History and uses
Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals.
Pauling pointed out that a carbon atom forms four bonds by using one s
and three p orbitals, so that "it might be inferred" that a carbon atom
would form three bonds at right angles (using p orbitals) and a fourth
weaker bond using the s orbital in some arbitrary direction. In reality,
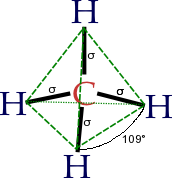
methane has four bonds of equivalent strength separated by the tetrahedral
bond angle of 109.5°. Pauling explained this by supposing that in the
presence of four hydrogen atoms, the s and p orbitals form four
equivalent combinations or hybrid orbitals, each denoted by sp3 to indicate its composition, which are directed along the four C-H bonds.
This concept was developed for such simple chemical systems, but the
approach was later applied more widely, and today it is considered an
effective heuristic for rationalising the structures of organic compounds. It gives a simple orbital picture equivalent to Lewis structures.
Hybridisation theory is an integral part of organic chemistry, one of the most compelling examples being Baldwin's rules. For drawing reaction mechanisms sometimes a classical bonding picture is needed with two atoms sharing two electrons. Hybridisation theory explains bonding in alkenes and methane.
The amount of p character or s character, which is decided mainly by
orbital hybridisation, can be used to reliably predict molecular
properties such as acidity or basicity.
Overview
Orbitals
are a model representation of the behaviour of electrons within
molecules. In the case of simple hybridisation, this approximation is
based on atomic orbitals, similar to those obtained for the hydrogen atom, the only neutral atom for which the Schrödinger equation
can be solved exactly. In heavier atoms, such as carbon, nitrogen, and
oxygen, the atomic orbitals used are the 2s and 2p orbitals, similar to
excited state orbitals for hydrogen.
Hybrid orbitals are assumed to be mixtures of atomic orbitals,
superimposed on each other in various proportions. For example, in methane, the C hybrid orbital which forms each carbon–hydrogen bond consists of 25% s character and 75% p character and is thus described as sp3 (read as s-p-three) hybridised. Quantum mechanics describes this hybrid as an sp3 wavefunction of the form N(s + √3pσ), where N is a normalisation constant (here 1/2) and pσ is a p orbital directed along the C-H axis to form a sigma bond. The ratio of coefficients (denoted λ in general) is √3 in this example. Since the electron density associated with an orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction, the ratio of p-character to s-character is λ2 = 3. The p character or the weight of the p component is N2λ2 = 3/4.
Types of hybridisation
sp3
Four sp3 orbitals.
Hybridisation describes the bonding atoms from an atom's point of view. For a tetrahedrally coordinated carbon (e.g., methane CH4), the carbon should have 4 orbitals with the correct symmetry to bond to the 4 hydrogen atoms.
Carbon's ground state configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p2 or more easily read:
| C | ↑↓ | ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | |
| 1s | 2s | 2p | 2p | 2p |
The carbon atom can use its two singly occupied p-type orbitals, to form two covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms, yielding the singlet methylene CH2, the simplest carbene.
The carbon atom can also bond to four hydrogen atoms by an excitation
(or promotion) of an electron from the doubly occupied 2s orbital to the
empty 2p orbital, producing four singly occupied orbitals.
| C* | ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 1s | 2s | 2p | 2p | 2p |
The energy released by formation of two additional bonds more than
compensates for the excitation energy required, energetically favouring
the formation of four C-H bonds.
Quantum mechanically, the lowest energy is obtained if the four
bonds are equivalent, which requires that they are formed from
equivalent orbitals on the carbon. A set of four equivalent orbitals can
be obtained that are linear combinations of the valence-shell (core
orbitals are almost never involved in bonding) s and p wave functions, which are the four sp3 hybrids.
| C* | ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 1s | sp3 | sp3 | sp3 | sp3 |
In CH4, four sp3 hybrid orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen 1s orbitals, yielding four σ (sigma) bonds (that is, four single covalent bonds) of equal length and strength.
sp2
Three sp2 orbitals.
Ethene structure
Other carbon compounds and other molecules may be explained in a similar way. For example, ethene (C2H4) has a double bond between the carbons.
