| Congenital heart defect | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Congenital heart anomaly, congenital heart disease |
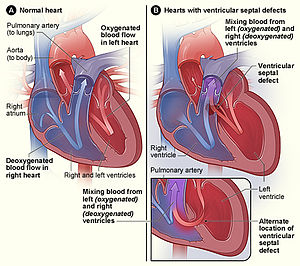 | |
| The normal structure of the heart (left) in comparison to two common locations for a ventricular septal defect (right), the most common form of congenital heart defect. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, feeling tired |
| Complications | Heart failure |
| Types | Cyanotic heart defects, non-cyanotic heart defects |
| Causes | Often unknown |
| Risk factors | Rubella infection during pregnancy, alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother |
| Treatment | None, catheter based procedures, heart surgery, heart transplantation |
| Prognosis | Generally good (with treatment) |
| Frequency | 48.9 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 303,300 (2015) |
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present they may include rapid breathing, bluish skin, poor weight gain, and feeling tired. It does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart problems do not occur with other diseases. Complications that can result from heart defects include heart failure.
The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Certain cases may be due to infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic conditions are associated with heart defects including Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Marfan syndrome. Congenital heart defects are divided into two main groups: cyanotic heart defects and non-cyanotic heart defects, depending on whether the child has the potential to turn bluish in color. The problems may involve the interior walls of the heart, the heart valves, or the large blood vessels that lead to and from the heart.
Congenital heart defects are partly preventable through rubella vaccination, the adding of iodine to salt, and the adding of folic acid to certain food products. Some defects do not need treatment. Others may be effectively treated with catheter based procedures or heart surgery. Occasionally a number of operations may be needed, or a heart transplant may be required. With appropriate treatment, outcomes are generally good, even with complex problems.
Heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015 they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births depending upon how they are diagnosed. About 6 to 19 per 1,000 cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are the leading cause of birth defect-related deaths. In 2015 they resulted in 303,300 deaths down from 366,000 deaths in 1990.
Signs and symptoms
Digital clubbing with cyanotic nail beds in an adult with tetralogy of Fallot
Signs and symptoms are related to type and severity of the heart
defect. Symptoms frequently present early in life, but it is possible
for some CHDs to go undetected throughout life. Some children have no signs while others may exhibit shortness of breath, cyanosis, fainting, heart murmur,
under-development of limbs and muscles, poor feeding or growth, or
respiratory infections. Congenital heart defects cause abnormal heart
structure resulting in production of certain sounds called heart murmur. These can sometimes be detected by auscultation; however, not all heart murmurs are caused by congenital heart defects.
Associated symptoms
Congenital heart defects are associated with an increased incidence of some other symptoms, together being called the VACTERL association:
- V — Vertebral anomalies
- A — Anal atresia
- C — Cardiovascular anomalies
- T — Tracheoesophageal fistula
- E — Esophageal atresia
- R — Renal (Kidney) and/or radial anomalies
- L — Limb defects
Ventricular septal defect (VSD), atrial septal defects, and tetralogy
of Fallot are the most common congenital heart defects seen in the
VACTERL association. Less common defects in the association are truncus
arteriosus and transposition of the great arteries.
Causes
The cause of congenital heart disease may be genetic, environmental, or a combination of both.
Genetic
Most of
the known causes of congenital heart disease are sporadic genetic
changes, either focal mutations or deletion or addition of segments of
DNA. Large chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomies 21, 13, and 18 cause about 5–8% of cases of CHD, with trisomy 21 being the most common genetic cause. Small chromosomal abnormalities also frequently lead to congenital heart disease, and examples include microdeletion of the long arm of chromosome 22 (22q11, DiGeorge syndrome), the long arm of chromosome 1 (1q21), the short arm of chromosome 8 (8p23) and many other, less recurrent regions of the genome, as shown by high resolution genome-wide screening (Array comparative genomic hybridization).
