| |
| General | |
|---|---|
| Name, symbol | Hydrogen-2,2H or D |
| Neutrons | 1 |
| Protons | 1 |
| Nuclide data | |
| Natural abundance | 0.0115% (Earth) |
| Isotope mass | 2.013553212745(40) u |
| Spin | 1+ |
| Excess energy | 13135.720± 0.001 keV |
| Binding energy | 2224.52± 0.20 keV |
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol
D
or 2H
, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of deuterium, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutron in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in 6420 of hydrogen. Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% (or, on a mass basis, 0.0312%) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another.
The deuterium isotope's name is formed from the Greek deuteros, meaning "second", to denote the two particles composing the nucleus. Deuterium was discovered and named in 1931 by Harold Urey. When the neutron was discovered in 1932, this made the nuclear structure of deuterium obvious, and Urey won the Nobel Prize in 1934. Soon after deuterium's discovery, Urey and others produced samples of "heavy water" in which the deuterium content had been highly concentrated.
Deuterium is destroyed in the interiors of stars faster than it is produced. Other natural processes are thought to produce only an insignificant amount of deuterium. Nearly all deuterium found in nature was produced in the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, as the basic or primordial ratio of hydrogen-1 to deuterium (about 26 atoms of deuterium per million hydrogen atoms) has its origin from that time. This is the ratio found in the gas giant planets, such as Jupiter. However, other astronomical bodies are found to have different ratios of deuterium to hydrogen-1. This is thought to be a result of natural isotope separation processes that occur from solar heating of ices in comets. Like the water cycle in Earth's weather, such heating processes may enrich deuterium with respect to protium. The analysis of deuterium/protium ratios in comets found results very similar to the mean ratio in Earth's oceans (156 atoms of deuterium per million hydrogens). This reinforces theories that much of Earth's ocean water is of cometary origin. The deuterium/protium ratio of the comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, as measured by the Rosetta space probe, is about three times that of earth water. This figure is the highest yet measured in a comet.
Deuterium/protium ratios thus continue to be an active topic of research in both astronomy and climatology.
Differences from common hydrogen (protium)
Chemical symbol
Deuterium discharge tube
Deuterium is frequently represented by the chemical symbol D. Since it is an isotope of hydrogen with mass number 2, it is also represented by 2H
. IUPAC allows both D and 2H
, although 2H
is preferred. A distinct chemical symbol is used for convenience because of the isotope's common use in various scientific processes. Also, its large mass difference with protium (1H) (deuterium has a mass of 2.014102 u, compared to the mean hydrogen atomic weight of 1.007947 u, and protium's mass of 1.007825 u) confers non-negligible chemical dissimilarities with protium-containing compounds, whereas the isotope weight ratios within other chemical elements are largely insignificant in this regard.
. IUPAC allows both D and 2H
, although 2H
is preferred. A distinct chemical symbol is used for convenience because of the isotope's common use in various scientific processes. Also, its large mass difference with protium (1H) (deuterium has a mass of 2.014102 u, compared to the mean hydrogen atomic weight of 1.007947 u, and protium's mass of 1.007825 u) confers non-negligible chemical dissimilarities with protium-containing compounds, whereas the isotope weight ratios within other chemical elements are largely insignificant in this regard.
Spectroscopy
In quantum mechanics the energy levels of electrons in atoms depend on the reduced mass of the system of electron and nucleus. For the hydrogen atom, the role of reduced mass is most simply seen in the Bohr model of the atom, where the reduced mass appears in a simple calculation of the Rydberg constant and Rydberg equation, but the reduced mass also appears in the Schrödinger equation, and the Dirac equation for calculating atomic energy levels.
The reduced mass of the system in these equations is close to the
mass of a single electron, but differs from it by a small amount about
equal to the ratio of mass of the electron to the atomic nucleus. For
hydrogen, this amount is about 1837/1836, or 1.000545, and for deuterium
it is even smaller: 3671/3670, or 1.0002725. The energies of
spectroscopic lines for deuterium and light hydrogen (hydrogen-1)
therefore differ by the ratios of these two numbers, which is 1.000272.
The wavelengths of all deuterium spectroscopic lines are shorter than
the corresponding lines of light hydrogen, by a factor of 1.000272. In
astronomical observation, this corresponds to a blue Doppler shift of
0.000272 times the speed of light, or 81.6 km/s.
