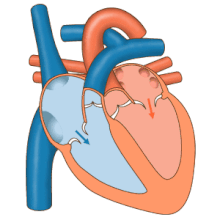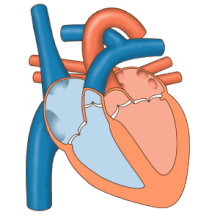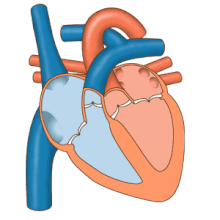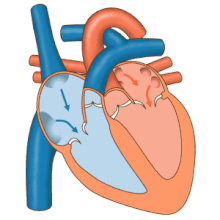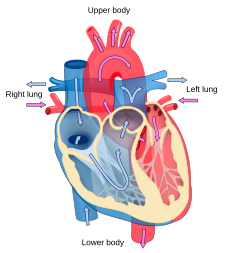
Blood
flow diagram of the human heart. Blue components indicate de-oxygenated
blood pathways and red components indicate oxygenated blood pathways.
| |
| System | Cardiovascular |
|---|---|
| Subdivisions | Interventional, Nuclear |
| Significant diseases | Heart disease, Cardiovascular disease, Atherosclerosis, Cardiomyopathy, Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
| Significant tests | Blood tests, electrophysiology study, cardiac imaging, ECG, echocardiograms, stress test |
| Specialist | Cardiologist |
| Glossary | Glossary of medicine |
Cardiology (from Greek καρδίᾱ kardiā, "heart" and -λογία -logia, "study") is a branch of medicine that deals with the disorders of the heart as well as some parts of the circulatory system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.
Although the cardiovascular system is inextricably linked to blood, cardiology is relatively unconcerned with hematology and its diseases. Some obvious exceptions that affect the function of the heart would be blood tests (electrolyte disturbances, troponins), decreased oxygen carrying capacity (anemia, hypovolemic shock), and coagulopathies.
Specializations
All
cardiologists study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult
and child heart disorders are through different training pathways.
Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is
inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric
cardiologists are not trained to take care of adult heart disease. The
surgical aspects are not included in cardiology and are in the domain of
cardiothoracic surgery. For example, coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), cardiopulmonary bypass and valve replacement
are surgical procedures performed by surgeons, not cardiologists.
However the insertion of stents and pacemakers are performed by
cardiologists
Adult cardiology
Cardiology is a specialty of internal medicine. To be a cardiologist in the United States,
a three-year residency in internal medicine is followed by a three-year
fellowship in cardiology. It is possible to specialize further in a
sub-specialty. Recognized sub-specialties in the United States by the ACGME are cardiac electrophysiology, echocardiography, interventional cardiology, and nuclear cardiology. Recognized subspecialties in the United States by the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists (AOABOS) include clinical cardiac electrophysiology and interventional cardiology.
Per doximity, adult cardiologists make an average of $436,849 in the United States.
Cardiac electrophysiology
Cardiac electrophysiology is the science of elucidating, diagnosing, and treating the electrical activities of the heart.
The term is usually used to describe studies of such phenomena by
invasive (intracardiac) catheter recording of spontaneous activity as
well as of cardiac responses to programmed electrical stimulation (PES). These studies are performed to assess complex arrhythmias, elucidate symptoms, evaluate abnormal electrocardiograms,
assess risk of developing arrhythmias in the future, and design
treatment. These procedures increasingly include therapeutic methods
(typically radiofrequency ablation, or cryoablation) in addition to diagnostic and prognostic procedures. Other therapeutic modalities employed in this field include antiarrhythmic drug therapy and implantation of pacemakers and automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (AICD).
The cardiac electrophysiology study
(EPS) typically measures the response of the injured or cardiomyopathic
myocardium to PES on specific pharmacological regimens in order to
assess the likelihood that the regimen will successfully prevent
potentially fatal sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation VF (VF) in the future. Sometimes a series
of EPS drug trials must be conducted to enable the cardiologist to
select the one regimen for long-term treatment that best prevents or
slows the development of VT or VF following PES. Such studies may also
be conducted in the presence of a newly implanted or newly replaced
cardiac pacemaker or AICD.
