The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a jus cogens rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It states that people, based on respect for the principle of equal rights and fair equality of opportunity, have the right to freely choose their sovereignty and international political status with no interference.
The concept was first expressed in the 1860s, and spread rapidly thereafter. During and after World War I, the principle was encouraged by both Vladimir Lenin and United States President Woodrow Wilson. Having announced his Fourteen Points
on 8 January 1918, on 11 February 1918 Wilson stated: "National
aspirations must be respected; people may now be dominated and governed
only by their own consent. 'Self determination' is not a mere phrase; it
is an imperative principle of action."
During World War II, the principle was included in the Atlantic Charter, signed on 14 August 1941, by Franklin D. Roosevelt, President of the United States, and Winston Churchill, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, who pledged The Eight Principal points of the Charter. It was recognized as an international legal right after it was explicitly listed as a right in the UN Charter.
The principle does not state how the decision is to be made, nor what the outcome should be, whether it be independence, federation, protection, some form of autonomy or full assimilation. Neither does it state what the delimitation between peoples should be—nor what constitutes a people. There are conflicting definitions and legal criteria for determining which groups may legitimately claim the right to self-determination.
By extension, the term self-determination has come to mean the free choice of one's own acts without external compulsion.
During World War II, the principle was included in the Atlantic Charter, signed on 14 August 1941, by Franklin D. Roosevelt, President of the United States, and Winston Churchill, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, who pledged The Eight Principal points of the Charter. It was recognized as an international legal right after it was explicitly listed as a right in the UN Charter.
The principle does not state how the decision is to be made, nor what the outcome should be, whether it be independence, federation, protection, some form of autonomy or full assimilation. Neither does it state what the delimitation between peoples should be—nor what constitutes a people. There are conflicting definitions and legal criteria for determining which groups may legitimately claim the right to self-determination.
By extension, the term self-determination has come to mean the free choice of one's own acts without external compulsion.
History
Pre-20th century
Origins
The employment of imperialism, through the expansion of empires, and the concept of political sovereignty, as developed after the Treaty of Westphalia, also explain the emergence of self-determination during the modern era. During, and after, the Industrial Revolution many groups of people recognized their shared history, geography, language, and customs. Nationalism
emerged as a uniting ideology not only between competing powers, but
also for groups that felt subordinated or disenfranchised inside larger
states; in this situation, self-determination can be seen as a reaction
to imperialism. Such groups often pursued independence and sovereignty
over territory, but sometimes a different sense of autonomy has been
pursued or achieved.
Empires
The world possessed several traditional, continental empires such as the Ottoman, Russian, Austrian/Habsburg, and the Qing Empire. Political scientists often define competition in Europe during the Modern Era as a balance of power struggle, which also induced various European states to pursue colonial empires, beginning with the Spanish and Portuguese, and later including the British, French, Dutch, and German.
During the early 19th century, competition in Europe produced multiple wars, most notably the Napoleonic Wars. After this conflict, the British Empire became dominant and entered its "imperial century", while nationalism became a powerful political ideology in Europe.
Later, after the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, "New Imperialism" was unleashed with France and later Germany
establishing colonies in Asia, the Pacific, and Africa. Japan also
emerged as a new power. Multiple theaters of competition developed
across the world:
- Africa: multiple European states competed for colonies in the "Scramble for Africa";
- Central Asia: Russia and Britain competed for domination in the "Great Game"
- Eastern Asia: colonies and various spheres of influence were established, largely to the detriment of the Qing Empire.
The Ottoman Empire, Austrian Empire, Russian Empire, Qing Empire and the new Empire of Japan
maintained themselves, often expanding or contracting at the expense of
another empire. All ignored notions of self-determination for those
governed.
Rebellions and emergence of nationalism
The revolt of New World
British colonists in North America, during the mid-1770s, has been seen
as the first assertion of the right of national and democratic
self-determination, because of the explicit invocation of natural law,
the natural rights of man, as well as the consent of, and sovereignty
by, the people governed; these ideas were inspired particularly by John Locke's enlightened writings of the previous century. Thomas Jefferson further promoted the notion that the will of the people was supreme, especially through authorship of the United States Declaration of Independence which inspired Europeans throughout the 19th century. The French Revolution was motivated similarly and legitimatized the ideas of self-determination on that Old World continent.
Within the New World during the early 19th century, most of the nations of Spanish America achieved independence from Spain. The United States supported that status, as policy in the hemisphere relative to European colonialism, with the Monroe Doctrine.
The American public, organized associated groups, and Congressional
resolutions, often supported such movements, particularly the Greek War of Independence (1821–29) and the demands of Hungarian revolutionaries in 1848. Such support, however, never became official government policy, due to balancing of other national interests. After the American Civil War and with increasing capability, the United States government did not accept self-determination as a basis during its Purchase of Alaska and attempted purchase of the West Indian islands of Saint Thomas and Saint John in the 1860s, or its growing influence in the Hawaiian Islands, that led to annexation in 1898. With its victory in the Spanish–American War in 1899 and its growing stature in the world, the United States supported annexation of the former Spanish colonies of Guam, Puerto Rico and the Philippines, without the consent of their peoples, and it retained "quasi-suzerainty" over Cuba, as well.
Nationalist sentiments emerged inside the traditional empires including: Pan-Slavism in Russia; Ottomanism, Kemalist ideology and Arab nationalism in the Ottoman Empire; State Shintoism and Japanese identity in Japan; and Han identity in juxtaposition to the Manchurian ruling class in China. Meanwhile, in Europe itself there was a rise of nationalism, with nations such as Greece, Hungary, Poland and Bulgaria seeking or winning their independence.
Karl Marx supported such nationalism, believing it might be a "prior condition" to social reform and international alliances. In 1914 Vladimir Lenin
wrote: "[It] would be wrong to interpret the right to
self-determination as meaning anything but the right to existence as a
separate state."
World Wars I and II
Europe, Asia and Africa
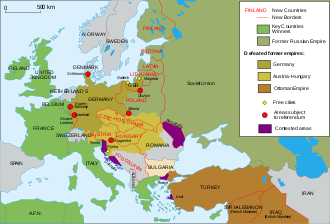
Map of territorial changes in Europe after World War I (as of 1923)
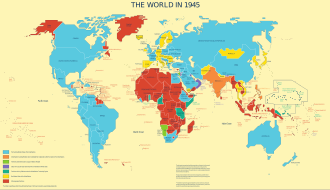
Map of the world in 1945, showing United Nations Trusteeship Council territories in green
Woodrow Wilson revived America's commitment to self-determination, at least for European states, during World War I. When the Bolsheviks came to power in Russia in November 1917, they called for Russia's immediate withdrawal as a member of the Allies of World War I. They also supported the right of all nations, including colonies, to self-determination." The 1918 Constitution of the Soviet Union acknowledged the right of secession for its constituent republics.