For this molecule, carbon sp2 hybridises, because one π (pi) bond is required for the double bond between the carbons and only three σ bonds are formed per carbon atom. In sp2 hybridisation the 2s orbital is mixed with only two of the three available 2p orbitals,
| C* | ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 1s | sp2 | sp2 | sp2 | 2p |
forming a total of three sp2 orbitals with one remaining p orbital. In ethylene (ethene) the two carbon atoms form a σ bond by overlapping one sp2
orbital from each carbon atom. The π bond between the carbon atoms
perpendicular to the molecular plane is formed by 2p–2p overlap. Each
carbon atom forms covalent C–H bonds with two hydrogens by s–sp2
overlap, all with 120° bond angles. The hydrogen–carbon bonds are all
of equal strength and length, in agreement with experimental data.
sp
Two sp orbitals
The chemical bonding in compounds such as alkynes with triple bonds is explained by sp hybridisation. In this model, the 2s orbital is mixed with only one of the three p orbitals,
| C* | ↑↓ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| 1s | sp | sp | 2p | 2p |
resulting in two sp orbitals and two remaining p orbitals. The chemical bonding in acetylene (ethyne) (C2H2) consists of sp–sp overlap between the two carbon atoms forming a σ bond and two additional π bonds formed by p–p overlap. Each carbon also bonds to hydrogen in a σ s–sp overlap at 180° angles.
Hybridisation and molecule shape
Hybridisation helps to explain molecule shape,
since the angles between bonds are (approximately) equal to the angles
between hybrid orbitals, as explained above for the tetrahedral geometry
of methane. As another example, the three sp2 hybrid orbitals are at angles of 120° to each other, so this hybridisation favours trigonal planar molecular geometry with bond angles of 120°. Other examples are given in the table below.
| Classification | Main group | Transition metal |
|---|---|---|
| AX2 |
|
|
| AX3 |
|
|
| AX4 |
|
|
| AX6 |
|
|
For two equivalent spx hybrids, the bond angle between them is given by , while for two equivalent sdx hybrids, the bond angle between them is given by . There are no shapes with ideal bond angles corresponding to sd4 hybridisation as there is no regular 10-vertex polyhedron. Nonetheless, molecules such as Ta(CH3)5 with sd4 hybridisation adopt a square pyramidal shape.
Hybridisation of hypervalent molecules
Valence shell expansion
Hybridisation is often presented for main group AX5 and above, as well as for many transition metal complexes, using the hybridisation scheme first proposed by Pauling.
|
| ||||||||||||||||
In this notation, d orbitals of main group atoms are listed after the
s and p orbitals since they have the same principal quantum number (n), while d orbitals of transition metals are listed first since the s and p orbitals have a higher n. Thus for AX6 molecules, sp3d2 hybridisation in the S atom involves 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals, while d2sp3 for Mo involves 4d, 5s and 5p orbitals.
Contrary evidence
In
1990, Magnusson published a seminal work definitively excluding the
role of d-orbital hybridisation in bonding in hypervalent compounds of
second-row (period 3)
elements, ending a point of contention and confusion. Part of the
confusion originates from the fact that d-functions are essential in the
basis sets used to describe these compounds (or else unreasonably high
energies and distorted geometries result). Also, the contribution of the
d-function to the molecular wavefunction is large. These facts were
incorrectly interpreted to mean that d-orbitals must be involved in
bonding.
For transition metal centres, the d and s orbitals are the
primary valence orbitals, which are only weakly supplemented by the p
orbitals.
The question of whether the p orbitals actually participate in bonding
has not been definitively resolved, but all studies indicate they play a
minor role.
Resonance
In light of computational chemistry, a better treatment would be to invoke sigma bond resonance
in addition to hybridisation, which implies that each resonance
structure has its own hybridisation scheme. For main group compounds,
all resonance structures must obey the octet (8-electron) rule. For transition metal compounds, the resonance structures that obey the duodectet (12-electron) rule suffice to describe bonding, with optional inclusion of dmspn resonance structures.
Isovalent hybridisation
Although ideal hybrid orbitals can be useful, in reality most bonds
require orbitals of intermediate character. This requires an extension
to include flexible weightings of atomic orbitals of each type (s, p, d)
and allows for a quantitative depiction of bond formation when the
molecular geometry deviates from ideal bond angles. The amount of
p-character is not restricted to integer values; i.e., hybridisations
like sp2.5 are also readily described.
The hybridisation of bond orbitals is determined by Bent's rule: "Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed towards electropositive substituents".
