| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iridium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ɪˈrɪdiəm/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery white | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar, std(Ir) | 192.217(2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iridium in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 77 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | d-block | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | transition metal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d7 6s2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell
| 2, 8, 18, 32, 15, 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 2719 K (2446 °C, 4435 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 4403 K (4130 °C, 7466 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 22.56 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at m.p.) | 19 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 41.12 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 564 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.10 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | −3, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, +7, +8, +9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | empirical: 136 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 141±6 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of iridium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | 4825 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal expansion | 6.4 µm/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 147 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | 47.1 nΩ·m (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | paramagnetic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | +25.6·10−6 cm3/mol (298 K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Young's modulus | 528 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shear modulus | 210 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 320 GPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poisson ratio | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mohs hardness | 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vickers hardness | 1760–2200 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brinell hardness | 1670 MPa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7439-88-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery and first isolation | Smithson Tennant (1803) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of iridium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Iridium is a chemical element with symbol Ir and atomic number 77. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum group, iridium is the second-densest metal (after osmium) with a density of 22.56 g/cm3 as defined by experimental X-ray crystallography. At room temperature and standard atmospheric pressure, iridium has a density of 22.65 g/cm3, 0.04 g/cm3 higher than osmium measured the same way. It is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C. Although only certain molten salts and halogens are corrosive to solid iridium, finely divided iridium dust is much more reactive and can be flammable.
Iridium was discovered in 1803 among insoluble impurities in natural platinum. Smithson Tennant, the primary discoverer, named iridium for the Greek goddess Iris, personification of the rainbow, because of the striking and diverse colors of its salts. Iridium is one of the rarest elements in Earth's crust, with annual production and consumption of only three tonnes. 191Ir and 193Ir are the only two naturally occurring isotopes of iridium, as well as the only stable isotopes; the latter is the more abundant.
The most important iridium compounds in use are the salts and acids it forms with chlorine, though iridium also forms a number of organometallic compounds used in industrial catalysis, and in research. Iridium metal is employed when high corrosion resistance at high temperatures is needed, as in high-performance spark plugs, crucibles for recrystallization of semiconductors at high temperatures, and electrodes for the production of chlorine in the chloralkali process. Iridium radioisotopes are used in some radioisotope thermoelectric generators.
Iridium is found in meteorites in much higher abundance than in the Earth's crust. For this reason, the unusually high abundance of iridium in the clay layer at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary gave rise to the Alvarez hypothesis that the impact of a massive extraterrestrial object caused the extinction of dinosaurs and many other species 66 million years ago. Similarly, an iridium anomaly in core samples from the Pacific Ocean suggested the Eltanin impact of about 2.5 million years ago.
It is thought that the total amount of iridium in the planet Earth is much higher than that observed in crustal rocks, but as with other platinum-group metals, the high density and tendency of iridium to bond with iron caused most iridium to descend below the crust when the planet was young and still molten.
Characteristics
Physical properties
One troy ounce (31.1035 g) of arc-melted iridium
A member of the platinum group metals, iridium is white, resembling platinum, but with a slight yellowish cast. Because of its hardness, brittleness, and very high melting point, solid iridium is difficult to machine, form, or work; thus powder metallurgy is commonly employed instead. It is the only metal to maintain good mechanical properties in air at temperatures above 1,600 °C (2,910 °F). It has the 10th highest boiling point among all elements and becomes a superconductor at temperatures below 0.14 K.
Iridium's modulus of elasticity is the second-highest among the metals, only being surpassed by osmium. This, together with a high shear modulus and a very low figure for Poisson's ratio (the relationship of longitudinal to lateral strain), indicate the high degree of stiffness
and resistance to deformation that have rendered its fabrication into
useful components a matter of great difficulty. Despite these
limitations and iridium's high cost, a number of applications have
developed where mechanical strength is an essential factor in some of
the extremely severe conditions encountered in modern technology.
The measured density of iridium is only slightly lower (by about 0.12%) than that of osmium, the densest metal known.
Some ambiguity occurred regarding which of the two elements was denser,
due to the small size of the difference in density and difficulties in
measuring it accurately, but, with increased accuracy in factors used for calculating density X-ray crystallographic data yielded densities of 22.56 g/cm3 for iridium and 22.59 g/cm3 for osmium.
