Regions with Mediterranean climates
Hot-summer mediterranean climate (Csa)
Warm-summer mediterranean climate (Csb)
Cold-summer mediterranean climate (Csc)
The coastal Mediterranean region of Costa Brava, Spain
A Mediterranean climate /ˌmɛdɪtəˈreɪniən/ or dry summer climate
is characterized by rainy winters and dry summers, with less than 40 mm
of precipitation for at least three summer months. While the climate
receives its name from the Mediterranean Basin,
these are generally located on the western coasts of continents,
between roughly 30 and 45 degrees north and south of the equator,
typically between oceanic climates towards the poles (where they tend to be wetter and cooler), and semi-arid and arid climates towards the equator (where they tend to be drier and hotter).
In essence, and due to the seasonal shift of the subtropical high-pressure belts
with the apparent movement of the Sun, a Mediterranean climate is an
intermediate type between these other climates, with winters warmer and
drier (and sunnier) than oceanic climates and summers imitating sunny
weather in semi-arid and arid climates.
The resulting vegetation of Mediterranean climates are the garrigue or maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, the chaparral in California, the fynbos in South Africa, the mallee in Australia, and the matorral
in Chile. Areas with this climate are where the so-called
"Mediterranean trinity" of agricultural products have traditionally
developed: wheat, vine and olive.
Most large, historic cities of the Mediterranean basin also lie within Mediterranean climatic zones, including Algiers, Athens, Beirut, İzmir, Jerusalem, Marseille, Naples, Rome, Tunis, and Valencia.
Examples of major cities with Mediterranean climates that lie outside
of the historic Mediterranean basin include major examples as Adelaide, Cape Town, Casablanca, Dushanbe, Los Angeles, Lisbon, Perth, San Francisco, Santiago and Victoria.
Köppen climate classification
Under the Köppen climate classification, "hot dry-summer" climates (classified as Csa) and "cool dry-summer" climates (classified as Csb)
are often referred to as "Mediterranean". Under the Köppen climate
system, the first letter indicates the climate group (in this case
temperate climates). Temperate climates or "C" zones have an
average temperature above 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C (27 °F)), but below
18 °C (64 °F), in their coolest months. The second letter indicates the
precipitation pattern ("s" represents dry summers). Köppen has
defined a dry summer month as a month with less than 30 mm (1.2 in) of
precipitation and with less than one-third that of the wettest winter
month. Some, however, use a 40 mm (1.6 in) level. The third letter indicates the degree of summer heat: "a" represents an average temperature in the warmest month above 22 °C (72 °F), while "b" indicates the average temperature in the warmest month below 22 °C (72 °F).
Under the Köppen classification, dry-summer climates (Csa, Csb) usually occur on the western sides of continents. Csb zones in the Köppen system include areas normally not associated with Mediterranean climates but with Oceanic climates, such as much of the Pacific Northwest, much of southern Chile, parts of west-central Argentina, and parts of New Zealand. Additional highland areas in the subtropics also meet Cs requirements, though they, too, are not normally associated with Mediterranean climates, as do a number of oceanic islands such as Madeira, the Juan Fernández Islands, the western part of the Canary Islands, and the eastern part of the Azores.
Under Trewartha's modified Köppen climate classification, the two major requirements for a Cs
climate are revised. Under Trewartha's system, at least eight months
must have average temperatures of 10 °C (50 °F) or higher (subtropical), and the average annual precipitation must not exceed 900 mm (35 in). Thus, under this system, many Csb zones in the Köppen system become Do (temperate oceanic), and the rare Csc zones become Eo
(subpolar oceanic), with only the classic dry-summer to warm winter,
low annual rainfall locations included in the Mediterranean type
climate.
Precipitation
During summer, regions of Mediterranean climate are strongly
influenced by cold ocean currents which keep the weather in the region
very dry, stable, and pleasant. Similar to desert climates, in many Mediterranean climates there is a strong diurnal
character to daily temperatures in the warm summer months due to strong
heating during the day from sunlight and rapid cooling at night.
In winter, Mediterranean climate zones are no longer influenced
by the cold ocean currents and therefore warmer water settles near land
and causes clouds to form and rainfall becomes much more likely. As a
result, areas with this climate receive almost all of their
precipitation during their winter and spring seasons, and may go
anywhere from 3 to 6 months during the summer without having any
significant precipitation. In the lower latitudes, precipitation usually decreases in both the winter and summer because they are closer to the Horse latitudes,
thus bringing smaller amounts of rain. Toward the polar latitudes,
total moisture usually increases; the Mediterranean climate in Southern
Europe has more rain. The rainfall also tends to be more evenly
distributed throughout the year in Southern Europe, while in the Eastern
Mediterranean (the Levant) and in Southern California the summer is nearly or completely dry. In places where evapotranspiration is higher, steppe climates tend to prevail, but still follow the weather pattern of the Mediterranean climate.