Clinical cardiac electrophysiology
Clinical cardiac electrophysiology
is a branch of the medical specialty of cardiology and is concerned
with the study and treatment of rhythm disorders of the heart.
Cardiologists with expertise in this area are usually referred to as
electrophysiologists. Electrophysiologists are trained in the mechanism,
function, and performance of the electrical activities of the heart.
Electrophysiologists work closely with other cardiologists and cardiac
surgeons to assist or guide therapy for heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias). They are trained to perform interventional and surgical procedures to treat cardiac arrhythmia.
The training required to become an electrophysiologist is long
and requires 7 to 8 years after medical school (in the U.S.). Three
years of internal medicine residency, three years of Clinical Cardiology
fellowship, and one to two (in most instances) years of clinical
cardiac electrophysiology.
Cardiogeriatrics
Cardiogeriatrics,
or geriatric cardiology, is the branch of cardiology and geriatric
medicine that deals with the cardiovascular disorders in elderly people.
Cardiac disorders such as coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, are common and are a major cause of mortality in elderly people. Vascular disorders such as atherosclerosis and peripheral arterial disease cause significant morbidity and mortality in aged people.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography uses standard two-dimensional, three-dimensional, and Doppler ultrasound to create images of the heart.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis,
management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart
diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic tests in
cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including
the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification),
pumping capacity, and the location and extent of any tissue damage. An
echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart
function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection
fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes).
Echocardiography can help detect cardiomyopathies, such as
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, and many others.
The use of stress echocardiography may also help determine whether any
chest pain or associated symptoms are related to heart disease. The
biggest advantage to echocardiography is that it is not invasive (does
not involve breaking the skin or entering body cavities) and has no
known risks or side effects.
Interventional cardiology
Interventional cardiology is a branch of cardiology that deals
specifically with the catheter based treatment of structural heart
diseases. A large number of procedures can be performed on the heart by
catheterization. This most commonly involves the insertion of a sheath
into the femoral artery (but, in practice, any large peripheral artery
or vein) and cannulating the heart under X-ray visualization (most
commonly Fluoroscopy).
The main advantages of using the interventional cardiology or
radiology approach are the avoidance of the scars and pain, and long
post-operative recovery. Additionally, interventional cardiology
procedure of primary angioplasty is now the gold standard of care for an
acute Myocardial infarction. This procedure can also be done proactively, when areas of the vascular system become occluded from Atherosclerosis.
The Cardiologist will thread this sheath through the vascular system to
access the heart. This sheath has a balloon and a tiny wire mesh tube
wrapped around it, and if the cardiologist finds a blockage or Stenosis,
they can inflate the balloon at the occlusion site in the vascular
system to flatten or compress the plaque against the vascular wall. Once
that is complete a Stent is placed as a type of scaffold to hold the vasculature open permanently.
Pediatric cardiology
Helen B. Taussig is known as the founder of pediatric cardiology. She became famous through her work with Tetralogy of Fallot, a congenital heart defect in which oxygenated and deoxygenated blood enters the circulatory system resulting from a ventricular septal defect (VSD) right beneath the aorta. This condition causes newborns to have a bluish-tint, cyanosis, and have a deficiency of oxygen to their tissues, hypoxemia. She worked with Alfred Blalock and Vivien Thomas at the Johns Hopkins Hospital
where they experimented with dogs to look at how they would attempt to
surgically cure these "blue babies." They eventually figured out how to
do just that by the anastomosis of the systemic artery to the pulmonary artery and called this the Blalock-Taussig Shunt.
Tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary atresia, double outlet right
ventricle, transposition of the great arteries, persistent truncus
arteriosus, and Ebsteins anomaly are various congenital cyanotic heart
diseases. Congenital cyanotic heart diseases is where something is wrong
with the heart of a newborn and it is not oxygenating the blood
efficiently.
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common congenital heart disease arising in 1–3 cases per 1,000 births. The cause of this defect is a ventricular septal defect (VSD) and an overriding aorta. These two defects combined causes deoxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and going right back into the circulatory system. The modified Blalock-Taussig shunt
is usually used to fix the circulation. This procedure is done by
placing a graft between the subclavian artery and the ipsilateral
pulmonary artery to restore the correct blood flow.
