The IBM Blue Gene/P supercomputer "Intrepid" at Argonne National Laboratory
runs 164,000 processor cores using normal data center air conditioning,
grouped in 40 racks/cabinets connected by a high-speed 3-D torus
network.
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there are supercomputers which can perform up to nearly a hundred quadrillion FLOPS. Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in China, the United States, the European Union, Taiwan and Japan to build even faster, more powerful and more technologically superior exascale supercomputers.
Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in various fields, including quantum mechanics, weather forecasting, climate research, oil and gas exploration, molecular modeling (computing the structures and properties of chemical compounds, biological macromolecules,
polymers, and crystals), and physical simulations (such as simulations
of the early moments of the universe, airplane and spacecraft
aerodynamics, the detonation of nuclear weapons, and nuclear fusion). Throughout their history, they have been essential in the field of cryptanalysis.
Supercomputers were introduced in the 1960s, and for several decades the fastest were made by Seymour Cray at Control Data Corporation (CDC), Cray Research
and subsequent companies bearing his name or monogram. The first such
machines were highly tuned conventional designs that ran faster than
their more general-purpose contemporaries. Through the 1960s, they began
to add increasing amounts of parallelism with one to four processors being typical. From the 1970s, vector processors operating on large arrays of data came to dominate. A notable example is the highly successful Cray-1 of 1976. Vector computers remained the dominant design into the 1990s. From then until today, massively parallel supercomputers with tens of thousands of off-the-shelf processors became the norm.
The US has long been the leader in the supercomputer field, first
through Cray's almost uninterrupted dominance of the field, and later
through a variety of technology companies. Japan made major strides in
the field in the 1980s and 90s, but since then China has become
increasingly active in the field. As of November 2018, the fastest
supercomputer on the TOP500 supercomputer list is the Summit, in the United States, with a LINPACK benchmark score of 143.5 PFLOPS, followed by, Sierra, by around 48.860 PFLOPS. The US has five of the top 10 and China has two.
In June 2018, all supercomputers on the list combined have broken the 1 exabyte mark.
History
A circuit board from the IBM 7030
The
CDC 6600. Behind the system console are two of the "arms" of the
plus-sign shaped cabinet with the covers opened. Each arm of the machine
had up to four such racks. On the right is the cooling system.
A Cray-1 preserved at the Deutsches Museum
In 1960 Sperry Rand built the Livermore Atomic Research Computer
(LARC), today considered among the first supercomputers, for the US
Navy Research and Development Centre. It still used high-speed drum memory, rather than the newly emerging disk drive technology. Also among the first supercomputers was the IBM 7030 Stretch. The IBM 7030 was built by IBM for the Los Alamos National Laboratory, which in 1955 had requested a computer 100 times faster than any existing computer. The IBM 7030 used transistors, magnetic core memory, pipelined
instructions, prefetched data through a memory controller and included
pioneering random access disk drives. The IBM 7030 was completed in 1961
and despite not meeting the challenge of a hundredfold increase in
performance, it was purchased by the Los Alamos National Laboratory.
Customers in England and France also bought the computer and it became
the basis for the IBM 7950 Harvest, a supercomputer built for cryptanalysis.
The third pioneering supercomputer project in the early 1960s was the Atlas at the University of Manchester, built by a team led by Tom Kilburn.
He designed the Atlas to have memory space for up to a million words of
48 bits, but because magnetic storage with such a capacity was
unaffordable, the actual core memory of Atlas was only 16,000 words,
with a drum providing memory for a further 96,000 words. The Atlas operating system swapped data in the form of pages between the magnetic core and the drum. The Atlas operating system also introduced time-sharing to supercomputing, so that more than one programe could be executed on the supercomputer at any one time. Atlas was a joint venture between Ferranti and the Manchester University
and was designed to operate at processing speeds approaching
one microsecond per instruction, about one million instructions per
second.
The CDC 6600, designed by Seymour Cray, was finished in 1964 and marked the transition from germanium to silicon
transistors. Silicon transistors could run faster and the overheating
problem was solved by introducing refrigeration to the supercomputer
design.
Thus the CDC6600 became the fastest computer in the world. Given that
the 6600 outperformed all the other contemporary computers by about 10
times, it was dubbed a supercomputer and defined the supercomputing market, when one hundred computers were sold at $8 million each.