Chemical properties
Iridium is the most corrosion-resistant metal known: it is not attacked by almost any acid, aqua regia, molten metals, or silicates at high temperatures. It can, however, be attacked by some molten salts, such as sodium cyanide and potassium cyanide, as well as oxygen and the halogens (particularly fluorine) at higher temperatures. Iridium also reacts directly with sulfur at atmospheric pressure to yield iridium disulfide.
Compounds
Iridium forms compounds in oxidation states between −3 and +9; the most common oxidation states are +3 and +4. Well-characterized examples of the high +6 oxidation state are rare, but include IrF
6 and two mixed oxides Sr
2MgIrO
6 and Sr
2CaIrO
6. In addition, it was reported in 2009 that iridium(VIII) oxide (IrO
4) was prepared under matrix isolation conditions (6 K in Ar) by UV irradiation of an iridium-peroxo complex. This species, however, is not expected to be stable as a bulk solid at higher temperatures. The highest oxidation state (+9), which is also the highest recorded for any element, is only known in one cation, IrO+
4; it is only known as gas-phase species and is not known to form any salts.
6 and two mixed oxides Sr
2MgIrO
6 and Sr
2CaIrO
6. In addition, it was reported in 2009 that iridium(VIII) oxide (IrO
4) was prepared under matrix isolation conditions (6 K in Ar) by UV irradiation of an iridium-peroxo complex. This species, however, is not expected to be stable as a bulk solid at higher temperatures. The highest oxidation state (+9), which is also the highest recorded for any element, is only known in one cation, IrO+
4; it is only known as gas-phase species and is not known to form any salts.
Iridium dioxide, IrO
2, a blue black solid, is the only well-characterized oxide of iridium. A sesquioxide, Ir
2O
3, has been described as a blue-black powder which is oxidized to IrO
2 by HNO
3. The corresponding disulfides, diselenides, sesquisulfides, and sesquiselenides are known, and IrS
3 has also been reported. Iridium also forms iridates with oxidation states +4 and +5, such as K
2IrO
3 and KIrO
3, which can be prepared from the reaction of potassium oxide or potassium superoxide with iridium at high temperatures.
2, a blue black solid, is the only well-characterized oxide of iridium. A sesquioxide, Ir
2O
3, has been described as a blue-black powder which is oxidized to IrO
2 by HNO
3. The corresponding disulfides, diselenides, sesquisulfides, and sesquiselenides are known, and IrS
3 has also been reported. Iridium also forms iridates with oxidation states +4 and +5, such as K
2IrO
3 and KIrO
3, which can be prepared from the reaction of potassium oxide or potassium superoxide with iridium at high temperatures.
Although no binary hydrides of iridium, Ir
xH
y are known, complexes are known that contain IrH4−
5 and IrH3−
6, where iridium has the +1 and +3 oxidation states, respectively. The ternary hydride Mg
6Ir
2H
11 is believed to contain both the IrH4−
5 and the 18-electron IrH5−
4 anion.
xH
y are known, complexes are known that contain IrH4−
5 and IrH3−
6, where iridium has the +1 and +3 oxidation states, respectively. The ternary hydride Mg
6Ir
2H
11 is believed to contain both the IrH4−
5 and the 18-electron IrH5−
4 anion.
No monohalides or dihalides are known, whereas trihalides, IrX
3, are known for all of the halogens. For oxidation states +4 and above, only the tetrafluoride, pentafluoride and hexafluoride are known. Iridium hexafluoride, IrF
6, is a volatile and highly reactive yellow solid, composed of octahedral molecules. It decomposes in water and is reduced to IrF
4, a crystalline solid, by iridium black. Iridium pentafluoride has similar properties but it is actually a tetramer, Ir
4F
20, formed by four corner-sharing octahedra. Iridium metal dissolves in molten alkali-metal cyanides to produce the Ir(CN)3+
6 (hexacyanoiridate) ion.
3, are known for all of the halogens. For oxidation states +4 and above, only the tetrafluoride, pentafluoride and hexafluoride are known. Iridium hexafluoride, IrF
6, is a volatile and highly reactive yellow solid, composed of octahedral molecules. It decomposes in water and is reduced to IrF
4, a crystalline solid, by iridium black. Iridium pentafluoride has similar properties but it is actually a tetramer, Ir
4F
20, formed by four corner-sharing octahedra. Iridium metal dissolves in molten alkali-metal cyanides to produce the Ir(CN)3+
6 (hexacyanoiridate) ion.