The differences are much more pronounced in vibrational spectroscopy such as infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy, and in rotational spectra such as microwave spectroscopy because the reduced mass of the deuterium is markedly higher than that of protium. In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, deuterium has a very different NMR
frequency (e.g. 61 MHz when protium is at 400 MHz) and is much less
sensitive. Deuterated solvents are usually used in protium NMR to
prevent the solvent from overlapping with the signal, although deuterium NMR on its own right is also possible.
Big Bang nucleosynthesis
Deuterium is thought to have played an important role in setting the
number and ratios of the elements that were formed in the Big Bang.
Combining thermodynamics and the changes brought about by cosmic
expansion, one can calculate the fraction of protons and neutrons based
on the temperature at the point that the universe cooled enough to allow
formation of nuclei. This calculation indicates seven protons for every
neutron at the beginning of nucleogenesis, a ratio that would remain
stable even after nucleogenesis was over. This fraction was in favor of
protons initially, primarily because the lower mass of the proton
favored their production. As the universe expanded, it cooled. Free neutrons
and protons are less stable than helium nuclei, and the protons and
neutrons had a strong energetic reason to form helium-4. However,
forming helium-4 requires the intermediate step of forming deuterium.
Through much of the few minutes after the big bang during which
nucleosynthesis could have occurred, the temperature was high enough
that the mean energy per particle was greater than the binding energy of
weakly bound deuterium; therefore any deuterium that was formed was
immediately destroyed. This situation is known as the deuterium bottleneck.
The bottleneck delayed formation of any helium-4 until the universe
became cool enough to form deuterium (at about a temperature equivalent
to 100 keV). At this point, there was a sudden burst of element
formation (first deuterium, which immediately fused to helium). However,
very shortly thereafter, at twenty minutes after the Big Bang, the
universe became too cool for any further nuclear fusion and
nucleosynthesis to occur. At this point, the elemental abundances were
nearly fixed, with the only change as some of the radioactive products of big bang nucleosynthesis (such as tritium) decay.
The deuterium bottleneck in the formation of helium, together with the
lack of stable ways for helium to combine with hydrogen or with itself
(there are no stable nuclei with mass numbers of five or eight) meant
that an insignificant amount of carbon, or any elements heavier than
carbon, formed in the Big Bang. These elements thus required formation
in stars. At the same time, the failure of much nucleogenesis during the
Big Bang ensured that there would be plenty of hydrogen in the later
universe available to form long-lived stars, such as our Sun.
Abundance
Deuterium occurs in trace amounts naturally as deuterium gas, written 2H
2 or D2, but most natural occurrence in the universe is bonded with a typical 1H
atom, a gas called hydrogen deuteride (HD or 1H
2H
).
2 or D2, but most natural occurrence in the universe is bonded with a typical 1H
atom, a gas called hydrogen deuteride (HD or 1H
2H
).
The existence of deuterium on Earth, elsewhere in the solar system (as confirmed by planetary probes), and in the spectra of stars, is also an important datum in cosmology.
Gamma radiation from ordinary nuclear fusion dissociates deuterium into
protons and neutrons, and there are no known natural processes other
than the Big Bang nucleosynthesis, which might have produced deuterium at anything close to its observed natural abundance (deuterium is produced by the rare cluster decay,
and occasional absorption of naturally occurring neutrons by light
hydrogen, but these are trivial sources). There is thought to be little
deuterium in the interior of the Sun and other stars, as at temperatures
there nuclear fusion reactions that consume deuterium happen much faster than the proton-proton reaction
that creates deuterium. However, deuterium persists in the outer solar
atmosphere at roughly the same concentration as in Jupiter, and this has
probably been unchanged since the origin of the Solar System. The
natural abundance of deuterium seems to be a very similar fraction of
hydrogen, wherever hydrogen is found, unless there are obvious processes
at work that concentrate it.
The existence of deuterium at a low but constant primordial
fraction in all hydrogen is another one of the arguments in favor of the
Big Bang theory over the Steady State theory
of the universe. The observed ratios of hydrogen to helium to deuterium
in the universe are difficult to explain except with a Big Bang model.
It is estimated that the abundances of deuterium have not evolved
significantly since their production about 13.8 billion years ago.
Measurements of Milky Way galactic deuterium from ultraviolet spectral
analysis show a ratio of as much as 23 atoms of deuterium per million
hydrogen atoms in undisturbed gas clouds, which is only 15% below the WMAP
estimated primordial ratio of about 27 atoms per million from the Big
Bang. This has been interpreted to mean that less deuterium has been
destroyed in star formation in our galaxy than expected, or perhaps
deuterium has been replenished by a large in-fall of primordial hydrogen
from outside the galaxy.