Cray left CDC in 1972 to form his own company, Cray Research. Four years after leaving CDC, Cray delivered the 80 MHz Cray-1 in 1976, which became one of the most successful supercomputers in history. The Cray-2 was released in 1985. It had eight central processing units (CPUs), liquid cooling and the electronics coolant liquid fluorinert was pumped through the supercomputer architecture. It performed at 1.9 gigaFLOPS and was the world's second fastest after M-13 supercomputer in Moscow.
Massively parallel designs
The only computer to seriously challenge the Cray-1's performance in the 1970s was the ILLIAC IV. This machine was the first realized example of a true massively parallel
computer, in which many processors worked together to solve different
parts of a single larger problem. In contrast with the vector systems,
which were designed to run a single stream of data as quickly as
possible, in this concept, the computer instead feeds separate parts of
the data to entirely different processors and then recombines the
results. The ILLIAC's design was finalized in 1966 with 256 processors
and offer speed up to 1 GFLOPS, compared to the 1970s Cray-1's peak of
250 MFLOPS. However, development problems led to only 64 processors
being built, and the system could never operate faster than about 200
MFLOPS while being much larger and more complex than the Cray. Another
problem was that writing software for the system was difficult, and
getting peak performance from it was a matter of serious effort.
But the partial success of the ILLIAC IV was widely seen as
pointing the way to the future of supercomputing. Cray argued against
this, famously quipping that "If you were plowing a field, which would
you rather use? Two strong oxen or 1024 chickens?" But by the early 1980s, several teams were working on parallel designs with thousands of processors, notably the Connection Machine (CM) that developed from research at MIT. The CM-1 used as many as 65,536 simplified custom microprocessors connected together in a network
to share data. Several updated versions followed; the CM-5
supercomputer is a massively parallel processing computer capable of
many billions of arithmetic operations per second.
In 1982, Osaka University's LINKS-1 Computer Graphics System used a massively parallel processing architecture, with 514 microprocessors, including 257 Zilog Z8001 control processors and 257 iAPX 86/20 floating-point processors. It was mainly used for rendering realistic 3D computer graphics. Fujitsu's Numerical Wind Tunnel supercomputer used 166 vector processors to gain the top spot in 1994 with a peak speed of 1.7 gigaFLOPS (GFLOPS) per processor. The Hitachi SR2201 obtained a peak performance of 600 GFLOPS in 1996 by using 2048 processors connected via a fast three-dimensional crossbar network. The Intel Paragon could have 1000 to 4000 Intel i860 processors in various configurations and was ranked the fastest in the world in 1993. The Paragon was a MIMD machine which connected processors via a high speed two dimensional mesh, allowing processes to execute on separate nodes, communicating via the Message Passing Interface.
Software development remained a problem, but the CM series
sparked off considerable research into this issue. Similar designs using
custom hardware were made by many companies, including the Evans & Sutherland ES-1, MasPar, nCUBE, Intel iPSC and the Goodyear MPP.
But by the mid-1990s, general-purpose CPU performance had improved so
much in that a supercomputer could be built using them as the individual
processing units, instead of using custom chips. By the turn of the
21st century, designs featuring tens of thousands of commodity CPUs were
the norm, with later machines adding graphic units to the mix.
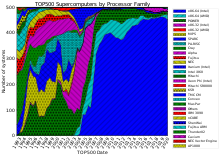
The CPU share of TOP500
Systems with a massive number of processors generally take one of two paths. In the grid computing
approach, the processing power of many computers, organised as
distributed, diverse administrative domains, is opportunistically used
whenever a computer is available. In another approach, a large number of processors are used in proximity to each other, e.g. in a computer cluster. In such a centralized massively parallel system the speed and flexibility of the interconnect becomes very important and modern supercomputers have used various approaches ranging from enhanced Infiniband systems to three-dimensional torus interconnects. The use of multi-core processors combined with centralization is an emerging direction, e.g. as in the Cyclops64 system.
