminate sprawl.
Since aviation relies mainly on jet fuels derived from crude oil, commercial aviation has been predicted to go into decline with the global oil production.
Mitigation
To avoid the serious social and economic implications a global decline in oil production could entail, the Hirsch report
emphasized the need to find alternatives, at least ten to twenty years
before the peak, and to phase out the use of petroleum over that time. This was similar to a plan proposed for Sweden that same year. Such mitigation
could include energy conservation, fuel substitution, and the use of
unconventional oil. The timing of mitigation responses is critical.
Premature initiation would be undesirable, but if initiated too late
could be more costly and have more negative economic consequences.
Positive aspects
Permaculture
sees peak oil as holding tremendous potential for positive change,
assuming countries act with foresight. The rebuilding of local food
networks, energy production, and the general implementation of "energy descent culture" are argued to be ethical responses to the acknowledgment of finite fossil resources. Majorca
is an island currently diversifying its energy supply from fossil fuels
to alternative sources and looking back at traditional construction and
permaculture methods.
The Transition Towns movement, started in Totnes, Devon and spread internationally by "The Transition Handbook" (Rob Hopkins)
and Transition Network, sees the restructuring of society for more
local resilience and ecological stewardship as a natural response to the
combination of peak oil and climate change.
Criticisms
General arguments
The
theory of peak oil is controversial and became an issue of political
debate in the USA and Europe in the mid-2000s. Critics argued that newly
found oil reserves forestalled a peak oil event. Some argued that oil
production from new oil reserves and existing fields will continue to
increase at a rate that outpaces demand, until alternate energy sources
for current fossil fuel dependence are found.
In 2015, analysts in the petroleum and financial industries claimed
that the "age of oil" had already reached a new stage where the excess
supply that appeared in late 2014 may continue.
A consensus was emerging that parties to an international agreement
would introduce measures to constrain the combustion of hydrocarbons in
an effort to limit global temperature rise to the nominal 2 °C that
scientists predicted would limit environmental harm to tolerable levels.
Another argument against the peak oil theory is reduced demand from various options and technologies substituting oil. US federal funding to develop algae fuels increased since 2000 due to rising fuel prices. Many other projects are being funded in
Australia, New Zealand, Europe, the Middle East, and elsewhere and private companies are entering the field.
Oil industry representatives
The president of Royal Dutch Shell's
U.S. operations John Hofmeister, while agreeing that conventional oil
production would soon start to decline, criticized the analysis of peak
oil theory by Matthew Simmons for being "overly focused on a single country: Saudi Arabia, the world's largest exporter and OPEC swing producer." Hofmeister pointed to the large reserves at the US outer continental shelf, which held an estimated 100 billion barrels (16×109 m3)
of oil and natural gas. However, only 15% of those reserves were
currently exploitable, a good part of that off the coasts of Texas,
Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama.
Hofmeister also pointed to unconventional sources of oil such as the oil sands
of Canada, where Shell was active. The Canadian oil sands—a natural
combination of sand, water, and oil found largely in Alberta and
Saskatchewan—are believed to contain one trillion barrels of oil.
Another trillion barrels are also said to be trapped in rocks in
Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming, in the form of oil shale.
Environmentalists argue that major environmental, social, and economic
obstacles would make extracting oil from these areas excessively
difficult.
Hofmeister argued that if oil companies were allowed to drill more in
the United States enough to produce another 2 million barrels per day
(320×103 m3/d),
oil and gas prices would not be as high as they were in the late 2000s.
He thought in 2008 that high energy prices would cause social unrest
similar to the 1992 Rodney King riots.
In 2009, Dr. Christoph Rühl, chief economist of BP, argued against the peak oil
hypothesis:
Physical peak oil, which I have no reason to accept as a valid statement either on theoretical, scientific or ideological grounds, would be insensitive to prices. ... In fact the whole hypothesis of peak oil – which is that there is a certain amount of oil in the ground, consumed at a certain rate, and then it's finished – does not react to anything ... Therefore there will never be a moment when the world runs out of oil because there will always be a price at which the last drop of oil can clear the market. And you can turn anything into oil into if you are willing to pay the financial and environmental price ... (Global Warming) is likely to be more of a natural limit than all these peak oil theories combined. ... Peak oil has been predicted for 150 years. It has never happened, and it will stay this way.
— Dr. Christoph Rühl, BP
Rühl argued that the main limitations for oil availability are "above
ground" factors such as the availability of staff, expertise,
technology, investment security, funds, and global warming, and that the
oil question was about price and not the physical availability.
In 2008, Daniel Yergin of CERA
suggest that a recent high price phase might add to a future demise of
the oil industry, not of complete exhaustion of resources or an
apocalyptic shock but the timely and smooth setup of alternatives.
Yergin went on to say, "This is the fifth time that the world is said
to be running out of oil. Each time-whether it was the 'gasoline famine'
at the end of WWI or the 'permanent shortage' of the 1970s-technology
and the opening of new frontier areas have banished the spectre of
decline. There's no reason to think that technology is finished this
time."
In 2006, Clive Mather, CEO of Shell Canada, said the Earth's supply of bitumen hydrocarbons was "almost infinite", referring to hydrocarbons in oil sands.
Others
In 2006 attorney and mechanical engineer Peter W. Huber
asserted that the world was just running out of "cheap oil," explaining
that as oil prices rise, unconventional sources become economically
viable. He predicted that, "[t]he tar sands of Alberta alone contain
enough hydrocarbon to fuel the entire planet for over 100 years."
Environmental journalist George Monbiot responded to a 2012 report by Leonardo Maugeri
by suggesting that there is more than enough oil (from unconventional
sources) for capitalism to "deep-fry" the world with climate change. Stephen Sorrell, senior lecturer Science and Technology Policy Research, Sussex Energy Group, and lead author of the UKERC
Global Oil Depletion report, and Christophe McGlade, doctoral
researcher at the UCL Energy Institute have criticized Maugeri's
assumptions about decline rates.