Hexachloroiridic(IV) acid, H
2IrCl
6, and its ammonium salt are the most important iridium compounds from an industrial perspective. They are involved in the purification of iridium and used as precursors for most other iridium compounds, as well as in the preparation of anode coatings. The IrCl2−
6 ion has an intense dark brown color, and can be readily reduced to the lighter-colored IrCl3−
6 and vice versa. Iridium trichloride, IrCl
3, which can be obtained in anhydrous form from direct oxidation of iridium powder by chlorine at 650 °C, or in hydrated form by dissolving Ir
2O
3 in hydrochloric acid, is often used as a starting material for the synthesis of other Ir(III) compounds. Another compound used as a starting material is ammonium hexachloroiridate(III), (NH
4)
3IrCl
6. Iridium(III) complexes are diamagnetic (low-spin) and generally have an octahedral molecular geometry.
2IrCl
6, and its ammonium salt are the most important iridium compounds from an industrial perspective. They are involved in the purification of iridium and used as precursors for most other iridium compounds, as well as in the preparation of anode coatings. The IrCl2−
6 ion has an intense dark brown color, and can be readily reduced to the lighter-colored IrCl3−
6 and vice versa. Iridium trichloride, IrCl
3, which can be obtained in anhydrous form from direct oxidation of iridium powder by chlorine at 650 °C, or in hydrated form by dissolving Ir
2O
3 in hydrochloric acid, is often used as a starting material for the synthesis of other Ir(III) compounds. Another compound used as a starting material is ammonium hexachloroiridate(III), (NH
4)
3IrCl
6. Iridium(III) complexes are diamagnetic (low-spin) and generally have an octahedral molecular geometry.
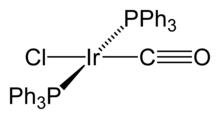
Organoiridium compounds contain iridium–carbon bonds where the metal is usually in lower oxidation states. For example, oxidation state zero is found in tetrairidium dodecacarbonyl, Ir
4(CO)
12, which is the most common and stable binary carbonyl of iridium. In this compound, each of the iridium atoms is bonded to the other three, forming a tetrahedral cluster. Some organometallic Ir(I) compounds are notable enough to be named after their discoverers. One is Vaska's complex, IrCl(CO)[P(C
6H
5)
3]
2, which has the unusual property of binding to the dioxygen molecule, O
2. Another one is Crabtree's catalyst, a homogeneous catalyst for hydrogenation reactions. These compounds are both square planar, d8 complexes, with a total of 16 valence electrons, which accounts for their reactivity.
4(CO)
12, which is the most common and stable binary carbonyl of iridium. In this compound, each of the iridium atoms is bonded to the other three, forming a tetrahedral cluster. Some organometallic Ir(I) compounds are notable enough to be named after their discoverers. One is Vaska's complex, IrCl(CO)[P(C
6H
5)
3]
2, which has the unusual property of binding to the dioxygen molecule, O
2. Another one is Crabtree's catalyst, a homogeneous catalyst for hydrogenation reactions. These compounds are both square planar, d8 complexes, with a total of 16 valence electrons, which accounts for their reactivity.
An iridium-based organic LED material has been documented, and found to be much brighter than DPA or PPV, so could be the basis for flexible OLED lighting in the future.
Isotopes
Iridium has two naturally occurring, stable isotopes, 191Ir and 193Ir, with natural abundances of 37.3% and 62.7%, respectively. At least 37 radioisotopes have also been synthesized, ranging in mass number from 164 to 202. 192Ir, which falls between the two stable isotopes, is the most stable radioisotope, with a half-life of 73.827 days, and finds application in brachytherapy and in industrial radiography,
particularly for nondestructive testing of welds in steel in the oil
and gas industries; iridium-192 sources have been involved in a number
of radiological accidents. Three other isotopes have half-lives of at
least a day—188Ir, 189Ir, and 190Ir. Isotopes with masses below 191 decay by some combination of β+ decay, α decay, and (rare) proton emission, with the exceptions of 189Ir, which decays by electron capture. Synthetic isotopes heavier than 191 decay by β− decay, although 192Ir also has a minor electron capture decay path. All known isotopes of iridium were discovered between 1934 and 2008, with the most recent discoveries being 200-202Ir.