As the price, performance and energy efficiency of general purpose graphic processors (GPGPUs) have improved, a number of petaFLOPS supercomputers such as Tianhe-I and Nebulae have started to rely on them. However, other systems such as the K computer continue to use conventional processors such as SPARC-based designs and the overall applicability of GPGPUs
in general-purpose high-performance computing applications has been the
subject of debate, in that while a GPGPU may be tuned to score well on
specific benchmarks, its overall applicability to everyday algorithms
may be limited unless significant effort is spent to tune the
application towards it. However, GPUs are gaining ground and in 2012 the Jaguar supercomputer was transformed into Titan by retrofitting CPUs with GPUs.
High-performance computers have an expected life cycle of about three years before requiring an upgrade.
Special purpose supercomputers
A number of "special-purpose" systems have been designed, dedicated
to a single problem. This allows the use of specially programmed FPGA chips or even custom ASICs, allowing better price/performance ratios by sacrificing generality. Examples of special-purpose supercomputers include Belle, Deep Blue, and Hydra, for playing chess, Gravity Pipe for astrophysics, MDGRAPE-3 for protein structure computation
molecular dynamics and Deep Crack, for breaking the DES cipher.
Energy usage and heat management
Throughout the decades, the management of heat density has remained a key issue for most centralized supercomputers.
The large amount of heat generated by a system may also have other
effects, e.g. reducing the lifetime of other system components. There have been diverse approaches to heat management, from pumping Fluorinert through the system, to a hybrid liquid-air cooling system or air cooling with normal air conditioning temperatures.
A typical supercomputer consumes large amounts of electrical power,
almost all of which is converted into heat, requiring cooling. For
example, Tianhe-1A consumes 4.04 megawatts (MW) of electricity.
The cost to power and cool the system can be significant, e.g. 4 MW at
$0.10/kWh is $400 an hour or about $3.5 million per year.
Heat management is a major issue in complex electronic devices and affects powerful computer systems in various ways. The thermal design power and CPU power dissipation issues in supercomputing surpass those of traditional computer cooling technologies. The supercomputing awards for green computing reflect this issue.
The packing of thousands of processors together inevitably generates significant amounts of heat density that need to be dealt with. The Cray 2 was liquid cooled, and used a Fluorinert "cooling waterfall" which was forced through the modules under pressure.
However, the submerged liquid cooling approach was not practical for
the multi-cabinet systems based on off-the-shelf processors, and in System X a special cooling system that combined air conditioning with liquid cooling was developed in conjunction with the Liebert company.
In the Blue Gene system, IBM deliberately used low power processors to deal with heat density.
The IBM Power 775, released in 2011, has closely packed elements that require water cooling. The IBM Aquasar system uses hot water cooling to achieve energy efficiency, the water being used to heat buildings as well.
The energy efficiency of computer systems is generally measured in terms of "FLOPS per watt". In 2008, IBM's Roadrunner operated at 3.76 MFLOPS/W. In November 2010, the Blue Gene/Q reached 1,684 MFLOPS/W. In June 2011 the top 2 spots on the Green 500 list were occupied by Blue Gene machines in New York (one achieving 2097 MFLOPS/W) with the DEGIMA cluster in Nagasaki placing third with 1375 MFLOPS/W.
Because copper wires can transfer energy into a supercomputer
with much higher power densities than forced air or circulating
refrigerants can remove waste heat,
the ability of the cooling systems to remove waste heat is a limiting factor.
As of 2015, many existing supercomputers have more infrastructure
capacity than the actual peak demand of the machine – designers
generally conservatively design the power and cooling infrastructure to
handle more than the theoretical peak electrical power consumed by the
supercomputer. Designs for future supercomputers are power-limited –
the thermal design power
of the supercomputer as a whole, the amount that the power and cooling
infrastructure can handle, is somewhat more than the expected normal
power consumption, but less than the theoretical peak power consumption
of the electronic hardware.
Software and system management
Operating systems
Since the end of the 20th century, supercomputer operating systems have undergone major transformations, based on the changes in supercomputer architecture.
While early operating systems were custom tailored to each
supercomputer to gain speed, the trend has been to move away from
in-house operating systems to the adaptation of generic software such as
Linux.
Since modern massively parallel supercomputers typically separate computations from other services by using multiple types of nodes, they usually run different operating systems on different nodes, e.g. using a small and efficient lightweight kernel such as CNK or CNL on compute nodes, but a larger system such as a Linux-derivative on server and I/O nodes.