Molecules with lone pairs
For molecules with lone pairs, the bonding orbitals are isovalent spx hybrids. For example, the two bond-forming hybrid orbitals of oxygen in water can be described as sp4.0 to give the interorbital angle of 104.5°. This means that they have 20% s character and 80% p character and does not
imply that a hybrid orbital is formed from one s and four p orbitals on
oxygen since the 2p subshell of oxygen only contains three p orbitals.
The shapes of molecules with lone pairs are:
- Trigonal pyramidal (>90°)
- Three spx bond hybrids
- E.g., NH3
- Bent (>90°)
- Two spx bond hybrids
- E.g., SO2, H2O
In such cases, there are two mathematically equivalent ways of
representing lone pairs. They can be represented by orbitals of sigma
and pi symmetry similar to molecular orbital theory or by equivalent
orbitals similar to VSEPR theory.
Hypervalent molecules
For
hypervalent molecules with lone pairs, the bonding scheme can be split
into a hypervalent component and a component consisting of isovalent spx
bond hybrids. The hypervalent component consists of resonant bonds
using p orbitals. The table below shows how each shape is related to the
two components and their respective descriptions.
Hybridisation defects
Hybridisation of s and p orbitals to form effective spx
hybrids requires that they have comparable radial extent. While 2p
orbitals are on average less than 10% larger than 2s, in part
attributable to the lack of a radial node in 2p orbitals, 3p orbitals
which have one radial node, exceed the 3s orbitals by 20–33%.
The difference in extent of s and p orbitals increases further down a
group. The hybridisation of atoms in chemical bonds can be analysed by
considering localised molecular orbitals, for example using natural
localised molecular orbitals in a natural bond orbital (NBO) scheme. In methane, CH4, the calculated p/s ratio is approximately 3 consistent with "ideal" sp3 hybridisation, whereas for silane, SiH4,
the p/s ratio is closer to 2. A similar trend is seen for the other 2p
elements. Substitution of fluorine for hydrogen further decreases the
p/s ratio.
The 2p elements exhibit near ideal hybridisation with orthogonal hybrid
orbitals. For heavier p block elements this assumption of orthogonality
cannot be justified. These deviations from the ideal hybridisation were
termed hybridisation defects by Kutzelnigg.
Photoelectron spectra
One misconception concerning orbital hybridisation is that it incorrectly predicts the ultraviolet photoelectron spectra of many molecules. While this is true if Koopmans' theorem
is applied to localised hybrids, quantum mechanics requires that the
(in this case ionised) wavefunction obey the symmetry of the molecule
which implies resonance in valence bond theory. For example, in methane, the ionised states (CH4+) can be constructed out of four resonance structures attributing the ejected electron to each of the four sp3 orbitals. A linear combination of these four structures, conserving the number of structures, leads to a triply degenerate T2 state and a A1 state.
The difference in energy between each ionised state and the ground
state would be an ionisation energy, which yields two values in
agreement with experiment.
Localized MOs vs canonical MOs
Bonding orbitals formed from hybrid atomic orbitals may be considered
as localized molecular orbitals, which can be formed from the
delocalised orbitals of molecular orbital theory by an appropriate
mathematical transformation. For molecules in the ground state, this
transformation of the orbitals leaves the total many-electron wave
function unchanged. The hybrid orbital description of the ground state
is therefore equivalent to the delocalised orbital description
for ground state total energy and electron density, as well as the
molecular geometry that corresponds to the minimum total energy value.
Two localized representations
Molecules with multiple bonds or multiple lone pairs can have
orbitals represented in terms of sigma and pi symmetry or equivalent
orbitals. Different valence bond methods use either of the two
representations, which have mathematically equivalent total
many-electron wave functions and are related by a unitary transformation of the set of occupied molecular orbitals.
For multiple bonds, the sigma-pi representation is the predominant one compared to the equivalent orbital (bent bond)
representation. In contrast, for multiple lone pairs, most textbooks
use the equivalent orbital representation. However, the sigma-pi
representation is also used, such as by Weinhold and Landis within the
context of natural bond orbitals,
a localized orbital theory containing modernized analogs of classical
(valence bond/Lewis structure) bonding pairs and lone pairs.
For the hydrogen fluoride molecule, for example, two F lone pairs are
essentially unhybridized p orbitals, while the other is an spx hydrid orbital. An analogous consideration applies to water (one O lone pair is in a pure p orbital, another is in an spx hybrid orbital).