At least 32 metastable isomers have been characterized, ranging in mass number from 164 to 197. The most stable of these is 192m2Ir, which decays by isomeric transition with a half-life of 241 years, making it more stable than any of iridium's synthetic isotopes in their ground states. The least stable isomer is 190m3Ir with a half-life of only 2 µs. The isotope 191Ir was the first one of any element to be shown to present a Mössbauer effect. This renders it useful for Mössbauer spectroscopy for research in physics, chemistry, biochemistry, metallurgy, and mineralogy.
History
Platinum group
The Greek goddess Iris, after whom iridium was named.
The discovery of iridium is intertwined with that of platinum and the other metals of the platinum group. Native platinum used by ancient Ethiopians and by South American cultures always contained a small amount of the other platinum group metals, including iridium. Platinum reached Europe as platina ("silverette"), found in the 17th century by the Spanish conquerors in a region today known as the department of Chocó in Colombia. The discovery that this metal was not an alloy of known elements, but instead a distinct new element, did not occur until 1748.
Discovery
Chemists who studied platinum dissolved it in aqua regia (a mixture of hydrochloric and nitric acids) to create soluble salts. They always observed a small amount of a dark, insoluble residue. Joseph Louis Proust thought that the residue was graphite. The French chemists Victor Collet-Descotils, Antoine François, comte de Fourcroy, and Louis Nicolas Vauquelin also observed the black residue in 1803, but did not obtain enough for further experiments.
In 1803, British scientist Smithson Tennant
(1761–1815) analyzed the insoluble residue and concluded that it must
contain a new metal. Vauquelin treated the powder alternately with
alkali and acids and obtained a volatile new oxide, which he believed to be of this new metal—which he named ptene, from the Greek word πτηνός ptēnós, "winged".
Tennant, who had the advantage of a much greater amount of residue,
continued his research and identified the two previously undiscovered
elements in the black residue, iridium and osmium. He obtained dark red crystals (probably of Na
2[IrCl
6]·nH
2O) by a sequence of reactions with sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. He named iridium after Iris (Ἶρις), the Greek winged goddess of the rainbow and the messenger of the Olympian gods, because many of the salts he obtained were strongly colored. Discovery of the new elements was documented in a letter to the Royal Society on June 21, 1804.
2[IrCl
6]·nH
2O) by a sequence of reactions with sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. He named iridium after Iris (Ἶρις), the Greek winged goddess of the rainbow and the messenger of the Olympian gods, because many of the salts he obtained were strongly colored. Discovery of the new elements was documented in a letter to the Royal Society on June 21, 1804.
Metalworking and applications
British scientist John George Children
was the first to melt a sample of iridium in 1813 with the aid of "the
greatest galvanic battery that has ever been constructed" (at that
time). The first to obtain high-purity iridium was Robert Hare in 1842. He found it had a density of around 21.8 g/cm3 and noted the metal is nearly immalleable and very hard. The first melting in appreciable quantity was done by Henri Sainte-Claire Deville and Jules Henri Debray in 1860. They required burning more than 300 liters of pure O
2 and H
2 gas for each kilogram of iridium.
2 and H
2 gas for each kilogram of iridium.
These extreme difficulties in melting the metal limited the possibilities for handling iridium. John Isaac Hawkins
was looking to obtain a fine and hard point for fountain pen nibs, and
in 1834 managed to create an iridium-pointed gold pen. In 1880, John Holland and William Lofland Dudley were able to melt iridium by adding phosphorus and patented the process in the United States; British company Johnson Matthey later stated they had been using a similar process since 1837 and had already presented fused iridium at a number of World Fairs. The first use of an alloy of iridium with ruthenium in thermocouples was made by Otto Feussner in 1933. These allowed for the measurement of high temperatures in air up to 2000 °C.
In Munich, Germany in 1957 Rudolf Mössbauer, in what has been called one of the "landmark experiments in twentieth-century physics", discovered the resonant and recoil-free emission and absorption of gamma rays by atoms in a solid metal sample containing only 191Ir. This phenomenon, known as the Mössbauer effect (which has since been observed for other nuclei, such as 57Fe), and developed as Mössbauer spectroscopy, has made important contributions to research in physics, chemistry, biochemistry, metallurgy, and mineralogy. Mössbauer received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1961, at the age 32, just three years after he published his discovery. In 1986 Rudolf Mössbauer was honored for his achievements with the Albert Einstein Medal and the Elliot Cresson Medal.