Temperature
The
majority of the regions with Mediterranean climates have relatively
mild winters and very warm summers. However winter and summer
temperatures can vary greatly between different regions with a
Mediterranean climate. For instance, in the case of winters, Valencia and Los Angeles experience mild temperatures in the winter, with frost and snowfall almost unknown, whereas Tashkent has colder winters with annual frosts and snowfall. Or to consider summer, Athens experiences rather high temperatures in that season (48 °C (118 °F) has been measured in nearby Eleusis). In contrast, San Francisco has cool summers with daily highs around 21 °C (70 °F) due to the continuous upwelling of cold subsurface waters along the coast.
Because most regions with a Mediterranean climate are near large bodies of water, temperatures
are generally moderate with a comparatively small range of temperatures
between the winter low and summer high (although the daily range of
temperature during the summer is large due to dry and clear conditions,
except along the immediate coasts). Temperatures during winter only
occasionally fall below the freezing point and snow
is generally seldom seen. In the summer, the temperatures range from
mild to very hot, depending on distance from a large body of water,
elevation, and latitude. Even in the warmest locations with a
Mediterranean-type climate, however, temperatures usually do not reach
the highest readings found in adjacent desert
regions because of cooling from water bodies, although strong winds
from inland desert regions can sometimes boost summer temperatures,
quickly increasing the risk of wildfires.
As in every climatologic domain, the highland locations of the
Mediterranean domain can present cooler temperatures in winter than the
lowland areas, temperatures which can sometimes prohibit the growth of
typical Mediterranean plants. Some Spanish authors opt to use the term
"Continental Mediterranean climate" for some regions with lower
temperature in winter than the coastal areas (direct translation from Clima Mediterráneo Continentalizado), but most climate classifications (including Köppen's Cs zones) show no distinction.
Additionally, the temperature and rainfall pattern for a Csa or even a Csb climate can exist as a microclimate in some high-altitude locations adjacent to a rare tropical As (tropical savanna climate with dry summers, typically in a rainshadow region).
These have a favourable climate with mild wet winters and fairly warm, dry summers.
Mediterranean biome
The Ionian Sea, view from the island Lefkada, Greece
The Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome
is closely associated with Mediterranean climate zones, as are unique
freshwater communities. Particularly distinctive of the climate are sclerophyll shrublands, called maquis in the Mediterranean Basin, chaparral in California, matorral in Chile, fynbos in South Africa, and mallee and kwongan shrublands in Australia. Aquatic communities in Mediterranean climate regions are adapted to a yearly cycle in which abiotic (environmental) controls of stream populations and community structure dominate during floods, biotic components
(e.g. competition and predation) controls become increasingly important
as the discharge declines, and environmental controls regain dominance
as environmental conditions become very harsh (i.e. hot and dry); as a
result, these communities are well suited to recover from droughts, floods, and fires. Aquatic organisms in these regions show distinct long-term patterns in structure and function, and are also highly sensitive to the effects of climate change.
Natural vegetation
The
native vegetation of Mediterranean climate lands must be adapted to
survive long, hot summer droughts and prolonged wet periods in winter.
Mediterranean vegetation examples include the following:
- Evergreen trees: such as bay laurel, pine, and cypress
- Deciduous trees: such as sycamore, oak, and buckeyes
- Fruit trees such as olive, figs, walnuts and grapes
- Shrubs: rosemary, Erica, Banksia, and chamise
- Sub-shrubs: such as lavender, Halimium, and sagebrush
- Grasses: grassland types, Themeda triandra, bunchgrasses; sedges, and rushes
- Herbs: such as Achillea, Dietes, Helichrysum and Penstemon
Much native vegetation in Mediterranean climate area valleys have been cleared for agriculture. In places such as the Sacramento Valley and Oxnard Plain in California,
draining marshes and estuaries combined with supplemental irrigation
has led to a century of intensive agriculture. Much of the Overberg in the southern Cape of South Africa, once covered with renosterveld, has likewise been largely converted to agriculture, mainly wheat. In hillside and mountainous areas, away from urban sprawl, ecosystems and habitats of native vegetation are more sustained.
