Herbig–Haro object HH34, imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope. It resides about 1400 light-years away, near the Orion Nebula.
Herbig–Haro (HH) objects are turbulent looking patches of nebulosity associated with newborn stars. They are formed when narrow jets of partially ionized gas
ejected by said stars collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at
speeds of several hundred kilometres per second. Herbig–Haro objects are
ubiquitous in star-forming regions, and several are often seen around a single star, aligned with its rotational axis. Most of them lie within about one parsec
of the source, although some have been observed several parsecs away.
HH objects are transient phenomena that last around a few tens of
thousand years. They can change visibly over quite short timescales of a
few years as they move rapidly away from their parent star into the gas
clouds of interstellar space (the interstellar medium or ISM). Hubble Space Telescope
observations have revealed the complex evolution of HH objects over the
period of a few years, as parts of the nebula fade while others
brighten as they collide with the clumpy material of the interstellar
medium.
First observed in the late 19th century by Sherburne Wesley Burnham, Herbig–Haro objects were not recognised as being a distinct type of emission nebula until the 1940s. The first astronomers to study them in detail were George Herbig and Guillermo Haro, after whom they have been named. Herbig and Haro were working independently on studies of star formation when they first analysed the objects, and recognised that they were a by-product of the star formation process.
Although HH objects are a visible wavelength phenomena, many
remain invisible at these wavelengths due to dust and gas envelope and
are only visible at infrared wavelengths. Such objects, when observed in
near infrared, are called MHOs.
Discovery and history of observations
HH objects HH1 and HH2 lie about a light year apart, symmetrically flanking a young star which is ejecting material along its polar axis
The first HH object was observed in the late 19th century by Sherburne Wesley Burnham, when he observed the star T Tauri with the 36-inch (910 mm) refracting telescope at Lick Observatory and noted a small patch of nebulosity nearby. However, it was catalogued merely as an emission nebula, later becoming known as Burnham's Nebula, and was not recognised as a distinct class of object. T Tauri was found to be a very young and variable star, and is the prototype of the class of similar objects known as T Tauri stars which have yet to reach a state of hydrostatic equilibrium between gravitational collapse and energy generation through nuclear fusion at their centres.
Fifty years after Burnham's discovery, several similar nebulae
were discovered which were so small as to be almost star-like in
appearance. Both Haro and Herbig made independent observations of
several of these objects in the Orion Nebula during the 1940s. Herbig also looked at Burnham's Nebula and found it displayed an unusual electromagnetic spectrum, with prominent emission lines of hydrogen, sulfur and oxygen. Haro found that all the objects of this type were invisible in infrared light.
This three-colour composite of the young object HH34 reveals the jet and the nebular emission.
Following their independent discoveries, Herbig and Haro met at an astronomy conference in Tucson, Arizona
in December 1949. Herbig had initially paid little attention to the
objects he had discovered, being primarily concerned with the nearby
stars, but on hearing Haro's findings he carried out more detailed
studies of them. The Soviet astronomer Viktor Ambartsumian
gave the objects their name (Herbig–Haro objects, normally shortened to
HH objects), and based on their occurrence near young stars (a few
hundred thousand years old), suggested they might represent an early
stage in the formation of T Tauri stars.
Studies of the HH objects showed they were highly ionized, and early theorists speculated that they were reflection nebulae
containing low-luminosity hot stars deep inside. However, the absence
of infrared radiation from the nebulae meant there could not be stars
within them, as these would have emitted abundant infrared light. In
1975 American astronomer R. D. Schwartz
theorized that winds from T Tauri stars produce shocks in ambient
medium on encounter, resulting in generation of visible light.
With discovery of collimated jet in HH 46/47, it became clear
that HH objects are indeed shock induced phenomenon with shocks being
driven by collimated jet from protostars.
Formation
Schematic diagram of how HH objects arise
Stars form by gravitational collapse of interstellar gas clouds. As the collapse increases the density, radiative energy loss decreases due to increased opacity. This raises the temperature of the cloud which prevents further collapse, and a hydrostatic equilibrium is established. Gas continues to fall towards the core in a rotating disk. This is called a protostar. Some of the accreting material is ejected out along the star's axis of rotation in two jets of partially-ionized gas (plasma).
In this image of HH24, similarities with the above schematic can be seen.