This presented a challenge to Wilson's more limited demands. In January 1918 Wilson issued his Fourteen Points
of January 1918 which, among other things, called for adjustment of
colonial claims, insofar as the interests of colonial powers had equal
weight with the claims of subject peoples. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
in March 1918 led to Soviet Russia's exit from the war and the nominal
independence of Armenia, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Ukraine, Lithuania,
Georgia and Poland, though in fact those territories were under German
control. The end of the war led to the dissolution of the defeated Austro-Hungarian Empire and Czechoslovakia and the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia
as new states out of the wreckage of the Habsburg empire. However, this
imposition of states where some nationalities (especially Poles,
Czechs, and Serbs and Romanians)
were given power over nationalities who disliked and distrusted them
eventually used as a pretext for German aggression in World War II.
One of the German objections to the Treaty of Versailles was a
somewhat selective application of the principle of self-determination as
the majority of the people in Austria and in the Sudetenland region of
Czechoslovakia wanted to join Germany while the majority of people in
Danzig wanted to remain within the Reich, but the Allies ignored
the German objections. Wilson's 14 Points had called for Polish
independence to be restored and Poland to have "secure access to the
sea", which would imply that the German city of Danzig (modern Gdańsk,
Poland), which occupied a strategic location where the Vistula river
flowed into the Baltic sea, be ceded to Poland. At the Paris peace conference in 1919, the Polish delegation led by Roman Dmowski
asked for Wilson to honor point 14 of the 14 points by transferring
Danzig to Poland. arguing that Poland would not be economically viable
without Danzig.
However, as the 90% of the people in Danzig in this period were German,
the Allied leaders at the Paris peace conference compromised by
creating the Free City of Danzig, a city-state in which Poland had certain special rights.
Through the city of Danzig was 90% German and 10% Polish, the
surrounding countryside around Danzig was overwhelmingly Polish, and the
ethnically Polish rural areas included in the Free City of Danzig
objected, arguing that they wanted to be part of Poland.
Neither the Poles nor the Germans were happy with this compromise and
the Danzig issue became a flash-point of German-Polish tension
throughout the interwar period.
Germany lost land after WWI: Northern Schleswig voted to return to Denmark after a referendum. On 11 July 1920, the East Prussian plebiscite
called for by the Treaty of Versailles led to two disputed regions
between Germany and Poland choosing the former. In 1921, a plebiscite in
Silesia concerning partitioning the region between Germany and Poland
led to fighting breaking out between the ethnic German and ethnic Polish
residents of Silesia. The defeated Ottoman empire was dissolved into the Republic of Turkey and several smaller nations, including Yemen, plus the new Middle East Allied "mandates" of Syria and Lebanon (future Syria, Lebanon and Hatay State), Palestine (future Transjordan and Israel), Mesopotamia
(future Iraq). In 1919, a Greek attempt to add the mostly
Greek-speaking western regions of Anatolia led to a war between Greece
and Turkey when the Greeks occupied the largely Greek-speaking city of
Smyrna (modern İzmir, Turkey) in May 1919.
In 1922, the Greeks were defeated and under the terms of the 1923
Treaty of Lausanne compulsorily population exchanges led to almost all
the Turks in Greece being expelled into Turkey and almost all of the
Greeks in Turkey being expelled into Greece. The League of Nations was proposed as much as a means of consolidating these new states, as a path to peace.
During the 1920s and 1930s there were some successful movements for self-determination in the beginnings of the process of decolonization. In the Statute of Westminster the United Kingdom granted independence to Canada, New Zealand, Newfoundland, the Irish Free State, the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Union of South Africa after the British parliament
declared itself as incapable of passing laws over them without their
consent. Egypt, Afghanistan and Iraq also achieved independence from
Britain and Lebanon from France. Other efforts were unsuccessful, like
the Indian independence movement.
And Italy, Japan and Germany all initiated new efforts to bring certain
territories under their control, leading to World War II. In
particular, the National Socialist Program invoked this right of nations in its first point (out of 25), as it was publicly proclaimed on 24 February 1920 by Adolf Hitler.
In Asia, Japan became a rising power and gained more respect from Western powers after its victory in the Russo-Japanese War. Japan joined the Allied Powers in World War I and attacked German colonial possessions in the Far East, adding former German possessions to its own empire. In the 1930s, Japan gained significant influence in Inner Mongolia and Manchuria after it invaded Manchuria. It established Manchukuo, a puppet state
in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia. This was essentially the model
Japan followed as it invaded other areas in Asia and established the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere.
Japan went to considerable trouble to argue that Manchukuo was
justified by the principle of self-determination, claiming that people
of Manchuria wanted to break away from China and asked the Kwantung Army
to intervene on their behalf. However, the Lytton commission which had
been appointed by the League of Nations to decide if Japan had committed
aggression or not, stated the majority of people in Manchuria who were
Han Chinese who did not wish to leave China.
In 1912, the Republic of China officially succeeded the Qing Dynasty, while Outer Mongolia, Tibet and Tuva proclaimed their independence. Independence was not accepted by the government of China. By the Treaty of Kyakhta (1915) Outer Mongolia
recognized China's sovereignty. However, the Soviet threat of seizing
parts of Inner Mongolia induced China to recognize Outer Mongolia's
independence, provided that a referendum was held. The referendum took
place on October 20, 1945, with (according to official numbers) 100% of
the electorate voting for independence.
Many of Eastern Asia's current disputes to sovereignty and
self-determination stem from unresolved disputes from World War II.
After its fall, the Empire of Japan renounced control over many of its former possessions including Korea, Sakhalin Island, and Taiwan.
In none of these areas were the opinions of affected people consulted,
or given significant priority. Korea was specifically granted
independence but the receiver of various other areas was not stated in
the Treaty of San Francisco, giving Taiwan de facto independence although its political status continues to be ambiguous.
The Cold War world
The UN Charter and resolutions
In 1941 Allies of World War II declared the Atlantic Charter and accepted the principle of self-determination. In January 1942 twenty-six states signed the Declaration by United Nations,
which accepted those principles. The ratification of the United Nations
Charter in 1945 at the end of World War II placed the right of
self-determination into the framework of international law and
diplomacy.
- Chapter 1, Article 1, part 2 states that purpose of the UN Charter is: "To develop friendly relations among nations based on respect for the principle of equal rights and self-determination of peoples, and to take other appropriate measures to strengthen universal peace."
- Article 1 in both the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) reads: "All peoples have the right of self-determination. By virtue of that right they freely determine their political status and freely pursue their economic, social and cultural development. "
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights article 15 states that everyone has the right to a nationality and that no one should be arbitrarily deprived of a nationality or denied the right to change nationality.
Western European colonial empires in Asia and Africa disintegrated after World War II
On 14 December 1960, the United Nations General Assembly adopted United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1514 (XV) subtitled "Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples", which supported the granting of independence to colonial
countries and people by providing an inevitable legal linkage between
self-determination and its goal of decolonization. It postulated a new
international law-based right of freedom to exercise economic self-determination. Article 5 states: Immediate steps shall be taken in Trust and Non-Self-Governing Territories,
or all other territories which have not yet attained independence, to
transfer all powers to the people of those territories, without any
conditions or reservations, in accordance with their freely expressed
will and desire, without any distinction as to race, creed or color, in
order to enable them to enjoy complete independence and freedom.