In space a few hundred light years from the Sun, deuterium abundance is
only 15 atoms per million, but this value is presumably influenced by
differential adsorption of deuterium onto carbon dust grains in
interstellar space.
The abundance of deuterium in the atmosphere of Jupiter has been directly measured by the Galileo space probe as 26 atoms per million hydrogen atoms. ISO-SWS observations find 22 atoms per million hydrogen atoms in Jupiter. and this abundance is thought to represent close to the primordial solar system ratio. This is about 17% of the terrestrial deuterium-to-hydrogen ratio of 156 deuterium atoms per million hydrogen atoms.
Cometary bodies such as Comet Hale-Bopp and Halley's Comet
have been measured to contain relatively more deuterium (about 200
atoms D per million hydrogens), ratios which are enriched with respect
to the presumed protosolar nebula ratio, probably due to heating, and
which are similar to the ratios found in Earth seawater. The recent
measurement of deuterium amounts of 161 atoms D per million hydrogen in
Comet 103P/Hartley (a former Kuiper belt
object), a ratio almost exactly that in Earth's oceans, emphasizes the
theory that Earth's surface water may be largely comet-derived. Most recently the deuterium/protium (D/H) ratio of 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko as measured by Rosetta is about three times that of Earth water, a figure that is high. This has caused renewed interest in suggestions that Earth's water may be partly of asteroidal origin.
Deuterium has also observed to be concentrated over the mean
solar abundance in other terrestrial planets, in particular Mars and
Venus.
Production
Deuterium is produced for industrial, scientific and military
purposes, by starting with ordinary water—a small fraction of which is
naturally-occurring heavy water—and then separating out the heavy water by the Girdler sulfide process, distillation, or other methods.
In theory, deuterium for heavy water could be created in a
nuclear reactor, but separation from ordinary water is the cheapest bulk
production process.
The world's leading supplier of deuterium was Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, in Canada, until 1997, when the last heavy water plant was shut down. Canada uses heavy water as a neutron moderator for the operation of the CANDU reactor design.
Another major producer of heavy water is India. All but one of
India's atomic energy plants are pressurised heavy water plants, which
use natural (i.e., not enriched) uranium. India has eight (seven are in
operation) heavy water plants, six (five) based on D-H exchange in
ammonia gas and two plants extract deuterium from natural water in a
process that uses hydrogen sulphide gas at high pressure.
While India is self-sufficient in heavy water for its own use, India now also exports reactor-grade heavy water.
Properties
Physical properties
The physical properties of deuterium compounds can exhibit significant kinetic isotope effects and other physical and chemical property differences from the hydrogen analogs. D2O, for example, is more viscous than H2O.
Chemically, there are differences in bond energy and length for
compounds of heavy hydrogen isotopes compared to normal hydrogen, which
are larger than the isotopic differences in any other element. Bonds
involving deuterium and tritium
are somewhat stronger than the corresponding bonds in hydrogen, and
these differences are enough to cause significant changes in biological
reactions. Pharmaceutical firms are interested in the fact that
deuterium is harder to remove from carbon than hydrogen.
Deuterium can replace the normal hydrogen in water molecules to form heavy water (D2O),
which is about 10.6% denser than normal water (so that ice made from it
sinks in ordinary water). Heavy water is slightly toxic in eukaryotic
animals, with 25% substitution of the body water causing cell division
problems and sterility, and 50% substitution causing death by cytotoxic
syndrome (bone marrow failure and gastrointestinal lining failure). Prokaryotic organisms, however, can survive and grow in pure heavy water, though they develop slowly. Despite this toxicity, consumption of heavy water under normal circumstances does not pose a health threat
to humans. It is estimated that a 70 kg (154 lb) person might drink 4.8
litres (1.3 US gal) of heavy water without serious consequences.
Small doses of heavy water (a few grams in humans, containing an amount
of deuterium comparable to that normally present in the body) are
routinely used as harmless metabolic tracers in humans and animals.
Quantum properties
The deuteron has spin +1 ("triplet") and is thus a boson. The NMR frequency of deuterium is significantly different from common light hydrogen. Infrared spectroscopy
also easily differentiates many deuterated compounds, due to the large
difference in IR absorption frequency seen in the vibration of a
chemical bond containing deuterium, versus light hydrogen. The two
stable isotopes of hydrogen can also be distinguished by using mass spectrometry.
The triplet deuteron nucleon is barely bound at EB = 2.23 MeV, and none of the higher energy states are bound. The singlet deuteron is a virtual state, with a negative binding energy of ~60 keV.
