| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allotropes | alpha, α (gray); beta, β (white) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery-white (beta, β) or gray (alpha, α) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Sn) | 118.710(7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tin in the periodic table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 14 (carbon group) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | p-block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | post-transition metal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell
| 2, 8, 18, 18, 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 505.08 K (231.93 °C, 449.47 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 2875 K (2602 °C, 4716 °F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | white, β: 7.265 g/cm3 gray, α: 5.769 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 6.99 g/cm3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | white, β: 7.03 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | white, β: 296.1 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | white, β: 27.112 J/(mol·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −4, −3, −2, −1, +1, +2, +3, +4 (an amphoteric oxide) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.96 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 140 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 139±4 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 217 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of tin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | body-centered tetragonal
white (β) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered diamond-cubic
gray (α) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 2730 m/s (at r.t.) (rolled) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 22.0 µm/(m·K) (at 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 66.8 W/(m·K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 115 nΩ·m (at 0 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | gray: diamagnetic white (β): paramagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | (white) +3.1·10−6 cm3/mol (298 K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 50 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 18 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 58 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.36 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 50–440 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-31-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | around 3500 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of tin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from Latin: stannum) and atomic number 50. It is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, SnO2. Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest number of stable isotopes in the periodic table, thanks to its magic number of protons. It has two main allotropes: at room temperature, the stable allotrope is β-tin, a silvery-white, malleable metal, but at low temperatures it transforms into the less dense grey α-tin, which has the diamond cubic structure. Metallic tin does not easily oxidize in air.
The first tin alloy used on a large scale was bronze, made of 1/8 tin and 7/8 copper, from as early as 3000 BC. After 600 BC, pure metallic tin was produced. Pewter, which is an alloy of 85–90% tin with the remainder commonly consisting of copper, antimony, and lead, was used for flatware from the Bronze Age until the 20th century. In modern times, tin is used in many alloys, most notably tin/lead soft solders, which are typically 60% or more tin, and in the manufacture of transparent, electrically conducting films of indium tin oxide in optoelectronic applications. Another large application for tin is corrosion-resistant tin plating of steel. Because of the low toxicity of inorganic tin, tin-plated steel is widely used for food packaging as tin cans. However, some organotin compounds can be almost as toxic as cyanide.
Characteristics
Physical
Droplet of solidified molten tin
Tin is a soft, malleable, ductile and highly crystalline silvery-white metal. When a bar of tin is bent, a crackling sound known as the "tin cry" can be heard from the twinning of the crystals.
Tin melts at low temperatures of about 232 °C (450 °F), the lowest in
group 14. The melting point is further lowered to 177.3 °C (351.1 °F)
for 11 nm particles.
β-tin (the metallic form, or white tin, BCT structure), which is
stable at and above room temperature, is malleable. In contrast, α-tin
(nonmetallic form, or gray tin), which is stable below 13.2 °C
(55.8 °F), is brittle. α-tin has a diamond cubic crystal structure, similar to diamond, silicon or germanium.
α-tin has no metallic properties at all because its atoms form a
covalent structure in which electrons cannot move freely. It is a
dull-gray powdery material with no common uses other than a few
specialized semiconductor applications. These two allotropes, α-tin and β-tin, are more commonly known as gray tin and white tin, respectively. Two more allotropes, γ and σ, exist at temperatures above 161 °C (322 °F) and pressures above several GPa. In cold conditions, β-tin tends to transform spontaneously into α-tin, a phenomenon known as "tin pest".
Although the α-β transformation temperature is nominally 13.2 °C
(55.8 °F), impurities (e.g. Al, Zn, etc.) lower the transition
temperature well below 0 °C (32 °F) and, on the addition of antimony or bismuth, the transformation might not occur at all, increasing the durability of the tin.
Commercial grades of tin (99.8%) resist transformation because of
the inhibiting effect of the small amounts of bismuth, antimony, lead,
and silver present as impurities. Alloying elements such as copper,
antimony, bismuth, cadmium, and silver increase its hardness. Tin tends
rather easily to form hard, brittle intermetallic phases, which are
often undesirable. It does not form wide solid solution ranges in other
metals in general, and few elements have appreciable solid solubility in
tin. Simple eutectic systems, however, occur with bismuth, gallium, lead, thallium and zinc.