On 15 December 1960 the United Nations General Assembly adopted United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1541 (XV),
subtitled "Principles which should guide members in determining whether
or nor an obligation exists to transmit the information called for
under Article 73e of the United Nations Charter
in Article 3", which provided that "[t]he inadequacy of political,
economic, social and educational preparedness should never serve as a
pretext for delaying the right to self-determination and independence."
To monitor the implementation of Resolution 1514, in 1961 the General Assembly created the Special Committee referred to popularly as the Special Committee on Decolonization to ensure decolonization complete compliance with the principles of self-determination in General Assembly Resolution 1541 (XV).
However, the charter and other resolutions did not insist on full independence as the best way of obtaining self-government, nor did they include an enforcement mechanism. Moreover, new states were recognized by the legal doctrine of uti possidetis juris,
meaning that old administrative boundaries would become international
boundaries upon independence if they had little relevance to linguistic,
ethnic, and cultural boundaries.
Nevertheless, justified by the language of self-determination, between
1946 and 1960, thirty-seven new nations in Asia, Africa, and the Middle
East gained independence from colonial powers.
The territoriality issue inevitably would lead to more conflicts and
independence movements within many states and challenges to the
assumption that territorial integrity is as important as self-determination.
The communist versus capitalist worlds
Decolonization in the world was contrasted by the Soviet Union's successful post-war expansionism. Tuva and several regional states in Eastern Europe,
the Baltic, and Central Asia had been fully annexed by the Soviet Union
during World War II. Now, it extended its influence by establishing satellite states
Eastern Germany and the countries of Eastern Europe, along with support
for revolutionary movements in China and North Korea. Although
satellite states were independent and possessed sovereignty, the Soviet
Union violated principles of self-determination by suppressing the Hungarian revolution of 1956 and the Prague Spring Czechoslovak reforms of 1968. It invaded Afghanistan to support a communist government assailed by local tribal groups. However, Marxism–Leninism and its theory of imperialism were also strong influences in the national emancipation movements of Third World nations rebelling against colonial or puppet regimes. In many Third World countries, communism became an ideology that united groups to oppose imperialism or colonization.
Soviet actions were contained
by the United States which saw communism as a menace to its interests.
Throughout the cold war, the United States created, supported, and
sponsored regimes with various success that served their economic and
political interests, among them anti-communist regimes such as that of Augusto Pinochet in Chile and Suharto in Indonesia.
To achieve this, a variety of means was implemented, including the
orchestration of coups, sponsoring of anti-communist countries and
military interventions. Consequently, many self-determination movements,
which spurned some type of anti-communist government, were accused of
being Soviet-inspired or controlled.
Asia
In Asia, the Soviet Union had already converted Mongolia into a satellite state but abandoned propping up the Second East Turkestan Republic and gave up its Manchurian claims to China. The new People's Republic of China had gained control of mainland China in the Chinese Civil War. The Korean War shifted the focus of the Cold War from Europe to Asia, where competing superpowers took advantage of decolonization to spread their influence.
In 1947, India gained independence from the British Empire. The empire was in decline but adapted to these circumstances by creating the British Commonwealth—since 1949 the Commonwealth of Nations—which
is a free association of equal states. As India obtained its
independence, multiple ethnic conflicts emerged in relation to the
formation of a statehood during the Partition of India which resulted in Islamic Pakistan and Secular India. Before the advent of the British,
no empire based in mainland India had controlled any part of what now
makes up the country's Northeast, part of the reason for the ongoing insurgency in Northeast India. In 1971 Bangladesh obtained independence from Pakistan.
Burma also gained independence from the British Empire, but declined membership in the Commonwealth.
Indonesia gained independence from the Netherlands in 1949 after
the latter failed to restore colonial control. As mentioned above,
Indonesia also wanted a powerful position in the region that could be
lessened by the creation of united Malaysia. The Netherlands retained Dutch New Guinea, but Indonesia threatened to invade and annex it. A vote was supposedly taken under the UN sponsored Act of Free Choice
to allow West New Guineans to decide their fate, although many dispute
its veracity. Later, Portugal relinquished control over East Timor in 1975, at which time Indonesia promptly invaded and annexed it.
After the Cold War
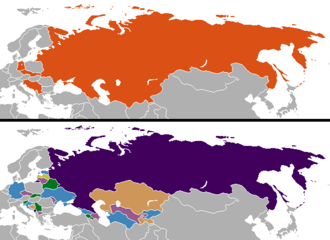
Changes in national boundaries after the end of the Cold War
The Cold War began to wind down after Mikhail Gorbachev assumed power in March 1985. With the cooperation of the American president Ronald Reagan, Gorbachev wound down the size of the Soviet Armed Forces and reduced nuclear arms in Europe, while liberalizing the economy.
In 1989 – 90, the communist regimes of Soviet satellite states
collapsed in rapid succession in Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East
Germany, Bulgaria, Romania, and Mongolia. East and West Germany united,
Czechoslovakia peacefully split into Czech Republic and Slovakia, while in 1990 Yugoslavia began a violent break up into its former 6 sub-unit republics. Kosovo,
which was previously an autonomous unit of Serbia declared independence
in 2008, but has received less international recognition.
In December 1991, Gorbachev resigned as president and the Soviet Union dissolved
relatively peacefully into fifteen sovereign republics, all of which
rejected communism and most of which adopted democratic reforms and
free-market economies. Inside those new republics, four major areas have claimed their own independence, but not received widespread international recognition.
After decades of civil war, Indonesia finally recognized the independence of East Timor in 2002.
In 1949, the Communists won the civil war and established the People's Republic of China in Mainland China. The Kuomintang-led Republic of China government retreated to Taipei, its jurisdiction now limited to Taiwan
and several outlying islands. Since then, the People's Republic of
China has been involved in disputes with the ROC over issues of
sovereignty and the political status of Taiwan.
As noted, self-determination movements remain strong in some areas of the world. Some areas possess de facto independence, such as Taiwan, North Cyprus, Kosovo, and South Ossetia,
but their independence is disputed by one or more major states.
Significant movements for self-determination also persist for locations
that lack de facto independence, such as Kurdistan, Balochistan, Chechnya, and the State of Palestine
Current issues
Southern Sudanese expressed joy and jubilation on their day of independence, July 9, 2011, from Sudan.
Since the early 1990s, the legitimatization of the principle of
national self-determination has led to an increase in the number of
conflicts within states, as sub-groups seek greater self-determination
and full secession, and as their conflicts for leadership within groups
and with other groups and with the dominant state become violent.
The international reaction to these new movements has been uneven and
often dictated more by politics than principle. The 2000 United Nations
Millennium Declaration failed to deal with these new demands, mentioning
only "the right to self-determination of peoples which remain under
colonial domination and foreign occupation."
In an issue of Macquarie University Law Journal
Associate Professor Aleksandar Pavkovic and Senior Lecturer Peter Radan
outlined current legal and political issues in self-determination. These include:
Defining "peoples"
There is not yet a recognized legal definition of "peoples" in international law. Vita Gudeleviciute of Vytautas Magnus University
Law School, reviewing international law and UN resolutions, finds in
cases of non-self-governing peoples (colonized and/or indigenous) and
foreign military occupation "a people" is the entire population of the
occupied territorial unit, no matter their other differences. In cases
where people lack representation by a state's government, the
unrepresented become a separate people. Present international law does
not recognize ethnic and other minorities as separate peoples, with the
notable exception of cases in which such groups are systematically
disenfranchised by the government of the state they live in.