Occurrence
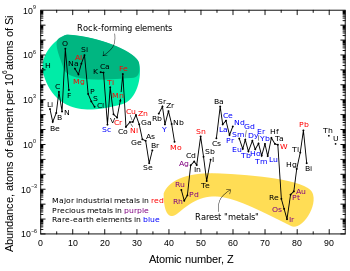
Iridium is one of the least abundant elements in Earth's crust.
The Willamette Meteorite, the sixth-largest meteorite found in the world, has 4.7 ppm iridium.
Iridium is one of the nine least abundant stable elements in Earth's crust, having an average mass fraction of 0.001 ppm in crustal rock; platinum is 10 times more abundant, gold is 40 times more abundant, and silver and mercury are 80 times more abundant. Tellurium is about as abundant as iridium. In contrast to its low abundance in crustal rock, iridium is relatively common in meteorites, with concentrations of 0.5 ppm or more.
The overall concentration of iridium on Earth is thought to be much
higher than what is observed in crustal rocks, but because of the
density and siderophilic ("iron-loving") character of iridium, it descended below the crust and into Earth's core when the planet was still molten.
Iridium is found in nature as an uncombined element or in natural alloys; especially the iridium–osmium alloys, osmiridium (osmium-rich), and iridosmium (iridium-rich). In the nickel and copper deposits, the platinum group metals occur as sulfides (i.e. (Pt,Pd)S), tellurides (i.e. PtBiTe), antimonides (PdSb), and arsenides (i.e. PtAs
2). In all of these compounds, platinum is exchanged by a small amount of iridium and osmium. As with all of the platinum group metals, iridium can be found naturally in alloys with raw nickel or raw copper. A number of iridium-dominant minerals, with iridium as the species-forming element, are known. They are exceedingly rare and often represent the iridium analogues of the above-given ones. The examples are irarsite and cuproiridsite, to mention some.
2). In all of these compounds, platinum is exchanged by a small amount of iridium and osmium. As with all of the platinum group metals, iridium can be found naturally in alloys with raw nickel or raw copper. A number of iridium-dominant minerals, with iridium as the species-forming element, are known. They are exceedingly rare and often represent the iridium analogues of the above-given ones. The examples are irarsite and cuproiridsite, to mention some.
Within Earth's crust, iridium is found at highest concentrations
in three types of geologic structure: igneous deposits (crustal
intrusions from below), impact craters, and deposits reworked from one
of the former structures. The largest known primary reserves are in the Bushveld igneous complex in South Africa, (near the largest known impact crater, the Vredefort crater) though the large copper–nickel deposits near Norilsk in Russia, and the Sudbury Basin (also an impact crater) in Canada are also significant sources of iridium. Smaller reserves are found in the United States. Iridium is also found in secondary deposits, combined with platinum and other platinum group metals in alluvial deposits. The alluvial deposits used by pre-Columbian people in the Chocó Department of Colombia are still a source for platinum-group metals. As of 2003, world reserves have not been estimated.
Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary presence
The red arrow points to the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary.
The [Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary] of 66 million years ago, marking the temporal border between the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods of geological time, was identified by a thin stratum of iridium-rich clay. A team led by Luis Alvarez proposed in 1980 an extraterrestrial origin for this iridium, attributing it to an asteroid or comet impact. Their theory, known as the Alvarez hypothesis, is now widely accepted to explain the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs.
A large buried impact crater structure with an estimated age of about
66 million years was later identified under what is now the Yucatán Peninsula (the Chicxulub crater). Dewey M. McLean and others argue that the iridium may have been of volcanic origin instead, because Earth's core is rich in iridium, and active volcanoes such as Piton de la Fournaise, in the island of Réunion, are still releasing iridium.
Production
Iridium is also obtained commercially as a by-product from nickel and copper mining and processing. During electrorefining of copper and nickel, noble metals such as silver, gold and the platinum group metals as well as selenium and tellurium settle to the bottom of the cell as anode mud, which forms the starting point for their extraction.
To separate the metals, they must first be brought into solution.
Several separation methods are available depending on the nature of the
mixture; two representative methods are fusion with sodium peroxide followed by dissolution in aqua regia, and dissolution in a mixture of chlorine with hydrochloric acid.