While in a traditional multi-user computer system job scheduling is, in effect, a tasking
problem for processing and peripheral resources, in a massively
parallel system, the job management system needs to manage the
allocation of both computational and communication resources, as well as
gracefully deal with inevitable hardware failures when tens of
thousands of processors are present.
Although most modern supercomputers use a Linux-based
operating system, each manufacturer has its own specific
Linux-derivative, and no industry standard exists, partly due to the
fact that the differences in hardware architectures require changes to
optimize the operating system to each hardware design.
Software tools and message passing
Wide-angle view of the ALMA correlator
The parallel architectures of supercomputers often dictate the use of
special programming techniques to exploit their speed. Software tools
for distributed processing include standard APIs such as MPI and PVM, VTL, and open source-based software solutions such as Beowulf.
In the most common scenario, environments such as PVM and MPI for loosely connected clusters and OpenMP
for tightly coordinated shared memory machines are used. Significant
effort is required to optimize an algorithm for the interconnect
characteristics of the machine it will be run on; the aim is to prevent
any of the CPUs from wasting time waiting on data from other nodes. GPGPUs have hundreds of processor cores and are programmed using programming models such as CUDA or OpenCL.
Moreover, it is quite difficult to debug and test parallel programs. Special techniques need to be used for testing and debugging such applications.
Distributed supercomputing
Opportunistic approaches
Example architecture of a grid computing system connecting many personal computers over the internet
Opportunistic Supercomputing is a form of networked grid computing whereby a "super virtual computer" of many loosely coupled volunteer computing machines performs very large computing tasks. Grid computing has been applied to a number of large-scale embarrassingly parallel problems that require supercomputing performance scales. However, basic grid and cloud computing approaches that rely on volunteer computing cannot handle traditional supercomputing tasks such as fluid dynamic simulations.
The fastest grid computing system is the distributed computing project Folding@home (F@h). F@h reported 101 PFLOPS of x86 processing power As of October 2016. Of this, over 100 PFLOPS are contributed by clients running on various GPUs, and the rest from various CPU systems.
The Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) platform hosts a number of distributed computing projects. As of February 2017, BOINC recorded a processing power of over 166 PetaFLOPS through over 762 thousand active Computers (Hosts) on the network.
As of October 2016, Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search's (GIMPS) distributed Mersenne Prime search achieved about 0.313 PFLOPS through over 1.3 million computers. The Internet PrimeNet Server supports GIMPS's grid computing approach, one of the earliest and most successful grid computing projects, since 1997.
Quasi-opportunistic approaches
Quasi-opportunistic supercomputing is a form of distributed computing
whereby the "super virtual computer" of many networked geographically
disperse computers performs computing tasks that demand huge processing
power. Quasi-opportunistic supercomputing aims to provide a higher quality of service than opportunistic grid computing
by achieving more control over the assignment of tasks to distributed
resources and the use of intelligence about the availability and
reliability of individual systems within the supercomputing network.
However, quasi-opportunistic distributed execution of demanding parallel
computing software in grids should be achieved through implementation
of grid-wise allocation agreements, co-allocation subsystems,
communication topology-aware allocation mechanisms, fault tolerant
message passing libraries and data pre-conditioning.
HPC in the Cloud
Cloud Computing
with its recent and rapid expansions and development have grabbed the
attention of HPC users and developers in recent years. Cloud Computing
attempts to provide HPC-as-a-Service exactly like other forms of
services currently available in the Cloud such as Software-as-a-Service, Platform-as-a-Service, and Infrastructure-as-a-Service.
HPC users may benefit from the Cloud in different angles such as
scalability, resources being on-demand, fast, and inexpensive. On the
other hand, moving HPC applications have a set of challenges too. Good
examples of such challenges are virtualization overhead in the Cloud, multi-tenancy of resources, and network latency issues. Much research is currently being done to overcome these challenges and make HPC in the cloud a more realistic possibility.
Performance measurement
Capability versus capacity
Supercomputers generally aim for the maximum in capability computing rather than capacity computing.
Capability computing is typically thought of as using the maximum
computing power to solve a single large problem in the shortest amount
of time. Often a capability system is able to solve a problem of a size
or complexity that no other computer can, e.g., a very complex weather simulation application.