Other definitions offered are "peoples" being self-evident (from
ethnicity, language, history, etc.), or defined by "ties of mutual
affection or sentiment", i.e. "loyalty", or by mutual obligations among
peoples.
Or the definition may be simply that a people is a group of individuals
who unanimously choose a separate state. If the "people" are unanimous
in their desire for self-determination, it strengthens their claim. For
example, the populations of federal units of the Yugoslav federation
were considered a people in the breakup of Yugoslavia, although some of
those units had very diverse populations.
Libertarians who argue for self-determination distinguish between the
voluntary nation (the land, the culture, the terrain, the people) and
the state, the coercive apparatus, which they have a right to choose or
self-determine.
Abulof suggests that self-determination entails the "moral double
helix" of duality (personal right to align with a people, and the
people's right to determine their politics) and mutuality (the right is
as much the other's as the self’s). Thus, self-determination grants
individuals the right to form "a people," which then has the right to
establish an independent state, as long as they grant the same to all
other individuals and peoples.
Criteria for the definition of "people having the right of
self-determination" was proposed during 2010 Kosovo case decision of the
International Court of Justice: 1. traditions and culture 2. ethnicity
3. historical ties and heritage 4. language 5. religion 6. sense of
identity or kinship 7. the will to constitute a people 8. common
suffering.
Self-determination versus territorial integrity
Celebration of the Declaration of Independence of Kosovo in 2008
National self-determination appears to challenge the principle of territorial integrity (or sovereignty)
of states as it is the will of the people that makes a state
legitimate. This implies a people should be free to choose their own
state and its territorial boundaries. However, there are far more
self-identified nations than there are existing states and there is no
legal process to redraw state boundaries according to the will of these
peoples.
According to the Helsinki Final Act of 1975, the UN, ICJ and
international law experts, there is no contradiction between the
principles of self-determination and territorial integrity, with the
latter taking precedence.
Pavkovic and Radan describe three theories of international relations relevant to self-determination.
- The realist theory of international relations insists that territorial sovereignty is more important than national self-determination. This policy was pursued by the major powers during the Cold War.
- Liberal internationalism has become an alternative since that time. It promotes the abolition of war among states as well as increased individual liberty within states, and holds the expansion of global markets and cross-border cooperation diminishes the significance of territorial integrity, allowing for somewhat greater recognition of greater self-determination of peoples.
- Cosmopolitan liberalism calls for political power to shift to a world government which would make secession and change of boundaries a relatively easy administrative matter. However, it also would mean the de facto end of self-determination of national groups.
Donetsk status referendum organized by separatists in Ukraine. A line to enter a polling place, 11 May 2014
Allen Buchanan,
author of seven books on self-determination and secession, supports
territorial integrity as a moral and legal aspect of constitutional
democracy. However, he also advances a "Remedial Rights Only Theory"
where a group has "a general right to secede if and only if it has
suffered certain injustices, for which secession is the appropriate
remedy of last resort. " He also would recognize secession if the state
grants, or the constitution includes, a right to secede.
Vita Gudeleviciute holds that in cases of non-self-governing
peoples and foreign military occupation the principle of
self-determination trumps that of territorial integrity. In cases where
people lack representation by a state's government, they also may be
considered a separate people, but under current law cannot claim the
right to self-determination. On the other hand, she finds that secession
within a single state is a domestic matter not covered by international
law. Thus there are no on what groups may constitute a seceding people.
A number of states have laid claim to territories, which they
allege were removed from them as a result of colonialism. This is
justified by reference to Paragraph 6 of UN Resolution 1514(XV), which
states that any attempt "aimed at partial or total disruption of the
national unity and the territorial integrity of a country is
incompatible with the purposes and principles of the Charter". This, it
is claimed, applies to situations where the territorial integrity of a
state had been disrupted by colonisation, so that the people of a
territory subject to a historic territorial claim are prevented from
exercising a right to self-determination. This interpretation is
rejected by many states, who argue that Paragraph 2 of UN Resolution
1514(XV) states that "all peoples have the right to self-determination"
and Paragraph 6 cannot be used to justify territorial claims. The
original purpose of Paragraph 6 was "to ensure that acts of
self-determination occur within the established boundaries of colonies,
rather than within sub-regions". Further, the use of the word attempt in Paragraph 6 denotes future action and cannot be construed to justify territorial redress for past action.
An attempt sponsored by Spain and Argentina to qualify the right to
self-determination in cases where there was a territorial dispute was
rejected by the UN General Assembly, which re-iterated the right to
self-determination was a universal right.
Methods of increasing minority rights
In order to accommodate demands for minority rights and avoid secession and the creation of a separate new state, many states decentralize or devolve greater decision-making power to new or existing subunits or autonomous areas.
More limited measures might include restricting demands to the
maintenance of national cultures or granting non-territorial autonomy in
the form of national associations which would assume control over
cultural matters. This would be available only to groups that abandoned
secessionist demands and the territorial state would retain political
and judicial control, but only if would remain with the territorially
organized state.
Self-determination versus majority rule/equal rights
Pavković
explores how national self-determination, in the form of creation of a
new state through secession, could override the principles of majority rule and of equal rights,
which are primary liberal principles. This includes the question of how
an unwanted state can be imposed upon a minority. He explores five
contemporary theories of secession. In "anarcho-capitalist" theory only
landowners have the right to secede. In communitarian theory, only those
groups that desire direct or greater political participation have the
right, including groups deprived of rights, per Allen Buchanan. In two
nationalist theories, only national cultural groups have a right to
secede. Australian professor Harry Beran's democratic theory endorses
the equality of the right of secession to all types of groups.
Unilateral secession against majority rule is justified if the group
allows secession of any other group within its territory.
Constitutional law
Most sovereign states
do not recognize the right to self-determination through secession in
their constitutions. Many expressly forbid it. However, there are
several existing models of self-determination through greater autonomy
and through secession.
In liberal constitutional democracies the principle of majority rule has dictated whether a minority can secede. In the United States Abraham Lincoln acknowledged that secession might be possible through amending the United States Constitution. The Supreme Court in Texas v. White held secession could occur "through revolution, or through consent of the States." The British Parliament in 1933 held that Western Australia
only could secede from Australia upon vote of a majority of the country
as a whole; the previous two-thirds majority vote for secession via
referendum in Western Australia was insufficient.
The Chinese Communist Party
followed the Soviet Union in including the right of secession in its
1931 constitution in order to entice ethnic nationalities and Tibet into
joining. However, the Party eliminated the right to secession in later
years, and had anti-secession clause written into the Constitution
before and after the founding the People's Republic of China. The 1947
Constitution of the Union of Burma
contained an express state right to secede from the union under a
number of procedural conditions. It was eliminated in the 1974
constitution of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma (officially
the "Union of Myanmar"). Burma still allows "local autonomy under
central leadership".