Tin becomes a superconductor below 3.72 K and was one of the first superconductors to be studied; the Meissner effect, one of the characteristic features of superconductors, was first discovered in superconducting tin crystals.
Chemical
Tin resists corrosion from water, but can be attacked by acids and alkalis. Tin can be highly polished and is used as a protective coat for other metals. A protective oxide (passivation) layer prevents further oxidation, the same that forms on pewter and other tin alloys. Tin acts as a catalyst when oxygen is in solution and helps to accelerate the chemical reaction.
Isotopes
Tin has ten stable isotopes, with atomic masses of 112, 114 through 120, 122 and 124, the greatest number of any element. Of these, the most abundant are 120Sn (almost a third of all tin), 118Sn, and 116Sn, while the least abundant is 115Sn. The isotopes with even mass numbers have no nuclear spin, while those with odd have a spin of +1/2. Tin, with its three common isotopes 116Sn, 118Sn and 120Sn, is among the easiest elements to detect and analyze by NMR spectroscopy, and its chemical shifts are referenced against SnMe
4.
4.
This large number of stable isotopes is thought to be a direct result of the atomic number 50, a "magic number"
in nuclear physics. Tin also occurs in 29 unstable isotopes,
encompassing all the remaining atomic masses from 99 to 137. Apart from 126Sn, with a half-life of 230,000 years, all the radioisotopes have a half-life of less than a year. The radioactive 100Sn, discovered in 1994, and 132Sn are one of the few nuclides with a "doubly magic"
nucleus: despite being unstable, having very lopsided proton–neutron
ratios, they represent endpoints beyond which stability drops off
rapidly. Another 30 metastable isomers have been characterized for isotopes between 111 and 131, the most stable being 121mSn with a half-life of 43.9 years.
The relative differences in the abundances of tin's stable isotopes can be explained by their different modes of formation in stellar nucleosynthesis. 116Sn through 120Sn inclusive are formed in the s-process (slow neutron capture) in most stars and hence they are the most common isotopes, while 122Sn and 124Sn are only formed in the r-process (rapid neutron capture) in supernovae and are less common. (The isotopes 117Sn through 120Sn also receive contributions from the r-process.) Finally, the rarest proton-rich isotopes, 112Sn, 114Sn, and 115Sn, cannot be made in significant amounts in the s- or r-processes and are considered among the p-nuclei, whose origins are not well understood yet. Some speculated mechanisms for their formation include proton capture as well as photodisintegration, although 115Sn might also be partially produced in the s-process, both directly, and as the daughter of long-lived 115In.
Etymology
The word tin is shared among Germanic languages and can be traced back to reconstructed Proto-Germanic *tin-om; cognates include German Zinn, Swedish tenn and Dutch tin. It is not found in other branches of Indo-European, except by borrowing from Germanic (e.g., Irish tinne from English).
The Latin name stannum originally meant an alloy of silver and lead, and came to mean 'tin' in the 4th century—the earlier Latin word for it was plumbum candidum, or "white lead". Stannum apparently came from an earlier stāgnum (meaning the same substance), the origin of the Romance and Celtic terms for tin. The origin of stannum/stāgnum is unknown; it may be pre-Indo-European.
The Meyers Konversations-Lexikon speculates on the contrary that stannum is derived from (the ancestor of) Cornish stean, and is proof that Cornwall in the first centuries AD was the main source of tin.
History
Ceremonial giant bronze dirk of the Plougrescant-Ommerschans type, Plougrescant, France, 1500–1300 BC.
Tin extraction and use can be dated to the beginnings of the Bronze Age around 3000 BC, when it was observed that copper objects formed of polymetallic ores with different metal contents had different physical properties.
The earliest bronze objects had a tin or arsenic content of less than
2% and are therefore believed to be the result of unintentional alloying due to trace metal content in the copper ore. The addition of a second metal to copper increases its hardness, lowers the melting temperature, and improves the casting process by producing a more fluid melt that cools to a denser, less spongy metal. This was an important innovation that allowed for the much more complex shapes cast in closed molds of the Bronze Age. Arsenical bronze objects appear first in the Near East where arsenic is commonly found in association with copper ore, but the health risks were quickly realized and the quest for sources of the much less hazardous tin ores began early in the Bronze Age. This created the demand for rare tin metal and formed a trade network that linked the distant sources of tin to the markets of Bronze Age cultures.