Capacity computing, in contrast, is typically thought of as using
efficient cost-effective computing power to solve a few somewhat large
problems or many small problems.
Architectures that lend themselves to supporting many users for routine
everyday tasks may have a lot of capacity but are not typically
considered supercomputers, given that they do not solve a single very
complex problem.
Performance metrics
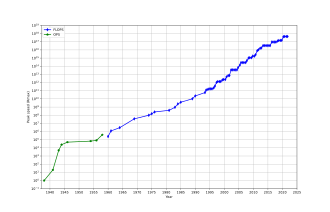
Top supercomputer speeds: logscale speed over 60 years
In general, the speed of supercomputers is measured and benchmarked in "FLOPS" (FLoating point Operations Per Second), and not in terms of "MIPS" (Million Instructions Per Second), as is the case with general-purpose computers. These measurements are commonly used with an SI prefix such as tera-, combined into the shorthand "TFLOPS" (1012 FLOPS, pronounced teraflops), or peta-, combined into the shorthand "PFLOPS" (1015 FLOPS, pronounced petaflops.) "Petascale" supercomputers can process one quadrillion (1015) (1000 trillion) FLOPS. Exascale is computing performance in the exaFLOPS (EFLOPS) range. An EFLOPS is one quintillion (1018) FLOPS (one million TFLOPS).
No single number can reflect the overall performance of a
computer system, yet the goal of the Linpack benchmark is to approximate
how fast the computer solves numerical problems and it is widely used
in the industry.
The FLOPS measurement is either quoted based on the theoretical
floating point performance of a processor (derived from manufacturer's
processor specifications and shown as "Rpeak" in the TOP500 lists),
which is generally unachievable when running real workloads, or the
achievable throughput, derived from the LINPACK benchmarks and shown as "Rmax" in the TOP500 list. The LINPACK benchmark typically performs LU decomposition of a large matrix.
The LINPACK performance gives some indication of performance for some
real-world problems, but does not necessarily match the processing
requirements of many other supercomputer workloads, which for example
may require more memory bandwidth, or may require better integer
computing performance, or may need a high performance I/O system to
achieve high levels of performance.
The TOP500 list
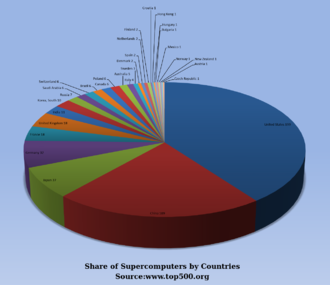
Distribution of TOP500 supercomputers among different countries, as of November 2015
Since 1993, the fastest supercomputers have been ranked on the TOP500 list according to their LINPACK benchmark
results. The list does not claim to be unbiased or definitive, but it
is a widely cited current definition of the "fastest" supercomputer
available at any given time.
This is a recent list of the computers which appeared at the top of the TOP500 list, and the "Peak speed" is given as the "Rmax" rating.
Top 20 Supercomputers in the World, as of June 2014
| Year | Supercomputer | Peak speed (Rmax) |
Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | IBM Summit | 122.3 PFLOPS | Oak Ridge, U.S. |
| 2016 | Sunway TaihuLight | 93.01 PFLOPS | Wuxi, China |
| 2013 | NUDT Tianhe-2 | 33.86 PFLOPS | Guangzhou, China |
| 2012 | Cray Titan | 17.59 PFLOPS | Oak Ridge, U.S. |
| 2012 | IBM Sequoia | 17.17 PFLOPS | Livermore, U.S. |
| 2011 | Fujitsu K computer | 10.51 PFLOPS | Kobe, Japan |
| 2010 | Tianhe-IA | 2.566 PFLOPS | Tianjin, China |
| 2009 | Cray Jaguar | 1.759 PFLOPS | Oak Ridge, U.S. |
| 2008 | IBM Roadrunner | 1.026 PFLOPS | Los Alamos, U.S. |
| 1.105 PFLOPS |
Applications
The stages of supercomputer application may be summarized in the following table:
| Decade | Uses and computer involved |
|---|---|
| 1970s | Weather forecasting, aerodynamic research (Cray-1). |
| 1980s | Probabilistic analysis, radiation shielding modeling (CDC Cyber). |
| 1990s | Brute force code breaking (EFF DES cracker). |
| 2000s | 3D nuclear test simulations as a substitute for legal conduct Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (ASCI Q). |
| 2010s | Molecular Dynamics Simulation (Tianhe-1A) |
The IBM Blue Gene/P
computer has been used to simulate a number of artificial neurons
equivalent to approximately one percent of a human cerebral cortex,
containing 1.6 billion neurons with approximately 9 trillion
connections. The same research group also succeeded in using a
supercomputer to simulate a number of artificial neurons equivalent to
the entirety of a rat's brain.