There is no such stable particle, but this virtual particle transiently
exists during neutron-proton inelastic scattering, accounting for the
unusually large neutron scattering cross-section of the proton.
Nuclear properties (the deuteron)
Deuteron mass and radius
The nucleus of deuterium is called a deuteron. It has a mass of 2.013553212745(40) u (equal to 1875.612 928(12) MeV)
The charge radius of the deuteron is 2.1413(25) fm. Like the proton radius, measurements using muonic deuterium produce a significantly smaller result: 2.12562(78) fm. This is 6σ less than the accepted CODATA 2014 value, measured using electrons, and confirms the unresolved proton charge radius anomaly.
Spin and energy
Deuterium is one of only five stable nuclides with an odd number of protons and an odd number of neutrons. (2H
, 6Li
, 10B
, 14N
, 180mTa
; also, the long-lived radioactive nuclides 40K
, 50V
, 138La
, 176Lu
occur naturally.) Most odd-odd nuclei are unstable with respect to beta decay, because the decay products are even-even, and are therefore more strongly bound, due to nuclear pairing effects. Deuterium, however, benefits from having its proton and neutron coupled to a spin-1 state, which gives a stronger nuclear attraction; the corresponding spin-1 state does not exist in the two-neutron or two-proton system, due to the Pauli exclusion principle which would require one or the other identical particle with the same spin to have some other different quantum number, such as orbital angular momentum. But orbital angular momentum of either particle gives a lower binding energy for the system, primarily due to increasing distance of the particles in the steep gradient of the nuclear force. In both cases, this causes the diproton and dineutron nucleus to be unstable.
, 6Li
, 10B
, 14N
, 180mTa
; also, the long-lived radioactive nuclides 40K
, 50V
, 138La
, 176Lu
occur naturally.) Most odd-odd nuclei are unstable with respect to beta decay, because the decay products are even-even, and are therefore more strongly bound, due to nuclear pairing effects. Deuterium, however, benefits from having its proton and neutron coupled to a spin-1 state, which gives a stronger nuclear attraction; the corresponding spin-1 state does not exist in the two-neutron or two-proton system, due to the Pauli exclusion principle which would require one or the other identical particle with the same spin to have some other different quantum number, such as orbital angular momentum. But orbital angular momentum of either particle gives a lower binding energy for the system, primarily due to increasing distance of the particles in the steep gradient of the nuclear force. In both cases, this causes the diproton and dineutron nucleus to be unstable.
The proton and neutron making up deuterium can be dissociated through neutral current interactions with neutrinos. The cross section for this interaction is comparatively large, and deuterium was successfully used as a neutrino target in the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory experiment.
Isospin singlet state of the deuteron
Due
to the similarity in mass and nuclear properties between the proton and
neutron, they are sometimes considered as two symmetric types of the
same object, a nucleon. While only the proton has an electric charge, this is often negligible due to the weakness of the electromagnetic interaction relative to the strong nuclear interaction. The symmetry relating the proton and neutron is known as isospin and denoted I (or sometimes T).
Isospin is an SU(2) symmetry, like ordinary spin, so is completely analogous to it. The proton and neutron form an isospin doublet, with a "down" state (↓) being a neutron, and an "up" state (↑) being a proton.
A pair of nucleons can either be in an antisymmetric state of isospin called singlet, or in a symmetric state called triplet. In terms of the "down" state and "up" state, the singlet is
This is a nucleus with one proton and one neutron, i.e. a deuterium nucleus. The triplet is
and thus consists of three types of nuclei, which are supposed to be symmetric: a deuterium nucleus (actually a highly excited state of it), a nucleus with two protons, and a nucleus with two neutrons. These states are not stable.
Approximated wavefunction of the deuteron
The
deuteron wavefunction must be antisymmetric if the isospin
representation is used (since a proton and a neutron are not identical
particles, the wavefunction
need not be antisymmetric in general). Apart from their isospin, the two
nucleons also have spin and spatial distributions of their
wavefunction. The latter is symmetric if the deuteron is symmetric under
parity
(i.e. have an "even" or "positive" parity), and antisymmetric if the
deuteron is antisymmetric under parity (i.e. have an "odd" or "negative"
parity). The parity is fully determined by the total orbital angular
momentum of the two nucleons: if it is even then the parity is even
(positive), and if it is odd then the parity is odd (negative).