Pulmonary Atresia
Pulmonary Atresia
happens in 7–8 per 100,000 births and is characterized by the aorta
branching out of the right ventricle. This causes the deoxygenated blood
to bypass the lungs and enter the circulatory system. Surgeries can fix
this by redirecting the aorta and fixing the right ventricle and
pulmonary artery connection.
There are two types of pulmonary atresia, classified by whether or not the baby also has a ventricular septal defect.
- Pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum: This type of pulmonary atresia is associated with complete and intact septum between the ventricles.
- Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect: This type of pulmonary atresia happens when a ventricular septal defect allows blood to flow into and out of the right ventricle.
Double Outlet Right Ventricle (DORV)
Double outlet right ventricle
is when both great arteries, the pulmonary artery and the aorta, are
connected to the right ventricle. There is usually a VSD in different
particular places depending on the variations of DORV, typically 50% are
subaortic and 30%. The surgeries that can be done to fix this defect
can vary due to the different physiology and blood flow in the defected
heart. One way it can be cured is by a VSD closure and placing conduits
to restart the blood flow between the left ventricle and the aorta and
between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. Another way is
systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt in cases associated with pulmonary stenosis. Also, a balloon atrial septostomy can be done to fix DORV with the Taussig-Bing anomaly.
Transposition of Great Arteries
Dextro-transposition of the Great Arteries
There are two different types of transposition of the great arteries, Dextro-transposition of the great arteries and Levo-transposition of the great arteries,
depending on where the chambers and vessels connect.
Dextro-transposition happens in about 1 in 4,000 newborns and is when
the right ventricle pumps blood into the aorta and deoxygenated blood
enters the blood stream. The temporary procedure is to create an atrial septal defect
(ASD). A permanent fix is more complicated and involves redirecting the
pulmonary return to the right atrium and the systemic return to the
left atrium, which is known as the Senning procedure. The Rastelli procedure
can also be done by rerouting the left ventricular outflow, dividing
the pulmonary trunk, and placing a conduit in between the right
ventricle and pulmonary trunk. Levo-transposition happens in about 1 in
13,000 newborns and is characterized by the left ventricle pumping blood
into the lungs and the right ventricle pumping the blood into the
aorta. This may not produce problems at the beginning, but will
eventually due to the different pressures each ventricle uses to pump
blood. Switching the left ventricle to be the systemic ventricle and the
right ventricle to pump blood into the pulmonary artery can repair
levo-transposition.
Persistent Truncus Arteriosis
Persistent truncus arteriosus is when the truncus arteriosus
fails to split into the aorta and pulmonary trunk. This occurs in about
1 in 11,000 live births and allows both oxygenated and deoxygenated
blood into the body. The repair consists of a VSD closure and the
Rastelli procedure.
Ebstein Anomaly
Ebstein's anomaly
is characterized by a right atrium that is significantly enlarged and a
heart that is shaped like a box. This is very rare and happens in less
than 1% of congenital heart disease cases. The surgical repair varies
depending on the severity of the disease.
Pediatric cardiology is a sub-specialty of pediatrics. To become a pediatric cardiologist in the United States, one must complete a three-year residency in pediatrics, followed by a three-year fellowship in pediatric cardiology. Per doximity, pediatric cardiologists make an average of $303,917 in the United States.
The heart
Blood flow through the valves
As the center focus of cardiology, the heart has numerous anatomical features (e.g., atria, ventricles, heart valves) and numerous physiological features (e.g., systole, heart sounds, afterload) that have been encyclopedically documented for many centuries.
Disorders of the heart lead to heart disease and cardiovascular disease and can lead to a significant number of deaths: cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States and caused 24.95% of total deaths in 2008.
The primary responsibility of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body.
It pumps blood from the body — called the systemic circulation — through the lungs — called the pulmonary circulation — and then back out to the body.
This means that the heart is connected to and affects the entirety of the body. Simplified, the heart is a circuit of the Circulation.
