U.S. NRC image of a modern steam turbine generator (STG).
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) into electrical power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids.
The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor,
and motors and generators have many similarities. Many motors can be
mechanically driven to generate electricity and frequently make
acceptable manual generators.
Terminology
Early Ganz Generator in Zwevegem, West Flanders, Belgium
Electromagnetic generators fall into one of two broad categories, dynamos and alternators.
- Dynamos generate pulsing direct current through the use of a commutator.
- Alternators generate alternating current.
Mechanically a generator consists of a rotating part and a stationary part:
- Rotor
- The rotating part of an electrical machine.
- Stator
- The stationary part of an electrical machine, which surrounds the rotor.
One of these parts generates a magnetic field, the other has a wire
winding in which the changing field induces an electric current:
- Field winding or field (permanent) magnets
- The magnetic field producing component of an electrical machine. The magnetic field of the dynamo or alternator can be provided by either wire windings called field coils or permanent magnets. Electrically-excited generators include an excitation system to produce the field flux. A generator using permanent magnets (PMs) is sometimes called a magneto, or permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSMs).
- Armature
- The power-producing component of an electrical machine. In a generator, alternator, or dynamo, the armature windings generate the electric current, which provides power to an external circuit. The armature can be on either the rotor or the stator, depending on the design, with the field coil or magnet on the other part.
History
Before the connection between magnetism and electricity was discovered, electrostatic generators were invented. They operated on electrostatic principles, by using moving electrically charged
belts, plates, and disks that carried charge to a high potential
electrode. The charge was generated using either of two mechanisms: electrostatic induction or the triboelectric effect. Such generators generated very high voltage and low current. Because of their inefficiency and the difficulty of insulating
machines that produced very high voltages, electrostatic generators had
low power ratings, and were never used for generation of commercially
significant quantities of electric power. Their only practical
applications were to power early X-ray tubes, and later in some atomic particle accelerators.
Faraday disk generator
The Faraday disk was the first electric generator. The horseshoe-shaped magnet (A) created a magnetic field through the disk (D).
When the disk was turned, this induced an electric current radially
outward from the center toward the rim. The current flowed out through
the sliding spring contact m, through the external circuit, and back into the center of the disk through the axle.
The operating principle of electromagnetic generators was discovered in the years of 1831–1832 by Michael Faraday. The principle, later called Faraday's law, is that an electromotive force is generated in an electrical conductor which encircles a varying magnetic flux.
He also built the first electromagnetic generator, called the Faraday disk; a type of homopolar generator, using a copper disc rotating between the poles of a horseshoe magnet. It produced a small DC voltage.
This design was inefficient, due to self-cancelling counterflows of current
in regions of the disk that were not under the influence of the
magnetic field. While current was induced directly underneath the
magnet, the current would circulate backwards in regions that were
outside the influence of the magnetic field. This counterflow limited
the power output to the pickup wires, and induced waste heating of the
copper disc. Later homopolar generators would solve this problem by
using an array of magnets arranged around the disc perimeter to maintain
a steady field effect in one current-flow direction.
Another disadvantage was that the output voltage
was very low, due to the single current path through the magnetic flux.
Experimenters found that using multiple turns of wire in a coil could
produce higher, more useful voltages. Since the output voltage is
proportional to the number of turns, generators could be easily designed
to produce any desired voltage by varying the number of turns. Wire
windings became a basic feature of all subsequent generator designs.
Jedlik and the self-excitation phenomenon
Independently of Faraday, Ányos Jedlik started experimenting in 1827 with the electromagnetic rotating devices which he called electromagnetic self-rotors.
In the prototype of the single-pole electric starter (finished between
1852 and 1854) both the stationary and the revolving parts were
electromagnetic. It was also the discovery of the principle of dynamo self-excitation, which replaced permanent magnet designs. He also may have formulated the concept of the dynamo in 1861 (before Siemens and Wheatstone) but didn't patent it as he thought he wasn't the first to realize this.
Direct current generators
Hippolyte Pixii's dynamo. The commutator is located on the shaft below the spinning magnet.