Cassiterite (SnO2),
the tin oxide form of tin, was most likely the original source of tin
in ancient times. Other forms of tin ores are less abundant sulfides such as stannite that require a more involved smelting process. Cassiterite often accumulates in alluvial channels as placer deposits because it is harder, heavier, and more chemically resistant than the accompanying granite. Cassiterite is usually black or generally dark in color, and these deposits can be easily seen in river banks. Alluvial (placer) deposits could be easily collected and separated by methods similar to gold panning.
Compounds and chemistry
In the great majority of its compounds, tin has the oxidation state II or IV.
Inorganic compounds
Halide compounds are known for both oxidation states. For Sn(IV), all four halides are well known: SnF4, SnCl4, SnBr4, and SnI4.
The three heavier members are volatile molecular compounds, whereas the
tetrafluoride is polymeric. All four halides are known for Sn(II) also:
SnF2, SnCl2, SnBr2, and SnI2. All are polymeric solids. Of these eight compounds, only the iodides are colored.
Tin(II) chloride
(also known as stannous chloride) is the most important tin halide in a
commercial sense. Illustrating the routes to such compounds, chlorine reacts with tin metal to give SnCl4 whereas the reaction of hydrochloric acid and tin produces SnCl2 and hydrogen gas. Alternatively SnCl4 and Sn combine to stannous chloride by a process called comproportionation:
- SnCl4 + Sn → 2 SnCl2
Tin can form many oxides, sulfides, and other chalcogenide derivatives. The dioxide SnO2 (cassiterite) forms when tin is heated in the presence of air. SnO2 is amphoteric, which means that it dissolves in both acidic and basic solutions. Stannates with the structure [Sn(OH)6]2−, like K2[Sn(OH)6], are also known, though the free stannic acid H2[Sn(OH)6] is unknown.
Sulfides of tin exist in both the +2 and +4 oxidation states: tin(II) sulfide and tin(IV) sulfide (mosaic gold).
Ball-and-stick models of the structure of solid stannous chloride (SnCl2).
Hydrides
Stannane (SnH4), with tin in the +4 oxidation state, is unstable. Organotin hydrides are however well known, e.g. tributyltin hydride (Sn(C4H9)3H). These compound release transient tributyl tin radicals, which are rare examples of compounds of tin(III).
Organotin compounds
Organotin compounds, sometimes called stannanes, are chemical compounds with tin–carbon bonds. Of the compounds of tin, the organic derivatives are the most useful commercially. Some organotin compounds are highly toxic and have been used as biocides. The first organotin compound to be reported was diethyltin diiodide ((C2H5)2SnI2), reported by Edward Frankland in 1849.
Most organotin compounds are colorless liquids or solids that are
stable to air and water. They adopt tetrahedral geometry. Tetraalkyl-
and tetraaryltin compounds can be prepared using Grignard reagents:
- SnCl
4 + 4 RMgBr → R
4Sn + 4 MgBrCl
The mixed halide-alkyls, which are more common and more important
commercially than the tetraorgano derivatives, are prepared by redistribution reactions:
- SnCl
4 + R
4Sn → 2 SnCl2R2
Divalent organotin compounds are uncommon, although more common than related divalent organogermanium and organosilicon compounds. The greater stabilization enjoyed by Sn(II) is attributed to the "inert pair effect". Organotin(II) compounds include both stannylenes (formula: R2Sn, as seen for singlet carbenes) and distannylenes (R4Sn2), which are roughly equivalent to alkenes. Both classes exhibit unusual reactions.
Occurrence
Sample of cassiterite, the main ore of tin.
Granular pieces of cassiterite, collected by placer mining
Tin is generated via the long s-process in low-to-medium mass stars (with masses of 0.6 to 10 times that of Sun), and finally by beta decay of the heavy isotopes of indium.