The genes regulating the complex developmental sequence have only
been partly elucidated. Some genes are associated with specific
defects. A number of genes have been associated with cardiac
manifestations. Mutations of a heart muscle protein, α-myosin heavy
chain (MYH6)
are associated with atrial septal defects. Several proteins that
interact with MYH6 are also associated with cardiac defects. The
transcription factor GATA4 forms a complex with the TBX5 which interacts with MYH6. Another factor, the homeobox (developmental) gene, NKX2-5
also interacts with MYH6. Mutations of all these proteins are
associated with both atrial and ventricular septal defects; In addition,
NKX2-5 is associated with defects in the electrical conduction of the
heart and TBX5 is related to the Holt-Oram syndrome which includes electrical conduction defects and abnormalities of the upper limb. Another T-box gene, TBX1, is involved in velo-cardio-facial syndrome DiGeorge syndrome, the most common deletion which has extensive symptoms including defects of the cardiac outflow tract including tetralogy of Fallot.
| MYH6 | GATA4 | NKX2-5 | TBX5 | TBX1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locus | 14q11.2-q13 | 8p23.1-p22 | 5q34 | 12q24.1 | 22q11.2 |
| Syndrome | Holt-Oram | DiGeorge | |||
| Atrial septal defects | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
| Ventricular septal defects | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| |
| Electrical conduction abnormalities | ✔ | ✔ |
| ||
| Outflow tract abnormalities | ✔ | ||||
| Non-cardiac manifestations[19] | Upper limb abnormalities | Small or absent thymus Small or absent parathyroids Facial abnormalities |
Molecular pathways
The notch signaling pathway,
a regulatory mechanism for cell growth and differentiation, plays broad
roles in several aspects of cardiac development. Notch elements are
involved in determination of the right and left sides of the body plan,
so the directional folding of the heart tube can be impacted. Notch
signaling is involved early in the formation of the endocardial cushions
and continues to be active as the develop into the septa and valves. It
is also involved in the development of the ventricular wall and the
connection of the outflow tract to the great vessels. Mutations in the
gene for one of the notch ligands, Jagged1, are identified in the majority of examined cases of arteriohepatic dysplasia (Alagille syndrome), characterized by defects of the great vessels (pulmonary artery stenosis), heart (tetralogy of Fallot in 13% of cases), liver, eyes, face, and bones. Though less than 1% of all cases, where no defects are found in the Jagged1 gene, defects are found in Notch2 gene. In 10% of cases, no mutation is found in either gene. For another member of the gene family, mutations in the Notch1 gene are associated with bicuspid aortic valve, a valve with two leaflets instead of three. Notch1 is also associated with calcification of the aortic valve, the third most common cause of heart disease in adults.
Mutations of a cell regulatory mechanism, the Ras/MAPK pathway are responsible for a variety of syndromes, including Noonan syndrome, LEOPARD syndrome, Costello syndrome and cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome in which there is cardiac involvement.
While the conditions listed are known genetic causes, there are likely
many other genes which are more subtle. It is known that the risk for
congenital heart defects is higher when there is a close relative with
one.
Environmental
Known environmental factors include certain infections during pregnancy such as Rubella, drugs (alcohol, hydantoin, lithium and thalidomide) and maternal illness (diabetes mellitus, phenylketonuria, and systemic lupus erythematosus).
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of congenital heart disease. Additionally, as maternal obesity increases, the risk of heart defects also increases.
A distinct physiological mechanism has not been identified to explain
the link between maternal obesity and CHD, but both prepregnancy folate
deficiency and diabetes have been implicated in some studies.
Mechanism
There is a complex sequence of events that result in a well formed
heart at birth and disruption of any portion may result in a defect. The orderly timing of cell growth, cell migration, and programmed cell death ("apoptosis") has been studied extensively and the genes that control the process are being elucidated.
Around day 15 of development, the cells that will become the heart exist
in two horseshoe shaped bands of the middle tissue layer (mesoderm), and some cells migrate from a portion of the outer layer (ectoderm), the neural crest,
which is the source of a variety of cells found throughout the body. On
day 19 of development, a pair of vascular elements, the "endocardial
tubes", form. The tubes fuse when cells between then undergo programmed
death and cells from the first heart field migrate to the tube, and form
a ring of heart cells (myocytes) around it by day 21. On day 22, the heart begins to beat and by day 24, blood is circulating.