The mechanism for producing these collimated bipolar jets is not entirely understood, but it is believed that interaction between the accretion disk and the stellar magnetic field accelerates some of the accreting material from within a few astronomical units
of the star away from the disk plane. At these distances the outflow is
divergent, with fanning out at an angle in the range of 10−30°, but it
becomes increasingly collimated at distances of tens to hundreds of astronomical units from the source, as its expansion is constrained. The jets also carry away the excess angular momentum resulting from accretion of material onto the star, which would otherwise cause the star to rotate rapidly and disintegrate. When these jets collide with the interstellar medium, they give rise to the small patches of bright emission which comprise HH objects.
Properties
Electromagnetic emission from HH objects is caused when shock waves collide with the interstellar medium, creating what is called the "terminal working surfaces". Spectroscopic observations of their doppler shifts indicate velocities of several hundred kilometres per second, but the emission lines in those spectra
are weaker than what would be expected from such high speed collisions.
This suggests that some of the material they are colliding with is also
moving along the beam, although at a lower speed. Spectroscopic observations of HH objects show they are moving away from the source stars at speeds of several hundred km/s. In recent years, the high optical resolution of Hubble Space Telescope has revealed the proper motion of many HH objects in observations spaced several years apart.
As they move away from the parent star, HH objects evolve
significantly, varying in brightness on timescales of a few years.
Individual knots within an object may brighten and fade or disappear
entirely, while new knots have been seen to appear. This is because of the precession of the jets and their pulsating, rather than steady, eruption from the parent stars.
Faster jets catch up with earlier slower jets, creating the so-called
"internal working surfaces", where streams of gas collide and generate
shock waves and consequently emissions.
Hubble
Space Telescope images of HH30 over a period of five years.
Discontinuities in the jet are caused by the pulsating nature of the
eruptions. Variations in brightness can also be noted.
The total mass being ejected to form typical HH objects is estimated to be of the order of 10−8–10−6 M☉ per year, a very small amount of material compared to the mass of the stars themselves but amounts to about 1–10% of the total mass accreted in a year. Mass loss tends to decrease with increasing age of the source. The temperatures observed in HH objects are typically about 8000–12,000 K, similar to those found in other ionized nebulae such as H II regions and planetary nebulae.
Densities, on the other hand, are higher than in other nebulae, ranging
from a few thousand to a few tens of thousands of particles per cm3, compared to generally less than 1000/cm3 in H II regions and planetary nebulae.
Densities also decrease as the source evolves over time. HH objects consist mostly of hydrogen and helium, which account for about 75% and 24% of their mass respectively. Around 1% of the mass of HH objects is made up of heavier chemical elements, including oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen, iron, calcium and magnesium. Abundances of these elements, determined from emission lines of respective ions, are generally similar to their cosmic abundances. Many chemical compounds found in surrounding interstellar medium, but not present in the source material, such as metal hydrides, are believed to have been produced by shock induced chemical reactions.
Near to the source star, about 20–30% of the gas in HH objects is
ionized, but this proportion decreases at increasing distances. This
implies the material is ionized in the polar jet, and recombines as it
moves away from the star, rather than being ionized by later collisions. Shocking at the end of the jet can re-ionize some material, however, giving rise to bright "caps" at the ends of the jets.
Numbers and distribution
Episodically
ejected by young stars like cannon salvos, the brightly glowing lobes
travel through space at more than 700,000 kilometres per hour
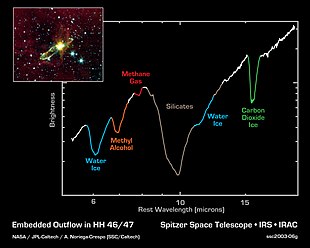
Infrared spectrum of the gaseous envelope of HH 46/47, obtained by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. The medium in immediate vicinity of the star is silicate-rich.
HH objects are named in order of their discovery; HH1 and HH2 being the earliest such objects to be identified. About 500 individual objects are now known. They are ubiquitous in star-forming H II regions, and are often found in large groups. They are typically observed near Bok globules (dark nebulae
which contain very young stars) and often emanate from them. Several HH
objects have been seen near a single energy source, forming a string of
objects along the line of the polar axis of the parent star.