As of 1996 the constitutions of Austria, Ethiopia, France, and Saint Kitts and Nevis have express or implied rights to secession. Switzerland allows for the secession from current and the creation of new cantons. In the case of proposed Quebec separation from Canada the Supreme Court of Canada
in 1998 ruled that only both a clear majority of the province and a
constitutional amendment confirmed by all participants in the Canadian
federation could allow secession.
The 2003 draft of the European Union Constitution
allowed for the voluntary withdrawal of member states from the union,
although the State wanted to leave could not be involved in the vote
deciding whether or not they can leave the Union. There was much discussion about such self-determination by minorities before the final document underwent the unsuccessful ratification process in 2005.
As a result of the successful constitutional referendum held in 2003, every municipality in the Principality of Liechtenstein has the right to secede from the Principality by a vote of a majority of the citizens residing in this municipality.
Drawing new borders
In determining international borders between sovereign states, self-determination has yielded to a number of other principles.
Once groups exercise self-determination through secession, the issue of
the proposed borders may prove more controversial than the fact of
secession. The bloody Yugoslav wars in the 1990s were related mostly to
border issues because the international community applied a version of uti possidetis juris
in transforming the existing internal borders of the various Yugoslav
republics into international borders, despite the conflicts of ethnic
groups within those boundaries. In the 1990s indigenous populations of
the northern two-thirds of Quebec province opposed being incorporated
into a Quebec nation and stated a determination to resist it by force.
The border between Northern Ireland and the Irish Free State was based on the borders of existing counties and did not include all of historic Ulster. A Boundary Commission
was established to consider re-drawing it. Its proposals, which
amounted to a small net transfer to Northern Ireland, were leaked to the
press and then not acted upon. In December 1925, the governments of the
Irish Free State, Northern Ireland, and the United Kingdom agreed to
accept the existing border.
Notable cases
Artsakh (Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh)
Republic of Artsakh
(Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh) declared its independence basing on
self-determination rights on September 2, 1991. It successfully
defended its independence in subsequent war with Azerbaijan, but remains largely unrecognized by UN states today.
Australia
From 2003 onwards, self-determination has become the topic of some debate in Australia in relation to Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders.
In the 1970s, the Indigenous community approached the Federal
Government and requested the right to administer their own communities.
This encompassed basic local government functions, ranging from land
dealings and management of community centers to road maintenance and
garbage collection, as well as setting education programs and
standards in their local schools.
Azawad
The traditional homeland of the Tuareg peoples was divided up by the modern borders of Mali, Algeria and Niger.
Numerous rebellions occurred over the decades, but in 2012 the Tuaregs
succeeded in occupying their land and declaring the independence of Azawad. However, their movement was hijacked by the Islamist terrorist group Ansar Dine.
Basque Country
The Basque Country (Basque: Euskal Herria, Spanish: País Vasco, French: Pays Basque) as a cultural region (not to be confused with the homonym Autonomous Community of the Basque country) is a European region in the western Pyrenees
that spans the border between France and Spain, on the Atlantic coast.
It comprises the autonomous communities of the Basque Country and Navarre in Spain and the Northern Basque Country in France.
Since the 19th century, Basque nationalism has demanded the right of some kind of self-determination. This desire for independence is particularly stressed among leftist Basque nationalists. The right of self-determination was asserted by the Basque Parliament in 1990, 2002 and 2006.
Since self-determination is not recognized in the Spanish Constitution of 1978,
some Basques abstained and some voted against it in the referendum of
December 6 of that year. It was approved by a clear majority at the
Spanish level, and with 74.6% of the votes in the Basque Country.
However, the overall turnout in the Basque Country was 45% when the
Spanish overall turnover was 67.9%. The derived autonomous regime for
the BAC was approved by Spanish Parliament and also by the Basque
citizens in referendum. The autonomous statue of Navarre (Amejoramiento del Fuero:
"improvement of the charter") was approved by the Spanish Parliament
and, like the statues of 13 out of 17 Spanish autonomous communities, it
didn´t need a referendum to enter into force.
Euskadi Ta Askatasuna or ETA (English: Basque Homeland and Freedom; pronounced), is an armed Basque nationalist, separatist and terrorist organization. Founded in 1959, it evolved from a group advocating traditional cultural ways to a paramilitary group with the goal of Basque independence. Its ideology is Marxist–Leninist.
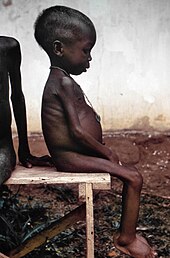
A girl during the Nigerian Civil War of the late 1960s. Pictures of the famine caused by Nigerian blockade garnered sympathy for the Biafrans worldwide.
Biafra
The Nigerian Civil War was fought between Biafran secessionists of the Republic of Biafra
and the Nigerian central government. From 1999 to the present day, the
indigenous people of Biafra have been agitating for independence to
revive their country. They have registered a human rights organization
known as Bilie Human Rights Initiative both in Nigeria and in the United
Nations to advocate for their right to self-determination and achieve
independence by the rule of law.
Catalonia
Catalan general strike following Catalonia's referendum on independence, 3 October 2017
After the 2012 Catalan march for independence, in which between 600,000 and 1.5 million citizens marched, the President of Catalonia, Artur Mas, called for new parliamentary elections on 25 November 2012 to elect a new parliament
that would exercise the right of self-determination for Catalonia, a
right not recognized under the Spanish constitution. The Parliament of
Catalonia voted to hold a votee in the next four-year legislature on the
question of self-determination. The parliamentary decision was approved
by a large majority of MPs: 84 voted for, 21 voted against, and 25
abstained.
The Catalan Parliament applied to the Spanish Parliament for the power
to call a referendum to be devolved, but this was turned down. In
December 2013 the President of the Generalitat Artur Mas and the
governing coalition agreed to set the referendum for self-determination
on 9 November 2014, and legislation specifically saying that the
consultation would not be a "referendum" was enacted, only to be blocked
by the Spanish Constitutional Court, at the request of the Spanish
government. Given the block, the Government turned it into a simple
"consultation to the people" instead.
The question in the consultation was "Do you want Catalonia to be
a State?" and, if the answer to this question was yes, "Do you want
this State to be an independent State?". However, as the consultation
was not a formal referendum, these (printed) answers were just
suggestions and other answers were also accepted and catalogued as
"other answers" instead as null votes. The turnout in this consultation
was about 2·3m people out of 6·2m people that were called to vote (this
figure does not coincide with the census figure of 5·3m for two main
reasons: first, because organizers had no access to an official census
due to the non-binding character of the consultation, and second,
because the legal voting age was set to 16 rather than 18). Due to the
lack of an official census, potential voters were assigned to electoral
tables according to home address and first family name. Participants had
to sign up first with their full name and national ID in a voter
registry before casting their ballot, which prevented participants from
potentially casting multiple ballots. The overall result was 80·76% in
favor of both questions, 11% in favor of the first question but not of
the second questions, 4·54% against both; the rest were classified as
"other answers". The voter turnout was around 37% (most people against
the consultation didn't go to vote). Four top members of Catalonia's
political leadership were barred from public office for having defied
the Constitutional court's last-minute ban.