This large belt-driven high-current dynamo produced 310 amperes at 7 volts. Dynamos are no longer used due to the size and complexity of the commutator needed for high power applications.
A coil of wire rotating in a magnetic field produces a current which changes direction with each 180° rotation, an alternating current (AC). However many early uses of electricity required direct current (DC). In the first practical electric generators, called dynamos, the AC was converted into DC with a commutator,
a set of rotating switch contacts on the armature shaft. The commutator
reversed the connection of the armature winding to the circuit every
180° rotation of the shaft, creating a pulsing DC current. One of the
first dynamos was built by Hippolyte Pixii in 1832.
The dynamo was the first electrical generator capable of delivering power for industry.
The Woolrich Electrical Generator of 1844, now in Thinktank, Birmingham Science Museum, is the earliest electrical generator used in an industrial process. It was used by the firm of Elkingtons for commercial electroplating.
The modern dynamo, fit for use in industrial applications, was invented independently by Sir Charles Wheatstone, Werner von Siemens
and Samuel Alfred Varley. Varley took out a patent on 24 December 1866,
while Siemens and Wheatstone both announced their discoveries on 17
January 1867, the latter delivering a paper on his discovery to the Royal Society.
The "dynamo-electric machine" employed self-powering
electromagnetic field coils rather than permanent magnets to create the
stator field.
Wheatstone's design was similar to Siemens', with the difference that
in the Siemens design the stator electromagnets were in series with the
rotor, but in Wheatstone's design they were in parallel.
The use of electromagnets rather than permanent magnets greatly
increased the power output of a dynamo and enabled high power generation
for the first time. This invention led directly to the first major
industrial uses of electricity. For example, in the 1870s Siemens used
electromagnetic dynamos to power electric arc furnaces for the production of metals and other materials.
The dynamo machine that was developed consisted of a stationary
structure, which provides the magnetic field, and a set of rotating
windings which turn within that field. On larger machines the constant
magnetic field is provided by one or more electromagnets, which are
usually called field coils.
Large power generation dynamos are now rarely seen due to the now nearly universal use of alternating current
for power distribution. Before the adoption of AC, very large
direct-current dynamos were the only means of power generation and
distribution. AC has come to dominate due to the ability of AC to be
easily transformed to and from very high voltages to permit low losses over large distances.
Synchronous generators (alternating current generators)
Ferranti alternating current generator, c. 1900.
Through a series of discoveries, the dynamo was succeeded by many later inventions, especially the AC alternator, which was capable of generating alternating current.
It is commonly known to be the Synchronous Generators (SGs). The
synchronous machines are directly connected to the grid and need to be
properly synchronized during startup. Moreover, they are excited with special control to enhance the stability of the power system.
Alternating current generating systems were known in simple forms from Michael Faraday's original discovery of the magnetic induction of electric current. Faraday himself built an early alternator. His machine was a "rotating rectangle", whose operation was heteropolar - each active conductor passed successively through regions where the magnetic field was in opposite directions.
Large two-phase alternating current generators were built by a British electrician, J.E.H. Gordon, in 1882. The first public demonstration of an "alternator system" was given by William Stanley, Jr., an employee of Westinghouse Electric in 1886.
Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti established Ferranti, Thompson and Ince in 1882, to market his Ferranti-Thompson Alternator, invented with the help of renowned physicist Lord Kelvin. His early alternators produced frequencies between 100 and 300 Hz. Ferranti went on to design the Deptford Power Station
for the London Electric Supply Corporation in 1887 using an alternating
current system. On its completion in 1891, it was the first truly
modern power station, supplying high-voltage AC power that was then
"stepped down" for consumer use on each street. This basic system
remains in use today around the world.
A small early 1900s 75 kVA direct-driven power station AC alternator, with a separate belt-driven exciter generator.
After 1891, polyphase alternators were introduced to supply currents of multiple differing phases.
Later alternators were designed for varying alternating-current
frequencies between sixteen and about one hundred hertz, for use with
arc lighting, incandescent lighting and electric motors.
Self-excitation
As the requirements for larger scale power generation increased, a
new limitation rose: the magnetic fields available from permanent
magnets. Diverting a small amount of the power generated by the
generator to an electromagnetic field coil allowed the generator to produce substantially more power. This concept was dubbed self-excitation.
The field coils are connected in series or parallel with the
armature winding. When the generator first starts to turn, the small
amount of remanent magnetism
present in the iron core provides a magnetic field to get it started,
generating a small current in the armature. This flows through the field
coils, creating a larger magnetic field which generates a larger
armature current. This "bootstrap" process continues until the magnetic
field in the core levels off due to saturation and the generator reaches a steady state power output.
Very large power station generators often utilize a separate
smaller generator to excite the field coils of the larger. In the event
of a severe widespread power outage where islanding of power stations has occurred, the stations may need to perform a black start to excite the fields of their largest generators, in order to restore customer power service.
Specialized types of generator
Direct current (DC)
An important class of direct-current generators are the dynamos - these are electrical machines with commutators to produce (DC) direct current, and are self excited
- their field electromagnets are powered by the machine's own output.
Other types of DC generator use a separate source of direct current to
energize their field magnets.
Homopolar generator
A homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator
comprising an electrically conductive disc or cylinder rotating in a
plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential
difference is created between the center of the disc and the rim (or
ends of the cylinder), the electrical polarity depending on the direction of rotation and the orientation of the field.
It is also known as a unipolar generator, acyclic generator, disk dynamo, or Faraday disc.
The voltage is typically low, on the order of a few volts in the case
of small demonstration models, but large research generators can produce
hundreds of volts, and some systems have multiple generators in series
to produce an even larger voltage. They are unusual in that they can produce tremendous electric current, some more than a million amperes, because the homopolar generator can be made to have very low internal resistance.
Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) generator
A magnetohydrodynamic generator directly extracts electric power from
moving hot gases through a magnetic field, without the use of rotating
electromagnetic machinery. MHD generators were originally developed
because the output of a plasma MHD generator is a flame, well able to
heat the boilers of a steam power plant.
The first practical design was the AVCO Mk. 25, developed in 1965. The
U.S. government funded substantial development, culminating in a 25 MW
demonstration plant in 1987. In the Soviet Union
from 1972 until the late 1980s, the MHD plant U 25 was in regular
commercial operation on the Moscow power system with a rating of 25 MW,
the largest MHD plant rating in the world at that time. MHD generators operated as a topping cycle are currently (2007) less efficient than combined cycle gas turbines.
Alternating current (AC)
Induction generator
Induction AC motors
may be used as generators, turning mechanical energy into electric
current. Induction generators operate by mechanically turning their
rotor faster than the synchronous speed, giving negative slip. A regular
AC asynchronous motor usually can be used as a generator, without any
internal modifications. Induction generators are useful in applications
such as minihydro power plants, wind turbines, or in reducing
high-pressure gas streams to lower pressure, because they can recover
energy with relatively simple controls. They do not require an exciter
circuit because the rotating magnetic field is provided by induction
from the stator circuit. They also do not require speed governor
equipment as they inherently operate at the connected grid frequency.
To operate, an induction generator must be excited with a leading
voltage; this is usually done by connection to an electrical grid, or
sometimes they are self-excited by using phase correcting capacitors.
Linear electric generator
In the simplest form of linear electric generator, a sliding magnet moves back and forth through a solenoid - a spool of copper wire. An alternating current is induced in the loops of wire by Faraday's law of induction each time the magnet slides through. This type of generator is used in the Faraday flashlight. Larger linear electricity generators are used in wave power schemes.
Variable-speed constant-frequency generators
Many renewable energy
efforts attempt to harvest natural sources of mechanical energy (wind,
tides, etc.) to produce electricity. Because these sources fluctuate in
power applied, standard generators using permanent magnets and fixed
windings would deliver unregulated voltage and frequency. The overhead
of regulation (whether before the generator via gear reduction or after
generation by electrical means) is high in proportion to the
naturally-derived energy available.
New generator designs such as the asynchronous or induction singly-fed generator, the doubly-fed generator, or the brushless wound-rotor doubly-fed generator are seeing success in variable speed constant frequency applications, such as wind turbines or other renewable energy technologies. These systems thus offer cost, reliability and efficiency benefits in certain use cases.
Common use cases
Vehicular generators
Roadway vehicles
Motor vehicles require electrical energy to power their
instrumentation, keep the engine itself operating, and recharge their
batteries. Until about the 1960s motor vehicles tended to use DC generators
with electromechanical regulators. Following the historical trend above
and for many of the same reasons, these have now been replaced by alternators with built-in rectifier circuits.
Bicycles
Bicycles
require energy to power running lights and other equipment. There are
two common kinds of generator in use on bicycles: bottle dynamos which engage the bicycle's tire on an as-needed basis, and hub dynamos
which are directly attached to the bicycle's drive train. The name is
conventional as these they are small permanent-magnet alternators, not
self-excited DC machines as are dynamos. Some electric bicycles are capable of regenerative braking, where the drive motor is used as a generator to recover some energy during braking.
Sailboats
Sailing boats may use a water- or wind-powered generator to trickle-charge the batteries. A small propeller, wind turbine or impeller is connected to a low-power generator to supply currents at typical wind or cruising speeds.
Electric scooters
Electric scooters with regenerative braking have become popular all over the world. Engineers use kinetic energy
recovery systems on the scooter to reduce energy consumption and
increase its range up to 40-60% by simply recovering energy using the
magnetic brake, which generates electric energy for further use. Modern vehicles reach speed up to 25-30 km/h and can run up to 35-40 km.
Genset
An engine-generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engine (prime mover)
mounted together to form a single piece of self-contained equipment.
The engines used are usually piston engines, but gas turbines can also
be used. And there are even hybrid diesel-gas units, called dual-fuel
units. Many different versions of engine-generators are available -
ranging from very small portable petrol
powered sets to large turbine installations. The primary advantage of
engine-generators is the ability to independently supply electricity,
allowing the units to serve as backup power solutions.
Human powered electrical generators
A generator can also be driven by human muscle power (for instance, in field radio station equipment).
Protesters at Occupy Wall Street using bicycles connected to a motor and one-way diode to charge batteries for their electronics
Human powered direct current generators are commercially available, and have been the project of some DIY
enthusiasts. Typically operated by means of pedal power, a converted
bicycle trainer, or a foot pump, such generators can be practically used
to charge batteries, and in some cases are designed with an integral
inverter. An average "healthy human" can produce a steady 75 Watts (0.1
horsepower) for a full eight hour period, while a "first class athlete"
can produce approximately 298 Watts (0.4 horsepower) for a similar
period. At the end of which an undetermined period of rest and recovery
will be required. At 298 Watts the average "healthy human" becomes
exhausted within 10 minutes.
The net electrical power that can be produced will be less, due to the
efficiency of the generator. Portable radio receivers with a crank are
made to reduce battery purchase requirements, see clockwork radio. During the mid 20th century, pedal powered radios were used throughout the Australian outback, to provide schooling (School of the Air), medical and other needs in remote stations and towns.
Mechanical measurement
Designed
to measure shaft speed, a tachogenerator is a device which produces an
output voltage proportional to that speed. Tachogenerators are
frequently used to power tachometers
to measure the speeds of electric motors, engines, and the equipment
they power. speed. With precise construction and design, generators can
be built to produce very precise voltages for certain ranges of shaft
speeds.
Equivalent circuit
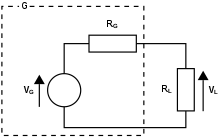
Equivalent circuit of generator and load.
- G, generator
- VG, generator open-circuit voltage
- RG, generator internal resistance
- VL, generator on-load voltage
- RL, load resistance
An equivalent circuit of a generator and load is shown in the adjacent diagram. The generator is represented by an abstract generator consisting of an ideal voltage source and an internal resistance. The generator's and parameters can be determined by measuring the winding resistance (corrected to operating temperature), and measuring the open-circuit and loaded voltage for a defined current load.
This is the simplest model of a generator, further elements may
need to be added for an accurate representation. In particular,
inductance can be added to allow for the machine's windings and magnetic
leakage flux, but a full representation can become much more complex than this.