While plenty is known about the healthy heart, the bulk of study in
cardiology is in disorders of the heart and restoration, and where
possible, of function.
The heart is a muscle that squeezes blood and functions like a
pump.
Each part of the heart is susceptible to failure or dysfunction and the
heart can be divided into the mechanical and the electrical parts.
The electrical part of the heart is centered on the periodic contraction (squeezing) of the muscle cells that is caused by the cardiac pacemaker located in the sinoatrial node.
The study of the electrical aspects is a sub-field of electrophysiology called cardiac electrophysiology and is epitomized with the electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG).
The action potentials
generated in the pacemaker propagate throughout the heart in a specific
pattern. The system that carries this potential is called the electrical conduction system.
Dysfunction of the electrical system manifests in many ways and may include Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome, ventricular fibrillation, and heart block.
The mechanical part of the heart is centered on the fluidic movement of blood and the functionality of the heart as a pump.
The mechanical part is ultimately the purpose of the heart and many of
the disorders of the heart disrupt the ability to move blood.
Failure to move sufficient blood can result in failure in other organs
and may result in death if severe.
Heart failure
is one condition in which the mechanical properties of the heart have
failed or are failing, which means insufficient blood is being
circulated.
Coronary circulation
Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the blood vessels of the heart muscle (myocardium). The vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood to the myocardium
are known as coronary arteries. The vessels that remove the
deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle are known as cardiac veins.
These include the great cardiac vein, the middle cardiac vein, the small cardiac vein and the anterior cardiac veins.
As the left and right coronary arteries run on the surface of the
heart, they can be called epicardial coronary arteries. These arteries,
when healthy, are capable of autoregulation to maintain coronary blood
flow at levels appropriate to the needs of the heart muscle. These relatively narrow vessels are commonly affected by atherosclerosis and can become blocked, causing angina or a heart attack. The coronary arteries that run deep within the myocardium are referred to as subendocardial.
The coronary arteries are classified as "end circulation", since
they represent the only source of blood supply to the myocardium; there
is very little redundant blood supply, which is why blockage of these
vessels can be so critical.
Cardiac examination
The cardiac examination (also called the "precordial exam"), is performed as part of a physical examination, or when a patient presents with chest pain suggestive of a cardiovascular pathology. It would typically be modified depending on the indication and integrated with other examinations especially the respiratory examination.
Like all medical examinations, the cardiac examination follows the standard structure of inspection, palpation and auscultation.
Heart disorders
Cardiology is concerned with the normal functionality of the heart and the deviation from a healthy heart.
Many disorders involve the heart itself but some are outside of the heart and in the vascular system.
Collectively, the two together are termed the cardiovascular system and diseases of one part tend to affect the other.
Hypertension
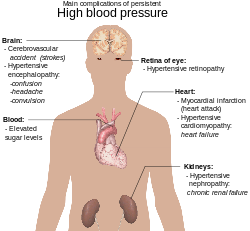
Diagram illustrating the main complications of persistent high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as "high blood pressure"", is a long term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long term high blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, vision loss, and chronic kidney disease.
Lifestyle factors can increase the risk of hypertension. These include excess salt in the diet, excess body weight, smoking, and alcohol. Hypertension can also be caused by other diseases, or as a side-effect of drugs.
Blood pressure is expressed by two measurements, the systolic and diastolic pressures, which are the maximum and minimum pressures, respectively. Normal blood pressure at rest is within the range of 100–140 millimeters mercury (mmHg) systolic and 60–90 mmHg diastolic. High blood pressure is present if the resting blood pressure is persistently at or above 140/90 mmHg for most adults. Different numbers apply to children. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring over a 24-hour period appears more accurate than office best blood pressure measurement.
Lifestyle changes and medications can lower blood pressure and decrease the risk of health complications. Lifestyle changes include weight loss, decreased salt intake, physical exercise, and a healthy diet. If lifestyle changes are not sufficient then blood pressure medications are used. Up to three medications can control blood pressure in 90% of people.