Almost three years later (1 October 2017), the Catalan government
called a referendum for independence under legislation adopted in
September 2017 (despite being blocked by the Constitutional Court of
Spain), with the question "Do you want Catalonia to become an
independent state in the form of a Republic?". On polling day, the
Catalan police prevented voting in over 500 polling stations, without
incident, while the Spanish police confiscated ballot boxes and closed
down 92,
with several incidents involving truncheon charges, the closure of some
voting centres and the seizure of ballot boxes. The opposition parties
had called for non-participation. The turnout (according to the votes
that were counted) was 2·3m out of 5·3m (43·03% of the census), and
90·18% of the ballots were in favor of independence. The turnout, ballot count and results were similar to those of the 2014 "consultation".
Chechnya
Under Dzhokhar Dudayev, Chechnya declared independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria,
using self-determination, Russia's history of bad treatment of
Chechens, and a history of independence before invasion by Russia as
main motives. Russia has restored control over Chechnya, but the
separatist government functions still in exile, though it has been split
into two entities: the Akhmed Zakayev-run secular Chechen Republic (based in Poland, the UK and the US), and the Islamic Caucasus Emirate.
Eastern Ukraine
Pro-Russian separatists in Donetsk during the Ukraine-Crisis, April 2015
There is an active secessionist movement based on the self-determination of the residents of the Donetsk and Luhansk regions of eastern Ukraine,
allegedly against the instability and corruption of the Ukrainian
government. However, many in the international community assert that referendums held there in 2014 regarding independence from Ukraine were illegitimate and undemocratic. Similarly, there are reports that presidential elections in May 2014
were prevented from taking place in the two regions after armed gunmen
took control of polling stations, kidnapped election officials, and
stole lists of electors, thus denying the population the chance to
express their will in a free, fair, and internationally recognized
election.
There are also arguments, that the de facto separation of Eastern
Ukraine from the rest of the country is not in fact an expression of
self-determination, but rather an invasion by neighboring Russia, with Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko reporting to MPs on the 4th June 2015 that up to nine thousand Russian soldiers were deployed in Ukraine.
Falkland Islands
Self-determination is referred to in the Falkland Islands Constitution and is a factor in the Falkland Islands sovereignty dispute. The population has existed for over nine generations, continuously for over 185 years. In the 2013 referendum organized by the Falkland Islands Government, 99.8% voted to remain British.
As administering power, the British Government considers since the
majority of inhabitants wish to remain British, transfer of sovereignty
to Argentina would be counter to their right to self-determination.
Argentina states the principle of self-determination is not
applicable since the current inhabitants are not aboriginal and were
brought to replace the Argentine population, which was expelled by an
'act of force', forcing the Argentinian inhabitants to directly leave
the islands. This refers to the re-establishment of British rule in the year 1833
during which Argentina claims the existing population living in the
islands was expelled. Argentina thus argues that, in the case of the
Falkland Islands, the principle of territorial integrity should have precedence over self-determination.
Historical records dispute Argentina's claims and whilst acknowledging
the garrison was expelled note the existing civilian population remained
at Port Louis and there was no attempt to settle the islands until 1841.
Gibraltar
Gibraltar National Day, September 2013
The right to self-determination is referred to in the pre-amble of Chapter 1 of the Gibraltar constitution,
and, since the United Kingdom also gave assurances that the right to
self-determination of Gibraltarians would be respected in any transfer
of sovereignty over the territory, is a factor in the dispute with Spain
over the territory. The impact of the right to self-determination of Gibraltarians was seen in the 2002 Gibraltar sovereignty referendum,
where Gibraltarian voters overwhelmingly rejected a plan to share
sovereignty over Gibraltar between the UK and Spain. However, the UK
government differs with the Gibraltarian government in that it considers
Gibraltarian self-determination to be limited by the Treaty of Utrecht,
which prevents Gibraltar achieving independence without the agreement
of Spain, a position that the Gibraltarian government does not accept.
The Spanish government denies that Gibraltarians have the right
to self-determination, considering them to be "an artificial population
without any genuine autonomy" and not "indigenous". However, the Partido Andalucista has agreed to recognize the right to self-determination of Gibraltarians.
Hong Kong
Before the United Nations's adoption of resolution 2908 (XXVII) on 2
November 1972, The People's Republic of China vetoed the former British
colony of Hong Kong's right to self-determination on 8 March 1972. This
sparked several nation's protest along with Great Britain's declaration
on 14 December that the decision is invalid.
A street sign during the 2014 Hong Kong Protests for Democracy.
Decades later, a nationalist independence movement, dubbed as the
Hong Kong independence movement emerged in the now Communist Chinese
controlled territory. It advocates the autonomous region to become a
fully independent sovereign state.
The city is considered a special administrative region (SAR)
which, according to the PRC, enjoys a high degree of autonomy under the
People's Republic of China (PRC), guaranteed under Article 2 of Hong Kong Basic Law (which is ratified under the Sino-British Joint Declaration), since the transfer of the sovereignty of Hong Kong from
the United Kingdom to the PRC in 1997. Since the handover, many
Hongkongers are increasingly concerned about Beijing's growing
encroachment on the territory's freedoms and the failure of the Hong
Kong government to deliver 'true' democracy.
Pro-independence Hong Kong flag put up before a football match between the Hong Kong Football Team and the China national football team.
The 2014–15 Hong Kong electoral reform package
deeply divided the city, as it allowed Hongkongers to have universal
suffrage, but Beijing would have authority to screen the candidates to
restrict the electoral method for the Chief Executive of Hong Kong (CE),
the highest-ranking official of the territory. This sparked the 79-day
massive peaceful protests which was dubbed as the "Umbrella Revolution" and the pro-independence movement emerged on the Hong Kong political scene.
Since then, localism has gained momentum, particularly after the failure of the peaceful Umbrella Movement.
Young localist leaders have led numerous protest actions against
pro-Chinese policies to raise awareness of social problems of Hong Kong
under Chinese rule. These include the sit-in protest against the Bill to Strengthen Internet Censorship, demonstrations against Chinese political interference in the University of Hong Kong, the Recover Yuen Long protests and the 2016 Mong Kok civil unrest. According to a survey conducted by the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK)
in July 2016, 17.4% of respondents supported the city becoming an
independent entity after 2047, while 3.6% stated that it is "possible".
Kashmir
Ever since Pakistan and India’s inception in 1947 the legal state of
Jammu and Kashmir, the land between India and Pakistan, has been
contested as Britain was resigning from their rule over this land.
Maharaja Hari Singh, the ruler residing over Kashmir at the time
accession, signed the Instrument of Accession Act on October 26, 1947 as
his territory was being attacked by Pakistani tribesmen. The passing of
this Act allowed Jammu and Kashmir to accede to India on legal terms.