After the mixture is dissolved, iridium is separated from the other platinum group metals by precipitating ammonium hexachloroiridate ((NH
4)
2IrCl
6) or by extracting IrCl2−
6 with organic amines. The first method is similar to the procedure Tennant and Wollaston used for their separation. The second method can be planned as continuous liquid–liquid extraction and is therefore more suitable for industrial scale production. In either case, the product is reduced using hydrogen, yielding the metal as a powder or sponge that can be treated using powder metallurgy techniques.
4)
2IrCl
6) or by extracting IrCl2−
6 with organic amines. The first method is similar to the procedure Tennant and Wollaston used for their separation. The second method can be planned as continuous liquid–liquid extraction and is therefore more suitable for industrial scale production. In either case, the product is reduced using hydrogen, yielding the metal as a powder or sponge that can be treated using powder metallurgy techniques.
Iridium prices have fluctuated over a considerable range. With a
relatively small volume in the world market (compared to other
industrial metals like aluminium or copper), the iridium price reacts strongly to instabilities in production, demand, speculation,
hoarding, and politics in the producing countries.
As a substance with rare properties, its price has been particularly
influenced by changes in modern technology:
The gradual decrease between 2001 and 2003 has been related to an
oversupply of Ir crucibles used for industrial growth of large single
crystals.
Likewise the prices above 1000 USD/oz between 2010 and 2014 have been
explained with the installation of production facilities for single
crystal sapphire used in LED backlights for TVs.
Applications
The
demand for iridium surged from 2.5 tonnes in 2009 to 10.4 tonnes in
2010, mostly because of electronics-related applications that saw a rise
from 0.2 to 6 tonnes – iridium crucibles
are commonly used for growing large high-quality single crystals,
demand for which has increased sharply. This increase in iridium
consumption is predicted to saturate due to accumulating stocks of
crucibles, as happened earlier in the 2000s. Other major applications
include spark plugs that consumed 0.78 tonnes of iridium in 2007,
electrodes for the chloralkali process (1.1 t in 2007) and chemical catalysts (0.75 t in 2007).
Industrial and medical
Molecular structure of Ir(mppy)
3
3
The high melting point, hardness and corrosion resistance of iridium
and its alloys determine most of its applications. Iridium (or sometimes
platinum alloys or osmium) and mostly iridium alloys have a low wear
and are used, for example, for multi-pored spinnerets, through which a plastic polymer melt is extruded to form fibers, such as rayon. Osmium–iridium is used for compass bearings and for balances.
Their resistance to arc erosion makes iridium alloys ideal for electrical contacts for spark plugs, and iridium-based spark plugs are particularly used in aviation.
Pure iridium is extremely brittle, to the point of being hard to
weld because the heat-affected zone cracks, but it can be made more
ductile by addition of small quantities of titanium and zirconium (0.2% of each apparently works well).
Corrosion and heat resistance makes iridium an important alloying
agent. Certain long-life aircraft engine parts are made of an iridium
alloy, and an iridium–titanium alloy is used for deep-water pipes because of its corrosion resistance. Iridium is also used as a hardening agent in platinum alloys. The Vickers hardness of pure platinum is 56 HV, whereas platinum with 50% of iridium can reach over 500 HV.
Devices that must withstand extremely high temperatures are often made from iridium. For example, high-temperature crucibles made of iridium are used in the Czochralski process to produce oxide single-crystals (such as sapphires) for use in computer memory devices and in solid state lasers. The crystals, such as gadolinium gallium garnet
and yttrium gallium garnet, are grown by melting pre-sintered charges
of mixed oxides under oxidizing conditions at temperatures up to
2100 °C.
Iridium compounds are used as catalysts in the Cativa process for carbonylation of methanol to produce acetic acid.
The radioisotope iridium-192 is one of the two most important sources of energy for use in industrial γ-radiography for non-destructive testing of metals. Additionally, 192Ir is used as a source of gamma radiation for the treatment of cancer using brachytherapy,
a form of radiotherapy where a sealed radioactive source is placed
inside or next to the area requiring treatment. Specific treatments
include high-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy, bilary duct
brachytherapy, and intracavitary cervix brachytherapy.
In February 2019, medical scientists announced that iridium attached to albumin, creating a photosensitized molecule, can penetrate cancer cells and, after being irradiated with light (a process called photodynamic therapy), destroy the cancer cells.