The fynbos
vegetation in the South-western Cape in South Africa is famed for its
high floral diversity, and includes such plant types as members of the Restionaceae, Ericas (Heaths) and Proteas. Representatives of the Proteaceae also grow in Australia, such as Banksias.
The palette of California native plants is also renowned for its species and cultivar diversity.
Hot-summer Mediterranean climate
Hot-summer mediterranean climate (Csa)
This subtype of the Mediterranean climate (Csa) is the most
common form of the Mediterranean climate, therefore it is also known as a
“typical Mediterranean climate”. As stated earlier, regions with this
form of a Mediterranean climate experience average monthly temperatures
in excess of 22 °C (71.6 °F) during its warmest month and an average in
the coldest month between 18 and −3 °C (64.4 and 26.6 °F) or, in some
applications, between 18 and 0 °C (64.4 and 32.0 °F). Also, at least
four months must average above 10 °C (50 °F). Regions with this form of
the Mediterranean climate typically experience hot, sometimes very hot
and dry summers and mild, wet winters. In a number of instances, summers
here can closely resemble summers seen in arid and semi-arid climates.
However, high temperatures during summers are generally not quite as
high as those in arid or semiarid climates due to the presence of a
large body of water. All areas with this subtype have wet winters.
However, some areas with a hot Mediterranean subtype can actually
experience very chilly winters, with occasional snowfall.
Csa climates are mainly found around the Mediterranean Sea, southwestern Australia, southwestern South Africa, sections of Central Asia, northern sections of Iran and Iraq, the interior of northern California west of the Sierra Nevada, and inland areas of southern Oregon west of the Cascade Mountains. Southern California's coasts also experience hot summers due to the shielding effect of the Channel Islands.
However, unshielded areas of that coastline can have warm-summer
Mediterranean climates with hot-summer areas just a few kilometres
inland.
| Valencia, Spain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Los Angeles, United States | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Perth, Australia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warm-summer Mediterranean climate
Warm-summer mediterranean climate (Csb)
Occasionally also termed “Cool-summer Mediterranean climate”, this subtype of the Mediterranean climate (Csb)
is the less common form of the Mediterranean climate. Cool ocean
currents and upwelling are often the reason for this cooler type of
Mediterranean climate. As stated earlier, regions with this subtype of
the Mediterranean climate experience warm (but not hot) and dry summers,
with no average monthly temperatures above 22 °C (72 °F) during its
warmest month and an average in the coldest month between 18 and −3 °C
(64 and 27 °F) or, in some applications, between 18 and 0 °C (64 and
32 °F). Also, at least four months must average above 10 °C (50 °F).
Winters are rainy and can be mild to chilly. In a few instances, snow
can fall on these areas. Precipitation occurs in the colder seasons, but
there are a number of clear sunny days even during the wetter seasons.
Csb climates are found in northwestern Iberia, namely Galicia and the north of Portugal, coastal California, western Washington and Oregon, southern portions of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, central Chile, parts of southern Australia and sections of southwestern South Africa.
| Porto, Portugal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Victoria, British Columbia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cape Town, South Africa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
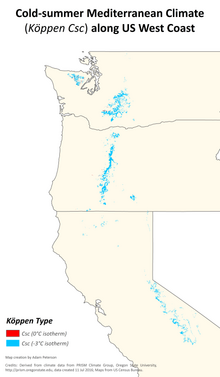
Cold-summer Mediterranean climate
Distribution of the relatively rare cold-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen type Csc) in Washington, Oregon and California.
The cold-summer subtype of the Mediterranean climate (Csc) is
rare and predominately found at scattered high-altitude locations along
the west coasts of North and South America. This type is characterized
by cool summers, with fewer than four months with a mean temperature at
or above 10 °C (50 °F), as well as with mild winters, with no winter
month having a mean temperature below 0 °C (32 °F) (or −3 °C [27 °F]),
depending on the isotherm used). Regions with this climate are
influenced by the dry-summer trend that extends considerably poleward
along the west coast of the Americas, as well as the moderating
influences of high altitude and relative proximity to the Pacific Ocean.
In North America, areas with Csc climate can be found in the Olympic, Cascade, Klamath, and Sierra Nevada
ranges in Washington, Oregon and California. These locations are found
at high altitude nearby lower altitude regions characterized by a
warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Csb) or hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Csa). A rare instance of this climate occurs in the tropics, on Haleakalā Summit in Hawaii.
In South America, Csc regions can be found along the Andes in Chile and Perú. The town of Balmaceda is one of the few towns confirmed to have this climate.
Small areas with a Csc climate can also be found at high elevations in Corsica.
| Balmaceda, Chile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Haleakala Summit, United States | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||