The deuteron, being an isospin singlet, is antisymmetric under
nucleons exchange due to isospin, and therefore must be symmetric under
the double exchange of their spin and location. Therefore, it can be in
either of the following two different states:
- Symmetric spin and symmetric under parity. In this case, the exchange of the two nucleons will multiply the deuterium wavefunction by (−1) from isospin exchange, (+1) from spin exchange and (+1) from parity (location exchange), for a total of (−1) as needed for antisymmetry.
- Antisymmetric spin and antisymmetric under parity. In this case, the exchange of the two nucleons will multiply the deuterium wavefunction by (−1) from isospin exchange, (−1) from spin exchange and (−1) from parity (location exchange), again for a total of (−1) as needed for antisymmetry.
In the first case the deuteron is a spin triplet, so that its total spin s is 1. It also has an even parity and therefore even orbital angular momentum l ; The lower its orbital angular momentum, the lower its energy. Therefore, the lowest possible energy state has s = 1, l = 0.
In the second case the deuteron is a spin singlet, so that its total spin s is 0. It also has an odd parity and therefore odd orbital angular momentum l. Therefore, the lowest possible energy state has s = 0, l = 1.
Since s = 1 gives a stronger nuclear attraction, the deuterium ground state is in the s =1, l = 0 state.
The same considerations lead to the possible states of an isospin triplet having s = 0, l = even or s = 1, l = odd. Thus the state of lowest energy has s = 1, l = 1, higher than that of the isospin singlet.
The analysis just given is in fact only approximate, both because
isospin is not an exact symmetry, and more importantly because the strong nuclear interaction between the two nucleons is related to angular momentum in spin-orbit interaction that mixes different s and l states. That is, s and l are not constant in time (they do not commute with the Hamiltonian), and over time a state such as s = 1, l = 0 may become a state of s = 1, l = 2. Parity is still constant in time so these do not mix with odd l states (such as s = 0, l = 1). Therefore, the quantum state of the deuterium is a superposition (a linear combination) of the s = 1, l = 0 state and the s = 1, l = 2 state, even though the first component is much bigger. Since the total angular momentum j is also a good quantum number (it is a constant in time), both components must have the same j, and therefore j = 1. This is the total spin of the deuterium nucleus.
To summarize, the deuterium nucleus is antisymmetric in terms of
isospin, and has spin 1 and even (+1) parity. The relative angular
momentum of its nucleons l is not well defined, and the deuteron is a superposition of mostly l = 0 with some l = 2.
Magnetic and electric multipoles
In order to find theoretically the deuterium magnetic dipole moment µ, one uses the formula for a nuclear magnetic moment
with
g(l) and g(s) are g-factors of the nucleons.
Since the proton and neutron have different values for g(l) and g(s), one must separate their contributions. Each gets half of the deuterium orbital angular momentum and spin . One arrives at
where subscripts p and n stand for the proton and neutron, and g(l)n = 0.
By using the same identities as here and using the value g(l)p = 1 µ
N, we arrive at the following result, in nuclear magneton units
N, we arrive at the following result, in nuclear magneton units
For the s = 1, l = 0 state (j = 1), we obtain
For the s = 1, l = 2 state (j = 1), we obtain
The measured value of the deuterium magnetic dipole moment, is 0.857 µ
N, which is 97.5% of the 0.879 µ
N value obtained by simply adding moments of the proton and neutron. This suggests that the state of the deuterium is indeed to a good approximation s = 1, l = 0 state, which occurs with both nucleons spinning in the same direction, but their magnetic moments subtracting because of the neutron's negative moment.
N, which is 97.5% of the 0.879 µ
N value obtained by simply adding moments of the proton and neutron. This suggests that the state of the deuterium is indeed to a good approximation s = 1, l = 0 state, which occurs with both nucleons spinning in the same direction, but their magnetic moments subtracting because of the neutron's negative moment.
But the slightly lower experimental number than that which
results from simple addition of proton and (negative) neutron moments
shows that deuterium is actually a linear combination of mostly s = 1, l = 0 state with a slight admixture of s = 1, l = 2 state.
The electric dipole is zero as usual.
The measured electric quadrupole of the deuterium is 0.2859 e·fm2. While the order of magnitude is reasonable, since the deuterium radius is of order of 1 femtometer (see below) and its electric charge is e, the above model does not suffice for its computation. More specifically, the electric quadrupole does not get a contribution from the l =0 state (which is the dominant one) and does get a contribution from a term mixing the l =0 and the l =2 states, because the electric quadrupole operator does not commute with angular momentum.