Iridium is a good catalyst for the decomposition of hydrazine (into hot nitrogen and ammonia), and this is used in practice in low-thrust rocket engines; there are more details in the monopropellant rocket article.
Scientific
An alloy of 90% platinum and 10% iridium was used in 1889 to construct the International Prototype Metre and kilogram mass, kept by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures near Paris. The meter bar was replaced as the definition of the fundamental unit of length in 1960 by a line in the atomic spectrum of krypton, but the kilogram prototype is still the international standard of mass (until 20 May 2019).
Iridium has been used in the radioisotope thermoelectric generators of unmanned spacecraft such as the Voyager, Viking, Pioneer, Cassini, Galileo, and New Horizons. Iridium was chosen to encapsulate the plutonium-238 fuel in the generator because it can withstand the operating temperatures of up to 2000 °C and for its great strength.
Another use concerns X-ray optics, especially X-ray telescopes. The mirrors of the Chandra X-ray Observatory are coated with a layer of iridium 60 nm
thick. Iridium proved to be the best choice for reflecting X-rays after
nickel, gold, and platinum were also tested. The iridium layer, which
had to be smooth to within a few atoms, was applied by depositing
iridium vapor under high vacuum on a base layer of chromium.
Iridium is used in particle physics for the production of antiprotons, a form of antimatter. Antiprotons are made by shooting a high-intensity proton beam at a conversion target, which needs to be made from a very high density material. Although tungsten may be used instead, iridium has the advantage of better stability under the shock waves induced by the temperature rise due to the incident beam.
Oxidative addition to hydrocarbons in organoiridium chemistry
Carbon–hydrogen bond activation (C–H activation) is an area of research on reactions that cleave carbon–hydrogen bonds, which were traditionally regarded as unreactive. The first reported successes at activating C–H bonds in saturated hydrocarbons, published in 1982, used organometallic iridium complexes that undergo an oxidative addition with the hydrocarbon.
Iridium complexes are being investigated as catalysts for asymmetric hydrogenation. These catalysts have been used in the synthesis of natural products
and able to hydrogenate certain difficult substrates, such as
unfunctionalized alkenes, enantioselectively (generating only one of the
two possible enantiomers).
Iridium forms a variety of complexes of fundamental interest in triplet harvesting.
Historical
Fountain pen nib labeled Iridium Point
Iridium–osmium alloys were used in fountain pen nib tips. The first major use of iridium was in 1834 in nibs mounted on gold. Since 1944, the famous Parker 51
fountain pen was fitted with a nib tipped by a ruthenium and iridium
alloy (with 3.8% iridium). The tip material in modern fountain pens is
still conventionally called "iridium", although there is seldom any
iridium in it; other metals such as ruthenium, osmium and tungsten have
taken its place.
An iridium–platinum alloy was used for the touch holes or vent pieces of cannon. According to a report of the Paris Exhibition of 1867, one of the pieces being exhibited by Johnson and Matthey
"has been used in a Withworth gun for more than 3000 rounds, and
scarcely shows signs of wear yet. Those who know the constant trouble
and expense which are occasioned by the wearing of the vent-pieces of
cannon when in active service, will appreciate this important
adaptation".
The pigment iridium black, which consists of very finely divided iridium, is used for painting porcelain an intense black; it was said that "all other porcelain black colors appear grey by the side of it".
Precautions
Iridium
in bulk metallic form is not biologically important or hazardous to
health due to its lack of reactivity with tissues; there are only about
20 parts per trillion of iridium in human tissue. Like most metals, finely divided iridium powder can be hazardous to handle, as it is an irritant and may ignite in air.
Very little is known about the toxicity of iridium compounds, because
they are used in very small amounts, but soluble salts, such as the
iridium halides, could be hazardous due to elements other than iridium
or due to iridium itself. However, most iridium compounds are insoluble, which makes absorption into the body difficult.
A radioisotope of iridium, 192Ir,
is dangerous, like other radioactive isotopes. The only reported
injuries related to iridium concern accidental exposure to radiation
from 192Ir used in brachytherapy. High-energy gamma radiation from 192Ir can increase the risk of cancer. External exposure can cause burns, radiation poisoning, and death. Ingestion of 192Ir can burn the linings of the stomach and the intestines. 192Ir, 192mIr, and 194mIr tend to deposit in the liver, and can pose health hazards from both gamma and beta radiation.