Modern-day weather forecasting also relies on supercomputers. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration uses supercomputers to crunch hundreds of millions of observations to help make weather forecasts more accurate.
In 2011, the challenges and difficulties in pushing the envelope in supercomputing were underscored by IBM's abandonment of the Blue Waters petascale project.
The Advanced Simulation and Computing Program currently uses supercomputers to maintain and simulate the United States nuclear stockpile.
Development and trends
Diagram of a three-dimensional torus interconnect used by systems such as Blue Gene, Cray XT3, etc.
In the 2010s, China, the United States, the European Union, and others competed to be the first to create a 1 exaFLOP (1018 or one quintillion FLOPS) supercomputer. Erik P. DeBenedictis of Sandia National Laboratories has theorized that a zettaFLOPS (1021 or one sextillion FLOPS) computer is required to accomplish full weather modeling, which could cover a two-week time span accurately. Such systems might be built around 2030.
Many Monte Carlo simulations use the same algorithm to process a randomly generated data set; particularly, integro-differential equations describing physical transport processes, the random paths, collisions, and energy and momentum depositions of neutrons, photons, ions, electrons, etc. The next step for microprocessors may be into the third dimension; and specializing to Monte Carlo, the many layers could be identical, simplifying the design and manufacture process.
The cost of operating high performance supercomputers has risen,
mainly due to increasing power consumption. In the mid 1990s a top 10
supercomputer required in the range of 100 kilowatt, in 2010 the top 10
supercomputers required between 1 and 2 megawatt. A 2010 study commissioned by DARPA identified power consumption as the most pervasive challenge in achieving Exascale computing.
At the time a megawatt per year in energy consumption cost about 1
million dollar. Supercomputing facilities were constructed to
efficiently remove the increasing amount of heat produced by modern
multi-core central processing units.
Based on the energy consumption of the Green 500 list of supercomputers
between 2007 and 2011, a supercomputer with 1 exaflops in 2011 would
have required nearly 500 megawatt. Operating systems were developed for
existing hardware to conserve energy whenever possible.
CPU cores not in use during the execution of a parallelised application
were put into low-power states, producing energy savings for some
supercomputing applications.
The increasing cost of operating supercomputers has been a
driving factor in a trend towards bundling of resources through a
distributed supercomputer infrastructure. National supercomputing
centres first emerged in the US, followed by Germany and Japan. The
European Union launched the Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe
(PRACE) with the aim of creating a persistent pan-European
supercomputer infrastructure with services to support scientists across
the European Union in porting, scaling and optimizing supercomputing applications. Iceland built the world's first zero-emission supercomputer. Located at the Thor Data Center in Reykjavik,
Iceland, this supercomputer relies on completely renewable sources for
its power rather than fossil fuels. The colder climate also reduces the
need for active cooling, making it one of the greenest facilities in the
world of computers.
Funding supercomputer hardware also became increasingly
difficult. In the mid 1990s a top 10 supercomputer cost about 10 Million
Euros, while in 2010 the top 10 supercomputers required an investment
of between 40 and 50 million Euros.
In the 2000s national governments put in place different strategies to
fund supercomputers. In the UK the national government funded
supercomputers entirely and high performance computing was put under the
control of a national funding agency. Germany developed a mixed funding
model, pooling local state funding and federal funding.
In fiction
Many science-fiction
writers have depicted supercomputers in their works, both before and
after the historical construction of such computers. Much of such
fiction deals with the relations of humans with the computers they build
and with the possibility of conflict eventually developing between
them. Some scenarios of this nature appear on the AI-takeover page.
Examples of supercomputers in fiction include HAL-9000, Multivac, The Machine Stops, GLaDOS, The Evitable Conflict and Vulcan's Hammer.