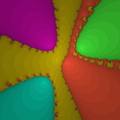
Julia set for the rational function associated to Newton's method for ƒ:z→z3−1.
The Newton fractal is a boundary set in the complex plane which is characterized by Newton's method applied to a fixed polynomial or transcendental function. It is the Julia set of the meromorphic function
which is given by Newton's method. When there are no attractive cycles
(of order greater than 1), it divides the complex plane into regions , each of which is associated with a root of the polynomial, . In this way the Newton fractal is similar to the Mandelbrot set, and like other fractals it exhibits an intricate appearance arising from a simple description. It is relevant to numerical analysis because it shows that (outside the region of quadratic convergence) the Newton method can be very sensitive to its choice of start point.
Many points of the complex plane are associated with one of the roots of the polynomial in the following way: the point is used as starting value for Newton's iteration , yielding a sequence of points If the sequence converges to the root , then was an element of the region .
However, for every polynomial of degree at least 2 there are points for
which the Newton iteration does not converge to any root: examples are
the boundaries of the basins of attraction of the various roots. There
are even polynomials for which open sets of starting points fail to
converge to any root: a simple example is , where some points are attracted by the cycle 0, 1, 0, 1 ... rather than by a root.
An open set for which the iterations converge towards a given root or cycle (that is not a fixed point), is a Fatou set
for the iteration. The complementary set to the union of all these, is
the Julia set. The Fatou sets have common boundary, namely the Julia
set. Therefore each point of the Julia set is a point of accumulation
for each of the Fatou sets. It is this property that causes the fractal
structure of the Julia set (when the degree of the polynomial is larger
than 2).
To plot interesting pictures, one may first choose a specified number of complex points and compute the coefficients of the polynomial
- .
Then for a rectangular lattice , , of points in , one finds the index of the corresponding root and uses this to fill an × raster grid by assigning to each point a colour . Additionally or alternatively the colours may be dependent on the distance , which is defined to be the first value such that for some previously fixed small .
Generalization of Newton fractals
A generalization of Newton's iteration is
where is any complex number. The special choice corresponds to the Newton fractal.
The fixed points of this map are stable when lies inside the disk of radius 1 centered at 1. When
is outside this disk, the fixed points are locally unstable, however
the map still exhibits a fractal structure in the sense of Julia set. If is a polynomial of degree , then the sequence is bounded provided that is inside a disk of radius centered at .
More generally, Newton's fractal is a special case of a Julia set.
Nova fractal
The Nova fractal invented in the mid 1990s by Paul Derbyshire, is a generalization of the Newton fractal with the addition of a value at each step:
The "Julia" variant of the Nova fractal keeps constant over the image and initializes to the pixel coordinates. The "Mandelbrot" variant of the Nova fractal initializes to the pixel coordinates and sets to a critial point, where . Commonly-used polynomials like or lead to a critical point at .
Implementation
In order to implement the Newton Fractal, it is necessary to have a starting function as well as its derivative function:
The roots of the function are
The above-defined functions can be translated in pseudocode as follows:
//z^3-1
float2 Function (float2 z)
{
return cpow(z, 3) - float2(1, 0); //cpow is an exponential function for complex numbers
}
//3*z^2
float2 Derivative (float2 z)
{
return 3 * cmul(z, z); //cmul is a function that handles multiplication of complex numbers
}
It is now just a matter of implementing the Newton method using the given functions.
For each pixel (x, y) on the target, do:
{
zx = scaled x coordinate of pixel (scaled to lie in the Mandelbrot X scale (-2.5, 1))
zy = scaled y coordinate of pixel (scaled to lie in the Mandelbrot Y scale (-1, 1))
float2 z = float2(zx, zy); //Z is originally set to the pixel coordinates
float2 roots[3] = //Roots (solutions) of the polynomial
{
float2(1, 0),
float2(-.5, sqrt(3)/2),
float2(-.5, -sqrt(3)/2)
};
color colors[3] = //Assign a color for each root
{
red,
green,
blue
}
for (int iteration = 0;
iteration < maxIteration;
iteration++;)
{
z -= cdiv(Function(z), Derivative(z)); //cdiv is a function for dividing complex numbers
float tolerance = 0.000001;
for (int i = 0; i < roots.Length; i++)
{
float difference = z - roots[i];
//If the current iteration is close enough to a root, color the pixel.
if (abs(difference.x) < tolerance && abs(difference.y) < tolerance)
{
return colors[i]; //Return the color corresponding to the root
}
}
}
return black; //If no solution is found
}

![p(Z)\in {\mathbb {C}}[Z]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9e05da01e2cb6c928fb40921c7081a9789480d29)