The latter contribution is dominant in the absence of a pure l = 0 contribution, but cannot be calculated without knowing the exact spatial form of the nucleons wavefunction inside the deuterium.
Higher magnetic and electric multipole moments cannot be calculated by the above model, for similar reasons.
Applications
Deuterium has a number of commercial and scientific uses. These include:
Nuclear reactors
Ionized deuterium in a fusor reactor giving off its characteristic pinkish-red glow
Deuterium is used in heavy water moderated fission reactors, usually as liquid D2O, to slow neutrons without the high neutron absorption of ordinary hydrogen. This is a common commercial use for larger amounts of deuterium.
In research reactors, liquid D2 is used in cold sources to moderate neutrons to very low energies and wavelengths appropriate for scattering experiments.
Experimentally, deuterium is the most common nuclide used in nuclear fusion reactor designs, especially in combination with tritium, because of the large reaction rate (or nuclear cross section) and high energy yield of the D–T reaction. There is an even higher-yield D–3He
fusion reaction, though the breakeven point of D–3He
is higher than that of most other fusion reactions; together with the scarcity of 3He
, this makes it implausible as a practical power source until at least D–T and D–D fusion reactions have been performed on a commercial scale. However, commercial nuclear fusion is not yet an accomplished technology.
fusion reaction, though the breakeven point of D–3He
is higher than that of most other fusion reactions; together with the scarcity of 3He
, this makes it implausible as a practical power source until at least D–T and D–D fusion reactions have been performed on a commercial scale. However, commercial nuclear fusion is not yet an accomplished technology.
NMR spectroscopy
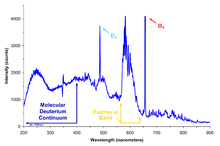
Emission spectrum of an ultraviolet deuterium arc lamp
Deuterium is most commonly used in hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (proton NMR)
in the following way. NMR ordinarily requires compounds of interest to
be analyzed as dissolved in solution. Because of deuterium's nuclear
spin properties which differ from the light hydrogen usually present in
organic molecules, NMR spectra of hydrogen/protium are highly
differentiable from that of deuterium, and in practice deuterium is not
"seen" by an NMR instrument tuned for light-hydrogen. Deuterated
solvents (including heavy water, but also compounds like deuterated
chloroform, CDCl3) are therefore routinely used in NMR
spectroscopy, in order to allow only the light-hydrogen spectra of the
compound of interest to be measured, without solvent-signal
interference.
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy can also be used to
obtain information about the deuteron's environment in isotopically
labelled samples (Deuterium NMR).
For example, the flexibility in the tail, which is a long hydrocarbon
chains, in deuterium-labelled lipid molecules can be quantified using
solid state deuterium NMR.
Deuterium NMR spectra are especially informative in the solid
state because of its relatively small quadrupole moment in comparison
with those of bigger quadrupolar nuclei such as chlorine-35, for
example.
Tracing
In chemistry, biochemistry and environmental sciences, deuterium is used as a non-radioactive, stable isotopic tracer, for example, in the doubly labeled water test. In chemical reactions and metabolic pathways,
deuterium behaves somewhat similarly to ordinary hydrogen (with a few
chemical differences, as noted). It can be distinguished from ordinary
hydrogen most easily by its mass, using mass spectrometry or infrared spectrometry. Deuterium can be detected by femtosecond infrared
spectroscopy, since the mass difference drastically affects the
frequency of molecular vibrations; deuterium-carbon bond vibrations are
found in spectral regions free of other signals.
Measurements of small variations in the natural abundances of deuterium, along with those of the stable heavy oxygen isotopes 17O and 18O, are of importance in hydrology, to trace the geographic origin of Earth's waters. The heavy isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in rainwater (so-called meteoric water)
are enriched as a function of the environmental temperature of the
region in which the precipitation falls (and thus enrichment is related
to mean latitude). The relative enrichment of the heavy isotopes in
rainwater (as referenced to mean ocean water), when plotted against
temperature falls predictably along a line called the global meteoric water line
(GMWL). This plot allows samples of precipitation-originated water to
be identified along with general information about the climate in which
it originated. Evaporative and other processes in bodies of water, and
also ground water processes, also differentially alter the ratios of
heavy hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in fresh and salt waters, in
characteristic and often regionally distinctive ways. The ratio of concentration of 2H to 1H is usually indicated with a delta as δ2H
and the geographic patterns of these values are plotted in maps termed
as isoscapes. Stable isotope are incorporated into plants and animals
and an analysis of the ratios in a migrant bird or insect can help
suggest a rough guide to their origins.