Tin is the 49th most abundant element in Earth's crust, representing 2 ppm compared with 75 ppm for zinc, 50 ppm for copper, and 14 ppm for lead.
Tin does not occur as the native element but must be extracted from various ores. Cassiterite (SnO2) is the only commercially important source of tin, although small quantities of tin are recovered from complex sulfides such as stannite, cylindrite, franckeite, canfieldite, and teallite. Minerals with tin are almost always associated with granite rock, usually at a level of 1% tin oxide content.
Because of the higher specific gravity of tin dioxide, about 80%
of mined tin is from secondary deposits found downstream from the
primary lodes. Tin is often recovered from granules washed downstream in
the past and deposited in valleys or the sea. The most economical ways
of mining tin are by dredging, hydraulicking, or open pits. Most of the world's tin is produced from placer deposits, which can contain as little as 0.015% tin.
About 253,000 tonnes of tin have been mined in 2011, mostly in China
(110,000 t), Indonesia (51,000 t), Peru (34,600 t), Bolivia (20,700 t)
and Brazil (12,000 t).
Estimates of tin production have historically varied with the dynamics
of economic feasibility and the development of mining technologies, but
it is estimated that, at current consumption rates and technologies, the
Earth will run out of mine-able tin in 40 years. Lester Brown has suggested tin could run out within 20 years based on an extremely conservative extrapolation of 2% growth per year.
Secondary, or scrap, tin is also an important source of the metal.
Recovery of tin through secondary production, or recycling of scrap tin,
is increasing rapidly. Whereas the United States has neither mined
since 1993 nor smelted tin since 1989, it was the largest secondary
producer, recycling nearly 14,000 tonnes in 2006.
New deposits are reported in southern Mongolia, and in 2009, new deposits of tin were discovered in Colombia by the Seminole Group Colombia CI, SAS.
Production
Tin is produced by carbothermic reduction of the oxide ore with carbon or coke. Both reverberatory furnace and electric furnace can be used.
Mining and smelting
Industry
Candlestick made of tin
The ten largest companies produced most of the world's tin in 2007. Most of the world's tin is traded on the London Metal Exchange (LME), from 8 countries, under 17 brands.
An International Tin Council was established in 1947 to control the price of tin, until it collapsed in 1985. In 1984, an Association of Tin Producing Countries was created, with Australia, Bolivia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, and Zaire as members.
Price and exchanges
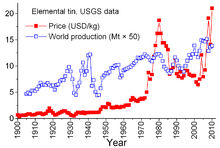
World production and price (US exchange) of tin.
Tin is unique among other mineral commodities because of the complex
agreements between producer countries and consumer countries dating back
to 1921. The earlier agreements tended to be somewhat informal and
sporadic and led to the "First International Tin Agreement" in 1956, the
first of a continuously numbered series that effectively collapsed in
1985. Through this series of agreements, the International Tin Council
(ITC) had a considerable effect on tin prices. The ITC supported the
price of tin during periods of low prices by buying tin for its buffer
stockpile and was able to restrain the price during periods of high
prices by selling tin from the stockpile. This was an anti-free-market
approach, designed to assure a sufficient flow of tin to consumer
countries and a profit for producer countries. However, the buffer
stockpile was not sufficiently large, and during most of those 29 years
tin prices rose, sometimes sharply, especially from 1973 through 1980
when rampant inflation plagued many world economies.
During the late 1970s and early 1980s, the U.S. Government tin
stockpile was in an aggressive selling mode, partly to take advantage of
the historically high tin prices. The sharp recession of 1981–82 proved
to be quite harsh on the tin industry. Tin consumption declined
dramatically. The ITC was able to avoid truly steep declines through
accelerated buying for its buffer stockpile; this activity required the
ITC to borrow extensively from banks and metal trading firms to augment
its resources. The ITC continued to borrow until late 1985 when it
reached its credit limit. Immediately, a major "tin crisis" followed —
tin was delisted from trading on the London Metal Exchange for about
three years, the ITC dissolved soon afterward, and the price of tin, now
in a free-market environment, plummeted sharply to $4 per pound and
remained at that level through the 1990s.
The price increased again by 2010 with a rebound in consumption
following the 2008–09 world economic crisis, accompanying restocking and
continued growth in consumption by the world's developing economies.