At day 22, the circulatory system is bilaterally symmetrical with
paired vessels on each side and the heart consisting of a simple tube
located in the midline of the body layout. The portions that will become
the atria
and will be located closest to the head are the most distant from the
head. From days 23 through 28, the heart tube folds and twists, with the
future ventricles moving left of center (the ultimate location of the heart) and the atria moving towards the head.
On day 28, areas of tissue in the heart tube begin to expand inwards; after about two weeks, these expansions, the membranous "septum primum" and the muscular "endocardial cushions",
fuse to form the four chambers of the heart. A failure to fuse properly
will result in a defect that may allow blood to leak between chambers.
After this happens, cells which have migrated from the neural crest
begin to divide the bulbus cordis,
the main outflow tract is divided in two by the growth a spiraling
septum, becoming the great vessels—the ascending segment of the aorta
and the pulmonary trunk. If the separation is incomplete, the result is a
"persistent truncus arteriosis". The vessels may be reversed ("transposition of the great vessels").
The two halves of the split tract must migrate into the correct
positions over the appropriate ventricles. A failure may result in some
blood flowing into the wrong vessel (e.g.overriding aorta).
The four-chambered heart and the great vessels have features required
for fetal growth. The lungs are unexpanded and cannot accommodate the
full circulatory volume. Two structures exist to shunt blood flow away
from the lungs. Cells in part of the septum primum die creating a hole
while muscle cells, the "septum secundum",
grow along the right atrial side the septum primum, except for one
region, leaving a gap through which blood can pass from the right artium
to the left atrium, the foramen ovale. A small vessel, the ductus arteriosus allows blood from the pulmonary artery to pass to the aorta.
Changes at birth
The ductus arteriosus stays open because of circulating factors including prostaglandins.
The foramen ovale stays open because of the flow of blood from the
right atrium to the left atrium. As the lungs expand, blood flows easily
through the lungs and the membranous portion of the foramen ovale (the
septum primum) flops over the muscular portion (the septum secundum). If
the closure is incomplete, the result is a patent foramen ovale.
The two flaps may fuse, but many adults have a foramen ovale that stays
closed only because of the pressure difference between the atria.
Theories
Rokitansky (1875) explained congenital heart defects as breaks in heart development at various ontogenesis stages. Spitzer (1923) treats them as returns to one of the phylogenesis stages.
Krimsky (1963), synthesizing two previous points of view, considered
congenital heart diseases as a stop of development at the certain stage
of ontogenesis, corresponding to this or that stage of the phylogenesis. Hence these theories can explain feminine and neutral types of defects only.
Diagnosis
Many congenital heart defects can be diagnosed prenatally by fetal echocardiography. This is a test which can be done during the second trimester of pregnancy, when the woman is about 18–24 weeks pregnant. It can be an abdominal ultrasound or transvaginal ultrasound.
If a baby is born with cyanotic heart disease, the diagnosis is
usually made shortly after birth due to the blue colour of their skin
(called cyanosis).
If a baby is born with a septal defect or an obstruction defect,
often their symptoms are only noticeable after several months or
sometimes even after many years.
Classification
A
number of classification systems exist for congenital heart defects. In
2000 the International Congenital Heart Surgery Nomenclature was
developed to provide a generic classification system.
Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia can affect the heart, typically resulting in the underdevelopment of the right ventricle or the left ventricle. This causes only one side of the heart to be capable of pumping blood to the body and lungs effectively. Hypoplasia of the heart is rare but is the most serious form of CHD. It is called hypoplastic left heart syndrome when it affects the left side of the heart and hypoplastic right heart syndrome when it affects the right side of the heart. In both conditions, the presence of a patent ductus arteriosus (and, when hypoplasia affects the right side of the heart, a patent foramen ovale)
is vital to the infant's ability to survive until emergency heart
surgery can be performed, since without these pathways blood cannot
circulate to the body (or lungs, depending on which side of the heart is
defective). Hypoplasia of the heart is generally a cyanotic heart defect.