Contrast properties
Neutron scattering
techniques particularly profit from availability of deuterated samples:
The H and D cross sections are very distinct and different in sign,
which allows contrast variation in such experiments. Further, a nuisance
problem of ordinary hydrogen is its large incoherent neutron cross
section, which is nil for D. The substitution of deuterium atoms for
hydrogen atoms thus reduces scattering noise.
Hydrogen is an important and major component in all materials of
organic chemistry and life science, but it barely interacts with X-rays.
As hydrogen (and deuterium) interact strongly with neutrons, neutron
scattering techniques, together with a modern deuteration facility, fills a niche in many studies of macromolecules in biology and many other areas.
Nuclear weapons
This
is discussed below. It is notable that although most stars, including
the Sun, generate energy over most of their lives by fusing hydrogen
into heavier elements, such fusion of light hydrogen (protium) has never
been successful in the conditions attainable on Earth. Thus, all
artificial fusion, including the hydrogen fusion that occurs in
so-called hydrogen bombs, requires heavy hydrogen (either tritium or
deuterium, or both) in order for the process to work.
Drugs
A deuterated drug is a small molecule medicinal product in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms contained in the drug molecule have been replaced by deuterium. Because of the kinetic isotope effect, deuterium-containing drugs may have significantly lower rates of metabolism, and hence a longer half-life. In 2017, deutetrabenazine became the first deuterated drug to receive FDA approval.
Reinforced essential nutrients
Deuterium can be used to reinforce specific oxidation-vulnerable C-H bonds within essential or conditionally essential nutrients, such as certain amino acids, or polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), making them more resistant to oxidative damage. Deuterated polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as linoleic acid, slow down the chain reaction of lipid peroxidation that damage living cells. Deuterated ethyl ester of linoleic acid (RT001), developed by Retrotope, is in a compassionate use trial in infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy and has successfully completed a Phase I/II trial in Friedreich’s ataxia.
History
Suspicion of lighter element isotopes
The
existence of nonradioactive isotopes of lighter elements had been
suspected in studies of neon as early as 1913, and proven by mass
spectrometry of light elements in 1920. The prevailing theory at the
time was that isotopes of an element differ by the existence of
additional protons in the nucleus accompanied by an equal number of nuclear electrons.
In this theory, the deuterium nucleus with mass two and charge one
would contain two protons and one nuclear electron. However it was
expected that the element hydrogen with a measured average atomic mass
very close to 1 u, the known mass of the
proton, always has a nucleus composed of a single proton (a known
particle), and could not contain a second proton. Thus, hydrogen could
have no heavy isotopes.
Deuterium detected
Harold Urey
It was first detected spectroscopically in late 1931 by Harold Urey, a chemist at Columbia University. Urey's collaborator, Ferdinand Brickwedde, distilled five liters of cryogenically produced liquid hydrogen to 1 mL
of liquid, using the low-temperature physics laboratory that had
recently been established at the National Bureau of Standards in
Washington, D.C. (now the National Institute of Standards and Technology).
The technique had previously been used to isolate heavy isotopes of
neon. The cryogenic boiloff technique concentrated the fraction of the
mass-2 isotope of hydrogen to a degree that made its spectroscopic
identification unambiguous.
Naming of the isotope and Nobel Prize
Urey
created the names protium, deuterium, and tritium in an article
published in 1934. The name is based in part on advice from G. N. Lewis
who had proposed the name "deutium". The name is derived from the,
Greek deuteros (second), and the nucleus to be called "deuteron" or
"deuton". Isotopes and new elements were traditionally given the name
that their discoverer decided. Some British scientists, such as Ernest Rutherford, wanted the isotope to be called "diplogen", from the Greek diploos (double), and the nucleus to be called diplon.
The amount inferred for normal abundance of this heavy isotope of
hydrogen was so small (only about 1 atom in 6400 hydrogen atoms in
ocean water (156 deuteriums per million hydrogens)) that it had not
noticeably affected previous measurements of (average) hydrogen atomic
mass. This explained why it hadn't been experimentally suspected before.
Urey was able to concentrate water to show partial enrichment of
deuterium. Lewis had prepared the first samples of pure heavy water in
1933. The discovery of deuterium, coming before the discovery of the neutron
in 1932, was an experimental shock to theory, but when the neutron was
reported, making deuterium's existence more explainable, deuterium won
Urey the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934. Lewis was embittered by being passed over for this recognition given to his former student.