London Metal Exchange (LME) is the principal trading site for tin. Other tin contract markets are Kuala Lumpur Tin Market (KLTM) and Indonesia Tin Exchange (INATIN).
The price per kg over years:
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | 18.51 | 13.57 | 20.41 | 26.05 | 21.13 |
Applications
World consumption of refined tin by end use, 2006
In 2006, about half of all tin produced was used in solder. The rest
was divided between tin plating, tin chemicals, brass and bronze alloys,
and niche uses.
Solder
A coil of lead-free solder wire
Tin has long been used in alloys with lead as solder, in amounts 5 to 70% w/w. Tin with lead forms a eutectic mixture
at the weight proportion of 61.9% tin and 38.1% lead (the atomic
proportion: 73.9% tin and 26.1% lead), with melting temperature of
183 °C (361.4 °F) . Such solders are primarily used for joining pipes or electric circuits. Since the European Union Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE Directive) and Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive
came into effect on 1 July 2006, the lead content in such alloys has
decreased. Replacing lead has many problems, including a higher melting
point, and the formation of tin whiskers causing electrical problems. Tin pest
can occur in lead-free solders, leading to loss of the soldered joint.
Replacement alloys are rapidly being found, although problems of joint
integrity remain.
Tin plating
Tin bonds readily to iron and is used for coating lead, zinc and steel to prevent corrosion. Tin-plated steel containers are widely used for food preservation,
and this forms a large part of the market for metallic tin. A tinplate
canister for preserving food was first manufactured in London in 1812. Speakers of British English call them "tins", while speakers of American English call them "cans" or "tin cans". One derivation of such use is the slang term "tinnie" or "tinny", meaning "can of beer" in Australia. The tin whistle is so called because it was first mass-produced in tin-plated steel.
Copper cooking vessels such as saucepans and frying pans are frequently
lined with a thin plating of tin, since the combination of acid foods
with copper can be toxic.
Specialized alloys
Pewter plate
Tin in combination with other elements forms a wide variety of useful alloys. Tin is most commonly alloyed with copper. Pewter is 85–99% tin; bearing metal has a high percentage of tin as well. Bronze is mostly copper (12% tin), while addition of phosphorus gives phosphor bronze. Bell metal
is also a copper–tin alloy, containing 22% tin. Tin has sometimes been
used in coinage; for example, it once formed a single-digit percentage
(usually five percent or less) of American and Canadian
pennies. Because copper is often the major metal in such coins,
sometimes including zinc, these could be called bronze and/or brass
alloys.
Tin plated metal from a can.
Artisan Alfonso Santiago Leyva and his son working with tin sheets.
The niobium–tin compound Nb3Sn is commercially used in coils of superconducting magnets for its high critical temperature (18 K) and critical magnetic field (25 T). A superconducting magnet weighing as little as two kilograms is capable of the magnetic field of a conventional electromagnet weighing tons.
A small percentage of tin is added to zirconium alloys for the cladding of nuclear fuel.
Most metal pipes in a pipe organ
are of a tin/lead alloy, with 50/50 being the most common composition.
The proportion of tin in the pipe defines the pipe's tone, since tin has
a desirable tonal resonance. When a tin/lead alloy cools, the lead
cools slightly faster and produces a mottled or spotted effect. This
metal alloy is referred to as spotted metal. Major advantages of using
tin for pipes include its appearance, its workability, and resistance to
corrosion.
Optoelectronics
The oxides of indium and tin
are electrically conductive and transparent, and are used to make
transparent electrically conducting films with applications in Optoelectronics devices such as liquid crystal displays.
Other applications
A 21st-century reproduction barn lantern made of punched tin.
Punched tin-plated steel, also called pierced tin, is an artisan
technique originating in central Europe for creating housewares that are
both functional and decorative. Decorative piercing designs exist in a
wide variety, based on local tradition and the artisan's personal
creations. Punched tin lanterns are the most common application of this
artisan technique. The light of a candle shining through the pierced
design creates a decorative light pattern in the room where it sits.
Lanterns and other punched tin articles were created in the New World
from the earliest European settlement. A well-known example is the
Revere lantern, named after Paul Revere.