The treatment of moderately high arterial blood pressure (defined as
>160/100 mmHg) with medications is associated with an improved life expectancy. The effect of treatment of blood pressure between 140/90 mmHg and 160/100 mmHg is less clear, with some reviews finding benefit and others finding a lack of evidence for benefit. High blood pressure affects between 16 and 37% of the population globally. In 2010 hypertension was believed to have been a factor in 18% (9.4 million) deaths.
Essential vs Secondary hypertension
Essential hypertension is the form of hypertension
that by definition has no identifiable cause. It is the most common
type of hypertension, affecting 95% of hypertensive patients, it tends to be familial and is likely to be the consequence of an interaction between environmental and genetic factors. Prevalence of essential hypertension increases with age, and individuals with relatively high blood pressure at younger ages are at increased risk for the subsequent development of hypertension.
Hypertension can increase the risk of cerebral, cardiac, and renal events.
Secondary hypertension is a type of hypertension
which is caused by an identifiable underlying secondary cause. It is
much less common than essential hypertension, affecting only 5% of
hypertensive patients. It has many different causes including endocrine diseases, kidney diseases, and tumors. It also can be a side effect of many medications.
Complications of hypertension
Main complications of persistent high blood pressure
Complications of hypertension are clinical outcomes that result from persistent elevation of blood pressure. Hypertension is a risk factor for all clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis since it is a risk factor for atherosclerosis itself. It is an independent predisposing factor for heart failure, coronary artery disease, stroke, renal disease, and peripheral arterial disease. It is the most important risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, in industrialized countries.
Cardiac arrhythmia
Cardiac arrhythmia, also known as "cardiac dysrhythmia" or "irregular heartbeat", is a group of conditions in which the heartbeat is irregular, too fast, or too slow. A heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia and a heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Many types of arrhythmia have no symptoms. When symptoms are present these may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. More seriously there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, or chest pain. While most types of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in cardiac arrest.
There are four main types of arrhythmia: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias, and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats include premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contractions, and premature junctional contractions. Supraventricular tachycardias include atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Ventricular arrhythmias include ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia. Arrhythmias are due to problems with the electrical conduction system of the heart. Arrhythmias may occur in children; however, the normal range for the heart rate is different and depends on age. A number of tests can help with diagnosis including an electrocardiogram (ECG) and Holter monitor.
Most arrhythmias can be effectively treated. Treatments may include medications, medical procedures such as a pacemaker, and surgery. Medications for a fast heart rate may include beta blockers or agents that attempt to restore a normal heart rhythm such as procainamide.
This later group may have more significant side effects especially if
taken for a long period of time. Pacemakers are often used for slow
heart rates. Those with an irregular heartbeat are often treated with blood thinners
to reduce the risk of complications. Those who have severe symptoms
from an arrhythmia may receive urgent treatment with a jolt of
electricity in the form of cardioversion or defibrillation.
Arrhythmia affects millions of people. In Europe and North America, as of 2014, atrial fibrillation affects about 2% to 3% of the population. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter resulted in 112,000 deaths in 2013, up from 29,000 in 1990. Sudden cardiac death is the cause of about half of deaths due to cardiovascular disease or about 15% of all deaths globally. About 80% of sudden cardiac death is the result of ventricular arrhythmias. Arrhythmias may occur at any age but are more common among older people.
Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease, also known as "ischemic heart disease", is a group of diseases that includes: stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial infarction, and sudden cardiac death. It is within the group of cardiovascular diseases of which it is the most common type. A common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. Usually symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and get better with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. The first sign is occasionally a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an irregular heartbeat.
Risk factors include: high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol, among others. Other risks include depression. The underlying mechanism involves atherosclerosis of the arteries of the heart. A number of tests may help with diagnoses including: electrocardiogram, cardiac stress testing, coronary computed tomographic angiography, and coronary angiogram, among others.
Prevention is by eating a healthy diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight and not smoking. Sometimes medication for diabetes, high cholesterol, or high blood pressure are also used. There is limited evidence for screening people who are at low risk and do not have symptoms. Treatment involves the same measures as prevention. Additional medications such as antiplatelets including aspirin, beta blockers, or nitroglycerin may be recommended. Procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be used in severe disease. In those with stable CAD it is unclear if PCI or CABG in addition to the other treatments improve life expectancy or decreases heart attack risk.