"Heavy water" experiments in World War II
Shortly before the war, Hans von Halban and Lew Kowarski
moved their research on neutron moderation from France to England,
smuggling the entire global supply of heavy water (which had been made
in Norway) across in twenty-six steel drums.
During World War II, Nazi Germany was known to be conducting experiments using heavy water as moderator for a nuclear reactor design. Such experiments were a source of concern because they might allow them to produce plutonium for an atomic bomb. Ultimately it led to the Allied operation called the "Norwegian heavy water sabotage", the purpose of which was to destroy the Vemork
deuterium production/enrichment facility in Norway. At the time this
was considered important to the potential progress of the war.
After World War II ended, the Allies discovered that Germany was
not putting as much serious effort into the program as had been
previously thought. They had been unable to sustain a chain reaction.
The Germans had completed only a small, partly built experimental
reactor (which had been hidden away). By the end of the war, the Germans
did not even have a fifth of the amount of heavy water needed to run
the reactor,
partially due to the Norwegian heavy water sabotage operation. However,
even had the Germans succeeded in getting a reactor operational (as the
U.S. did with a graphite reactor in late 1942), they would still have
been at least several years away from development of an atomic bomb
with maximal effort. The engineering process, even with maximal effort
and funding, required about two and a half years (from first critical
reactor to bomb) in both the U.S. and U.S.S.R., for example.
In thermonuclear weapons
A view of the Sausage device casing of the Ivy Mike hydrogen bomb,
with its instrumentation and cryogenic equipment attached. This bomb
held a cryogenic Dewar flask containing room for as much as 160
kilograms of liquid deuterium. The bomb was 20 feet tall. Note the
seated man at the right of the photo for the scale.
The 62-ton Ivy Mike device built by the United States and exploded on 1 November 1952, was the first fully successful "hydrogen bomb" or thermonuclear bomb. In this context, it was the first bomb in which most of the energy released came from nuclear reaction stages that followed the primary nuclear fission stage of the atomic bomb.
The Ivy Mike bomb was a factory-like building, rather than a
deliverable weapon. At its center, a very large cylindrical, insulated vacuum flask or cryostat, held cryogenic liquid deuterium in a volume of about 1000 liters (160 kilograms in mass, if this volume had been completely filled). Then, a conventional atomic bomb
(the "primary") at one end of the bomb was used to create the
conditions of extreme temperature and pressure that were needed to set
off the thermonuclear reaction.
Within a few years, so-called "dry" hydrogen bombs were developed
that did not need cryogenic hydrogen. Released information suggests
that all thermonuclear weapons built since then contain chemical compounds of deuterium and lithium in their secondary stages. The material that contains the deuterium is mostly lithium deuteride, with the lithium consisting of the isotope lithium-6. When the lithium-6 is bombarded with fast neutrons from the atomic bomb, tritium (hydrogen-3) is produced, and then the deuterium and the tritium quickly engage in thermonuclear fusion, releasing abundant energy, helium-4, and even more free neutrons.
Modern research
In August 2018, scientists announced the transformation of gaseous deuterium into a liquid metallic form. This may help researchers better understand giant gas planets, such as Jupiter, Saturn and related exoplanets,
since such planets are thought to contain a lot of liquid metallic
hydrogen, which may be responsible for their observed powerful magnetic fields.
Data for elemental deuterium
Formula: D2 or 2
1H
2
1H
2
- Density: 0.180 kg/m3 at STP (0 °C, 101.325 kPa).
- Atomic weight: 2.0141017926 u.
- Mean abundance in ocean water (from VSMOW) 155.76 ± 0.1 ppm (a ratio of 1 part per approximately 6420 parts), that is, about 0.015% of the atoms in a sample (by number, not weight)
Data at approximately 18 K for D2 (triple point):
- Density:
- Liquid: 162.4 kg/m3
- Gas: 0.452 kg/m3
- Viscosity: 12.6 µPa·s at 300 K (gas phase)
- Specific heat capacity at constant pressure cp:
- Solid: 2950 J/(kg·K)
- Gas: 5200 J/(kg·K)
Antideuterium
An antideuteron is the antimatter counterpart of the nucleus of deuterium, consisting of an antiproton and an antineutron. The antideuteron was first produced in 1965 at the Proton Synchrotron at CERN and the Alternating Gradient Synchrotron at Brookhaven National Laboratory. A complete atom, with a positron orbiting the nucleus, would be called antideuterium, but as of 2005 antideuterium has not yet been created. The proposed symbol for antideuterium is
D
, that is, D with an overbar.
D
, that is, D with an overbar.