Before the modern era, in some areas of the Alps, a goat or
sheep's horn would be sharpened and a tin panel would be punched out
using the alphabet and numbers from one to nine. This learning tool was
known appropriately as "the horn". Modern reproductions are decorated
with such motifs as hearts and tulips.
In America, pie safes
and food safes were in use in the days before refrigeration. These were
wooden cupboards of various styles and sizes – either floor standing or
hanging cupboards meant to discourage vermin and insects and to keep
dust from perishable foodstuffs. These cabinets had tinplate inserts in
the doors and sometimes in the sides, punched out by the homeowner,
cabinetmaker or a tinsmith in varying designs to allow for air
circulation while excluding flies. Modern reproductions of these
articles remain popular in North America.
Window glass is most often made by floating molten glass on molten tin (float glass), resulting in a flat and flawless surface. This is also called the "Pilkington process".
Tin is also used as a negative electrode in advanced Li-ion batteries. Its application is somewhat limited by the fact that some tin surfaces catalyze decomposition of carbonate-based electrolytes used in Li-ion batteries.
Tin(II) fluoride is added to some dental care products as stannous fluoride (SnF2). Tin(II) fluoride can be mixed with calcium abrasives while the more common sodium fluoride gradually becomes biologically inactive in the presence of calcium compounds. It has also been shown to be more effective than sodium fluoride in controlling gingivitis.
Organotin compounds
Of all the chemical compounds of tin, the organotin compounds are most heavily used. Worldwide industrial production probably exceeds 50,000 tonnes.
PVC stabilizers
The major commercial application of organotin compounds is in the stabilization of PVC
plastics. In the absence of such stabilizers, PVC would otherwise
rapidly degrade under heat, light, and atmospheric oxygen, resulting in
discolored, brittle products. Tin scavenges labile chloride ions (Cl−), which would otherwise initiate loss of HCl from the plastic material. Typical tin compounds are carboxylic acid derivatives of dibutyltin dichloride, such as the dilaurate.
Biocides
Some organotin compounds are relatively toxic, with both advantages and problems. They are used for biocidal properties as fungicides, pesticides, algaecides, wood preservatives, and antifouling agents. Tributyltin oxide is used as a wood preservative. Tributyltin
was used as additive for ship paint to prevent growth of marine
organisms on ships, with use declining after organotin compounds were
recognized as persistent organic pollutants with an extremely high toxicity for some marine organisms (the dog whelk, for example). The EU banned the use of organotin compounds in 2003,
while concerns over the toxicity of these compounds to marine life and
damage to the reproduction and growth of some marine species (some reports describe biological effects to marine life at a concentration of 1 nanogram per liter) have led to a worldwide ban by the International Maritime Organization. Many nations now restrict the use of organotin compounds to vessels greater than 25 m (82 ft) long.
Organic chemistry
Some tin reagents are useful in organic chemistry. In the largest application, stannous chloride is a common reducing agent for the conversion of nitro and oxime groups to amines. The Stille reaction couples organotin compounds with organic halides or pseudohalides.
Li-ion batteries
Tin forms several inter-metallic phases with lithium metal, making it
a potentially attractive material for battery applications. Large
volumetric expansion of tin upon alloying with lithium and instability
of the tin-organic electrolyte interface at low electrochemical
potentials are the greatest challenges to employment in commercial
cells. The problem was partially solved by Sony. Tin inter-metallic
compound with cobalt and carbon has been implemented by Sony in its
Nexelion cells released in the late 2000s. The composition of the active
material is approximately Sn0.3Co0.4C0.3.
Recent research showed that only some crystalline facets of tetragonal
(beta) Sn are responsible for undesirable electrochemical activity.
Precautions
Cases of poisoning from tin metal, its oxides, and its salts are almost unknown. On the other hand, certain organotin compounds are almost as toxic as cyanide.
Exposure to tin in the workplace can occur by inhalation, skin contact, and eye contact. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (permissible exposure limit) for tin exposure in the workplace as 2 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has determined a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 2 mg/m3 over an 8-hour workday. At levels of 100 mg/m3, tin is immediately dangerous to life and health.