Obstruction defects
Obstruction defects occur when heart valves, arteries, or veins are abnormally narrow or blocked. Common defects include pulmonic stenosis, aortic stenosis, and coarctation of the aorta,
with other types such as bicuspid aortic valve stenosis and subaortic
stenosis being comparatively rare. Any narrowing or blockage can cause
heart enlargement or hypertension.
Septal defects
The septum is a wall of tissue which separates the left heart from the right heart. Defects in the interatrial septum or the interventricular septum allow blood to flow from the right side of the heart to the left, reducing the heart's efficiency. Ventricular septal defects are collectively the most common type of CHD, although approximately 30% of adults have a type of atrial septal defect called probe patent foramen ovale.
Cyanotic defects
Cyanotic heart defects are called such because they result in cyanosis, a bluish-grey discoloration of the skin due to a lack of oxygen in the body. Such defects include persistent truncus arteriosus, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great vessels, and tricuspid atresia.
Defects
- Aortic stenosis
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD)
- Bicuspid aortic valve
- Cardiomyopathy
- Complete heart block (CHB)
- Dextrocardia
- Double inlet left ventricle (DILV)
- Double outlet right ventricle (DORV)
- Ebstein's anomaly
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS)
- Hypoplastic right heart syndrome (HRHS)
- Mitral stenosis
- Persistent truncus arteriosus
- Pulmonary atresia
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Rhabdomyomas (Tumors of the Heart)
- Transposition of the great vessels
- Tricuspid atresia
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW)
Some conditions affect the great vessels or other vessels in close
proximity to the heart, but not the heart itself, but are often
classified as congenital heart defects.
- Coarctation of the aorta (CoA)
- Double aortic arch, aberrant subclavian artery, and other malformations of the great arteries
- Interrupted aortic arch (IAA)
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
- Scimitar syndrome (SS)
Some constellations of multiple defects are commonly found together.
- Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF)
- Pentalogy of Cantrell
- Shone's syndrome/ Shone's complex / Shone's anomaly
Treatment
Most
of the time CHD is serious and requires surgery and/or medications.
Medications include diuretics, which aid the body in eliminating water,
salts, and digoxin for strengthening the contraction of the heart. This
slows the heartbeat and removes some fluid from tissues. Some defects
require surgical procedures to restore circulation back to normal and in
some cases, multiple surgeries are needed.
Interventional cardiology now offers patients minimally invasive
alternatives to surgery for some patients. The Melody Transcatheter
Pulmonary Valve (TPV), approved in Europe in 2006 and in the U.S. in
2010 under a Humanitarian Device Exemption (HDE), is designed to treat
congenital heart disease patients with a dysfunctional conduit in their
right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT). The RVOT is the connection
between the heart and lungs; once blood reaches the lungs, it is
enriched with oxygen before being pumped to the rest of the body.
Transcatheter pulmonary valve technology provides a less-invasive means
to extend the life of a failed RVOT conduit and is designed to allow
physicians to deliver a replacement pulmonary valve via a catheter
through the patient’s blood vessels.
Most patients require lifelong specialized cardiac care, first
with a pediatric cardiologist and later with an adult congenital
cardiologist. There are more than 1.8 million adults living with
congenital heart defects.
Epidemiology
Congenital heart anomalies deaths per million persons in 2012
0-8
9-12
13-23
24-31
32-39
40-47
48-50
51-56
57-63
64-124
Heart defects are among the most common birth defect, occurring in 1% of live births (2-3% including bicuspid aortic valve). In 2013, 34.3 million people had CHD. In 2010, they resulted in 223,000 deaths, down from 278,000 deaths in 1990.
For congenital heart defects that arise without a family history (de novo), the recurrence risk in offspring is 3-5%. This risk is higher in left ventricular outflow tract obstructions, heterotaxy, and atrioventricular septal defects.
Terminology
Congenital
heart defects are known by a number of names including congenital heart
anomaly, congenital heart disease, heart defects, and congenital
cardiovascular malformations.