In 2013 CAD was the most common cause of death globally, resulting in 8.14 million deaths (16.8%) up from 5.74 million deaths (12%) in 1990. The risk of death from CAD for a given age has decreased between 1980 and 2010 especially in developed countries. The number of cases of CAD for a given age has also decreased between 1990 and 2010. In the United States in 2010 about 20% of those over 65 had CAD, while it was present in 7% of those 45 to 64, and 1.3% of those 18 to 45. Rates are higher among men than women of a given age.
Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is a sudden stop in effective blood flow due to the failure of the heart to contract effectively. Symptoms include loss of consciousness and abnormal or absent breathing. Some people may have chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea before this occurs. If not treated within minutes, death usually occurs.
The most common cause of cardiac arrest is coronary artery disease. Less common causes include major blood loss, lack of oxygen, very low potassium, heart failure, and intense physical exercise. A number of inherited disorders may also increase the risk including long QT syndrome. The initial heart rhythm is most often ventricular fibrillation. The diagnosis is confirmed by finding no pulse. While a cardiac arrest may be caused by heart attack or heart failure these are not the same.
Prevention includes not smoking, physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Treatment for cardiac arrest is immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and, if a shockable rhythm is present, defibrillation. Among those who survive targeted temperature management may improve outcomes. An implantable cardiac defibrillator may be placed to reduce the chance of death from recurrence.
In the United States, cardiac arrest outside of hospital occurs in about 13 per 10,000 people per year (326,000 cases). In hospital cardiac arrest occurs in an additional 209,000 Cardiac arrest becomes more common with age. It affects males more often than females. The percentage of people who survive with treatment is about 8%. Many who survive have significant disability. Many U.S. television shows, however, have portrayed unrealistically high survival rates of 67%.
Congenital heart defects
A congenital heart defect, also known as a "congenital heart anomaly" or "congenital heart disease", is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired. It does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart problems do not occur with other diseases. Complications that can result from heart defects include heart failure.
The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic conditions are associated with heart defects including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Marfan syndrome. Congenital heart defects are divided into two main groups: cyanotic heart defects and non-cyanotic heart defects, depending on whether the child has the potential to turn bluish in color. The problems may involve the interior walls of the heart, the heart valves, or the large blood vessels that lead to and from the heart.
Congenital heart defects are partly preventable through rubella vaccination, the adding of iodine to salt, and the adding of folic acid to certain food products. Some defects do not need treatment. Other may be effectively treated with catheter based procedures or heart surgery. Occasionally a number of operations may be needed. Occasionally heart transplantation is required. With appropriate treatment outcomes, even with complex problems, are generally good.
Heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2013 they were present in 34.3 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births depending upon how they are diagnosed. About 6 to 19 per 1,000 cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are the leading cause of birth defect-related deaths. In 2013 they resulted in 323,000 deaths down from 366,000 deaths in 1990.
Diagnostic tests in cardiology
Diagnostic tests in cardiology are the methods of identifying heart conditions associated with healthy vs. unhealthy, pathologic heart function. The starting point is obtaining a medical history, followed by Auscultation. Then blood tests, electrophysiological procedures, and cardiac imaging can be ordered for further analysis. Electrophysiological procedures include electrocardiogram, cardiac monitoring, cardiac stress testing, and the electrophysiology study.
Cardiology community
Associations
- American College of Cardiology
- American Heart Association
- European Society of Cardiology
- Heart Rhythm Society
- Canadian Cardiovascular Society
- Indian Heart Association
- National Heart Foundation of Australia
Journals
- Acta Cardiologica
- American Journal of Cardiology
- Annals of Cardiac Anaesthesia
- Cardiology
- Cardiology in Review
- Circulation
- Circulation Research
- Clinical and Experimental Hypertension
- Clinical Cardiology
- EP – Europace
- European Heart Journal
- Heart
- Heart Rhythm
- International Journal of Cardiology
- Journal of the American College of Cardiology
- Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology