Liquid breathing is a form of respiration in which a normally air-breathing organism breathes an oxygen-rich liquid (such as a perfluorocarbon), rather than breathing air.
This requires certain physical properties such as respiratory gas
solubility, density, viscosity, vapor pressure, and lipid solubility
which some, but not all, perfluorochemicals (perfluorocarbon) have.
Thus, it is critical to choose the appropriate PFC for a specific
biomedical application, such as liquid ventilation, drug delivery or
blood substitutes. The physical properties of PFC liquids vary
substantially; however, the one common property is their high solubility
for respiratory gases. In fact, these liquids carry more oxygen and carbon dioxide than blood.
In theory, liquid breathing could assist in the treatment of patients with severe pulmonary or cardiac trauma, especially in pediatric cases. Liquid breathing has also been proposed for use in deep diving and space travel. Despite some recent advances in liquid ventilation, a standard mode of application has not yet been established.
Approaches
| Gas solubility |
|
| Oxygen | 33–66 mL / 100 mL PFC |
| Carbon dioxide | 140–166 mL / 100 mL PFC |
| Vapor pressure | 0.2–400 torr |
| Density | 1.58–2.0 g/mL |
| Viscosity | 0.8–8.0 cS |
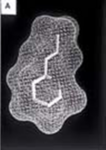
Computer models of three perfluorochemical molecules used for biomedical applications and for liquid ventilation studies: a) FC-75, b) perflubron, and c) perfluorodecalin.
Because liquid breathing is still a highly experimental technique, there are several proposed approaches.
Total liquid ventilation
Although total liquid ventilation (TLV) with completely liquid-filled lungs can be beneficial, the complex liquid-filled tube system required is a disadvantage compared to gas ventilation—the system must incorporate a membrane oxygenator, heater, and pumps to deliver to, and remove from the lungs tidal volume aliquots of conditioned perfluorocarbon (PFC). One research group led by Thomas H. Shaffer has maintained that with the use of microprocessors and new technology, it is possible to maintain better control of respiratory variables such as liquid functional residual capacity and tidal volume during TLV than with gas ventilation. Consequently, the total liquid ventilation necessitates a dedicated liquid ventilator similar to a medical ventilator except that it uses a breathable liquid. Many prototypes are used for animal experimentation, but experts recommend continued development of a liquid ventilator toward clinical applications.
Specific preclinical liquid ventilator (Inolivent) is currently under joint development in Canada and France. The main application of this liquid ventilator is the ultra-fast induction of therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. This has been demonstrated to be more protective than slower cooling method after experimental cardiac arrest.
Partial liquid ventilation
In
contrast, partial liquid ventilation (PLV) is a technique in which a
PFC is instilled into the lung to a volume approximating functional residual capacity (approximately 40% of total lung capacity). Conventional mechanical ventilation delivers tidal volume
breaths on top of it. This mode of liquid ventilation currently seems
technologically more feasible than total liquid ventilation, because PLV
could utilise technology currently in place in many neonatal intensive-care units (NICU) worldwide.
The influence of PLV on oxygenation, carbon dioxide removal and lung mechanics has been investigated in several animal studies using different models of lung injury. Clinical applications of PLV have been reported in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), meconium aspiration syndrome, congenital diaphragmatic hernia and respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of neonates. In order to correctly and effectively conduct PLV, it is essential to
- properly dose a patient to a specific lung volume (10–15 ml/kg) to recruit alveolar volume
- redose the lung with PFC liquid (1–2 ml/kg/h) to oppose PFC evaporation from the lung.
If PFC liquid is not maintained in the lung, PLV can not effectively
protect the lung from biophysical forces associated with the gas
ventilator.
New application modes for PFC have been developed.
Partial liquid ventilation (PLV) involves filling the lungs with a
fluid. This fluid is perfluorocarbon, also called Liquivent or
Perflubron. The liquid has some unique properties. It has a very low
surface tension, similar to surfactant, a substance that is produced in
the lungs to prevent the alveoli from collapsing and sticking together
during exhalation. It also has a high density, oxygen readily diffuses
through it, and it may have some anti-inflammatory properties. In PLV,
the lungs are filled with the liquid, the patient is then ventilated
with a conventional ventilator using a protective lung ventilation
strategy. This is called partial liquid ventilation. The hope is that
the liquid will help the transport of oxygen to parts of the lung that
are flooded and filled with debris, help remove this debris and open up
more alveoli improving lung function. The study of PLV involves
comparison to protocolized ventilator strategy designed to minimize lung
damage.
PFC vapor
Vaporization of perfluorohexane with two anesthetic vaporizers calibrated for perfluorohexane has been shown to improve gas exchange in oleic acid-induced lung injury in sheep.
Predominantly PFCs with high vapor pressure are suitable for vaporization.
Aerosol-PFC
With aerosolized perfluorooctane, significant improvement of oxygenation and pulmonary
mechanics was shown in adult sheep with oleic acid-induced lung injury.
In surfactant-depleted piglets, persistent improvement of gas exchange and lung mechanics was demonstrated with Aerosol-PFC.
The aerosol device is of decisive importance for the efficacy of PFC aerosolization, as aerosolization of PF5080 (a less purified FC77)
has been shown to be ineffective using a different aerosol device in
surfactant-depleted rabbits. Partial liquid ventilation and Aerosol-PFC
reduced pulmonary inflammatory response.
Proposed uses
Diving
Gas pressure increases with depth, rising 1 bar (14.5 psi (100 kPa)) every 10 meters to over 1,000 bar at the bottom of the Mariana Trench. Diving becomes more dangerous as depth increases, and deep diving presents many hazards. All surface-breathing animals are subject to decompression sickness, including aquatic mammals and free-diving humans. Breathing at depth can cause nitrogen narcosis and oxygen toxicity. Holding the breath while ascending after breathing at depth can cause air embolisms, burst lung, and collapsed lung.
Special breathing gas mixes such as trimix or heliox ameliorate the risk of decompression illness but do not eliminate it. Heliox further eliminates the risk of nitrogen narcosis but introduces the risk of helium tremors below about 500 feet (150 m). Atmospheric diving suits
maintain body and breathing pressure at 1 bar, eliminating most of the
hazards of descending, ascending, and breathing at depth. However, the
rigid suits are bulky, clumsy, and very expensive.
Liquid breathing offers a third option,
promising the mobility available with flexible dive suits and the
reduced risks of rigid suits. With liquid in the lungs, the pressure
within the diver's lungs could accommodate changes in the pressure of
the surrounding water without the huge gas partial pressure exposures
required when the lungs are filled with gas. Liquid breathing would not
result in the saturation of body tissues with high pressure nitrogen or
helium that occurs with the use of non-liquids, thus would reduce or
remove the need for slow decompression.
A significant problem, however, arises from the high viscosity of the liquid and the corresponding reduction in its ability to remove CO2.
All uses of liquid breathing for diving must involve total liquid
ventilation (see above). Total liquid ventilation, however, has
difficulty moving enough liquid to carry away CO2, because no matter how great the total pressure is, the amount of partial CO2 gas pressure available to dissolve CO2 into the breathing liquid can never be much more than the pressure at which CO2 exists in the blood (about 40 mm of mercury (Torr)).
At these pressures, most fluorocarbon liquids require about 70
mL/kg minute-ventilation volumes of liquid (about 5 L/min for a 70 kg
adult) to remove enough CO2 for normal resting metabolism.
This is a great deal of fluid to move, particularly as liquids are more
viscous and denser than gases, (for example water is about 850 times
the density of air). Any increase in the diver's metabolic activity also increases CO2 production and the breathing rate, which is already at the limits of realistic flow rates in liquid breathing.
It seems unlikely that a person would move 10 liters/min of
fluorocarbon liquid without assistance from a mechanical ventilator, so
"free breathing" may be unlikely. However, it has been suggested that a
liquid breathing system could be combined with a CO2 scrubber connected to the diver's blood supply; a US patent has been filed for such a method.
Medical treatment
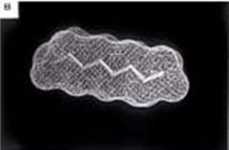
Computer-generated model of perflubron and gentamicin molecules in liquid suspension for pulmonary administration
The most promising area for the use of liquid ventilation is in the field of pediatric medicine. The first medical use of liquid breathing was treatment of premature babies and adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in the 1990s. Liquid breathing was used in clinical trials after the development by Alliance Pharmaceuticals of the fluorochemical perfluorooctyl bromide, or perflubron for short. Current methods of positive-pressure ventilation can contribute to the development of lung disease in pre-term neonates, leading to diseases such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Liquid ventilation removes many of the high pressure gradients responsible for this damage. Furthermore, perfluorocarbons have been demonstrated to reduce lung inflammation, improve ventilation-perfusion mismatch and to provide a novel route for the pulmonary administration of drugs.
In order to explore drug delivery techniques that would be useful
for both partial and total liquid ventilation, more recent studies have
focused on PFC drug delivery using a nanocrystal suspension. The first
image is a computer model of a PFC liquid (perflubron) combined with
gentamicin molecules.
The second image shows experimental results comparing both plasma and
tissue levels of gentamicin after an intratracheal (IT) and intravenous
(IV) dose of 5 mg/kg in a newborn lamb during gas ventilation. Note that
the plasma levels of the IV dose greatly exceed the levels of the IT
dose over the 4 hour study period; whereas, the lung tissue levels of
gentamicin when delivered by an intratracheal
(IT) suspension, uniformly exceed the intravenous (IV) delivery
approach after 4 hours. Thus, the IT approach allows more effective
delivery of the drug to the target organ while maintaining a safer level
systemically. Both images represent the in-vivo time course over 4
hours. Numerous studies have now demonstrated the effectiveness of PFC
liquids as a delivery vehicle to the lungs.
Comparison of IT and IV administration of gentamicin.
Clinical trials with premature infants, children and adults were
conducted. Since the safety of the procedure and the effectiveness were
apparent from an early stage, the US Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) gave the product "fast track" status (meaning an accelerated
review of the product, designed to get it to the public as quickly as is
safely possible) due to its life-saving potential. Clinical trials
showed that using perflubron with ordinary ventilators improved outcomes as much as using high frequency oscillating ventilation
(HFOV). But because perflubron was not better than HFOV, the FDA did
not approve perflubron, and Alliance is no longer pursuing the partial
liquid ventilation application. Whether perflubron would improve
outcomes when used with HFOV or has fewer long-term consequences than
HFOV remains an open question.
In 1996 Mike Darwin
and Steven B. Harris proposed using cold liquid ventilation with
perfluorocarbon to quickly lower the body temperature of victims of cardiac arrest and other brain trauma to allow the brain to better recover.
The technology came to be called gas/liquid ventilation (GLV), and was shown able to achieve a cooling rate of 0.5 °C per minute in large animals. It has not yet been tried in humans.
Most recently, hypothermic brain protection has been associated
with rapid brain cooling. In this regard, a new therapeutic approach is
the use of intranasal perfluorochemical spray for preferential brain
cooling.
The nasopharyngeal (NP) approach is unique for brain cooling due to
anatomic proximity to the cerebral circulation and arteries. Based on
preclinical studies in adult sheep, it was shown that independent of
region, brain cooling was faster during NP-perfluorochemical versus
conventional whole body cooling with cooling blankets. To date, there
have been four human studies including a completed randomized
intra-arrest study (200 patients).
Results clearly demonstrated that prehospital intra-arrest transnasal
cooling is safe, feasible and is associated with an improvement in
cooling time.
Space travel
Liquid immersion provides a way to reduce the physical stress of G forces.
Forces applied to fluids are distributed as omnidirectional pressures.
Because liquids cannot be practically compressed, they do not change
density under high acceleration such as performed in aerial maneuvers or
space travel. A person immersed in liquid of the same density as tissue
has acceleration forces distributed around the body, rather than
applied at a single point such as a seat or harness straps. This
principle is used in a new type of G-suit
called the Libelle G-suit, which allows aircraft pilots to remain
conscious and functioning at more than 10 G acceleration by surrounding
them with water in a rigid suit.
Acceleration protection by liquid immersion is limited by the
differential density of body tissues and immersion fluid, limiting the
utility of this method to about 15 to 20 G.
Extending acceleration protection beyond 20 G requires filling the lungs
with fluid of density similar to water. An astronaut totally immersed
in liquid, with liquid inside all body cavities, will feel little effect
from extreme G forces because the forces on a liquid are distributed
equally, and in all directions simultaneously. However effects will be
felt because of density differences between different body tissues, so
an upper acceleration limit still exists.
Liquid breathing for acceleration protection may never be
practical because of the difficulty of finding a suitable breathing
medium of similar density to water that is compatible with lung tissue. Perfluorocarbon fluids are twice as dense as water, hence unsuitable for this application.
Examples in fiction
Literary works
- Alexander Beliaev's 1928 science fiction novel Amphibian Man is based on a scientist and a maverick surgeon, who makes his son, Ichthyander (etymology: "fish" + "man") a life-saving transplant – a set of shark gills. There is a film based on the novel.
- L. Sprague de Camp's 1938 short story "The Merman" hinges on an experimental process to make lungs function as gills, thus allowing a human being to "breathe" under water.
