Relativistic quantum chemistry combines relativistic mechanics with quantum chemistry to explain elemental properties and structure, especially for the heavier elements of the periodic table. A prominent example of such an explanation is the color of gold: due to relativistic effects, it is not silvery like most other metals.
The term relativistic effects was developed in light of the history of quantum mechanics. Initially quantum mechanics was developed without considering the theory of relativity. Relativistic effects are those discrepancies between values calculated by models that consider and that do not consider relativity. Relativistic effects are important for the heavier elements with high atomic numbers. In the most common layout of the periodic table, these elements are shown in the lower area. Examples are the lanthanides and actinides.
Relativistic effects in chemistry can be considered to be perturbations, or small corrections, to the non-relativistic theory of chemistry, which is developed from the solutions of the Schrödinger equation. These corrections affect the electrons differently depending on the electron speed relative to the speed of light. Relativistic effects are more prominent in heavy elements because only in these elements do electrons attain sufficient speeds for the elements to have properties that differ from what non-relativistic chemistry predicts.
The term relativistic effects was developed in light of the history of quantum mechanics. Initially quantum mechanics was developed without considering the theory of relativity. Relativistic effects are those discrepancies between values calculated by models that consider and that do not consider relativity. Relativistic effects are important for the heavier elements with high atomic numbers. In the most common layout of the periodic table, these elements are shown in the lower area. Examples are the lanthanides and actinides.
Relativistic effects in chemistry can be considered to be perturbations, or small corrections, to the non-relativistic theory of chemistry, which is developed from the solutions of the Schrödinger equation. These corrections affect the electrons differently depending on the electron speed relative to the speed of light. Relativistic effects are more prominent in heavy elements because only in these elements do electrons attain sufficient speeds for the elements to have properties that differ from what non-relativistic chemistry predicts.
History
Beginning in 1935, Bertha Swirles described a relativistic treatment of a many-electron system, in spite of Paul Dirac's
1929 assertion that the only imperfections remaining in quantum
mechanics "give rise to difficulties only when high-speed particles are
involved, and are therefore of no importance in the consideration of
atomic and molecular structure and ordinary chemical reactions in which
it is, indeed, usually sufficiently accurate if one neglects relativity
variation of mass and velocity and assumes only Coulomb forces between the various electrons and atomic nuclei."
Theoretical chemists by and large agreed with Dirac's sentiment
until the 1970s, when relativistic effects were observed in heavy
elements. The Schrödinger equation had been developed without considering relativity in Schrödinger's 1926 paper. Relativistic corrections were made to the Schrödinger equation to explain the fine structure of atomic spectra, but this development and others did not immediately trickle into the chemical community. Since atomic spectral lines
were largely in the realm of physics and not in that of chemistry, most
chemists were unfamiliar with relativistic quantum mechanics, and their
attention was on lighter elements typical for the organic chemistry focus of the time.
Dirac's opinion on the role relativistic quantum mechanics would
play for chemical systems is wrong for two reasons. First, electrons in s
and p atomic orbitals
travel at a significant fraction of the speed of light. Second,
relativistic effects cause indirect consequences that are especially
evident for d and f atomic orbitals.
Qualitative treatment
Relativistic γ as a function of velocity. For a small velocity, the (ordinate) is equal to but as the goes to infinity.
One of the most important and familiar results of relativity is that the relativistic mass of the electron increases by
where are the electron rest mass, velocity of the electron, and speed of light
respectively. The figure at the right illustrates the relativistic
effects on the mass of an electron as a function of its velocity.
This has an immediate implication on the Bohr radius () which is given by
where is the reduced Planck's constant and α is the fine-structure constant (a relativistic correction for the Bohr model).
Arnold Sommerfeld calculated that, for a 1s electron of a hydrogen atom with an orbiting radius of 0.0529 nm, α ≈ 1/137. That is to say, the fine-structure constant shows the electron traveling at nearly 1/137 the speed of light.
One can extend this to a larger element by using the expression v ≈
Zc/137 for a 1s electron where v is its radial velocity. For gold with
(Z = 79) the 1s electron will be going (α = 0.58c) 58% of the speed of light. Plugging this in for v/c for the relativistic mass one finds that mrel = 1.22me and in turn putting this in for the Bohr radius above one finds that the radius shrinks by 22%.
If one substitutes in the relativistic mass into the equation for the Bohr radius it can be written
Ratio of relativistic and nonrelativistic Bohr radii, as a function of electron velocity
It follows that
At right, the above ratio of the relativistic and nonrelativistic
Bohr radii has been plotted as a function of the electron velocity.
Notice how the relativistic model shows the radius decreasing with
increasing velocity.
When the Bohr treatment is extended to hydrogenic atoms, the Bohr radius becomes
where is the principal quantum number and Z is an integer for the atomic number. From quantum mechanics the angular momentum is given as . Substituting into the equation above and solving for gives
From this point atomic units can be used to simplify the expression into
Substituting this into the expression for the Bohr ratio mentioned above gives
At this point one can see that for a low value of and a high value of that .
This fits with intuition: electrons with lower principal quantum
numbers will have a higher probability density of being nearer to the
nucleus. A nucleus with a large charge will cause an electron to have a
high velocity. A higher electron velocity means an increased electron
relativistic mass, as a result the electrons will be near the nucleus
more of the time and thereby contract the radius for small principal
quantum numbers.
Periodic table deviations
The periodic table
was constructed by scientists who noticed periodic trends in known
elements of the time. Indeed, the patterns found in it is what gives the
periodic table its power. Many of the chemical and physical differences
between the 6th period (Cs–Rn) and the 5th period (Rb–Xe) arise from the larger relativistic effects for the former. These relativistic effects are particularly large for gold and its neighbors, platinum and mercury.
Mercury
Mercury (Hg) is a liquid down to −39°C. Bonding forces are weaker for Hg–Hg bonds than for its immediate neighbors such as cadmium (m.p. 321°C) and gold (m.p. 1064°C). The lanthanide contraction is a partial explanation; however, it does not entirely account for this anomaly. In the gas phase mercury is alone in metals in that it is quite typically found in a monomeric form as Hg(g). Hg22+(g) also forms and it is a stable species due to the relativistic shortening of the bond.
Hg2(g) does not form because the 6s2
orbital is contracted by relativistic effects and may therefore only
weakly contribute to any bonding; in fact Hg–Hg bonding must be mostly
the result of van der Waals forces, which explains why the bonding for Hg–Hg is weak enough to allow for Hg to be a liquid at room temperature.
Au2(g) and Hg(g) are analogous, at the least in having the same nature of difference, to H2(g) and He(g). It is for the relativistic contraction of the 6s2 orbital that gaseous mercury can be called a pseudo noble gas.
Color of gold and caesium
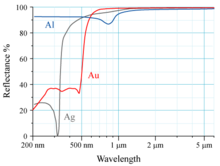
Spectral reflectance curves for aluminum (Al), silver (Ag), and gold (Au) metal mirrors
The reflectivity of aluminum
(Al), silver (Ag), and gold (Au) is shown in the graph above.
The human eye sees electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength near
600 nm as yellow. Gold appears yellow because it absorbs
blue light more than it absorbs other visible wavelengths of light; the
reflected light reaching the eye is therefore lacking in blue compared
to the incident light. Since yellow is complementary to blue, this makes a piece of gold under white light appear yellow to human eyes.
The electronic transition from the 5d orbital to the 6s orbital
is responsible for this absorption. An analogous transition occurs in
silver, but the relativistic effects are smaller than in gold. While
silver's 4d orbital experiences some relativistic expansion and the 5s
orbital some contraction, the 4d-5s distance in silver is still much
greater than the 5d-6s distance in gold. The relativistic effects
increase the 5d orbital's distance from the atom's nucleus and decrease
the 6s orbital's distance.
Caesium, the heaviest of the alkali metals
which can be collected in quantities sufficient for viewing, has a
golden hue, whereas the other alkali metals are silver-white. However,
relativistic effects are not very significant at Z = 55 for caesium (not far from Z
= 47 for silver). The golden colour of caesium comes from the
decreasing frequency of light required to excite electrons of the alkali
metals as the group is descended. For lithium through rubidium this
frequency is in the ultraviolet, but for caesium it enters the
blue–violet end of the spectrum; in other words, the plasmonic frequency
of the alkali metals becomes lower from lithium to caesium. Thus
caesium transmits and partially absorbs violet light preferentially
while other colours (having lower frequency) are reflected; hence it
appears yellowish.
Lead-acid battery
Without
relativity, lead would be expected to behave much like tin, so tin-acid
batteries should work just as well as the lead-acid batteries commonly
used in cars. However, calculations show that about 10 V of the 12 V
produced by a six-cell lead-acid battery arises purely from relativistic
effects, explaining why tin-acid batteries do not work.
Inert pair effect
In Tl(I) (thallium), Pb(II) (lead), and Bi(III) (bismuth) complexes a 6s2 electron pair exists. The inert pair effect is the tendency of this pair of electrons to resist oxidation due to a relativistic contraction of the 6s orbital.
Other effects
Additional phenomena commonly caused by relativistic effects are the following:
- Metallophilic interactions
- The stability of the gold anion, Au−, in compounds such as CsAu
- The crystal structure of lead, which is face-centered cubic instead of diamond-like
- The striking similarity between zirconium and hafnium
- The stability of the uranyl cation, as well as other high oxidation states in the early actinides (Pa-Am)
- The small atomic radii of francium and radium
- About 10% of the lanthanide contraction is attributed to the relativistic mass of high velocity electrons and the smaller Bohr radius that results
- In the case of gold, significantly more than 10% of its contraction is due to relativistically heavy electrons, and gold (element 79) is almost twice as dense as lead (element 82)