The number of known HH objects has increased rapidly over the
last few years, but that is a very small proportion of the estimated up
to 150,000 in the Milky Way, the vast majority of which are too far away to be resolved. Most HH objects lie within about one parsec of their parent star. Many, however, are seen several parsecs away.
HH46/47 is located about 450 parsecs away and is powered by class I protostar binary.
Bipolar jet is slamming into the surrounding medium at a velocity of
300 km/s, producing two emission caps about 2.6 parsecs apart. Jet
outflow is accompanied by a 0.3 parsec long molecular gas outflow which
is swept up by the jet itself. Infrared studies by Spitzer Space Telescope have revealed a variety of chemical compounds in the molecular outflow, including water (ice), methanol, methane, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide (dry ice) and various silicates.
Located around 460 parsecs away in Orion nebula, HH34
is produced by a highly collimated bipolar jet powered by class I
protostar. Matter in the jet is moving at about 220 km/s. Two bright bow
shocks, separated by about 0.44 parsec, are present on the opposite
sides of the source, followed by series of fainter ones at larger
distances, making the whole complex about 3 parsecs long. Jet is
surrounded by 0.3 parsec long weak molecular outflow near the source.
Source stars
Herbig–Haro object HH32 is one of the brightest HH objects
The stars from which HH jets are emitted are all very young stars,
few tens of thousands to about a million years old. Youngest of these
are still protostars in the process of collecting from their surrounding
gases. Astronomers divide these stars into classes 0, I, II and III,
according to how much infrared radiation the stars emit.
A greater amount of infrared radiation implies a larger amount of
cooler material surrounding the star, which indicates it is still
coalescing. The numbering of the classes arises because class 0 objects
(the youngest) were not discovered until classes I, II and III had
already been defined.
Class 0 objects are only a few thousand years old, so young that
they are not yet undergoing nuclear fusion reactions at their centres.
Instead, they are powered only by the gravitational potential energy released as material falls onto them.
Nuclear fusion has begun in the cores of Class I objects, but gas and
dust are still falling onto their surfaces from the surrounding nebula,
and most of luminosity is accounted for by gravitational energy. They
are generally still shrouded in dense clouds of dust and gas, which
obscure all their visible light and as a result can only be observed at infrared and radio
wavelengths. The in-fall of gas and dust has largely finished in Class
II objects (Classical T Tauri stars), but they are still surrounded by
disks of dust and gas, while class III objects (Weak-line T Tauri stars)
have only trace remnants of their original accretion disk.
About 80% of the stars giving rise to HH objects are in fact binary
or multiple systems (two or more stars orbiting each other), which is a
much higher proportion than that found for low mass stars on the main sequence.
This may indicate that binary systems are more likely to generate the
jets which give rise to HH objects, and evidence suggests the largest HH
outflows might be formed when multiple star systems disintegrate.
It is thought that most stars originate from multiple star systems, but
that a sizable fraction are disrupted before they reach the main
sequence by gravitational interactions with nearby stars and dense clouds of gas.
Infrared counterparts
Infrared image of molecular bow shocks (MHO 27) associated with bipolar outflows in Orion. Credit: UKIRT/Joint Astronomy Centre
HH objects associated with very young stars or very massive
protostars are often hidden from view at optical wavelengths by the
cloud of gas and dust from which they form. The intervening material can
diminish the visual magnitude by factors of tens or even hundreds at
optical wavelengths. Such deeply embedded objects can only be observed
at infrared or radio wavelengths, usually in the frequencies of hot molecular hydrogen or warm carbon monoxide emission.
In recent years, infrared images have revealed dozens of examples
of "infrared HH objects". Most look like bow waves (similar to the
waves at the head of a ship), and so are usually referred to as
molecular "bow shocks". The physics of infrared bow shocks can be
understood in much the same way as that of HH objects, since these
objects are essentially the same – supersonic shocks driven by
collimated jets from the opposite poles of a protostar.
It is only the conditions in the jet and surrounding cloud that are
different, causing infrared emission from molecules rather than optical
emission from atoms and ions.
In 2009 the acronym "MHO", for Molecular Hydrogen emission-line
Object, was approved for such objects, detected in near infrared, by the
International Astronomical Union
Working Group on Designations, and has been entered into their on-line
Reference Dictionary of Nomenclature of Celestial Objects. The MHO catalogue (see external links below) contains over 2000 objects.