- Hal Clement's 1973 novel Ocean on Top portrays a small underwater civilization living in a 'bubble' of oxygenated fluid denser than seawater.
- Joe Haldeman's 1975 novel The Forever War describes liquid immersion and breathing in great detail as a key technology to allow space travel and combat with acceleration up to 50 G.
- In the Star Trek: The Next Generation novel The Children of Hamlin (1988) the crew of the Enterprise-D encounter an alien race whose ships contain a breathable liquid environment.
- Peter Benchley's 1994 novel White Shark centers around a Nazi scientist's experimental attempts to create an amphibious human, whose lungs are surgically modified to breathe underwater, and trained to reflexively do so after being flooded with a fluorocarbon solution.
- Ben Bova's novel Jupiter (2000) features a craft in which the crew are suspended in a breathable liquid that allows them to survive in the high-pressure environment of Jupiter's atmosphere.
- In Scott Westerfeld's sci-fi novel The Risen Empire (2003), the lungs of soldiers performing insertion from orbit are filled with an oxygen-rich polymer gel with embedded pseudo-alveoli and a rudimentary artificial intelligence.
- The novel Mechanicum (2008) by Graham McNeill, Book 9 in the Horus Heresy book series, describes physically crippled Titan (gigantic war machine) pilots encased in nutrient fluid tanks. This allows them to continue operating beyond the limits normally imposed by the body.
- In the 2009 novel The Lost Symbol by Dan Brown, Robert Langdon (the protagonist) is completely submerged in breathable liquid mixed with hallucinogenic chemicals and sedatives as a torture and interrogation technique by Mal'akh (the antagonist). He goes through a near death experience when he inhales the liquid and blacks out, losing control over his body, but is soon revived.
- In Greg van Eekhout's 2014 novel California Bones, two characters are put into tanks filled with liquid: "They were given no breathing apparatus, but the water in the tank was rich with perfluorocarbon, which carried more oxygen than blood."
- In author A.L. Mengel's science fiction novel The Wandering Star (2016), several characters breathe oxygenated fluid during a dive to explore an underwater city. They submerge in high pressure "bubbles" filled with the perfluorocarbon fluid.
Films and television
- The aliens in the Gerry Anderson UFO series (1970-1971) use liquid-breathing spacesuits.
- The 1989 film The Abyss by James Cameron features a character using liquid breathing to dive thousands of feet without compressing. The Abyss also features a scene with a rat submerged in and breathing fluorocarbon liquid, filmed in real life.
- In the 1995 anime Neon Genesis Evangelion, the cockpits of the titular mecha are filled with a fictional oxygenated liquid called LCL which is required for the pilot to mentally sync with an Evangelion, as well as providing direct oxygenation of their blood, and dampening the impacts from battle. Once the cockpit is flooded the LCL is ionized, bringing its density, opacity, and viscosity close to that of air.
- In the movies Event Horizon (1997) and Mission to Mars (2000), a character is depicted as being immersed in apparent breathable fluid before a high-acceleration launch.
- In season 1, episode 13 of Seven Days (1998-2001) chrononaut Frank Parker is seen breathing a hyper-oxygenated perfluorocarbon liquid that is pumped through a sealed full body suit that he is wearing. This suit and liquid combination allow him to board a Russian submarine through open ocean at a depth of almost 1000 feet. Upon boarding the submarine he removes his helmet, expels the liquid from his lungs and is able to breathe air again.
- In an episode of the Adult Swim cartoon series Metalocalypse (2006-2013), the other members of the band submerge guitarist Toki in a "liquid oxygen isolation chamber" while recording an album in the Mariana Trench.
- In an episode of the Syfy Channel show Eureka (2006-2012), Sheriff Jack Carter is submerged in a tank of "oxygen rich plasma" to be cured of the effects of a scientific accident.
- In the anime series Aldnoah.Zero (2014-2015), episode 5 shows that Slaine Troyard was in a liquid-filled capsule when he crashed. Princess Asseylum witnessed the crash, helped him to get out of the capsule, then used CPR on him to draw out the liquid from his lungs.
Video games
- In the classic 1995 PC turn-based strategy game X-COM: Terror from the Deep, "Aquanauts" fighting in deep ocean conditions breathe a dense oxygen-carrying fluid.
- In the EVE Online Universe (2003), pilots in capsules (escape pods that function as the control center for the spacecraft) breathe an oxygen rich, nano-saturated, breathable glucose-based suspension solution.