When this Act was taken to Lord Mountbatten, the last viceroy of British
India, he agreed to it and stated that a referendum needed to be held
by the citizens in India, Pakistan, and Kashmir so that they could vote
as to where Kashmir should accede to. This referendum that Mountbatten
called for never took place and framed one of the legal disputes for
Kashmir. In 1948 the United Nations intervened and ordered a plebiscite
to be taken in order to hear the voices of the Kashmiris if they would
like to accede to Pakistan or India. This plebiscite left out the right
for Kashmiris to have the right of self-determination and become an
autonomous state. To this date the Kashmiris have been faced with
numerous human rights violations committed by both India and Pakistan
and have yet to gain complete autonomy which they have been seeking
through self-determination.
The insurgency in Kashmir against Indian rule has existed in
various forms. A widespread armed insurgency started in Kashmir against
India rule in 1989 after allegations of rigging by the Indian government
in the 1987 Jammu and Kashmir state election. This led to some parties
in the state assembly forming militant wings, which acted as a catalyst
for the emergence of armed insurgency in the region. The conflict over
Kashmir has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths.
Indian soldiers on the streets of Kashmir during the 2016 unrests.
The Inter-Services Intelligence of Pakistan has been accused by India
of supporting and training both pro-Pakistan and pro-independence
militants to fight Indian security forces in Jammu and Kashmir, a charge
that Pakistan denies. According to official figures released in the
Jammu and Kashmir assembly, there were 3,400 disappearance cases and the
conflict has left more than 47,000 to 100,000 people dead as of July
2009. However, violence in the state had fallen sharply after the start
of a slow-moving peace process between India and Pakistan. After the
peace process failed in 2008, mass demonstrations against Indian rule,
and also low-scale militancy have emerged again.
However, despite boycott calls by separatist leaders in 2014, the
Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections saw highest voters turnout in last
25 years since insurgency erupted. As per the Indian government, it
recorded more than 65% of voters turnout which was more than usual
voters turnout in other state assembly elections of India. It considered
as increase in faith of Kashmiri people in democratic process of India.
However, activists say that the voter turnout is highly exaggerated and
that elections are held under duress. Votes are cast because the people
want stable governance of the state, and this cannot be mistaken as an
endorsement of Indian rule. Nevertheless situation in Indian occupied Kashmir getting worse day by day.
Kurdistan
Kurdish Peshmerga fighters during the Syrian War
Kurdish flag in northern Iraq, 2007
Kurdistan is a historical region primarily inhabited by the Kurdish people
of the middle east. The territory is currently part of 4 states Turkey,
Iraq, Syria and Iran. There are Kurdish self-determination movements in
each of the 4 states. Iraqi Kurdistan has to date achieved the largest
degree of self-determination through the formation of the Kurdistan Regional Government, an entity recognised by the Iraqi Federal Constitution.
Although the right of the creation of a Kurdish state was recognized following World War I in the Treaty of Sèvres, the treaty was then annulled by the Treaty of Lausanne (1923). To date two separate Kurdish republics and one Kurdish Kingdom have declared sovereignty. The Republic of Ararat (Ağrı Province, Turkey), the Republic of Mehabad (West Azerbaijan Province, Iran) and the Kingdom of Kurdistan (Sulaymaniyah Province, Iraqi Kurdistan, Iraq), each of these fledgling states was crushed by military intervention. The Patriotic Union of Kurdistan which currently holds the Iraqi presidency and the Kurdistan Democratic Party which governs the Kurdistan Regional Government
both explicitly commit themselves to the development of Kurdish
self-determination, but opinions vary as to the question of
self-determination sought within the current borders and countries.
Nagalim
Naga
refers to a vaguely-defined conglomeration of distinct tribes living on
the border of India and Burma. Each of these tribes lived in a
sovereign village before the arrival of the British,
but developed a common identity as the area was Christianized. After
the British left India, a section of Nagas under the leadership of Angami Zapu Phizo sought to establish a separate country for the Nagas. Phizo's group, the Naga National Council
(NNC), claimed that 99. 9% of the Nagas wanted an independent Naga
country according to a referendum conducted by it. It waged a
secessionist insurgency against the Government of India. The NNC
collapsed after Phizo got his dissenters killed or forced them to seek
refuge with the Government.
Phizo escaped to London, while NNC's successor secessionist groups
continued to stage violent attacks against the Indian Government. The
Naga People's Convention (NPC), another major Naga organization, was
opposed to the secessionists. Its efforts led to the creation of a
separate Nagaland state within India in 1963. The secessionist violence declined considerably after the Shillong Accord of 1975. However, three factions of the National Socialist Council of Nagaland
(NSCN) continue to seek an independent country which would include
parts of India and Burma. They envisage a sovereign, predominantly
Christian nation called "Nagalim".
North Borneo and Sarawak
Another controversial episode with perhaps more relevance was the British beginning their exit from British Malaya. An experience concerned the findings of a United Nations Assessment Team that led the British territories of North Borneo and Sarawak in 1963 to determine whether or not the populations wished to become a part of the new Malaysia Federation. The United Nation Team's mission followed on from an earlier assessment by the British-appointed Cobbold Commission
which had arrived in the territories in 1962 and held hearings to
determine public opinion. It also sifted through 1600 letters and
memoranda submitted by individuals, organizations and political parties.
Cobbold concluded that around two thirds of the population favored to
the formation of Malaysia while the remaining third wanted either
independence or continuing control by the United Kingdom. The United
Nations team largely confirmed these findings, which were later accepted
by the General Assembly, and both territories subsequently wish to form
the new Federation of Malaysia. The conclusions of both the Cobbold Commission and the United Nations team were arrived at without any referendums self-determination being held. Unlike in Singapore, however, no referendum was ever conducted in Sarawak and North Borneo. they sought to consolidate several of the previous ruled entities then there was Manila Accord, an agreement between the Philippines, Federation of Malaya and Indonesia on 31 July 1963 to abide by the wishes of the people of North Borneo and Sarawak within the context of United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1541 (XV), Principle 9 of the Annex taking into account referendums in North Borneo and Sarawak that would be free and without coercion. This also triggered the Indonesian confrontation because Indonesia opposed the violation of the agreements.
Northern Cyprus
Atatürk Square, North Nicosia in 2006, with the Northern Cyprus and Turkish flags.
Cyprus was settled by Mycenaean Greeks in two waves in the 2nd
millennium BC. As a strategic location in the Middle East, it was
subsequently occupied by several major powers, including the empires of
the Assyrians, Egyptians and Persians, from whom the island was seized
in 333 BC by Alexander the Great. Subsequent rule by Ptolemaic Egypt,
the Classical and Eastern Roman Empire, Arab caliphates for a short
period and the French Lusignan dynasty. Following the death in 1473 of
James II, the last Lusignan king, the Republic of Venice assumed control
of the island, while the late king's Venetian widow, Queen Catherine
Cornaro, reigned as figurehead. Venice formally annexed the Kingdom of
Cyprus in 1489, following the abdication of Catherine. The Venetians
fortified Nicosia by building the Walls of Nicosia, and used it as an
important commercial hub.
Although the Lusignan French aristocracy remained the dominant
social class in Cyprus throughout the medieval period, the former
assumption that Greeks were treated only as serfs on the island is no
longer considered by academics to be accurate. It is now accepted that
the medieval period saw increasing numbers of Greek Cypriots elevated to
the upper classes, a growing Greek middle ranks, and the Lusignan royal
household even marrying Greeks. This included King John II of Cyprus
who married Helena Palaiologina.
Throughout Venetian rule, the Ottoman Empire frequently raided
Cyprus. In 1539 the Ottomans destroyed Limassol and so fearing the
worst, the Venetians also fortified Famagusta and Kyrenia.
Invaded in 1570, Turks controlled and solely governed all of the
Cyprus island from 1571 till its leasing to the United Kingdom in 1878.
Cyprus was placed under British administration based on Cyprus
Convention in 1878 and formally annexed by Britain in 1914. While
Turkish Cypriots made up 18% of the population, the partition of Cyprus
and creation of a Turkish state in the north became a policy of Turkish
Cypriot leaders and Turkey in the 1950s. Politically, there was no
majority/minority relation between Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots; and hence, in 1960, Republic of Cyprus was founded by the constituent communities in Cyprus (Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots) as a non-unitary state; the 1960 Constitution set both Turkish and Greek as the
official languages.
During 1963-74, the island experienced ethnic clashes and turmoil, the
coup to unify the island to Greece and eventual Turkish operation in
1974. The idea of separation for peace has been amplified by a
UN-implemented population exchange agreement in 1975. Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus was declared in 1983 and recognized only by Turkey. Turkish Cypriots had the right of self-determination, as well as Greek Cypriots. Before the Turkey's operation in 1974, Turkish Cypriots were concentrated in Turkish Cypriot enclaves in the island.
Northern Cyprus fulfills all the classical criteria of statehood. United Nations Peace Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) operates based on the laws of Northern Cyprus in north of Cyprus island. According to European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR), the laws of Northern Cyprus is valid in the north of Cyprus. ECtHR did not accept the claim that the Courts of Northern Cyprus lacked "independence and/or impartiality". ECtHR directed all Cypriots to exhaust "domestic remedies" applied by Northern Cyprus before taking their cases to ECtHR. In 2014, United States' Federal Court qualified Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus as a "democratic country".
In 2017, United Kingdom's High Court decided that "There was no duty in
UK law upon the UK's Government to refrain from recognising Northern
Cyprus. The United Nations itself works with Northern Cyprus law
enforcement agencies and facilitates cooperation between the two parts
of the island." UK's High Court also dismissed the claim that "cooperation between UK police and law agencies in northern Cyprus was illegal".
Quebec
In Canada, many in the province of Quebec have wanted the province to separate from Confederation. The Parti Québécois has asserted Quebec's "right to self-determination. " There is debate on under which conditions would this right be realized. French-speaking Quebec nationalism and support for maintaining Québécois culture would inspire Quebec nationalists, many of whom were supporters of the Quebec sovereignty movement during the late-20th century.
South Africa
Section 235 of the South African Constitution
allows for the right to self-determination of a community, within the
framework of "the right of the South African people as a whole to
self-determination", and pursuant to national legislation.
This section of the constitution was one of the negotiated settlements
during the handing over of political power in 1994. Supporters of an
independent Afrikaner homeland have argued that their goals are reasonable under this new legislation.
United States
A Native American woman in traditional dress.
The colonization of the North American continent and its Native American
population has been the source of legal battles since the early 19th
century. Many Native American tribes were resettled onto separate tracts
of land (reservations), which have retained a certain degree of autonomy within the United States. The federal government recognizes Tribal Sovereignty
and has established a number of laws attempting to clarify the
relationship among the federal, state, and tribal governments. The
Constitution and later federal laws recognize the local sovereignty of
tribal nations, but do not recognize full sovereignty equivalent to that
of foreign nations, hence the term "domestic dependent nations" to
qualify the federally recognized tribes.
Certain Chicano nationalist groups seek to "recreate" an ethnic-based state to be called Aztlán, after the legendary homeland of the Aztecs. It would comprise the Southwestern United States,
historic territory of indigenous peoples and their descendants, as well
as colonists and later settlers under the Spanish colonial and Mexican
governments. Black nationalists have argued that, by virtue of slaves' unpaid labor and the harsh experiences of African Americans under slavery and Jim Crow, African Americans have a moral claim to the black belt region of the American South. They believe this area should be the basis of forming an independent state of New Afrika, designed to have an African-American majority and political control.
There are several active Hawaiian autonomy or independence
movements, each with the goal of realizing some level of political
control over single or several islands. The groups range from those
seeking territorial units similar to Indian reservations under the
United States, with the least amount of independent control, to the Hawaiian sovereignty movement,
which is projected to have the most amount of independence. The
Hawaiian Sovereignty movement seeks to revive the Hawaiian nation under
the Hawaiian constitution. Supporters of this concept say that Hawaii retained its sovereignty while under control of the United States.
Native Americans and their supporters protest during the Washington Redskins name controversy.
Since 1972, the U.N. Decolonization Committee has called for Puerto Rico's
"decolonization" and for the US to recognize the island's right to
self-determination and independence. In 2007 the Decolonization
Subcommittee called for the United Nations General Assembly to review
the political status of Puerto Rico, a power reserved by the 1953
Resolution. This followed the 1967 passage of a plebiscite
act that provided for a vote on the status of Puerto Rico with three
status options: continued commonwealth, statehood, and independence. In
the first plebscite, the commonwealth option won with 60.4% of the
votes, but US congressional committees failed to enact legislation to
address the status issue. In subsequent plebiscites in 1993 and 1998,
the status quo was favored.
In a referendum
that took place in November 2012, a majority of Puerto Rican residents
voted to change the territory's relationship with the United States,
with the statehood option being the preferred option. But a large number
of ballots—one-third of all votes cast—were left blank on the question
of preferred alternative status. Supporters of the commonwealth status
had urged voters to blank their ballots. When the blank votes are
counted as anti-statehood votes, the statehood option would have
received less than 50% of all ballots received. As of January 2014, Washington has not taken action to address the results of this plebiscite.
Many current US state, regional and city secession groups use the language of self-determination. A 2008 Zogby International
poll revealed that 22% of Americans believe that "any state or region
has the right to peaceably secede and become an independent republic."
Since the late 20th century, some states periodically discuss
desires to secede from the United States. Unilateral secession was ruled
unconstitutional by the US Supreme Court in Texas v. White (1869).
In the case of Hawaii, the struggle for self-determination does
not fall under secession, as it is less a break from federal
administration, than a return to the process through which cession was
claimed to have occurred: namely the ongoing occupation via a US imposed
military coup; and/or removal from the UN list of Non-Self-Governing
Territories.
to educate or properly inform the citizenry of Hawaii of its options
for self-determination and sidestepped guidelines laid out in UN General
Assembly resolution 742 (1953).
West Papua
The self-determination of the West Papuan people has been violently suppressed by the Indonesian government since the withdrawal of Dutch colonial rule under the Netherlands New Guinea in 1962.
A demonstration in Madrid for the independence of Western Sahara, 2007
Western Sahara
There is an active movement based on the self-determination of the Sahrawi people in the Western Sahara region. Morocco also claims the entire territory, and maintains control of about two-thirds of the region.